Ochem 20 Functional Groups
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
alkane
Contains a carbon-carbon single bond (C-C)
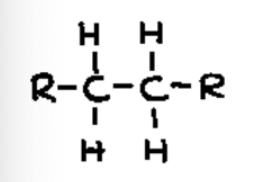
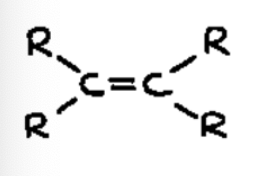
alkene
Contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C = C)
alkyne
Contains a carbon-carbon triple bond (𝐶≡𝐶)

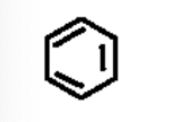
arene (aromatic ring)
A six-membered ring of carbon atoms with alternating double bonds.
halide
C bound with a halogen

fluoro
Carbon bound with Flourine
chloro
Carbon bound with Chlorine
bromo
Carbon bound with Bromide
iodo
Carbon bound with Iodine
alcohol
Contains a hydroxyl group (OH)
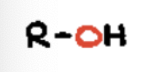
ether or alkoxy
Contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon groups (𝑅−𝑂−𝑅)
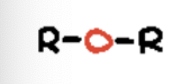
thiol
sulfhydryl functional group (R-SH)
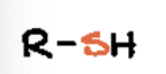
sulfide or sulfane
Sulfur attached to two Carbon’s
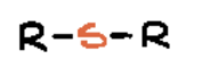
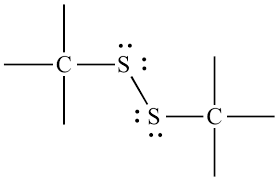
disulfide or disulfane
Two sulfurs bound together, and those sulfeus are bound to one Carbon
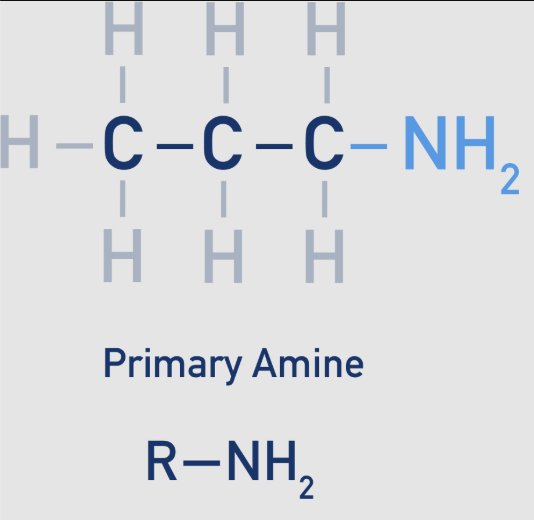
amine: 1 - primary
nitrogen atom is bonded to one alkyl group (R) and two hydrogen atoms
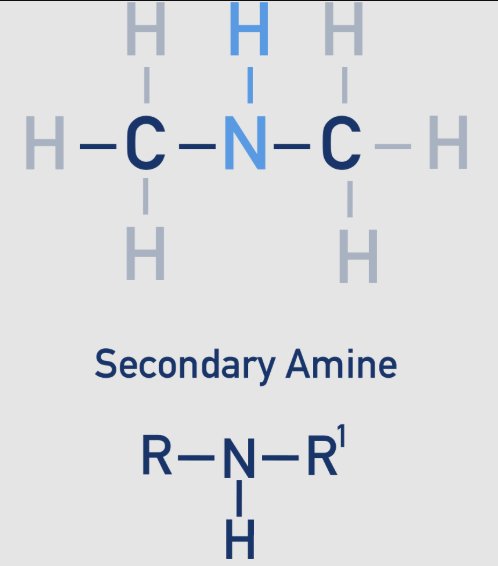
amine: 2 - secondary
The nitrogen atom is bonded to two alkyl groups (R and R') and one hydrogen atom.
