3.4 - Final Accounts (Profit and Loss, Balance Sheets, Intangible Assets)
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Final Accounts
The financial statements of an organization made up at the end of an accounting period, usually the fiscal year. These accounts report on the company’s performance
Key final accounts:
Profit and Loss account
Balance Sheet
Why produce final accounts?
Legal requirement for incorporated businesses
To inform stakeholders about performance
To calculate tax owed
To aid decision making
As part of a business plan
To gain finance
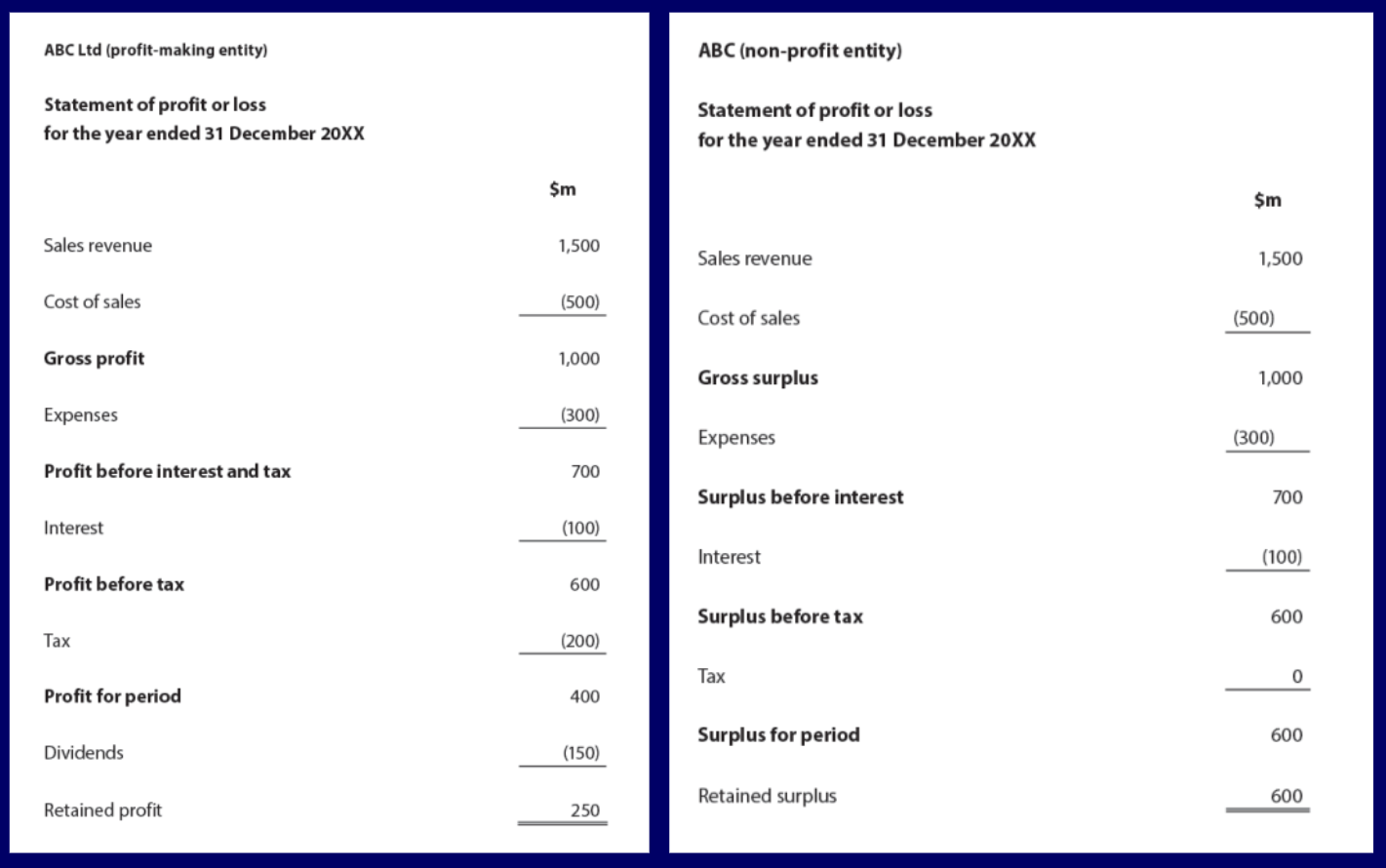
Profit and Loss account
A financial statement which shows the revenue and costs of the business over a period, usually a year.
