(5-6) Physical Metallurgy | Properties of Metal
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
PHYSICAL METALLURGY
deals with the physical and mechanical properties of metals
PROPERTY
response of a material to any external stimulus such as stress, heat, electricity, magnetic field or the environment
example: strength of a material, which is the response of a material
STRUCTURE
arrangement of the components and at the different level-microscope, atomic, or even subatomic
PROPERTY = f(STRUCTURE)
PROPERTY = f(STRUCTURE)
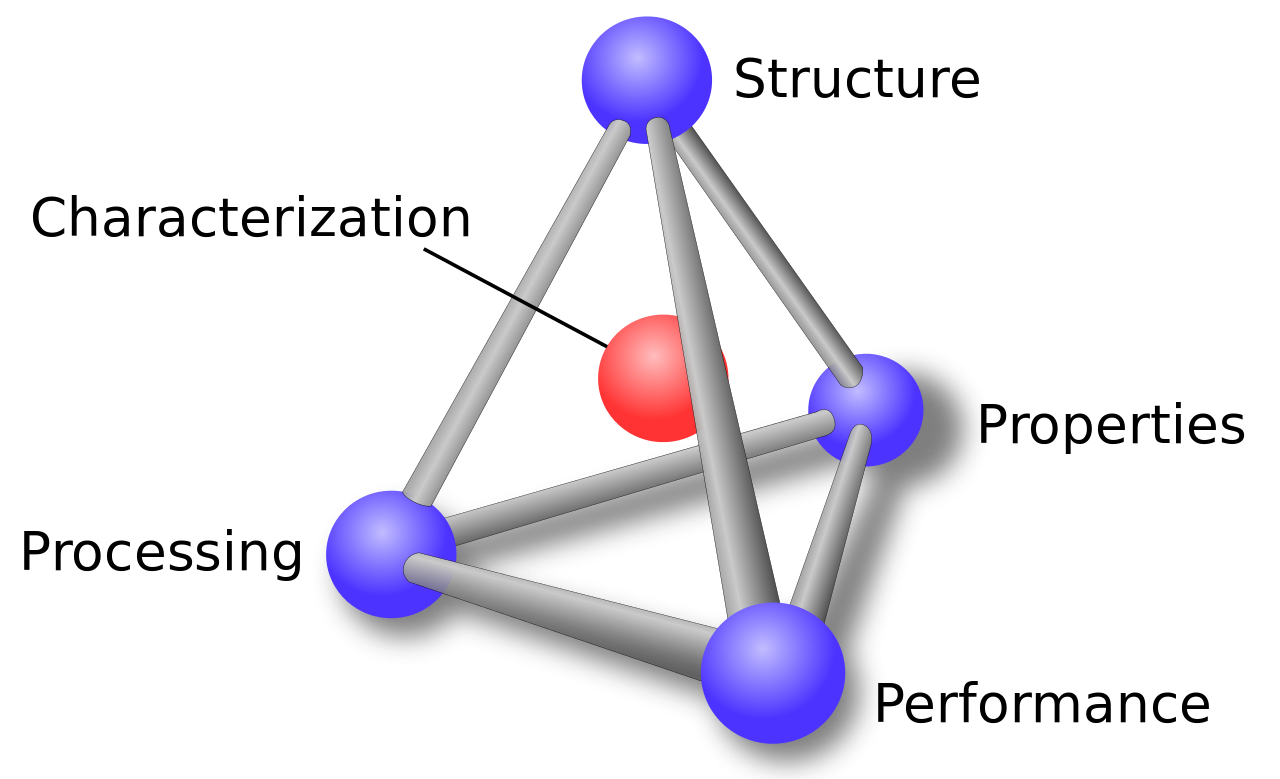
CHARACTERIZATION
STRUCTURE
PROPERTIES
PERFORMANCE
PROCESSING
Material Science Tetrahedron
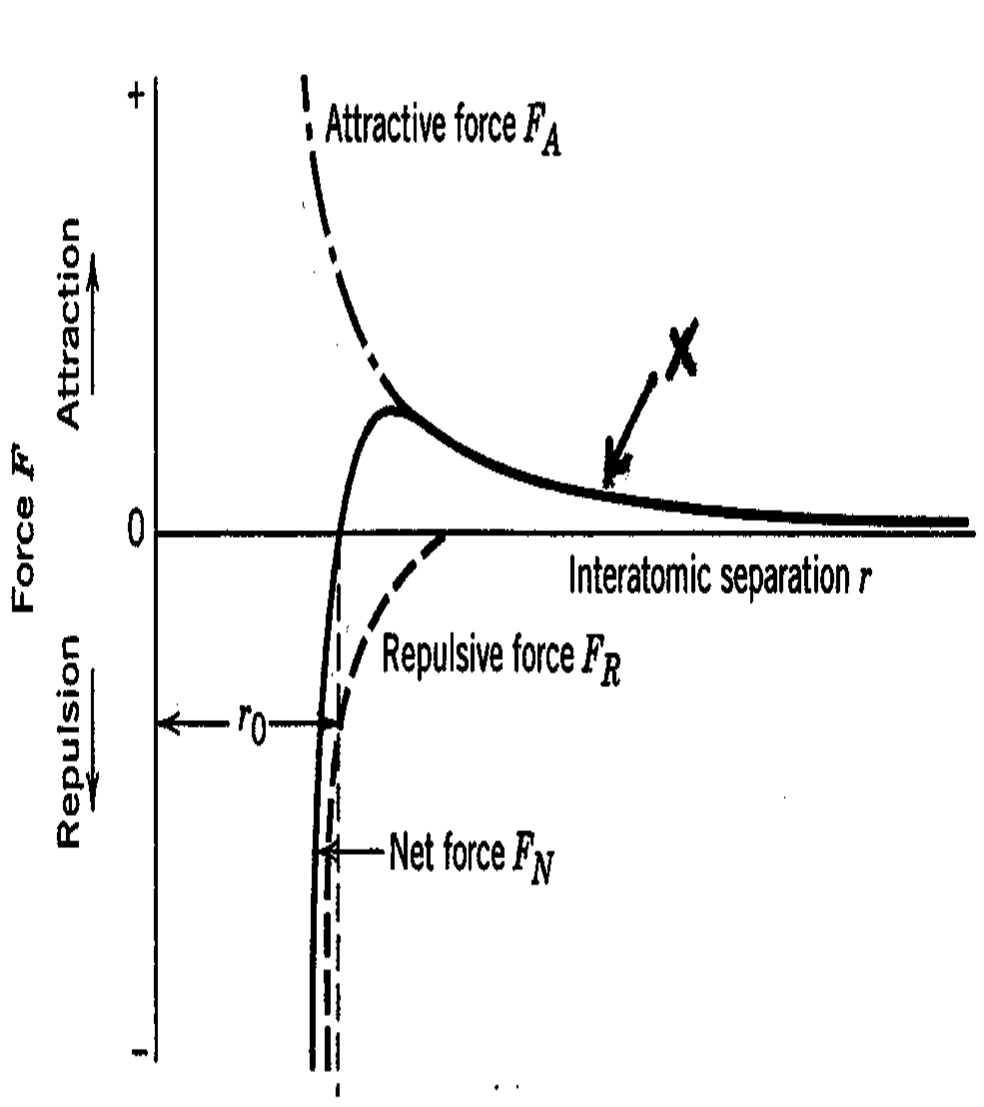
Atomic Bonding: Net Force
attractive and repulsive force merge at the center = equilibrium (Net Force)
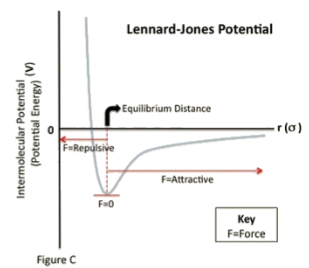
POTENTIAL WELL
equilibrium will be at the lowest point of well
the deeper the well, the better the equilibrium
deeper equilibrium is equal to higher energy needed to overcome that potential
Primary Bond
Ionic Bond
Covalent Bond
Metal Bond
Secondary Bond
Van der Waals
Hydrogen Bond
Types of Bond
IONIC BOND
type of bond where one or more electrons in the valence shell of an atom are transferred to the valence shell of another
between metallic and nonmetallic elements
COVALENT BOND
type of bond that involves sharing of electron
between nonmetallic elements
METALLIC BOND
type of bonding that occurs due to delocalized valence electrons
delocalized electrons can move freely within the solid in response to an electric field, creating a “sea of electrons”
VAN DER WAALS
type of bonding exists between virtually all atoms or molecules that arises from atomic dipoles or molecular dipoles
HYDROGEN BOND
special type of Van der Waals bonding
bond between a hydrogen ion and negatively charged ion
CRYSTALLOGRAPHY
arrangement of atoms within a structure of materials
Crystalline Solid
Amorphous Solid
Solid Structure is assembled into two:
CRYSTALLINE SOLID
contains regular and repeating atomic or molecular arrangements
includes metals and some ceramics and polymers
AMORPHOUS SOLID
non-dense, random ordering and packing
LATTICE
the 3D space filling repeating pattern on which atoms are placed
represents the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material.
