Chapter 3: Water and Life
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
why is water essential for life?
all living organisms require water
it makes up ~70% of cells and enables chemical reactions necessary for life
what 4 elements make up about 96% of living matter?
hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen
what is an element?
a pure substance made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down by ordinary chemical means
what is an atom?
the smallest unit of an element that retains chemical properties, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons
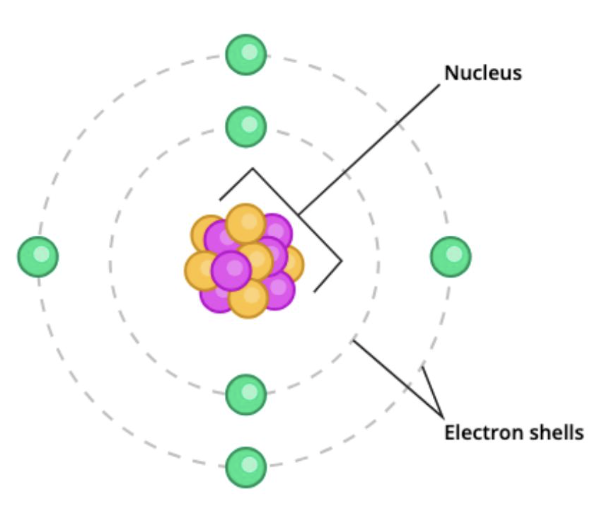
what is the max # of electrons that can occupy the first two electron shells?
max 2 electrons for 1st shell
max 4 electrons for 2nd shell
what is a molecule?
a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
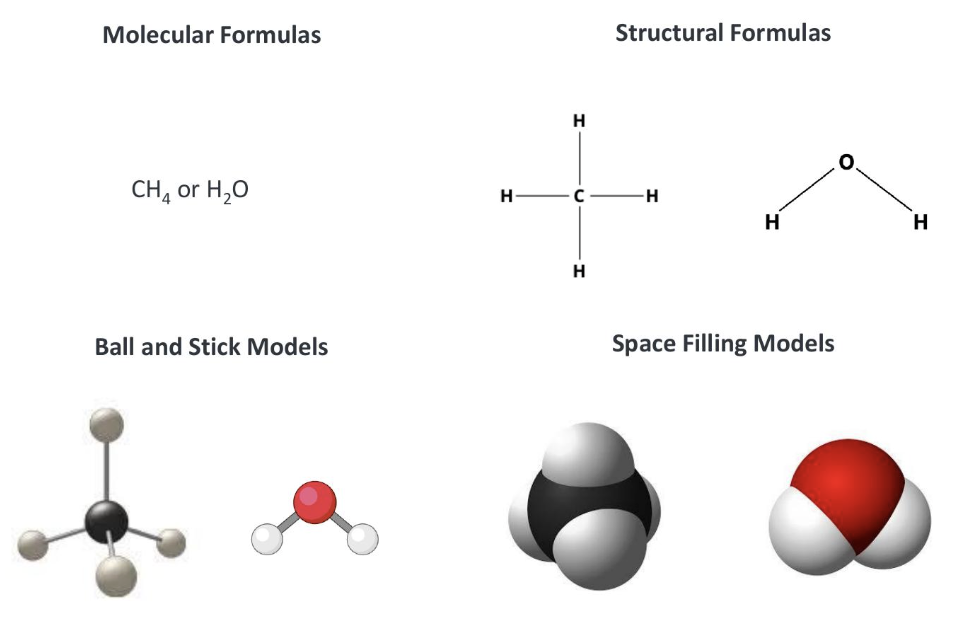
what are common ways molecules are represented?
molecular formulas, structural formulas, ball and stick models, and space filling models
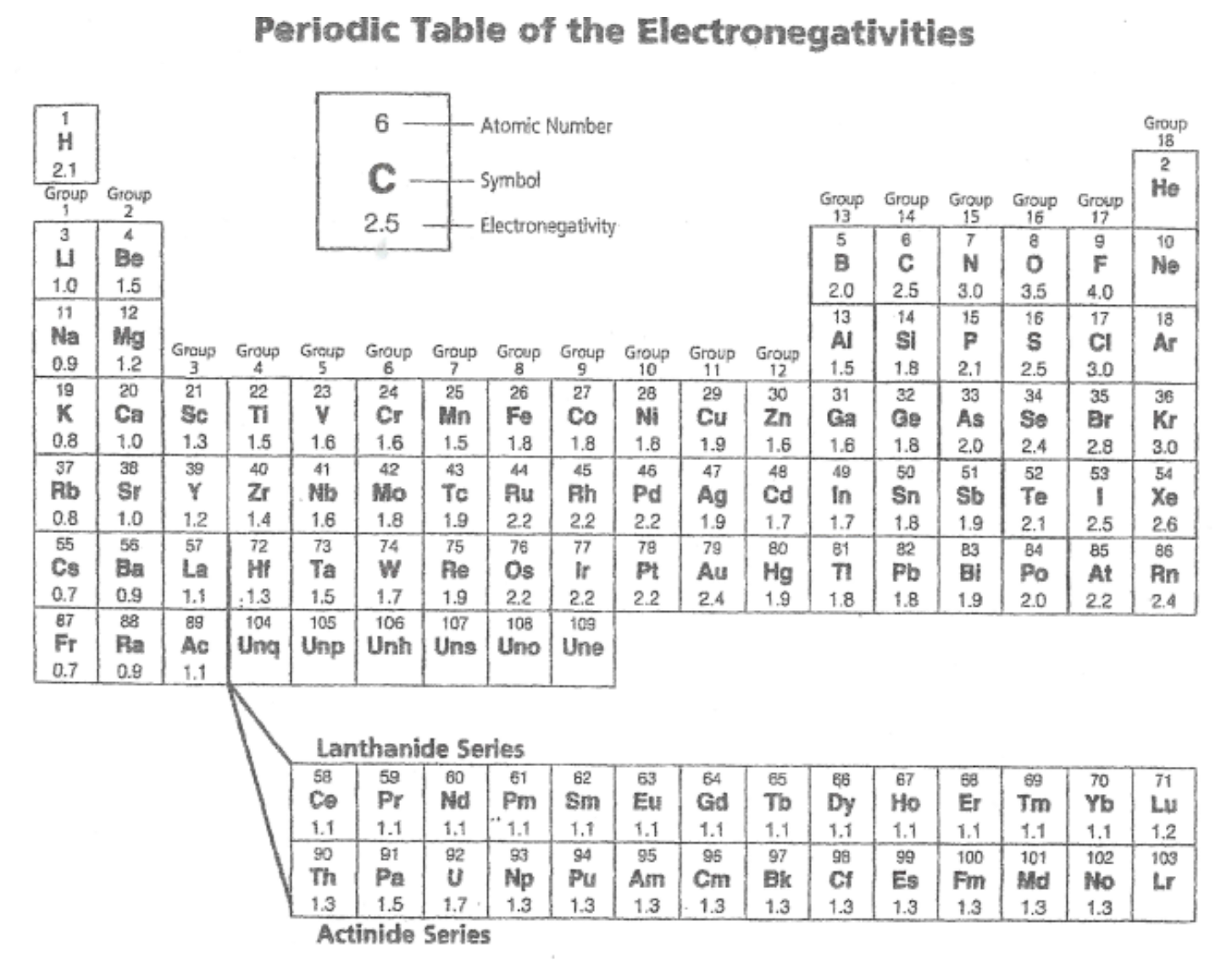
what is electronegativity?
