female reproductive system
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
topography es importante
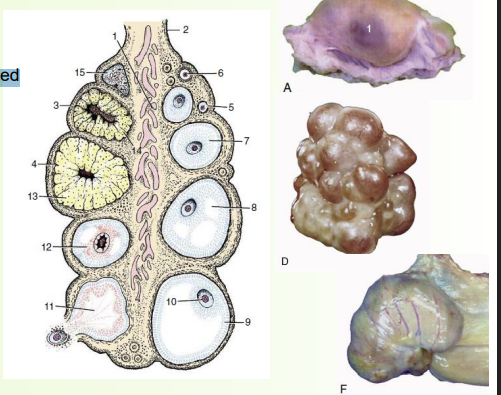
» Solid, ellipsoid organ
• Follicles (each containing a single ovum)
• Projection of follicles can make it irregular-shaped
• More follicles (e.g. polytocous species) = more lumpy
» In cross-section:
• Loose vascular zone/medulla in centre
• Outer dense parenchymatous zone
» Horses slightly different
• More kidney shaped
• Reversed structure (vascular zone outside, parenchymatous zone + follicles inside) F - and single location where they ovulate from - ovulation fossa
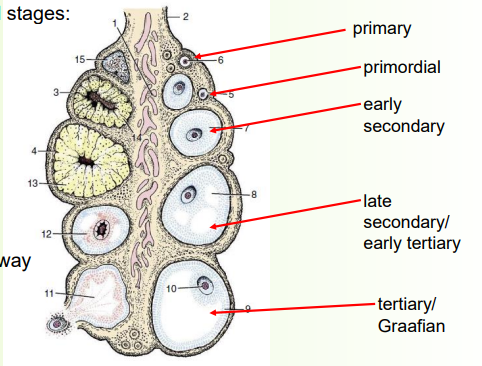
follicle production
» Follicles develop and progress through several stages:
1) Primordial follicle (smallest)
Single layer of flat granulosa cells
2) Primary follicle
Flat granulosa cells thicken→ cuboidal cells
3) Secondary follicle
Several layers of cells with fluid-filled spaces
4) Tertiary (Graafian) follicle
Mature, fluid spaces joint up
» Only a small number of follicles mature all the way
• There is atresia and regression at every stage
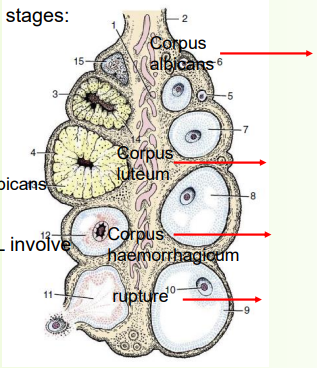
» Follicles develop and progress through several stages:
6) Graafian follicle ruptures (ovulation)
Fluid flushes ovum to uterine tube
7) The remaining follicle tissue bleeds a little
8) Proliferation of tissue to form corpus luteum
If pregnant, CL (corpus luteum-produces progesterone) persists
9) If not pregnant CL regresses
A connective tissue scar forms; the corpus albicans (white body)
» Ovulation and maintenance or regression of CL involve a complex interplay of hormones e.g.
• FSH and LH - ovulation
• Progesterone - persistent corpus luteum
• PGF2α - regression of corpus luteum
uterine tube
» AKA oviducts, salpinx/uterine tube. Not Fallopian!