UNIT CELL
smallest unit and simplest portion of the structure that describes the crystal pattern
LATTICE CONSTANTS
edge length along major axes
INTERAXIAL ANGLES
angles between axes
denoted as α (alpha), β (beta), and γ (gamma)
CRYSTAL SYSTEM
a scheme by which structures are classified according to unit cell geometry
Simple Cubic
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC)
Body-Centered Cubic (BCC)
Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP)
Types of Unit Cells
SIMPLE CUBIC
consists of atoms situated only at the (8) corners of a cube
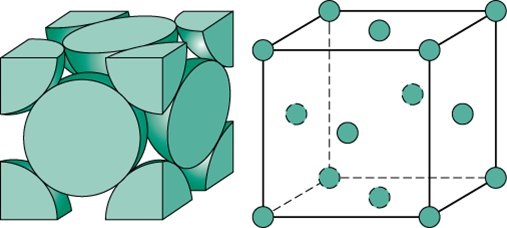
FACE-CENTERED CUBIC (FCC)
atoms are situated at the corners at the corners of the unit cell as well as the centers of each face
8 corner atoms, 6 face atoms
2 unit cells
Al (aluminum)
Cu (copper)
Ag (silver)
Au (gold)
Pb (lead)
Ni (nickel)
metals with FCC structure
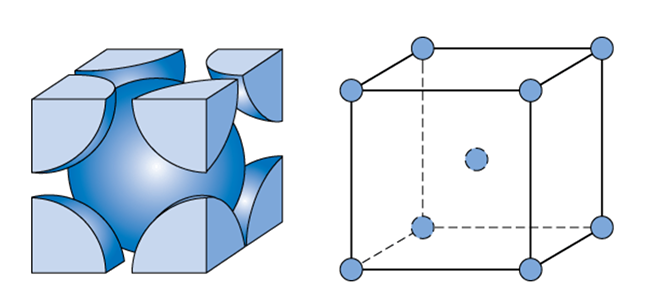
BODY-CENTERED CUBIC (BCC)
atoms are situated at the corners of the unit cell and at the center of the cube
Cr (chromium)
Fe (iron)
W (tungsten)
Metals with BCC structure:
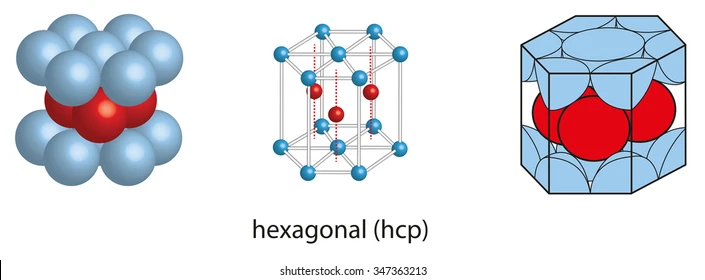
HEXAGONAL CLOSE-PACKED (HCP)
has 2 basal planes in the form of a regular hexagon and one atom at the center
12 coordination number, 6 atoms
Cd (cadmium)
Co (cobalt)
Ti (thallium)
Zn (zinc)
Metals with HCP structure:
Atomic Radius
Coordination Number
number of nearest neighboring atoms
Number of atoms per unit cell
Ratio of lattice constant to atomic radius (a:R)
Atomic Packing Factor
fraction of space filled by spherical volume
Unit Cell Parameters
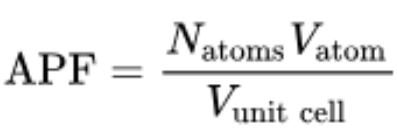
Atomic Packing Factor (APF) formula
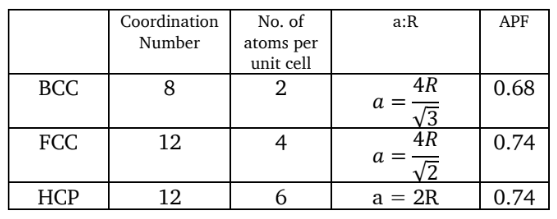
Unit Cell Parameters
SINGLE CRYSTAL
has perfect periodic arrangements of atoms that extends throughout the entire specimen
exists in nature but is very difficult to grow
quartz
POLYCRYSTALLINE
consists of many small crystals or grains
separated by grain boundaries
POLYMORPHISM
capability of some material to possess different crystal structures
Graphite vs Diamond
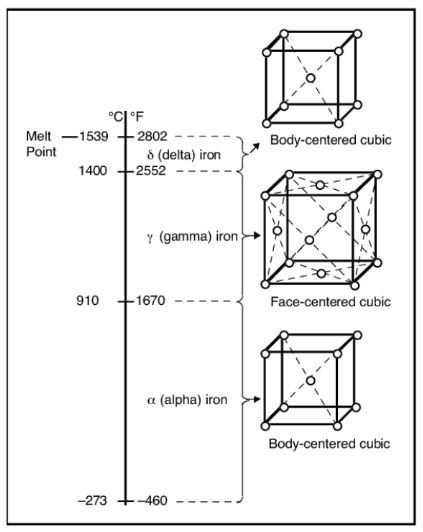
Polymorphism in Fe (Iron) with Carbon
ANISOTROPY
dependence of properties with crystallographic direction
degree increases with low structural symmetry
ISOTROPY
independence of properties with crystallographic direction
observed for polycrystalline materials even if individual grains are anisotropic
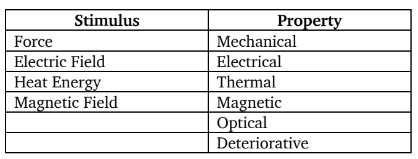
Stimulus and its Property
