Autoimmune Diseases + Misc
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Most common monomorphic and polymorphisms in immunoregulatory genes
monomorphic: AIRE, FOXP3, FAS/FASL
polymorphic: CD25 (IL-2 alpha chain), IL-10, CTLA-4
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Hypersensitivity Type: cytotoxic type II (organ)
Mechanism: Ab against RBCs, either via opsonization for phagocytosis (extravascular) or complement activation for lysis (intravascular)
Cold Agglutinin Disease = IgM Ab, react at <37*C
Warm Ab Hemolytic Anemia = IgG Ab, react at >37*C
Other: increased lymphocytosis + autoimmune cytopenia = signs of Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome (ALPS)
ID via Coombs test —> detect Ab on the RBCs
HLA association? no
Goodpasture Syndrome
Hypersensitivity Type: cytotoxic type II (organ)
Mechanism: IgG against type IV collagen induces antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) —> destroys pulm alveoli and glomerular basement membrane
Symptoms: fatigue, naus/vom, resp distress, hemoptysis, hematuria, HTN, urination discomfort, edema
- linear/smooth pattern on immunofluorescence of kidney biopsy
HLA association? no
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hypersensitivity Type: cytotoxic type II and type IV (organ)
Mechanism:
Type II: Ab against thyroid cells/Tg/TPO —> necrosis/apopt.
Type IV: Th1 and Th17 mediated inflammation, increase IL-23, attacks thyroid cells —> apopt.
Symptoms: hypothyroidism = cold sensitivity, high TSH, low T4, fatigue, weight gain, alopecia, goiter, increased risk of non-hodgkin’s lymphoma
HLA association? Yes DR3
Graves’ Disease
Hypersensitivity Type: non-cytotoxic type II, agonistic (organ)
Mechanism: IgG acts as anti-TSH receptor —> thyrotoxicosis (TSH receptor constituatively stimulated)
Symptoms: hyperthyroidism = heat intolerance, goiter, low TSH, high T3/T4, weight loss, opthalmopathy,
HLA association? no
Myasthenia Gravis
Hypersensitivity Type: non-cytotoxic type II, antagonistic (organ)
Mechanism: anti-AChR Ab —> bind AChR and trigger internalization of the receptors and degredation —> unable to have neuromusc. signaling
Symptoms: chronic musc. fatigue, weakness, ptosis, diplopia, worsens w/ musc. use, improves w/ ACh esterase inhibition
HLA association? no
LSE w/ Lupus Nephritis
Hypersensitivity Type: type III (systemic)
Mechanism: Tcell dependent Ab response to self-Ag (RNA, DNA, nuclear proteins, etc.)
Symptoms: butterfly rash, photo-sensitivity, arthritis, arthralgia, myositis, aseptic fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, fatigue, Raynauds, cytopenia, etc
HLA association?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Hypersensitivity Type: type III (systemic)
Mechanism: idk but it’s male predom.
Symptoms:
Early: sacroiliitis —> pain/stiffness in lower back + hips, esp after periods of inactivity
Eventually: fusion of vertebae restricts movement, can progress to other joints too
May have uveitis and photophobia
tx w/ TNF-a inhib.
HLA association? YES HLA-B27
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Hypersensitivity Type: type III and type IV (systemic)
Mechanism: anti-CCP and rheumatoid factor (IgM against IgG)
Symptoms: pain + stiffness in mult. joints (esp. hands/wrists/knees) that’s worse following extended inactivity, can cause non-hemolytic anemia from the systemic uveitis and inflamm.
