Intro Pharm/Receptors/Admin
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Disease, pregnancy
A drug is any agent used in treatment or prevention of __ and or __
Generic Name
Name of drug that is the same between companies
Ex: Ibuprofen, acetaminophen
Trade Name
Advil, motrin, others– brand name
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination
ADME of pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body (i.e. efficacy, toxicity)
Stimulation, depression
norepinephrine effect on heart rate =
barbiturates’ effect on CNS =
Replacement, cytotoxic action
working insulin given for tx diabetes =
carboplatin for infected/cancer cell DNA damage =
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
Activate in response to changes in the membrane potential OR ion concentration
Direct-ligand-activated ion channels
Activate in response to changes ion concentration (specific to Ca2+, K+, or Na+)
Benzodiazepines
Drug binds to GABAa receptor to enhance Cl- channels in brain allosterically
(ligand ion channel interaction)
Acetylcholine
Drug activates nicotinic receptor to open Na+ channel
(ligand ion channel interaction)
Voltage-Gated ion channels
Activate in response to membrane depolarization
Lidocaine
Drug acts as voltage-gated Na+ channel inhibitor, reduce pain
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Activated via protein phosphorylations in sequence // GTP activated proteins
Adenyl cyclase, cAMP, PKA
Gs/Gi = Activation/inactivation of __ __ (enzyme)
Converts ATP to ___ → Activates/inactivates ___ (enzyme) for further phosphorylations
Beta 1, beta 2, M2, alpha 2, opioids (Rs)
2 examples of Gs…
3 examples of Gi…
*Hint: QIQ QISS
M1, M3, alpha 1 (Rs)
Gq Rs
*Hint: QIQ QISS
phospholipase C, IP3, DAG, Ca2+, contraction, PKC
Gq = Activation of ___ (enzyme)
PIP2 becomes → __ and __, from PLC activity
IP3 stimulates release of __ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Net: Smooth muscle __
DAG then activates __ (enzyme)
Enzyme-linked Receptors (Intrinsic enzymes)
Activated via protein and receptor phosphorylation from kinases
Intrinsic Enzymes
Enzymatic domain is integral part of transmembrane receptor protein for phosphorylation
Growth factors, insulin
Examples of intrinsic enzyme Rs include:
epidermal __ __, __ Rs, and other RTKs
Extrinsic Enzymes
Enzyme is separate protein that associates/links with transmembrane receptor and phosphorylates
Cytokine, JAK-STAT
Examples of extrinsic enzyme Rs include:
__ Rs stimulating __-__ pathways (non-RTK)
Specific Receptors Class
Regulator proteins with endogenous ligands (i.e. glutamate Rs)
Intracellular Receptors
Activated via protein phosphorylation and later translocate to nucleus via diffusion → control gene expression
Steroid, thyroid
Intracellular Rs
In cytosol - __ hormone Rs
In nucleus - __ hormone Rs
First-Pass Effect
Metabolism of drug occurring during its first pass through liver immediately following absorption from GI tract
Oral, less, first-pass effect
Amount of active drug entering __ (route) systemic circulation after GI admin is __ (more/less), by amount of the __ __ __, than that after another route of admin
Oral, sublingual, rectal
3 types of Enteral Administration
PO advantages
Most used route of admin, convenient
Safe drug recall, inexpensive
Self-administration
PO disadvantages
Absorption is slow and highly variable between patients
Absorption also affected by pH in GI tract, presence of food/enzymes/bacteria, other drugs
Oral bioavailability less than 100% due to first-pass metabolism
Sublingual
Drug placed under the tongue then drug absorbed directly in bloodstream via small veins
Sublingual advantages
Rapid absorption directly into systemic circulation via mouth
NO first-pass effect
Sublingual disadvantages
Erratic absorption leads to unpredictable effects
Useful only for small doses
Requires prolonged contact with mucosa, inconvenient
intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous (IV, IM, SC)
3 routes of parenteral administration
IV advantages
Large fluid volumes possible
Avoids first-pass effect (100% bioavailability)
Rapid onset and subsequent control of drug concen.