an atoms ability to attract shared electrons in a covalent bond toward itself
why is water a polar molecule?
oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, creating partial charges
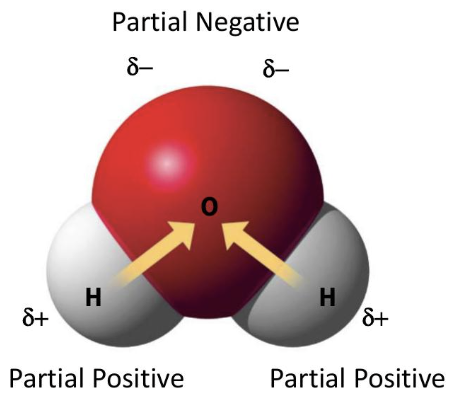
what partial charge does oxygen have in water?
partial negative
what partial charge do hydrogen atoms have in water?
partial positive
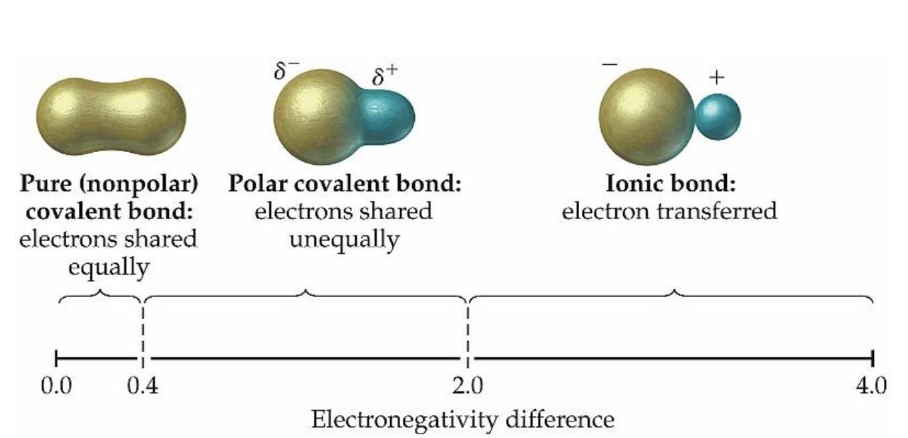
what is a nonpolar covalent bond?
a bond where electrons are shared equally between atoms
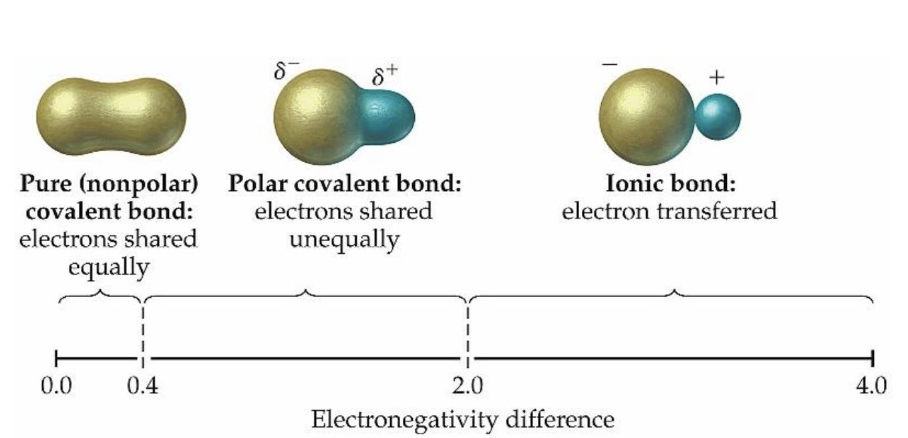
what is a polar covalent bond?
a bond where electrons are shared unequally due to electronegativity differences
give an example of nonpolar molecules
H2 and CH4 (methane)
what characteristics do polar molecules have?
unequal electron sharing, partial charges, often asymmetrical
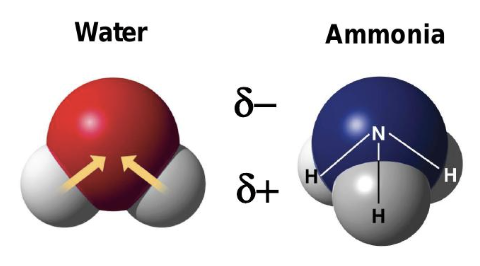
what is a hydrogen bond?
a weak attraction between a partially positive hydrogen and a partially negative atom (often oxygen or nitrogen)
why can water form hydrogen bonds?
because it is polar
how many hydrogen bonds can one water molecule form?