HLA association? yes
T1DM
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, endocrine (organ)
Mechanism: Th17 + Th1 mediated inflamm recruitment —> diffuse damage of pancreatic islet cells. Also autoreactive CTLs target beta-cells
+85% have Abs against insulin, glutamic acid decarboxylase, and/or other islet cell Ags
Symptoms: polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, ketoacidosis. Frequently comorbid w/ thyroid disease
HLA association? Yes! DQ2! Also CD25 & CTLA4 polymorphisms
Addison’s Disease
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, endocrine (organ)
Mechanism: Th1 mediated destruction of adrenal cortex, often w/ Ab involvement
Symptoms:
skin + mucosal hyperpigmentation from high MSH
no cortisol —> metabolic acidosis
no aldosterone —> hypotension (salt wasting) and hyperkalemia [Fuller is a dumb ass and said those sx are due to no cortisol >:/…]
Ab against 21-hydroxylase
HLA association? yes
Multiple Sclerosis
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, CNS (systemic)
Mechanism: autoreactive Tcells promote infiltration and assumed IgG in the CSF against myelin basic protein —> progressive demyelination of CNS
Symptoms: limb weakness, spasticity, sensory loss, diplopia and/or blurred vision, ataxia, bladder dysfunction, fatigue, facial weakness resembling Bell’s Palsy, paralysis
**consider how these sx could resemble late stage tertiary syphilis
HLA association? yes
Celiac Disease
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, GI
Mechanism: Th1 mediated destruction of gut epithelium with Abs generated (anti-tissue transglutaminase Ab)
Gliadin (from gluten) = allergen
transglutaminase is the auto-Ag that modifies the gliadin peptide
innate and adaptive immune responses
Symptoms: persistent diarrhea, weight loss/malabsorption, abdom distention, damage mainly to small intestine
often comorbid w/ T1DM, thyroid disease,CVID, or Selective IgA defic (would cause false neg on celiac Ab test)
can also result in extraintestinal sx: neuro, msk, etc
HLA association? yes
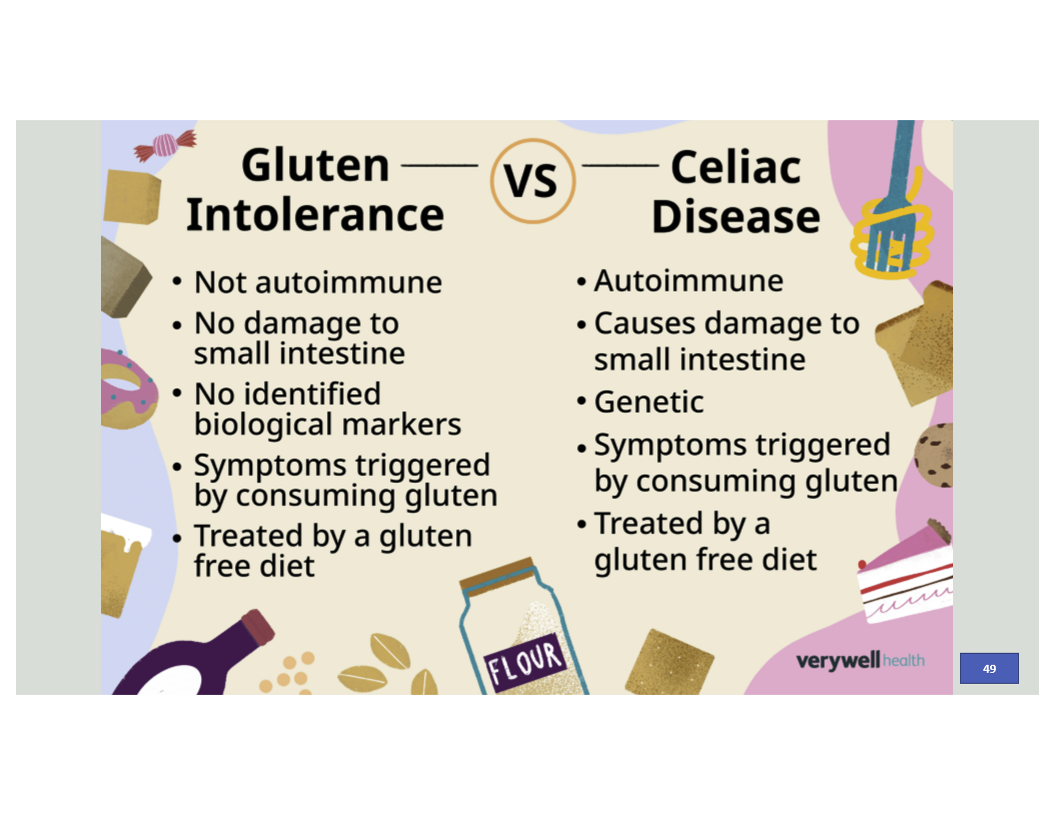
Celiac vs Gluten-Intolerance
Crohn’s Disease
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, GI
Mechanism: Th1 and Th17 mediated cytokines affecting GI tract, most commonly the ileum, uncontrolled activation of immune cells
Symptoms: persistent diarrhea, urgent need to defecate, LRQ abdom cramping, non-bloody diarrhea, weight loss, cobblestone mucosa, non-caseating granulomas, discontinuous patchy inflamm/lesions
Increased risk for primary sclerosing cholangitis and colorectal cancer
HLA association?