» Function: capture and transport ova to the uterus; usually site of fertilisation
» Lined internally by ciliated epithelium
» Expanded near ovary into the infundibulum
• Funnel shaped
• Fimbriae on free edge
» Ampulla (‘flask’) makes up middle portion
» Isthmus is the narrower (sometimes convoluted) portion
» Junction with uterine horn can be gradual or abrupt
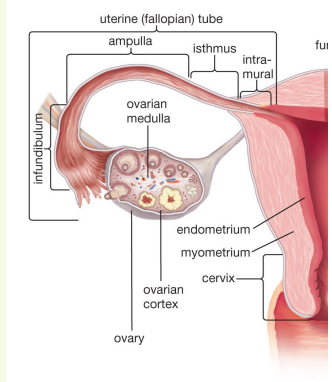
uterus
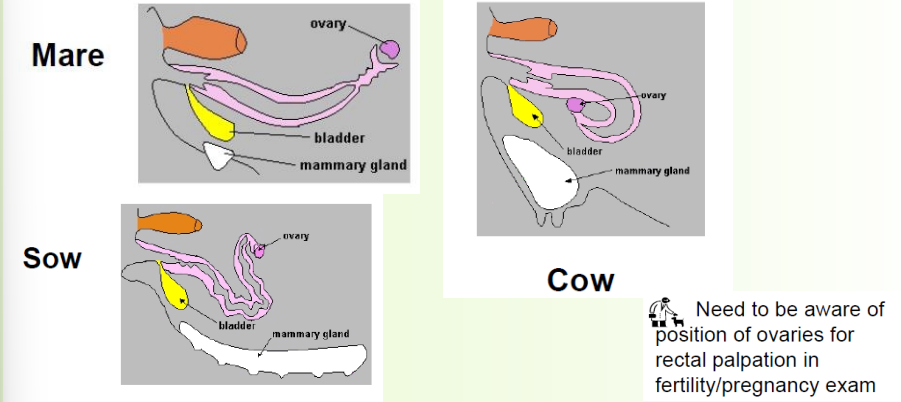
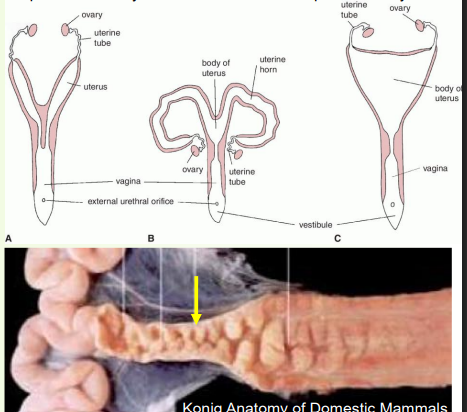
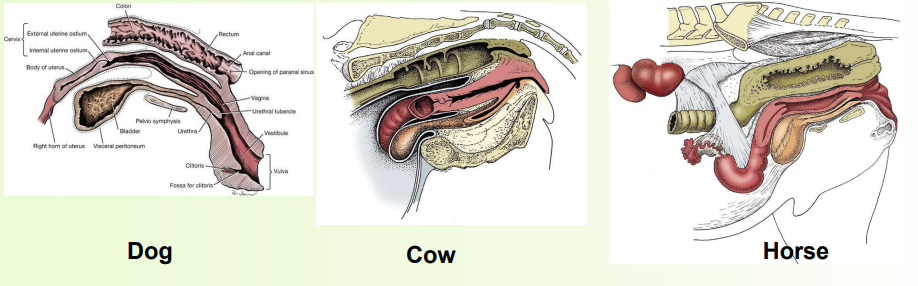
» Appearance varies considerably between species
• Develops from paramesonephric ducts that fuse
» Size, position and anatomy changes with age and physiological activity!
» Comprised of horns, body and cervix
» Cervix limits access from vagina
• Forms sphincter
• Thick mucosal folds interdigitate, can occlude cervical canal
• Cervical mucosa secrete mucus, forming a plug
uterine tube NOT the same as uterine horn
uterus zoomed in - tubular
» Uterine wall is three-layered
» Mucosal layer (endometrium) internal lining
• Thickness varies with oestrus cycle
• Numerous tubular glands
• Ruminants have uterine caruncles (attachment sites of embryonic membranes), attach to foetal cotyledons
» Muscle layer (myometrium)
• External longitudinal muscle layer
• Internal circular muscle layer
• Smooth (involuntary) muscle
• Responsible for uterine contractions
• Coordinated activity: longitudinal contractions ‘shorten utuerus’ while circular contractions push out contents.