4
are hydrogen bonds in liquid water stable?
no they are weak and constantly breaking and reforming
what causes water’s emergent properties?
hydrogen bonding
what are four emergent properties of water?
cohesion
temperature moderation
expansion upon freezing
versatility as solvent
what is cohesion?
the attraction between molecules of the same substance
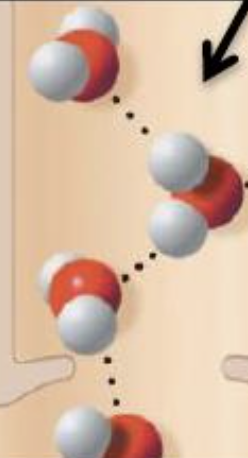
what is adhesion?
the attraction between molecules of different substances
why are cohesion and adhesion important?
they allow water and nutrients to move upward through xylem against gravity
what is heat?
total kinetic energy of molecules in a substance depends on the substances volume
what is temperature?
the average kinetic energy of a molecule doesn’t depend on volume
can be measured using a thermometer
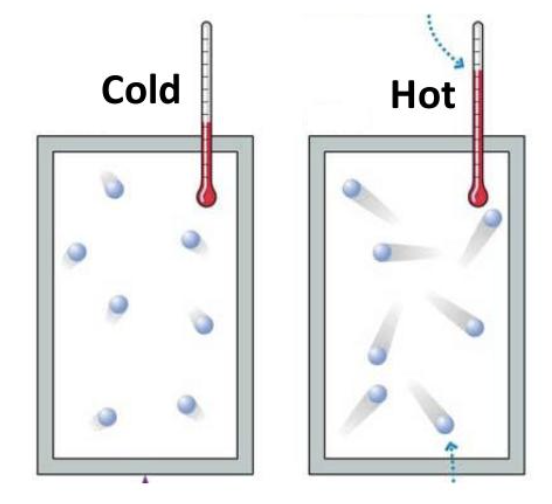
what is specific heat?
the amount of heat needed to raise 1g of a substance by 1C
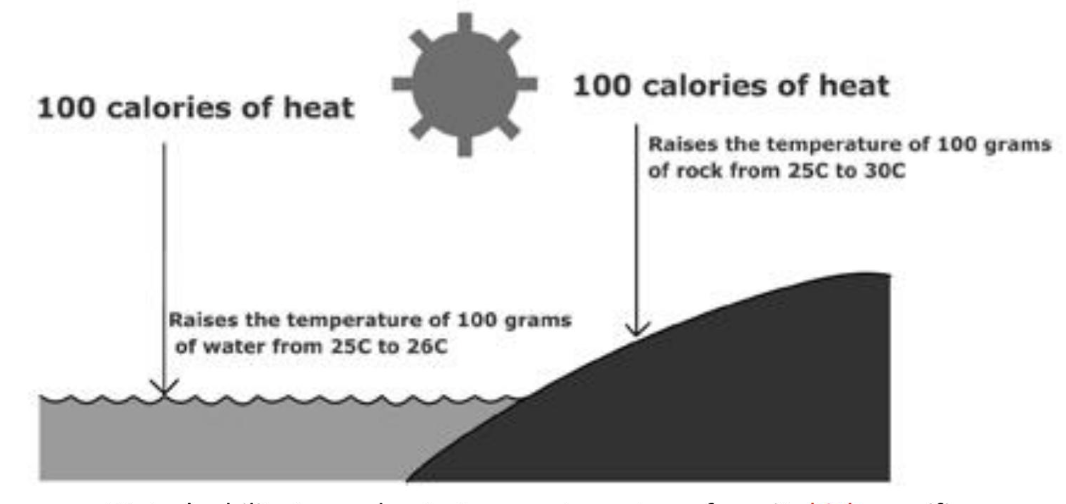
why does water have high specific heat?
hydrogen bonds absorb heat before temperature rises
how does water moderate earth’s climate?
large bodies of water absorb and release heat slowly
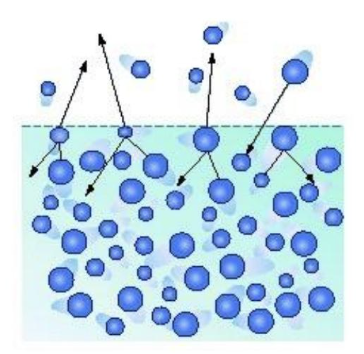
what is heat of vaporization?
the amount of heat required to convert liquid to gas
why does sweating cool the body?
evaporation removes high energy molecules, leaving behind cooler ones therefore lowering temperature
why does ice float on water?
ice is less dense because hydrogen bonds form a fixed crystal structure

at what temperature is liquid water most dense?