It also shows:
How much profit/loss was made
How much tax was paid
What happened to the profit
IB Structure for Profit and Loss account
Limitations of the Profit and Loss account
Shows the historical financial performance of a business. No guarantee that future performance is linked to past performance or success
Might be difficult to compare the profit or loss of different firms in different countries as there is no international standardized format
Window dressing may occur. This is the legal act of creative accounting by manipulating final accounts to make them appear more attractive, even though this disguises the underlying financial position of the company.
Key Formulas for Profit and Loss account
Gross Profit = Sales Revenue - Cost of Sales
Sales Revenue = Gross Profit + Cost of Sales
Cost of sales = Sales Revenue - Gross Profit
Profit before interest and tax = Gross Profit - Expenses
Profit for period = Profit before interest and tax - Interest - Tax
Formula for GROSS PROFIT
= Sales Revenue - Cost of Sales
Formula for SALES REVENUE
= Gross Profit + Cost of Sales
Formula for COST OF SALES
= Sales Revenue - Gross Profit
Formula for PROFIT BEFORE INTEREST AND TAX
= Gross Profit - Expenses
Formula for PROFIT FOR PERIOD
= Profit before interest and tax - interest - tax
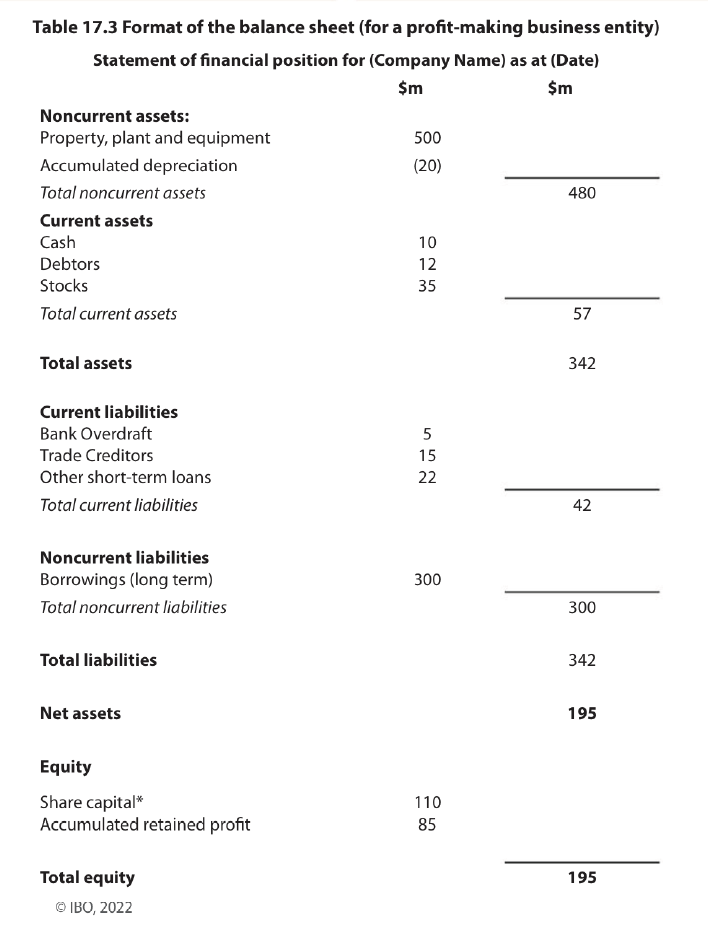
Balance Sheet
It contains information on the value of an organization’s assets, liabilities, and the capital invested by the owners. All companies are legally required to produce for auditing purposes.\
It is often described as a “snapshot” of the organizations financial situation
Assets
Items of monetary value that are owned by a business, such as cash, stocks, and property
Noncurrent Asset (also referred to as fixed asets)
An asset used for business operations and is likely to last for more than 12 months
Examples: property, factory, equipment
Current Asset
Refers to cash or any other liquid asset that is likely to be turned into cash within twelve months of the balance sheet date.
The three main types of current assets are: Cash, Debtors, and Stocks
Cash
The money that is held in the business or at the bank
Debtors
Refers to the people or other organizations that owe money to the business as they have purchased goods on credit.
Stocks
These are unsold supplies of raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished goods.
Liabilities
A legal obligation of a business to repay its lenders or suppliers at a later date. These are categorised into noncurrent ____________ and current ____________
Noncurrent liabilities (long-term liabilities)
Debts that are due to be repaid after twelve months of the balance sheet date and are a firm’s source of long-term borrowing.