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
external force is applied
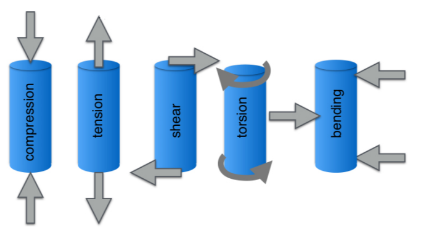
Tension
Compression
Shear
Torsion
Types of Loading (4)
Tensile Stress
Shear Stress
Engineering Stress
Engineering Strain
Types of Stress (4)
Tensile Stress
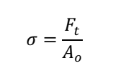
Shear Stress

Engineering Stress
instantaneous force divided by the original cross-sectional area
Engineering Strain
instantaneous deformation divided by the original length
the effect of stress
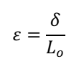
Universal Testing Machine (UTM)
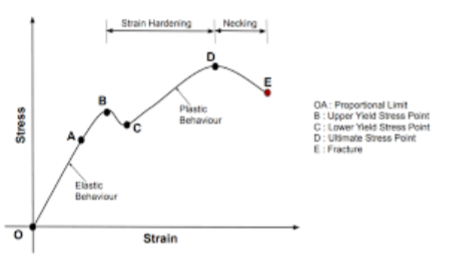
Necking
Types of Stress-Strain Testing
Universal Testing Machine (UTM)
used to uniaxially load as sample until material failure
Stress-Strain Diagram
to present data from UTM
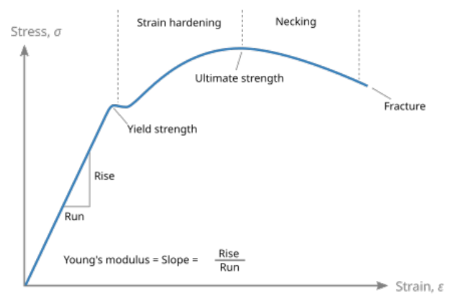
Necking
localized reduction in cross-sectional area, begins after UTS
Elastic Deformation - reversible
Plastic Deformation - irreversible
Tensile Properties

Hooke’s Law
used for Elastic Deformation
linear properties between stress and strain
Proportional Limit
Yielding
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
Fracture Stree
Elastic Behavior (4)
Proportional Limit
point wherein departure from linearity of stress-strain curve starts

Yielding
phenomena wherein it starts to transition from elastic to plastic
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
before necking
maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before it breaks
Fracture Stress
stress at the point of breaking of fracture
Ductility (%EL)
degree of plastic deformation that have been sustained at fracture
expressed as %elongation
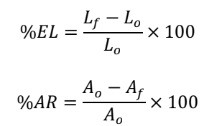
Resilience
capacity to absorb energy when it is plastically deformed, and to have its energy recovered upon unloading
strain energy per unit volume required to stress a material from an unloaded state
Toughness
energy to break a unit volume of a material
approximately by the area under stress-strain
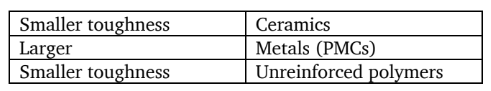
Hardness
a property that described the resistance to permanently indenting to the surface or localized plastic deformation
higher hardness means resistance to plastic deformation
Rockwell
Brinell
Knoop
Hardness Tests

Mohs Scale of Hardness
most are solid at normal temperature
relatively high density
some are very good conductors of heat and electricity
magnetic properties
Macroscopic Physical Properties of Metals (4)