4C
why is floating ice important for life?
it insulates water below, allowing organisms to survive in cold environments
what is a solution?
a homogeneous mixture of substances
what is a solvent?
the dissolving agent in a solution
what is a solute?
a substance that dissolves in the solvent
why is water a versatile solvent?
it’s polarity allows it to dissolve polar and ionic substances
what is a hydration shell?
water molecules surrounding dissolved ions or polar molecules
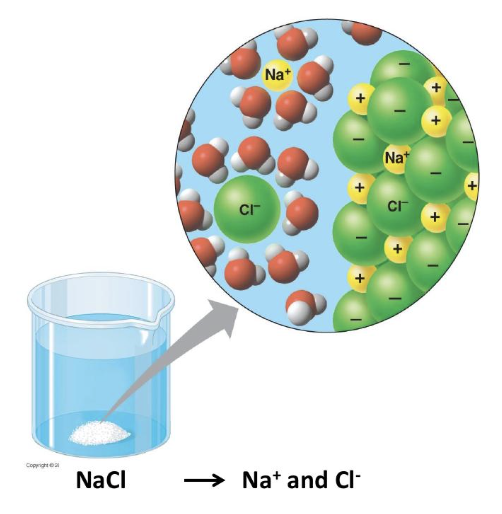
what is a hydrophilic substance?
a substance that interacts easily with water
what is a hydrophobic substance?
a substance that does not interacts easily with water
what happens when water dissociates?
it forms H3O+ (hydronium) and OH- (hydroxide) ions
what is an acid?
a substance that increases H+ concentration
what does the pH scale measure?
the acidity or basicity of a solution
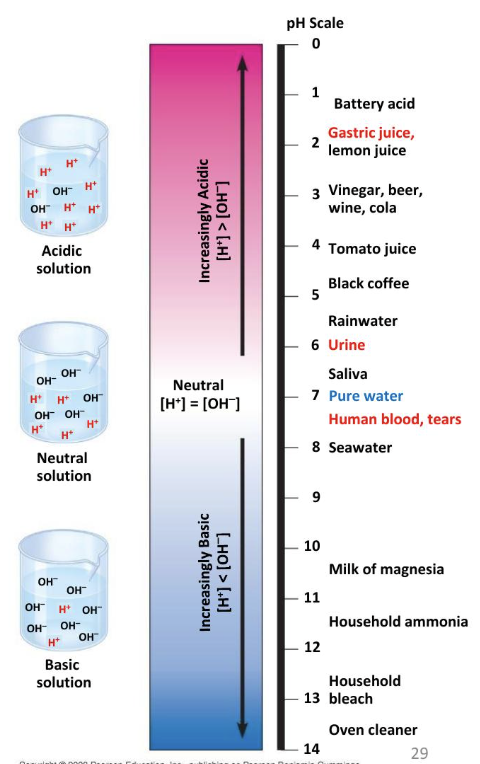
what is neutral pH?
pH 7, where H+ equals OH-
why is pH important to living organisms?
small changes can disrupt biological processes
what is the pH of the stomach?
around 2
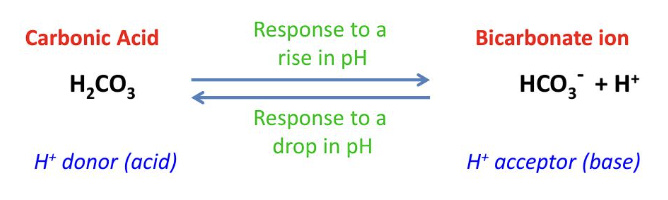
what is a buffer?
a substance that resists changes in pH contains a weak acid and its corresponding weak base which combine reversible with H+
what buffer system regulates blood pH?
carbonic acid-bicarbonate system
what is acidosis?
blood pH increases (below 7.35) reaction proceeds to the right
what is alkalosis?
blood pH drops (above 7.45) reaction proceeds to the left
how does carbonic acid work as a buffer? (equation)
H2CO3 <-> HCO3- + H+
(H+ donor) (H- acceptor, base)
which has more heat: water in a lukewarm swimming pool or boiling water in a teacup?
water in a lukewarm swimming pool
which has the highest temperature: water in a lukewarm swimming pool or boiling water in a teacup?
teacup
a partially positiive charged hydrogen atom must be present in a hydrogen bond
true
an increase in pH means that the concentration of H+ has ______
decreased
the lower the pH of a solution, the more ______ the solution
acidic
why do He, Ne, and Ar have no electronegativity value?
they have a full outer shell
is molecular oxygen (O2) polar or nonpolar?
nonpolar
a partially negative charged oxygen atom must be present to form a hydrogen bond
false
hydrogen bonding occurs when
partial charges from polar covalent bonds create electrostatic attractions
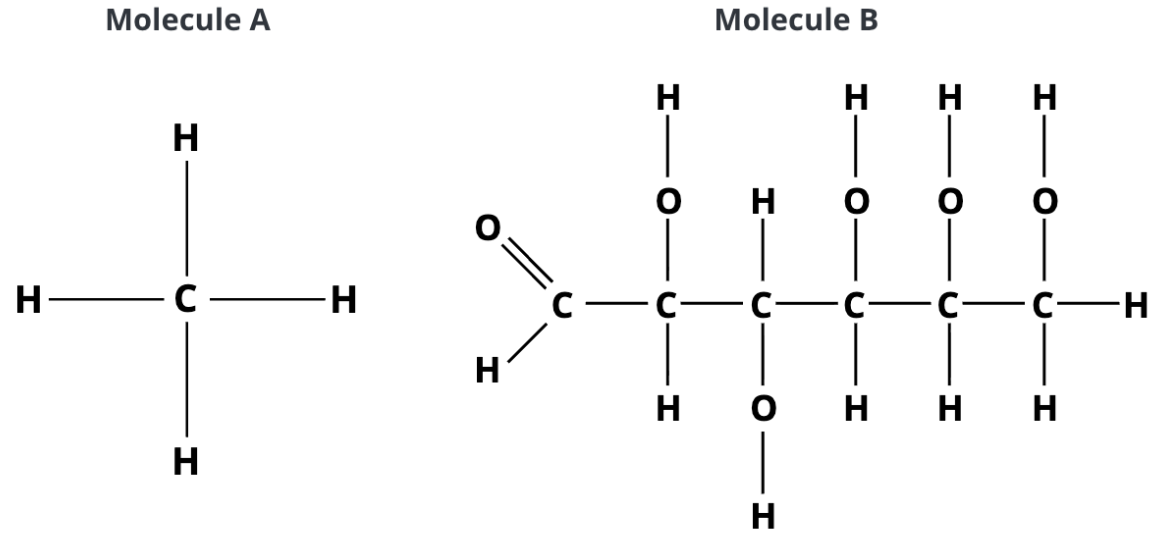
which molecule can form a hydrogen bond with water?