IV disadvantages
Higher cost compared to oral, difficult to admin, irreversible
Possible infections, hematoma
Unsuitable for non-aqueous solutions, drug must be soluble
IM advantages
Fairly rapid and complete absorption of water soluble drugs
Allows injection of depot preparations, larger volume than SC
Avoids first-pass effect
Patients can self-admin
IM disadvantages
Painful, inconvenient
Possible hematoma/bleeding
Subcutaneous
Needle inserted into fatty tissue layer beneath skin, then reaches capillaries to bloodstream via lymphatics
SC advantages
Slower absorption than IM since blood flow is less in fatty tissue
Used for many protein drugs (insulin)
Avoids first-pass effect
Patients can self-admin
SC disadvantages
Discomfort, inconvenient
Possible tissue irritation/injury
Intradermal
Commonly used for penicillin allergy and PPD tests
Cutaneous (topical), Percutaneous (transdermal), Inhalation, Nasal, Vaginal, Eye drops
Local routes of administration - (6)
IM, 90
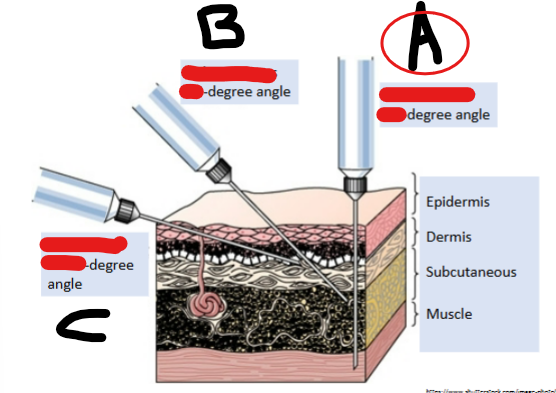
Subcutaneous, 45
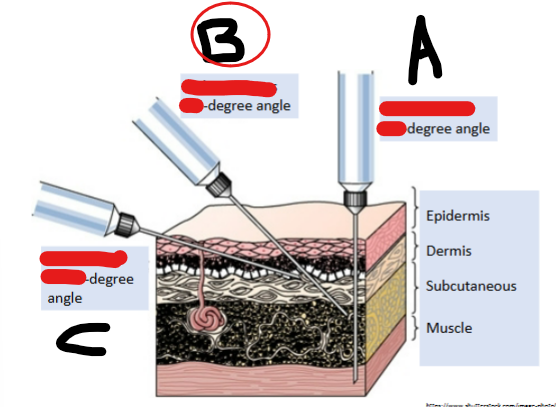
Intradermal, 10-15
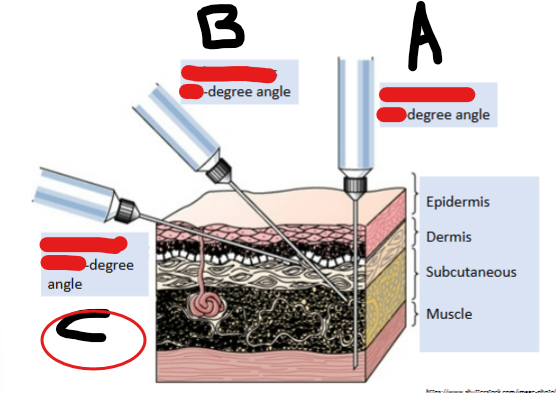
90
Degree angle for insulin pen delivered subQ
Drug Absorption
Transfer of a drug from site of administration to bloodstream and to site of action
Drug permeation, passive diffusion
Via __ __: In order to reach site of action, drugs have to pass through several biological membranes
Most important mechanism for permeation is __ __ of most drugs
Lipid, unionized, protein
__-soluble or __ (ionized/unionized) drugs most easily diffuse across membranes
__ Therapeutics - are injected as they are too large to cross membranes and would degraded by enzymes/acid in GI tract if oral admin
Ionization, water, excreted
Drug __ refers to drug molecule carrying an electric charge that is __ soluble and __ (absorbed/excreted)
Acidic, absorbed, acidic, basic, basic
Rules of AAA or BB for absorption
__ drugs are best __ from __ environments
__ drugs are absorbed best in __ environments
Acids, basic, bases, acidic, urine pH, ionized
Rules of AB or BA for excretion
Weak __ are usually excreted faster in __ urine (AB)
Weak __ are usually excreted faster in __ urine (BA)
Goal is to accelerate excretion of drug and adjust the __ __
Thus make certain most of drug is __ (ionized/unionized) state → drug gets “trapped” in urine
Bioavailability (F)
Fraction of administered dose of drug reaching systemic circulation in unchanged form
IV, lesser
F of ___ = 1, All other routes: F is __ (greater/lesser) than 1
IV, IM, SC, oral
Absorption Speed ~ __ > __ > __ > __
*Think first pass
Time course curve
Measured via drug plasma levels across different times points following routes of admin
AUC oral / AUC IV
When IM and IV doses are equal in time course curve:
F (bioavailability) = ___ / ___