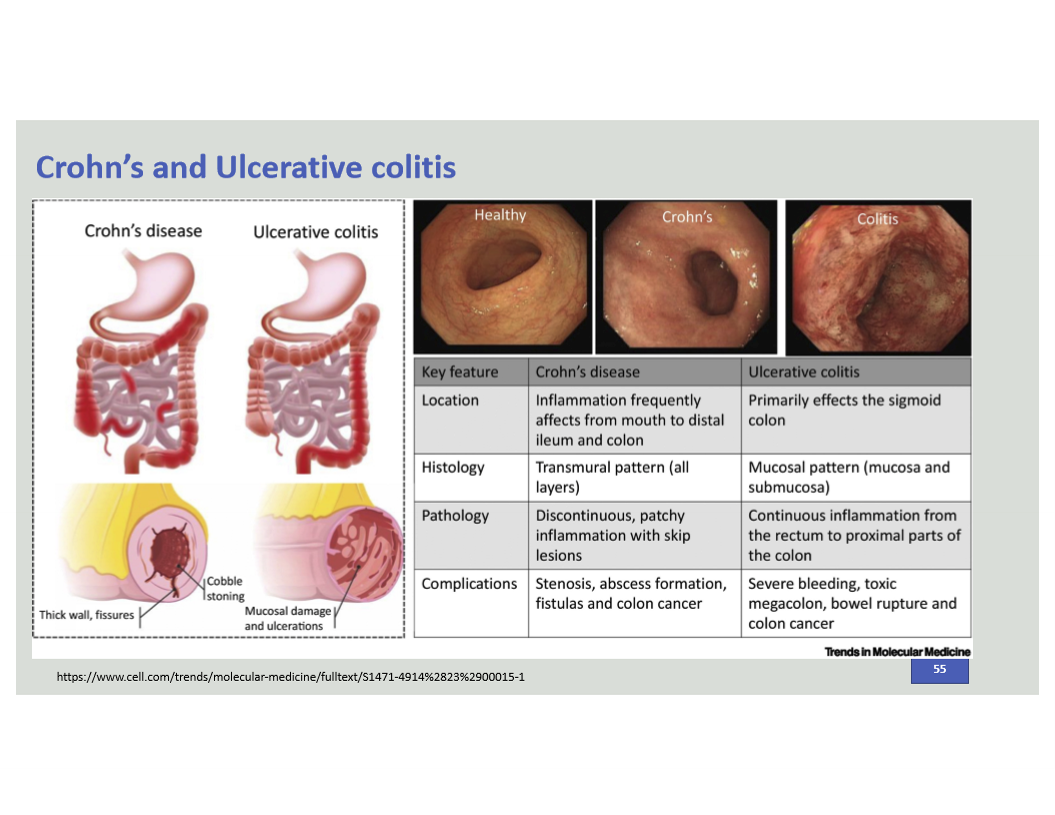
Compare Crohn’s vs Ulcerative Colitis
C. Diff major characteristics
assoc w/ Abx use
massive watery diarrhea, fecal leukocyte (+)
pseudomembrane formation (white/yellow plaques)
mucosal ulcerations, fibrin, inflamm cells
dx via Toxin A & B in stool
How to TNF treatments work for autoimmune diseases?
bind to TNF specifically or provide receptor mimic to decrease inflammation
Psoriasis (vulgaris/plaque subtype most common)
Hypersensitivity Type: type IV, integumentary
Mechanism: cytokine dysregulation —> skin cells rise to the surface too fast
Symptoms: red, scaly, well-defined, silvery-white, dry plaques, preferentially on elbows/knees/scalp/lumbar area. Plaques can be erythematous and pruritic.
often comorbid w/ psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s, psych disorders, and uveitis
HLA association?
APECED aka APS type I
(systemic)
Mechanism: defective AIRE —> impaired thymic (-) selection & Treg induction —> increased autoimmune disease
Symptoms: chronic mucocutaneus candidiasis (infancy), Ab against IL-17, hypoparathyroidism (before 10 yr) , adrenal failure (~15 yr)
HLA association? no
IPEX Syndrome
(systemic) X-linked
Mechanism: defective FOXP3 —> impaired immune regulation in the periphery —> increased autoimmune disease
Symptoms: presents w/in 1st days of life w/ severe enteropathy: chronic watery/mucoid/bloody diarrhea that’s typically unresponsive to dietary exclusions or bowel rest —> malabsorption and failure to thrive
endocrine: neonatal T1DM, thryoiditis (hypothyroidism most common)
skin: from mild dermatitis to severe diffuse erythematous exudative plaques that evolve to lichenification
excessive lymphoprolif. (hepatosplenomegagly, lymphadenopathy)
autoimmune cytopenia
kidney disease
HLA association? no