only molecule B. some of its atoms have partial charges, which are attracted to the partial charges in water.
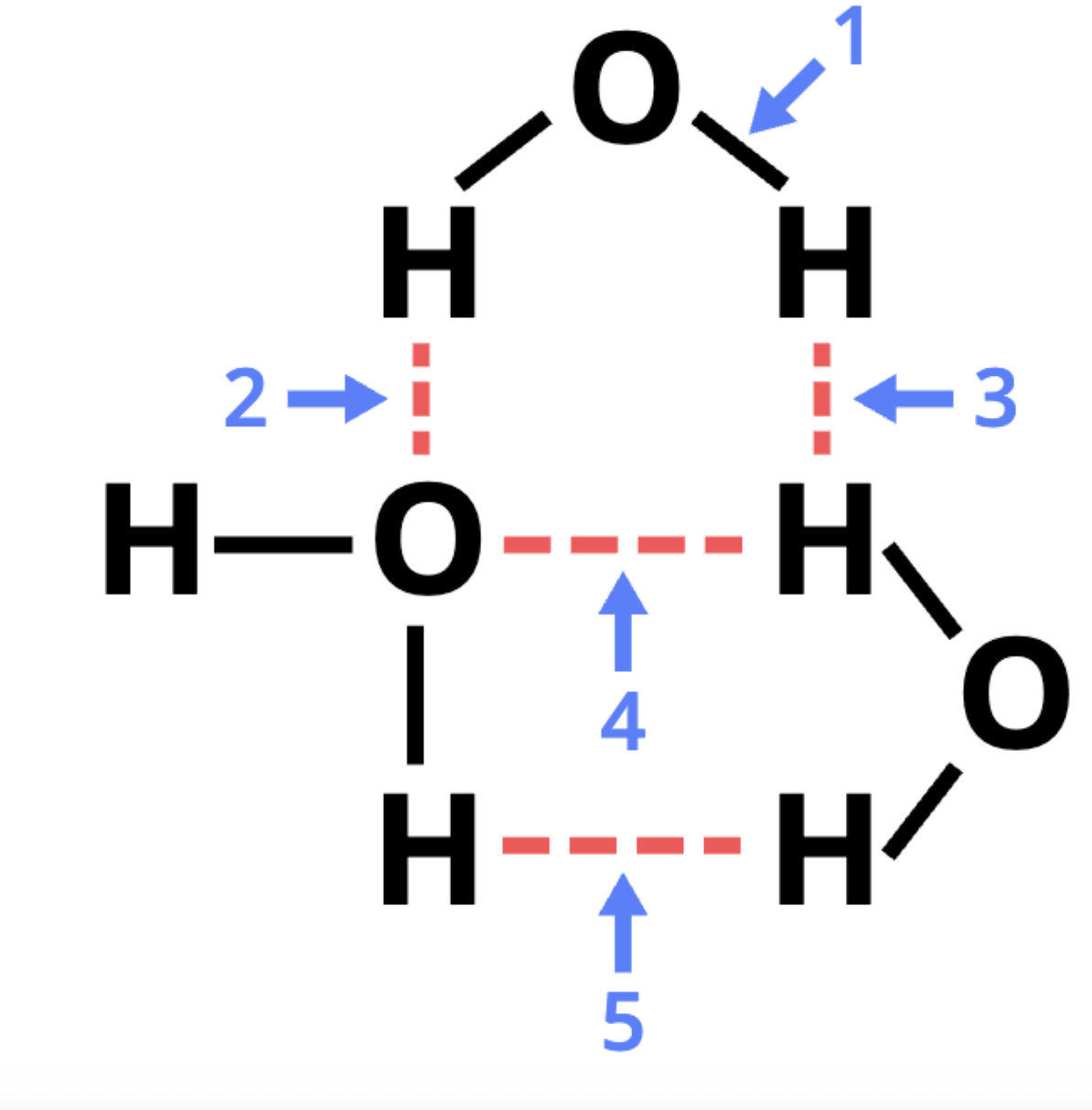
the diagram below represents three water molecules interacting. five different labeled arrows (1 through 5) point to different places of the diagram. which arrows point to hydrogen bonds? (wouldn't use this