Environmental Influences on Growth
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What is a “normal” environment?
Environment where most species grow: sea level, 20-40°C, neutral pH, 0.9% salt, ample nutrients
What are extremophiles?
Microbes that grow in non-”normal” environments
Stress response?
Measures that provide temporary protection from environmental stress
Suffix “-philic”, what is a thermophilic organism?
Organisms that like higher temperatures and has optimal growth/enzyme & protein function at them
Suffix “-tolerant”
Organisms that can survive at higher temperatures, but its optimal growth/enzyme & protein function at more moderate (lower) temperatures
Hyperthermophile*
growth > 80°C
Thermophile*
growth 50°C- 80°C
Mesophile
growth 15°C-45°C
Psychrophile*
growth < 15°/20°
Alkliphile*
growth > pH 9
Neutralophile
growth pH 5- pH 8
Acidophile*
growth < pH 3
Halophile*
growth in high salt, >2 M NaCl
Strict aerobe
growth only in O2
Facultative microbe
growth with or without O2
Mircoaerophile
growth only in small amounts of O2
Strict anaerobe
growth only without O2
Barophile/Piezophile*
growth at high pressure, greater than 380 atm
Barotolerant
growth between 10 and 500 atm
What are the three cardinal temperatures?
the optima, the minimum, and the maximum (very for each organisms)
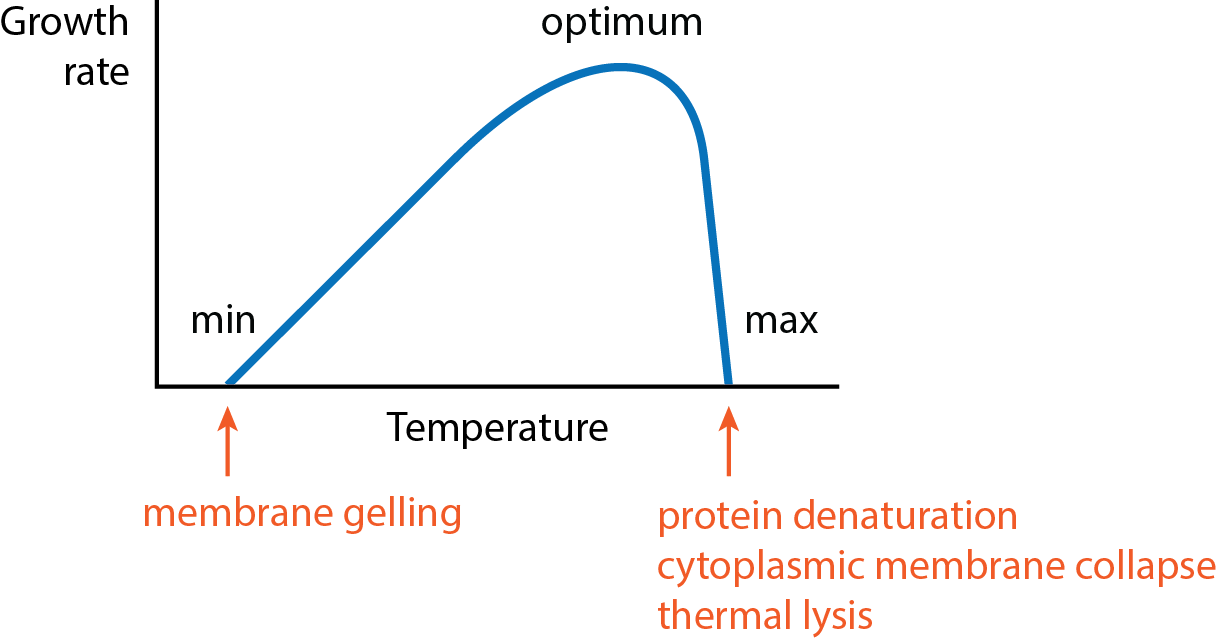
What happens at the cardinal minimum temperature?
Membrane gelling, transport processes too slow to support growth
What happens at the cardinal maximum temperature?
Protein denaturation, membrane damage, lysis
What is the relationship between growth rate and temperature?
The growth rate roughly doubles for every 10°C rise in temperature
What is special about thermophilic proteins?
Thermophilic proteins have a higher number of ionic interaction (smaller and more rigid/tightly packed than mesophilic counterparts
What is special about thermophilic membrane lipids?
Have more saturated fatty acids
Archaeal organisms have either lipids or tetraether lipids (monolayer)
What specific features do hyperthermophiles have?