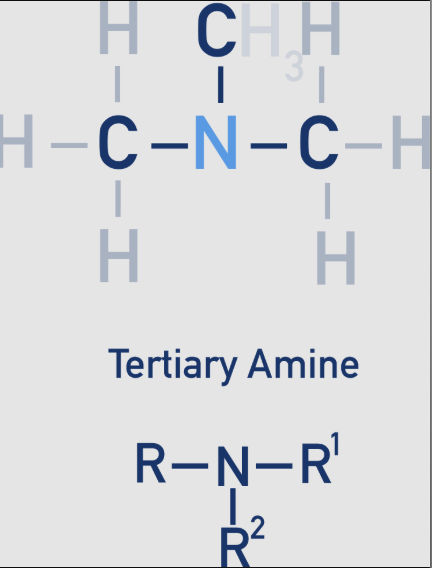
amine: 3 - tertiary
The nitrogen atom is bonded to three alkyl groups (R, R', and R'')
nitrile or cyano
organic compound that contains a cyano group (-C≡N), which consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom
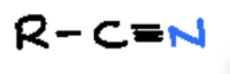
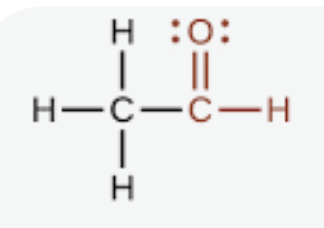
aldehyde
a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom) bonded to a hydrogen atom (R-CHO)
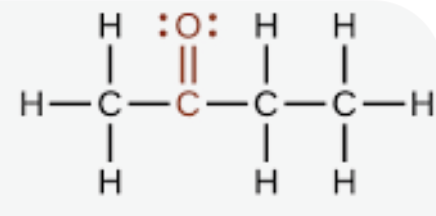
ketone
a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom) bonded to two other carbon atoms
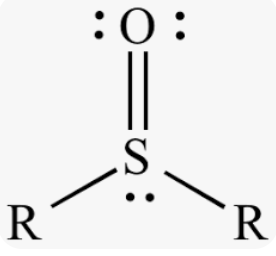
sulfoxide or sulfinyl
sulfur atom bonded to one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms
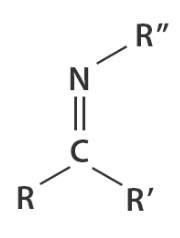
imine
a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon-nitrogen double bond (C=N)
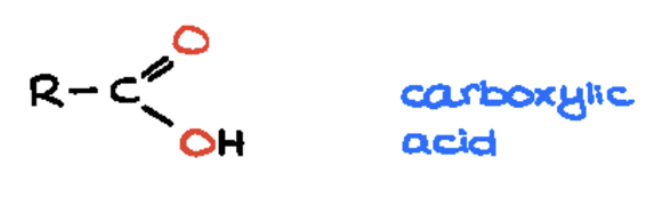
carboxylic acid (-oic acid)
carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (a carbonyl group) and also single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH)
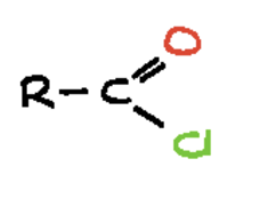
carboxylic acid chloride (-oyl chloride)
carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (a carbonyl group) and also single-bonded to a chloride
carboxylic acid anhydride (-oic anhyrdide)
two acyl groups (R-C=O) joined by a single oxygen atom, with the general formula 𝑅−𝐶(=𝑂)−𝑂−𝐶(=𝑂)−𝑅′
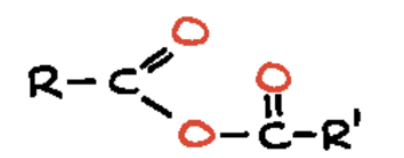
ester (-oate)
a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom) bonded to another oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to a carbon-based group
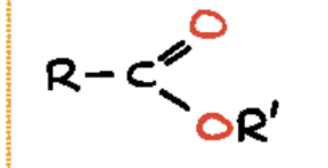
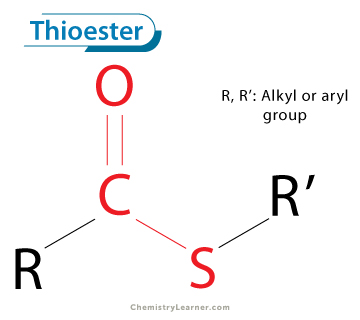
thioester (-thioate)
an organic compound that is similar in structure to an ester, but with a sulfur atom replacing the single-bonded oxygen atom
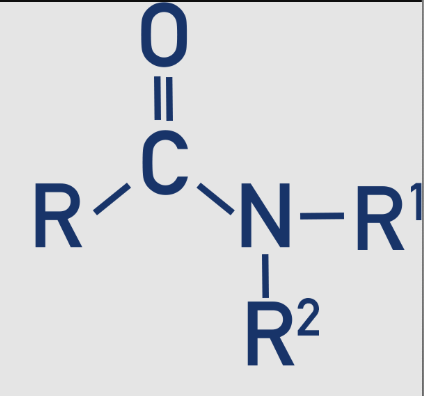
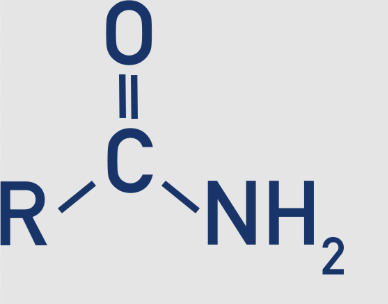
1 amide - primary
The nitrogen is bonded to two hydrogen atoms 𝑅−𝐶(=𝑂)−𝑁𝐻2
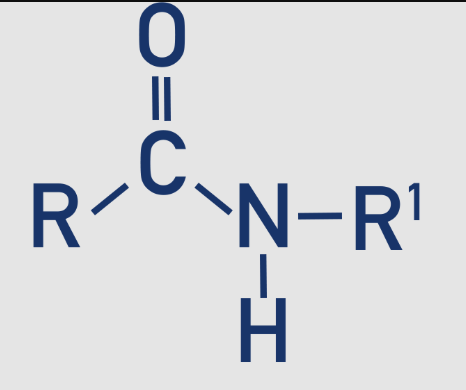
2 amide - secondary
The nitrogen is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one organic group (𝑅−𝐶(=𝑂)−𝑁𝐻𝑅′)
3 amide - tertiary
The nitrogen is bonded to two organic groups (𝑅−𝐶(=𝑂)−𝑁𝑅′𝑅′′)