image on the test...don't like dashed lines between H atoms for 3 and 5 that imply H bonds)
2 and 4 (hydrogen bonding generally occurs with another electronegative atom)
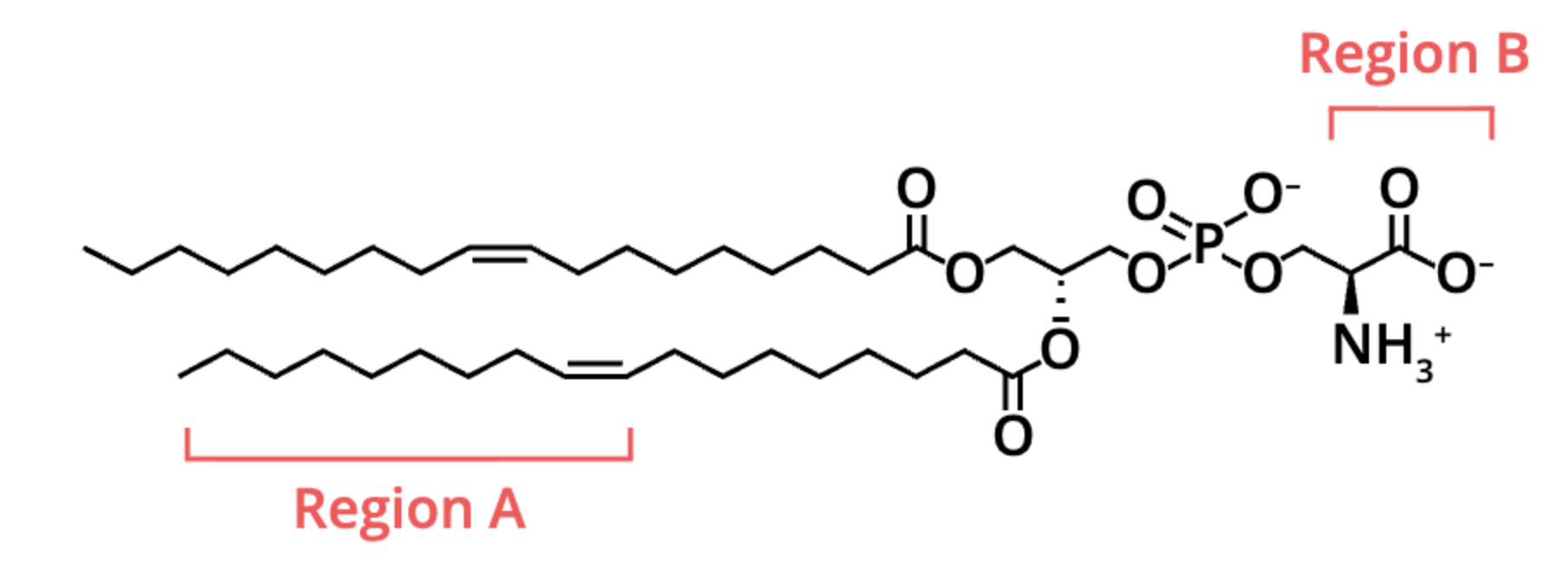
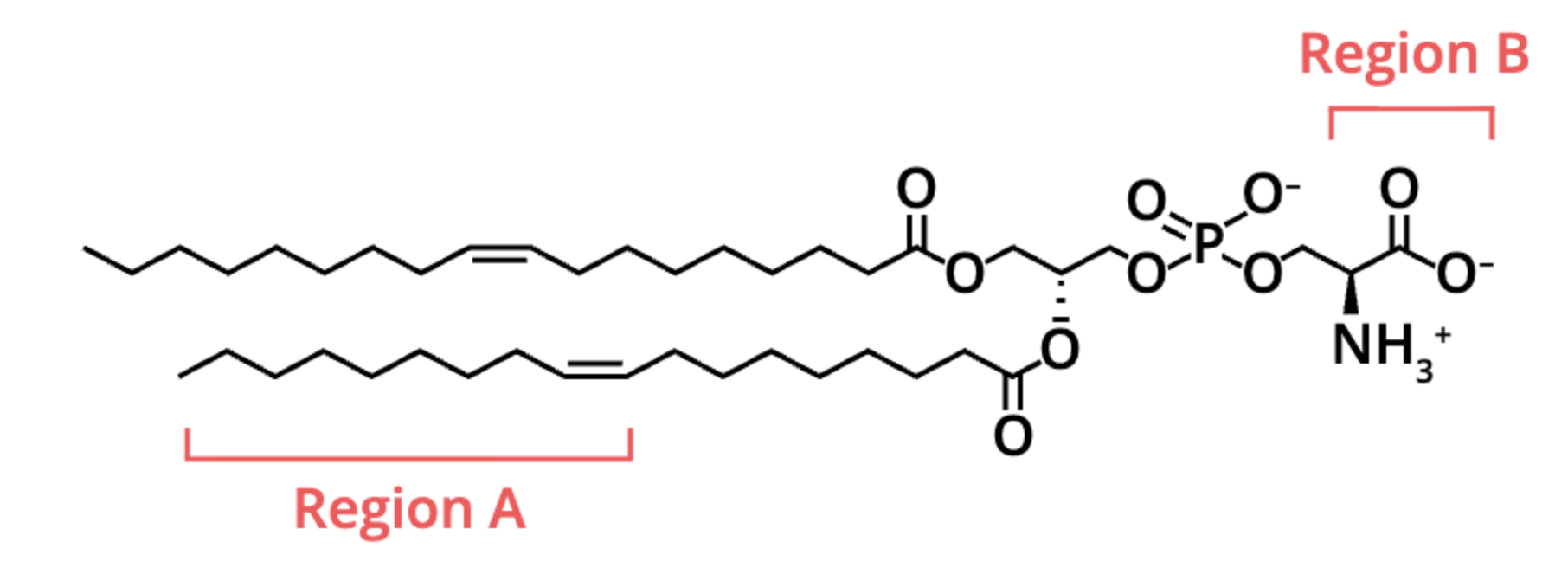
two regions of the molecule depicted both are labeled (A and B). Which region(s) contain polar covalent bonds?