Solutes that stabilize proteins
Have high internal salt concentrations & some have histone-like proteins (stabilize DNA)
Molecular chaperones/heat shock (stress) proteins purpose?
Assist in the folding of newly synthesized proteins and refolding denatured proteins
DnaK-DnaJ purpose? Energy?
Bind to hydrophobic regions of newly made proteins/denatured proteins to fold them.
Dependent on ATP hydrolysis
GroEL-GroES complex purpose? Energy?
If a protein is partially folded (DnaK-DnaJ couldn’t do it) GroEL-GroES complex encapsulates it and folds it
Dependent on ATP hydrolysis
Barophiles/piezophiles
Organisms adapted to grow at very high pressures
Barotolerant
Organisms that grow well over the range of 1-50 MPa, but their growth falls off afterwards
Water availability depends on?
Moisture/dryness of the environment and the concentrations of dissolved solutes (sugar/salts)
Water activity, (aw)? Formula?
A mesaure of how much water is available and free to use for organisms
solution vapor pressure (Vs) /the vapor pressure of water (Vw), with Aw being 0-1
Osmolarity?
The total concentration of dissolved particles (solutes) in a solution?
How are osmolarity and water activity related?
Inversely; the more solute you have in the medium the less “available” water, so the higher the osmolarity
Osmotic stress
when the solute concentration outside the cell is different from inside, causing water to move
How does water move?
from a region of higher water concentration (lower solute/salt concentration) to a region of lower water concentration (higher solute/salt concentration)
Aquaporins
membrane channels that allow water ro cross the membrane. These are a fast response to osmotic stresses (both hypertonic and hypotonic)
What do cells do under hypertonic stress conditions to prevent water loss?
They synthesize/import compatible solutes
Four types of solutes cells can synthesize/import:
Amino acid-type, carbohydrate type, alcohol type, other (dimethylsulfoniopropinate)
How can cells respond to hypotonic stress conditions?
solutes can be leaked from the cell by pressure-sensetive or mechanosensitive channels
What do halophilic archaea do?
Love salt
maintain an internal monovalent salt concentration (NaCl, KCl, LiCl) that equals their external environment.
Obligate acidophiles?
their membranes are destroyed at neutral pH. The cytoplasmic membrane must be stable
What’s special about Alkaliphiles proton motive force?
Some have sodium motive force rather than proton motive force
pH formula? One unit change in pH is how much of an H+ change?
pH= log (1/[H+])
One unit change in pH corresponds to a 10x change in [H+]
Terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration vs. in anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic: oxygen (this is favored)
Anaerobic: alternative, like nitrate
Does fermentation use anaerobic respiration?
No, because ATP is generated on a substrate level not by the respiratory chain
(Obligate) Aerobes? How do they detoxify O2?
Organism that can grow in the presence of full oxygen tension (air 21% O2)
SOD and Catalase
Aerotolerant anaerobes? How do they detoxify O2?
can tolerate small amounts of oxygen, but do not use it as an electron acceptor use fermentation)
SOD (+/- Catalase)
Facultative aerobes (anaerobes)? How do they detoxify O2?
Can generate ATP through aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but can also switch and grow anaerobically (or through fermentation) is not enough oxygen/right nutrients
SOD and Catalase
Microaerophiles? How do they detoxify O2?
A type of aerobe, but can only tolerate lower levels of O2
Decreased SOD and Catalase
(Obligate) Anaerobes? How do they detoxify O2?
Organisms that cannot tolerate O2 and are inhibited/killed by its presence
None
Electron/Redox Tower?
Ranks molecules by how much energy they can release when they gain or lose electrons
Bigger drop = more energy released (O2 has the biggest drop)
What must you do to the liquid media to grow aerobes?
liquid media requires forced aeration or vigorous shaking since oxygen is sparingly soluble in water (As temperature of water ↑, concentration/solubility of O2 in solution ↓)
What must you do to the media to grow anaerobes?
Exclude O2 but strictiness depends on the organism
What are the three Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)? Their toxicity?
Superoxide anion: •O2-, toxic
Hydrogen peroxide: H2O2, least toxic
Hydroxyl radical: •OH, very toxic and very reactive
Equations for breaking down superoxide?
Superoxide dismutase: 2O2 + 2H+ → H2O2 + O2
Superoxide reductase: O2 + 2H+ → H2O2
Equation for turning peroxide into something worse?
Fenton reaction: H2O2 + Fe2+ → OH- + •OH
Equations for breaking down peroxide before it becomes hydroxyl radical?
Peroxidase: H2O2 + NADH/H+ → 2 H2O + NAD+
Catalase: 2H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2