Examples: mortgages, bank loans, debentures
Current liabilities
Debts that must be settled within one year of the balance sheet date.
Examples: bank overdrafts, trade creditors, other short-term loans
Bank overdrafts
A short-term source of finance that enables a business to withdraw more from it’s bank account that the amount that exists. They need to be repaid quickly as interest rates tend to be very high
Trade Creditors
Suppliers need to be repaid for items that have been purchased on trade credit, usually within 30 to 60 days
WHAT MUST BALANCE??
Net Assets = Equity
Long formula for Net Assets
Net assets = (Noncurrent assets + Current assets) - (Noncurrent liabilities + Current liabilities)
Shortened formula for Net Assets
Net Assets = Total Assets - Total liabilities
Equity
Also known as capital and reserves, it refers to the value of the business that belongs to the owners
The two sections in a balance sheet related to this are: share capital and retained earnings
Share Capital
Refers to the amount of money raised through the sales of shares. For publicly traded companies, this is done via a Stock Exchange
Retained Earnings
The total amount of accrued profit after interest, tax, and dividends have been paid. The ________ ______ is then reinvested into the business.
IB Structure for Balance Sheet
Limitations of Balance Sheets
They are static documents, the financial position of a business might be very different in subsequent periods
The figures are, at best, only “accurate” estimates of the value of assets and liabilities. The true market value of a noncurrent asset is only known once the item has actually been sold.
There is no universal format for a balance sheet. This can make it difficult to compare the financial position of different firms, even if they operate in the same industry
Not all assets of a business are included in the balance sheet, especially intangible assets and the value of human capital
Intangible assets
Non-physical fixed assets that have the ability to earn revenue for a business, such as brand names, goodwill, trademarks, copyrights, and patents. They are legally protected by laws collectively known as intellecutal property rights
Branding
Brand recognition and brand value help to drive global sales yer after year. Branding is an indefinite asset as brand recognition and brand loyalty stay with the company for as long as it exists
Patents
Provide legal protection for inventors, preventing others from copying their creation for a fixed number of years. Allow the inventor to have exclusive rights to commercial production for a specified time period.
Other firms must apply and pay a fee to the patent holder if they wish to use or copy the ideas.
Copyright
Provide legal protection for the original artistic work of the creator, such as an author, photographer, painter, or musician. Anyone wishing to reproduce or modify the artist’s work must first seek permission from the copyright holder, usually for a fee.
Goodwill
An intangible asset which exists when the value exceeds its book value. It includes the value of an organization’s reputation and corproate image as well as its business connections.
It is difficult to place a value on ___________
Registered trademarks
Distinctive signs that uniquely identify a brand, a product, or a business entity. It can be expressed by names, symbols, phrases, or an image.
They provide legal protection against those who might copy.
As assets, registered ___________ can be sold
Limitations of final accounts
Using a single year’s accounts in isolation does not allow analysts to judge the financial performance of the business over time. Instead, a series of financial accouns would be more helpful to determine any trends in data
Human resources are totally ignored when examining final accounts. Skills, loyalty, goodwill, and motivation of employees are all overlooked. The inability to retain/motivate staff can have major financial repurcussions on the future financial position of the business
Final accounts do not reveal anything about the firm’s non-financial matters of priorities, such as its organizatoinal culture and contributions to local communities.
There also needs to be access to the final accounts of other businesses in order to benchmark the financial performance with competitors in the industry. This is time consuming
Companies can limit the financial information that they will disclose because their final accounts will be in the public domain and hence accessible by their competitors
Final accounts are historical accounts of the financial position of a business at one point in time. Past financial performance is not necessarily indicative of current or future performance or success
Depreciation
The fall in the value of noncurrent assets over time due to wear and tear, and obsolesence.
Wear and tear
Fixed assets such as computers and motor vehicles are used repeatedly over time, so they tend to wear out and raise maintenance costs.
Obsolesence
As newer and better products become available, the demand and hence the value of existing noncurrent assets will fall. Obsolete assets are out-of-date assets such as older versions of vehicles, computers, equipment, etc.
Why does depreciation need to be calculated?
In order to:
Calculate the value of a business more accurately.
Depreciating noncurrent assets will reduce the value of net assets.
Realistically assess the value of noncurrent assets over time.
The historic costs of fixed assets such as machinery and vehicles, are unlikely to be equal to their current market value.
Plans for the replacement of assets in the future
Provisions are made for purchasing new noncurrent assets