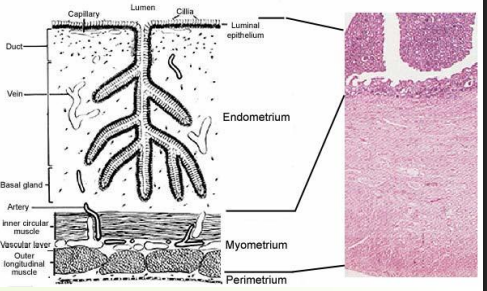
outer layer of uterus
Serosal layer (perimetrium) outer surface
• Continuous with the broad ligament (like a mesentery in gi tract)
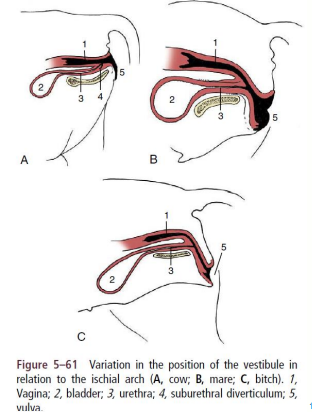
vagina, vestibule and vulva
» Vagina and vestibule together form the rest of the internal tract
» Vagina cranially, from cervix to urethra
• Purely reproductive passage
• Mostly retroperitoneal
» Vestibule caudally, from urethra to external vulva
• Combined reproductive and urinary functions
• Caudal to ischial arch, variable slope ventrally to vulva
• Urethral opening ventrally
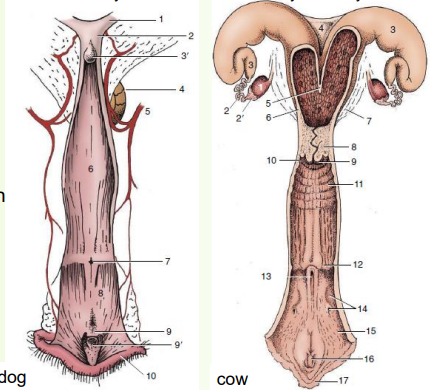
vagina, vestibule and vulva opened up
» Urethral opening – features nearby can complicate bladder catheterisation
• E.g. suburethral diverticulum in pig and cow
• E.g. flanked by two grooves in dog
» Vestibular glands
• Varies - small and numerous openings in dogs, large bilateral (on both sides) glandular mass each drained by single duct in cows
• Lubricate vestibule during copulation and parturition (birth)
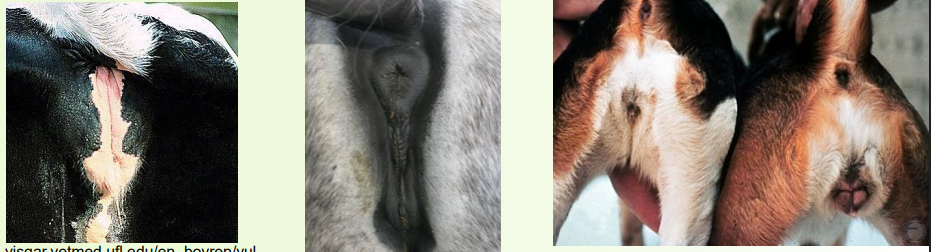
comparing vagigies
» Vulva is the external genital opening and tissues
• Labia either side
• Labia meet at dorsal and ventral commissures
• Clitoris, the female homologue of the penis (or vice versa!), lies within ventral commissure, contained within the clitoral fossa
ligaments
