restoration of endo treated teeth
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What was found to lead to a higher occurrence of fractures in endodontically treated with with the Sedgley and Messer study?
- loss of tooth structure associated with the access preparation (including caries and existing restorations)
- not the change in dentin
How do we assess if RCT was successful? Why is this important?
- Canal is well filled
- No pain on percussion or palpation
- Healthy periodontal tissues
- Healing at the apex
never restore a failing root canal
Considerations before restoring endodontically treated teeth/ when can we restore?
1. Good apical seal
2. No sensitivity to pressure
3. No drainage or fistula
5. No apical sensitivity
6. No active inflammation
What determines the restoration type of an endodontically treated tooth?
➡Tooth Position
➡Amount of Coronal Tooth Structure
➡Tooth Service (single restoration or abutment)
➡Occlusion
when deciding the treatment plan of a endodontically treated tooth, what type of restoration can be done on an anterior tooth if the coronal structures are largely intact and loading is favorable?
- a simple restoration / fill the access
when deciding the treatment plan of a endodontically treated tooth, what type of restoration can be done on an anterior tooth if there is substantial amounts of the coronal structure is missing?
- a post-and-core restoration is indicated
when deciding the treatment plan of a endodontically treated tooth, what type of restoration is done for molars?
- amalgam or composite resin
- post is rarely needed (unless there is major structure loss = post and core)
What are posts for
- retention of a core, not strength
what is a core? what is its purpose?
- replacement of missing coronal tooth structure
- Supports a crown
- Provide retention and resistance
when treating an endodontically treated tooth, what are the options of restoration material
- composite
- amalgam
- Gi
when treating an endodontically treated tooth, what type of material can be used to create a custom post and core?
- metal
- ceramics
when treating an endodontically treated tooth, what type of material is used for a prefabricated post?
- metal
- carbon fiber
- glass fiber
- ceramic post
Core restoration material: composite advantages
- rapid setting
- ease of use
- bonding
- tooth colored
- anatomic contour buildup
Core restoration material: composite disadvantages
- thermal expansion
- setting contraction
- microleakage
Core restoration material: composite recommended use
- most foundations/core restorations
Core restoration material: composite precautions
moisture control
- not recommended for teeth under lateral load
Core restoration material: glass ionomer advantages
- rapid setting
- adhesion
- fluoride
Core restoration material: glass ionomer disadvantages
- low strength
- moisture sensitive
Core restoration material: glass ionomer recommended uses
- smaller lesions
Core restoration material: glass ionomers precautions
moisture control
- not recommended for teeth under lateral load
Core restoration material: amalgam advantages
- good strength
- intermediate restoration
Core restoration material: amalgam disadvantages
- preparation delay
- condensation
- corrosion
- no bonding
Core restoration material: amalgam recommended uses
- large foundations/cores
Core restoration material: amalgam precautions
well-supported matrix
what is the primary purpose of a post?
- retain a core in a tooth / strengthen teeth
- prevent fracture
- does not strengthen the tooth
complications of a post
- perforation
- root fracture
- placing post beyond the root apex
Should a post be placed in an anterior tooth/considerations
- posts weaken anterior teeth
- anterior teeth do not always need a crown
- metal posts are not recommended in anterior teeth that do not require complete coverage restorations (bad esthetics)
- posts do not improve prognosis in anterior teeth
when are crowns placed on anterior teeth
- large structure loss
- tooth is used as abutment
Disadvantages of using a Cemented Post
- placement requires additional operative procedure
- removal of additional tooth structure
- may fail to retain core
- complicates future endodontic re-treatments
complete coverage of a tooth is recommended on what teeth
- teeth with a high risk of fractures
- posterior teeth
possible exceptions of complete cuspal coverage of posterior teeth
- mandibular premolars and first molars with intact marginal ridges
- areas of low occlusal forces
crown placement vs. tooth survival
- Teeth without crowns fail 6× more often
- crowns improve survival
Principles of Tooth Preparation: three main goals
•Conservation of Tooth Structure
•Retention Form
•Resistance Form
ways to conserve tooth structure during a canal prep
Keep apical seal
Minimal enlargement
Adequate post length
Avoid wedging forces
Extend margins onto sound tooth
how much is a canal enlarged for a prefabricated post canal prep
-1 to 2 file sizes
what is the biggest predictor of success of a tooth preparation
amount of remaining tooth structure / dentin
when preparing a Cast post-and-core restoration, how do you endure thin walls have good strength
- shorten the thin walls
What is a ferrule?
- vertical band of tooth structure above the crown margin
why is a ferrule important?