region B only
(region B has polar covalent bonds because it includes highly electronegative atoms (O and N) bonded to less electronegative atoms, while Region A is just hydrocarbon chains with nonpolar bonds)
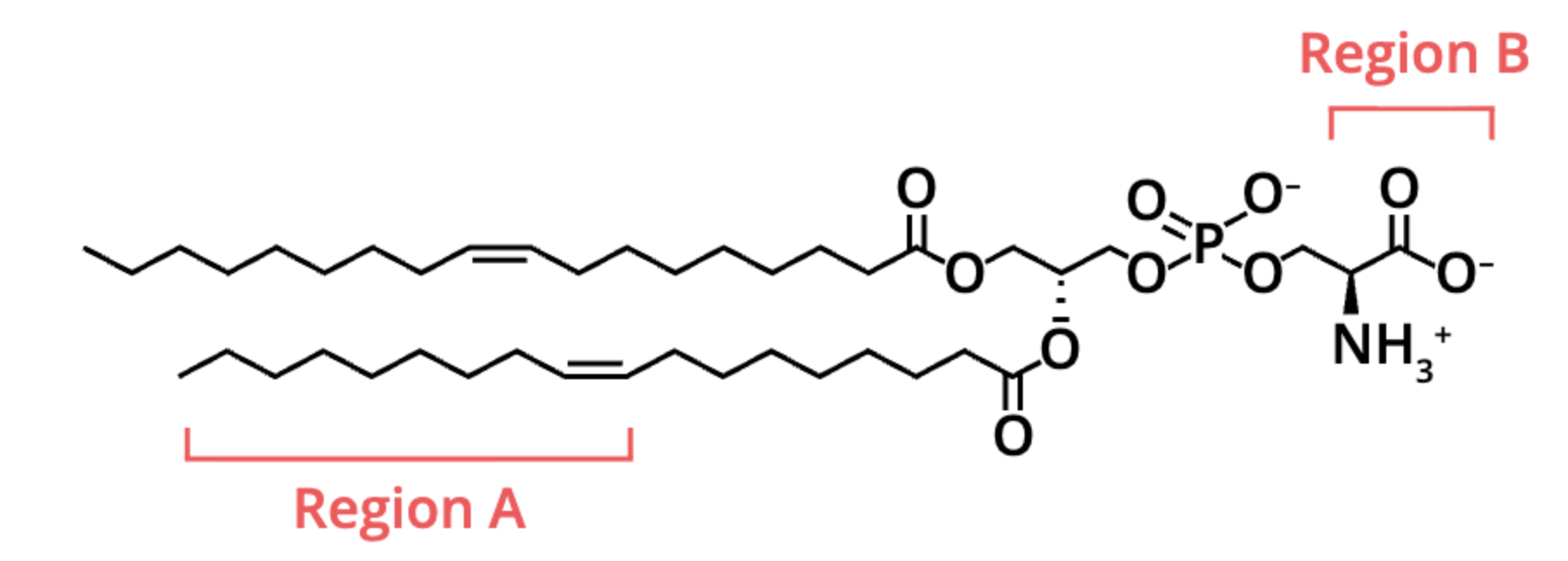
what regions can form hydrogen bonds with water?
region B
what type of biological molecule is depicted below?
lipid
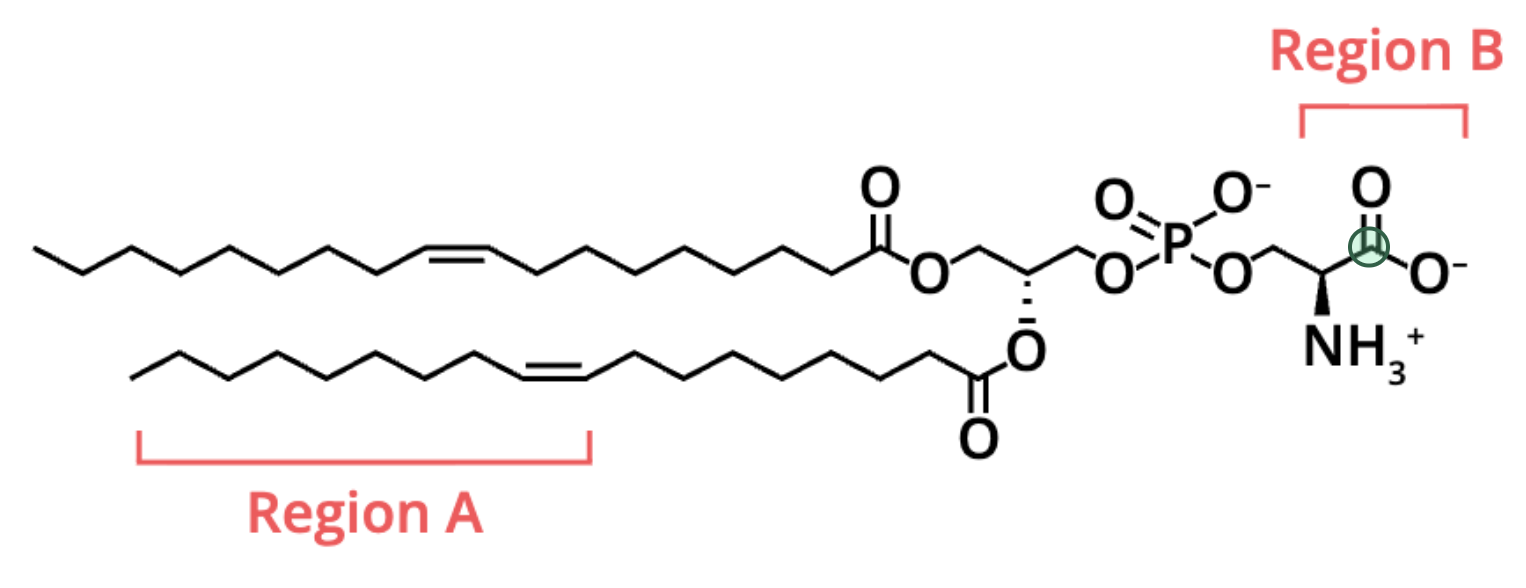
locate the carboxyl group on this molecule
its on the far right
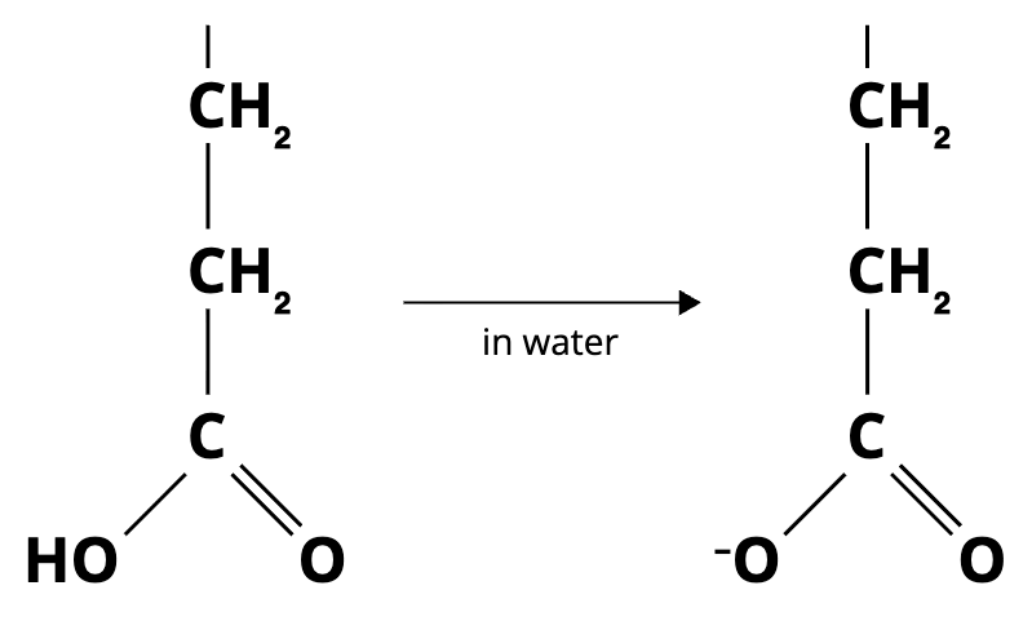
the diagram below shows part of a molecule that is found in proteins. when placed in water, the molecule "ionizes" to form the structure on the right:
the structure on the left releases a proton when placed in water
the structure on the left is an acid
C6H12O6 is a molecule that neither releases nor accepts protons (H+) when dissolved in water. where on the pH scale would a solution of C6H12O6 be found?
