Intro to Seed Plants PT.2 - Gymnosperms (not on exam 3)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the basic characteristics of plant kingdoms?
autotrophic, eukaryotic, multicellular, non-mobile, cellulose-rich cell walls, alternations of generations life cycle, special adaptations for life on land
What are the characteristics of seed plants?
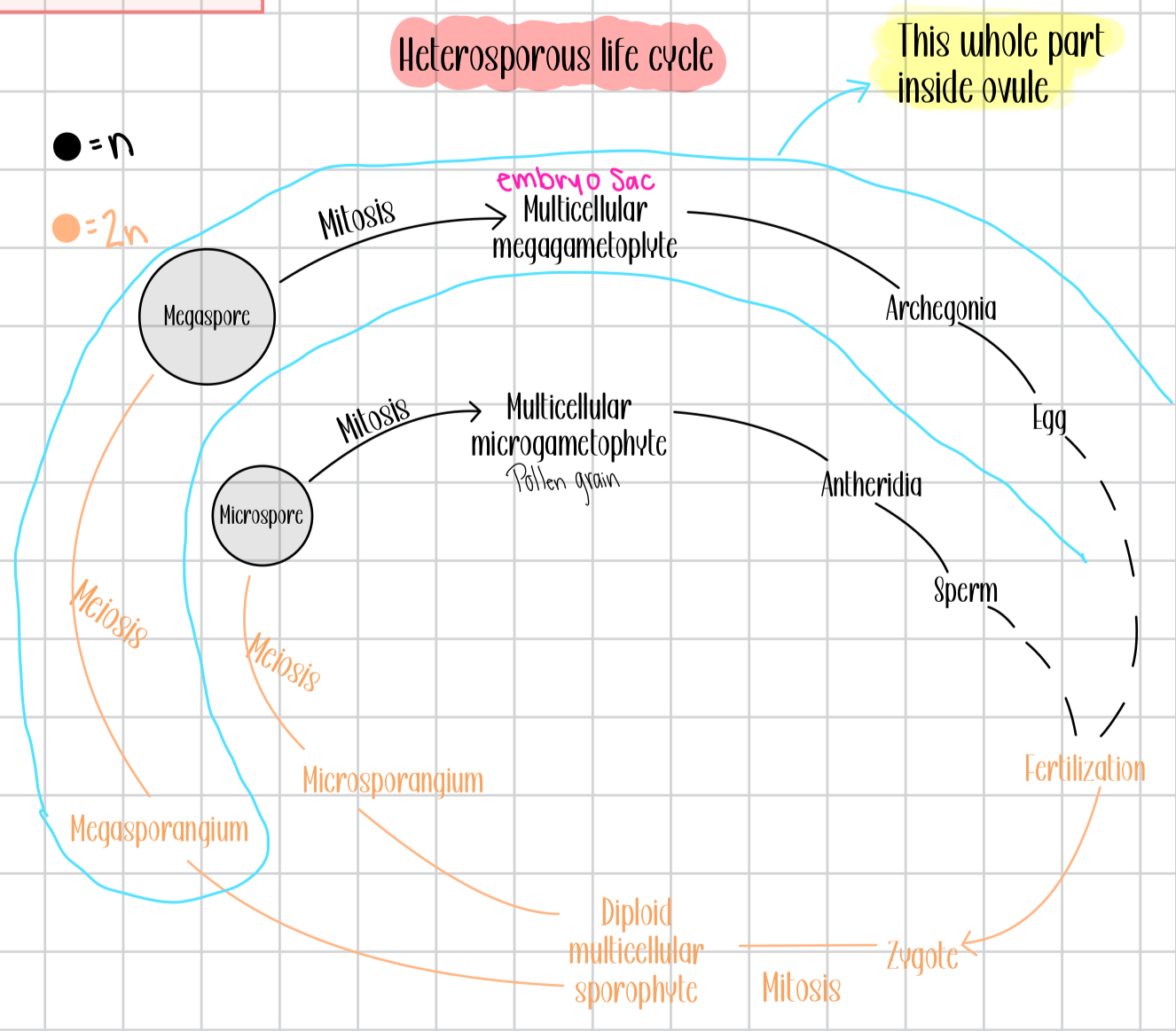
heterosporous, spores remain within sporangia, have seeds, have pollen
What is a seed?
a matured ovule containing an embryo
What does heterosporous mean?