- prevents root fracture
- improves resistance form
- critical when using a post and walls are thin
minimum height of a ferrule
1.5-2 mm
factors you must evaluate to decide whether the ferrule is adequate (partial ferrule factors)
➡ height of remaining dentin after tooth preparation: 2 mm of height
➡ thickness of remaining dentin after tooth preparation: 1 mm thick
➡The number of remaining dentin walls, and their location
➡The lateral vectors of load on the tooth: light or heavy lateral loads. (direction of forces)
options when no ferrule is present
- crown lengthening
- orthodontic extrusion
effects of Creating a ferrule with orthodontic extrusion
- reduces root length
- crown length remains unchanged. (preserves a better ratio)
effects of Creating a ferrule with Surgical crown lengthening
- reduces root length but increases crown length
--> This results in a less favorable crown-to-root ratio, which weakens the restoration.
what is the ideal crown to root ratio of an FPD
1:2
what is an acceptable crown to root ratio
1:1.5
Minimum crown/root ratio for abutment?
1:1
indications of surgical crown lengthening
- subgingival caries or fractures
- inadequate clinical crown length for retention
- unequal or unaesthetic gingival height
contraindications of surgical crown lengthening
- unaesthetic outcome
- deep caries or fracture requires excessive bone removal
- tooth is a poor restorative risk
Wait _____weeks before final prosthetic treatment after surgical crown lengthening
8-12
best post design for anterior teeth
parallel > tapered
considerations of the post length for anterior teeth
- retain apical seal
- avoid root perforation
-Must retain 3-5 mm of root canal filling material
(length matters more than width)
determining post length of anterior teeth
-The length of the clinical crown
-Two thirds of the root length
-Four fifths of the root length
-Ending halfway between crestal bone and apex: ½ the length of the root in bone
post diameter of anterior teeth
- want to retain as much dentin as possible
- should not exceed 1/3 of the cross sectional diameter of the root
- increasing diameter does not increase retention
effect of increasing post diameter on retention
none, increasing diameter does not increased retention
post surface texture for anterior teeth
•serrated or roughened> smooth
best luting agent to use for placing a post in anterior teeth
Adhesive resin cement > ZOE/ GI cement > polycarboxylate
effects of a shorter post
•Less retentive
•Higher risk of fracture
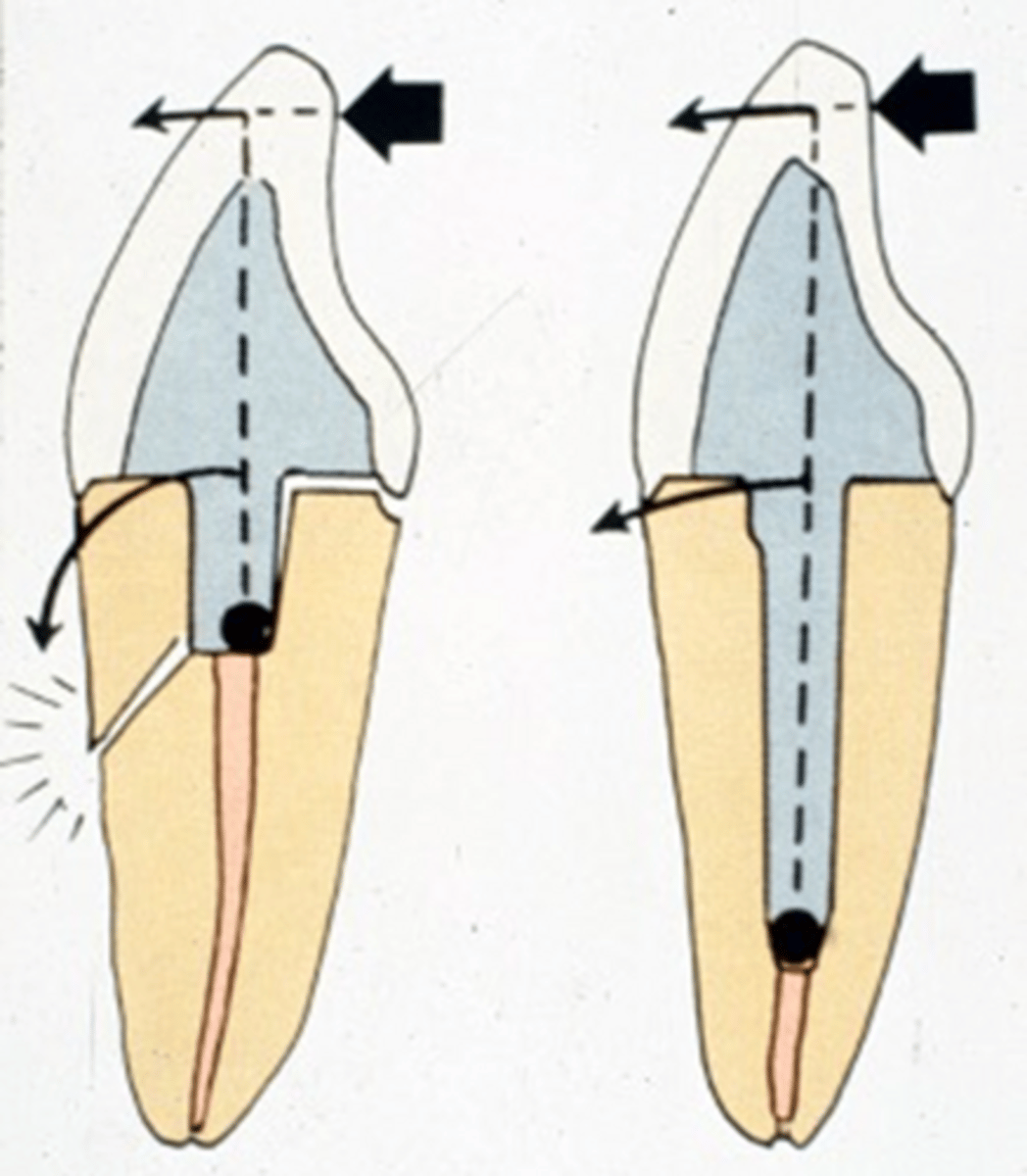
post considerations in posterior teeth
- posts are rarely indicated in molars b/c of root anatomy
- long posts should be avoided in posterior teeth
- if used, best to use multiple short posts
if a post is needed in a posterior tooth, which canal should i be placed in
- widest canal
- mandibular: distal canal
- maxillary: palatal canal
influence on stress of a tapered post
- wedge effect
influence on stress of a parallel post
- better stress distribution
- higher stress at apex
- high stress if cement vent not placed
influence on stress of a threaded post
- high stress during insertion & loading
- better stress distribution if backed off ½ turn
- stress concentration around threads
where is the greatest stress concentration of a post
- at finishline and apex
what do sharp angles of a prep create
- high stress during loading
As post length increases stress _______
decreases
how does a cement layer affect stress
- creates a better stress distribution
influence on stress of a glass fiber post