7
H2CO3 is a molecule that releases protons (H+) when dissolved in water. where on the pH scale would a solution of H2CO3 be found?
less than 7 (acidic)
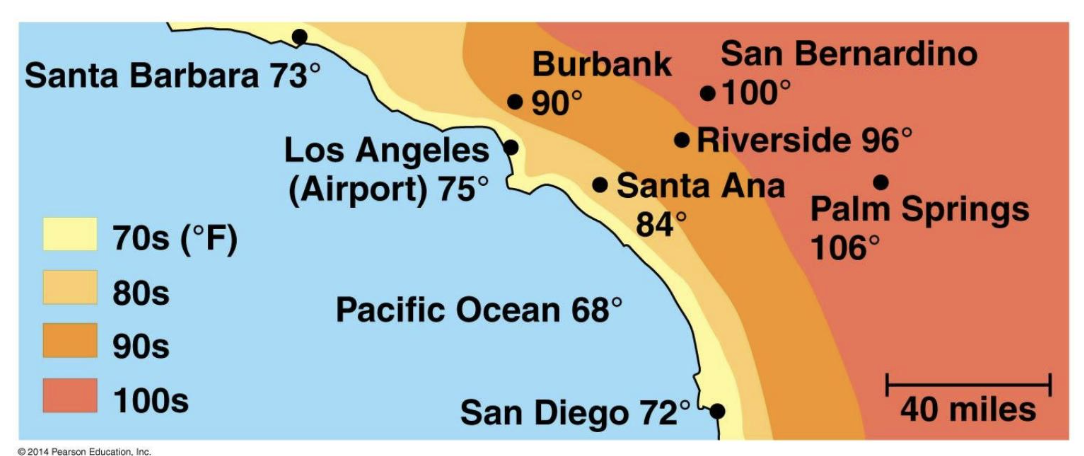
if two cities get the same amount of sunlight but one is on the coast and the other is inland, why does the coastal city have smaller air temperature range (less temperature swings)?
the high heat capacity of water allows the ocean to moderate the temperature of nearby air and land
why water is an effective solvent?
water’s polarity allows it to dissolve ionic and polar compounds
because of water's _____ heat of vaporization, sweating _____ your body temperature
high; decreases
why would a frozen ammonia ocean on Titan would pose major challenges for aquatic life?
ammonia does NOT expand upon freezing, so it would freeze from bottom up, potentially eliminating liquid habitats beneath the ice