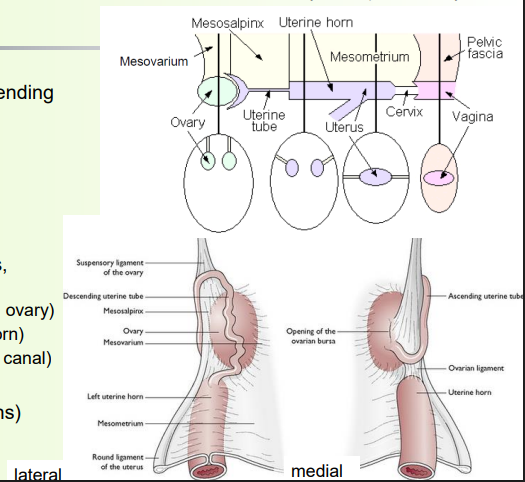
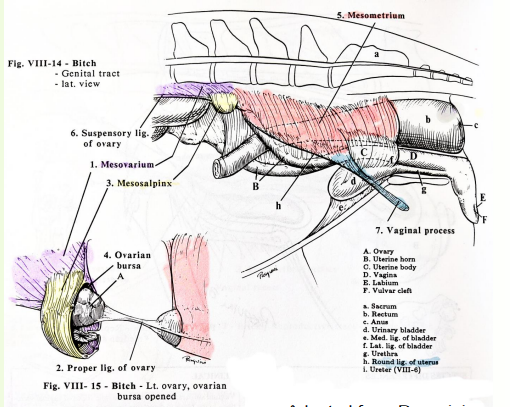
» Broad ligament = folds of peritoneum, suspending tract from dorsal body wall
• Ovary (mesovarium)
• Uterine tube (mesosalpinx)
• Uterine horns and uterus (mesometrium)
• Cervix
» Broad ligament also encloses blood vessels, nerves and some other ligaments
• Suspensory ligament of the ovary (last rib to ovary)
• Ovarian/proper ligament (ovary to uterine horn)
• Round ligament of uterus (uterus to inguinal canal)
» Intercornual ligament (connects uterine horns)
• Well developed in ruminants
broad ligament
Mesometrium
Mesovarium (and suspensory ligament of ovary)
Mesosalpinx
ovarian bursa = pouch of mesovarium and meosalpinx
Round ligament
Proper ligament
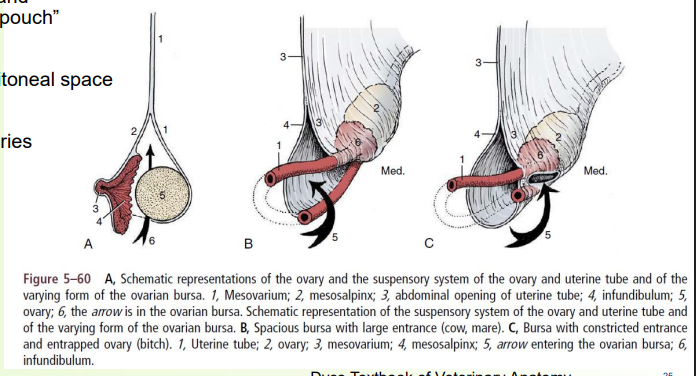
ovarian bursa
» Folding of mesovarium and mesosalpinx creates a “pouch”
» Communicates with peritoneal space
» Pouch opening width varies
• Species difference
» Can contain fat
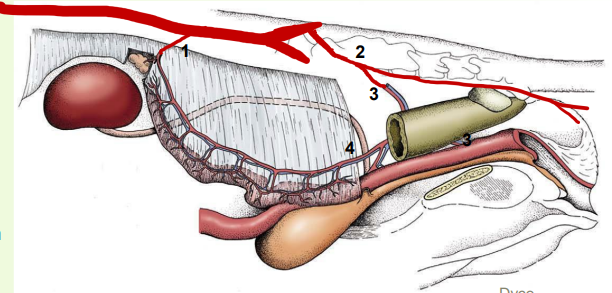
blood supply to reproductive tract
1. Ovarian artery
• Direct branch of aorta
• Variably convoluted
2. Internal pudendal arteries
• Supply external genitals
• Branch off to form:
3. Vaginal artery
• Supplies vagina and rectum
4. Uterine artery
• Branch of the vaginal artery
• Anastomoses w/ ovarian and vaginal arteries
» The veins broadly accompany the arteries