makes 2 different kinds of spores
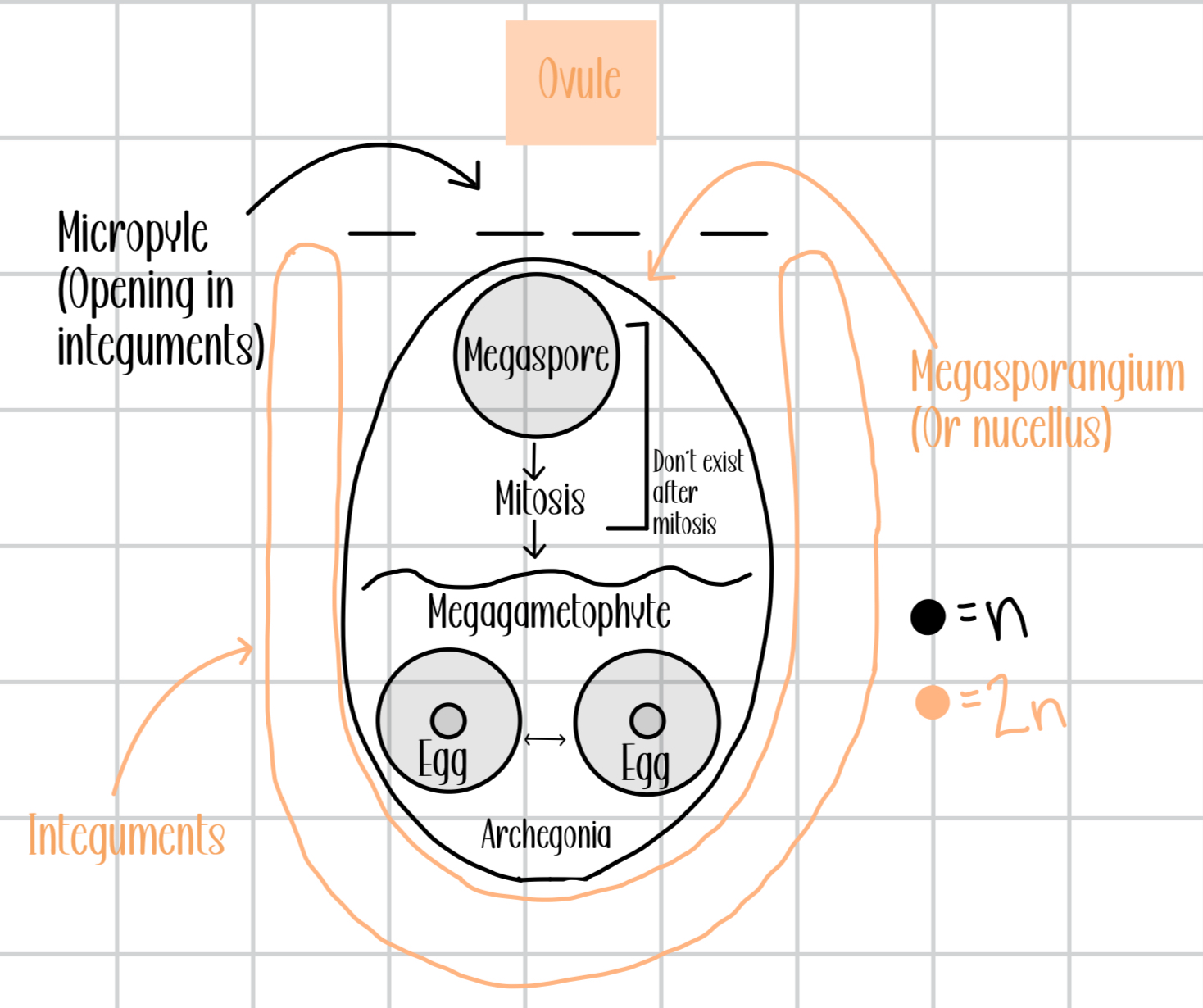
What does the ovule consist of?
a megasporangium
The ovule is surrounded by tissue called _____
integuments
What is a micropyle?
opening in integument tissue, allow entry of sperm
What is a nucellus?
fleshy megasporangium of seeds
Megaspores are _____ released from the megasporangium
never
After fertilization, what do seeds consist of?
embryo, stored food, seed coat
The seed coat is derived from ____
integuments
What are the 2 major groups of seed plants?
gymnosperms, angiosperms
Gymnosperms are called “naked seeds” because….
seeds aren’t enclosed within a fruit
Angiosperms are flowering plants with….
seeds enclosed within fruits
What are the 4 phyla of gymnosperms?
conifers, cycads, ginkgo, gnetophytes
Draw the heterosporous life cycle
Draw an ovule
Gymnosperms sperm is…
not motile
What is the microgametophyte also called?
pollen grain
How is the microgametophyte (pollen grain) transferred to the megagametophyte?
by wind
Microgametophyte
male, pollen grain
What is the megagametophyte also called?
embryo sac
Megagametophyte
female, embryo sac
Conifers include…
firs, pines, spruces, cedars, redwoods
Many conifers have great ____ ____ like ______ & ______
commercial value, paper, Christmas trees
Pines produce ___-____ leaves in bundles called _____
needle-like, fascicles
Pines produce ____ in separate cones or ____
sporangia, strobili
In pines, the megasporangiate or ____ ___ produce ____
ovulate cones, ovules
Pine microsporangiate (male) cones are ____ composed of ______ subtending ______
strobili, microsporophylls, microsporangia
In pines, where are microsporangia located?
inside each flap of microsporangiate
In seed plants, the _____ ____ is the microgametophyte
pollen grain
A pollen grain consists of what 2 cells?
generative cell, tube cell
Generative cell
divides to make 2 sperm
Tube cell
grows into pollen tube
Pollen grains are winged for better ____ ____
wind dispersal
In pine megasporangiate (female) cones, ovulate cones are composed of _____ ____ arranged around an ____
ovuliferous scales, axis
In Pine megasporangiate cones, Ovuliferous scales are modified ___
branches
In Pine megasporangiate cones, What is a ovuliferous scale?
flaps/points of pine cone, attached to axis in center of cone
In Pine megasporangiate cones: Each ovuliferous scale bears….
2 ovules
In Pine megasporangiate cones: Megasporocyte undergoes ____ to produce ____
meiosis, megaspores
In Pine megasporangiate cones, Only 1 ______ survives to become the _____
megaspore, megagametophyte
Spores ____ go out into the environment
never
Spores never leave the ____, they stay inside to _____
sporangia, grow
How does sperm enter the ovule?
through the micropyle
An egg is called ____ before fertilization, after fertilization it is called a ____
ovule, seed
What is the purpose of a seed coat?
protection
Megasporangium contains ____
megaspores
Where is the ovule located?
in megaspore, located in pinecone