Physics Definitions Unit 3
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Angular Velocity (circular motion)
Rate of change of angle with time
Radian (circular motion)
angle when arc length is equal to radius
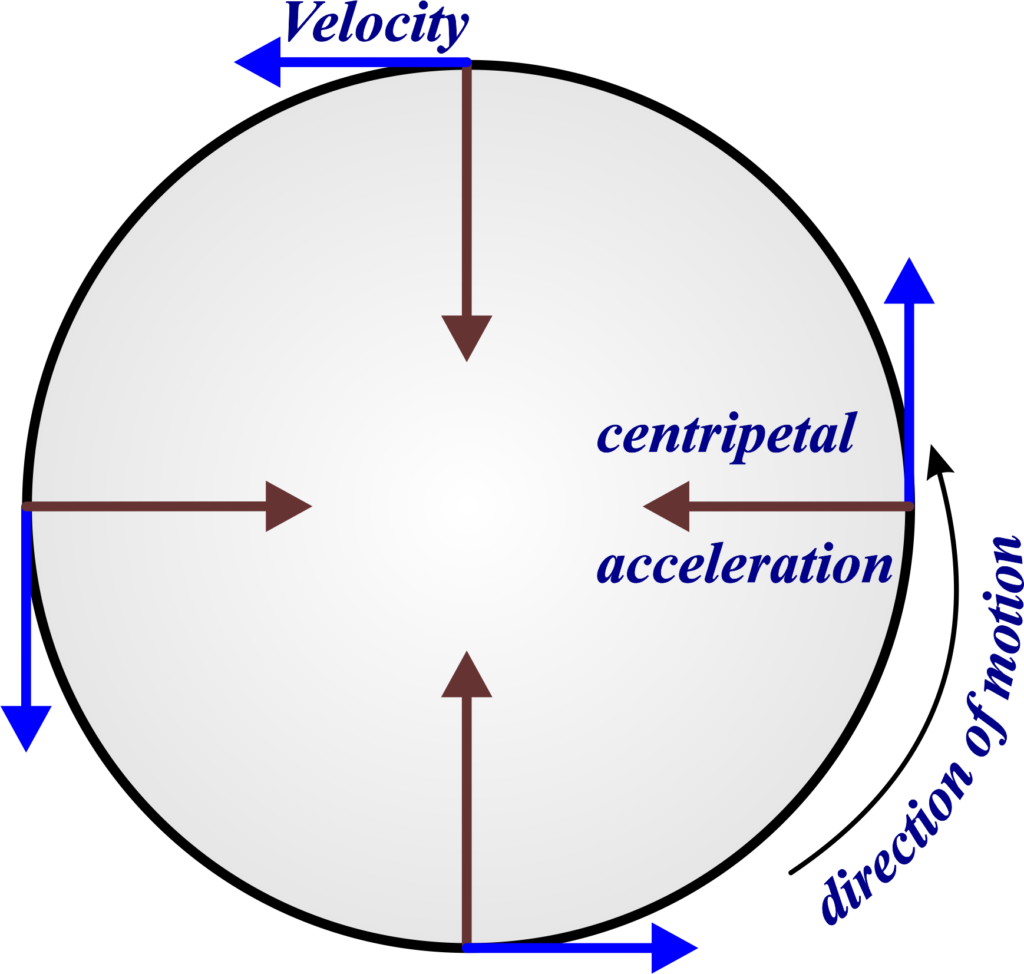
Why does and object moving at a constant speed in a circle have acceleration? (circular motion)
velocity is a vector - direction changes but not magnitude
acceleration = rate of change of velocity
Where is greatest tension in a vertical circle? (circular motion)
the bottom
Where is least tension in a vertical circle? (circular motion)
the top
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
The acceleration of the body is directly proportional to its distance from a fixed point and is always directed towards that point
Period (SHM)
The time for one complete oscillation or cycle
Frequency (SHM)
number of cycles completed per second
amplitude (SHM)
maximum displacement from equilibrium position
Phase constant (SHM)
angular displacement when displacement (x) = 0
Damping (SHM)
the process whereby energy is taken from an oscillating system and the oscillations decrease as a result
Types of damping (3) (SHM)
Light, Heavy, Critical
Time taken for system to return to equilibrium in critical damping? (SHM)
usually ¼ T
Free Oscillations (SHM)
Oscillating body has no force applied and vibrates at its natural frequency
(displacement applied then released)
Forced oscillations (SHM)
System vibrating due to periodic application of external force
Resonance (SHM)
driving force of a oscillating system with a frequency that matches the natural frequency
Ideal gas assumptions (kinetic theory) (4)
collisions of gas molecules are perfectly elastic
intermolecular forces are negligible, except during collision
gas molecules move rapidly and randomly
volume of molecules is negligible compared to volume of gas
Radioactive Atom (radioactivity)
atom with an unstable nucleus
alpha particle (radioactivity)
2 protons and 2 neutrons
helium nucleus
beta particle (radioactivity)
electron
gamma radiation (radioactivity)
high energy, high frequency electromagnetic wave
3 methods of distinguishing between alpha, beta and gamma radiation? (radioactivity)
differing penetration, deflection by electric field, deflection by magnetic field
results for differing penetration (radioactivity)
alpha - decrease with paper absorber
beta - further decrease with 3mm aluminium
gamma - further decrease with 3cm lead
results for deflection by electric field (radioactivity)
alpha - attracted by negative plate
beta - attracted by positive plate
gamma - no change
results for deflection by magnetic field (radioactivity)
alpha - deflected
beta - deflected more inn opposite direction
gamma - no change
ion (radioactivity)
an atom which has lost of gained one or more electrons
Activity (radioactivity)
number of radioactive disintegrations per second
Becquerel (Bq) (radioactivity)
one disintegration per second
Internal energy (thermal physics)
sum of the random KE and PE of the molecules
potential energy of gases (thermal physics)
0 because negligible intermolecular forces
Absolute zero (thermal physics)
the temperature when internal energy is a minimum
heat (thermal physics)
thermal energy moving from and area of high temperature to an area of low temperature
condition for bodies to be in thermal equilibrium (thermal physics)
they are the same temperature
what happens when a gas does work (thermal physics)
expands
what happens when work is done on a gas
contracts
clockwise cycle on a graph gives (Q and W) (thermal physics)
positive Q and W
anticlockwise cycle on a graph gives (Q and W) (thermal physics)
negative Q and W
specific heat capacity (thermal physics)
the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of material by 1K