- result in lower stress concentrations than do metal or ceramic posts (because they have an elastic modulus similar to dentin)
how do you create rotational resistance of a post
• create a antirotational groove in the bulkiest area of the root (lingual surface)
three steps of tooth preparation for endodontically treated teeth
➡Removal of gutta-percha
➡Enlargement of the canal
➡Preparation of the coronal tooth structure
When do you prepare the root canal?
- if working length is known --> before crown prep
- if NOT --> prep first, take PA, then prep canal.
what instruments are used to remove gutta percha from canal
•Peeso Reamer drills and Gates Glidden drills
rules of canal enlargement
Follow gutta-percha path
Avoid dentin cutting
Post ≤ 1/3 root width
Keep ≥ 1 mm dentin thickness
indications of custom made posts
- circular or extremely tapered canals
indications of prefabricated posts
- round conservative canals
what type of posts are recommended for teeth with roots of circular cross section.
Parallel-sided prefabricated posts
characteristics of a metal prefabricated post
- high modulus of elasticity
- strong but rigid
characteristics of a fiber prefabricated post
- easier to retreat
- less strength
- less stiffness
- lower fracture threshold
- fracture mode of tooth is better
what post material is often safest
fiber
characteristics of a zirconia prefabricated post
- rigid --> should not be used in patients with bruxism
- difficult to remove
- poor bonding --> problem with retention
what is a cast metal custom made post made out of
- type IV gold
- metal ceramic alloy
- base alloy
what is used for the fabrication of a custom-made pattern for a custom-made direct post.
acrylic
what is involved in the indirect method of a custom made post
impression and cast
what type of custom post can be made from CAD-CAM
-zirconia
-PICN
Advantages of composite resin, resin-modified glass ionomer, or amalgam for core fabrication
➡conservative --> undercuts do not need to be removed.
➡fewer patient visit.
➡fewer laboratory procedures.
-- Testing generally shows good resistance to fatigue test and good strength characteristics
advantages of a cast metal core
➡They can be cast directly onto a prefabricated post, which will provide the restoration with good strength characteristics. (Not recommended)
➡Conventional high noble-metal content alloys can be used.
➡An indirect procedure can be used, which will facilitate restoration of posterior teeth.
custom cast post and core restoration advantages
- high strength
- better fit than prefabricated
custom cast post and core restoration disadvantages
- less stiff
- time consuming/ complex procedure
wire post and cast core advantages
- high strength
- high stiffness
wire post and cast core disadvantages
- corrosion of base metal
tapered prefabricated post advantages
- conservative of tooth structure
- high strength and stiffness
tapered prefabricated post disadvantages
- less retentive
tapered prefabricated post indications
small circular canals
tapered prefabricated post contraindications
not recommended for flared canals
parallel sided prefabricated post advantages
- high strength
- good retention
- comprehensive system
parallel sided prefabricated post disadvantages
-corrosion of stainless steel
- less conservative of tooth structure
parallel sided prefabricated post indications
- small circular canals
why would a post need to be removed
•To retreat of a failed root canal
•To remove an incompletely seated post.
tools to remove a post
➡Ultrasonic device/ Forceps
➡High-speed bur
➡Trephine
➡Extractor