bsc2086L midterm
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
which region of the pharynx contains the pharyngeal tonsils and the auditory tube?
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
hypopharynx
nasopharynx
white pulp is dominated by BLANK...
red blood cells
platelets
lymphocytes
calcium
lymphocytes
BLANK is the air that remains in the lungs to help maintain the alveoil inflated or keep them from collapsing.
residual volume
tidal volume
inspiratory reserve volume
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
which pair of tonsils are the largest and most frequently infected?
lingual
palatine
pharyngeal
adenoids
palatine
red and white pulp can be found in which organ?
thyroid
spleen
thymus
tonsils
spleen
which vocal cords are elastic and vibrate to produce sound when air rushes from the lungs?
false vocal cords
vestibular folds
true vocal cords
epiglottic folds
true vocal cords
lymph capillaries, like veins, contain BLANK that keep the lymph flowing toward the thorax in this very low-pressure system.
valves
smooth muscle
lymph nodes
sphincters
valves
which hormones are primarily secreted by the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex?
epinephrine and norepinephrine
mineralocorticoids
androgens
glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone
glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone
BLANK large nodules that form a ring around the entrance to the pharynx are.
lymph nodes
lymph sinuses
t-lymphocytes
tonsils
tonsils
the BLANK duct drains the right side of the body superior to the diaphragm, and the BLANK duct drains the rest of the body.
right lymphatic, pulmonary
thoracic, left lymphatic
left lymphatic, thoracic
right lymphatic, thoracic
right lymphatic, thoracic
which lung has an indentation in its medical surface where the heart bulges into?
right
left
left
the parafollicular, or also known as the C-cells of the thyroid gland, produce which hormone?
insulin
calcitonin
calcium
glucagon
sodium
calcitonin
BLANK releases three types of hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens.
thymus gland
thyroid gland
adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla
adrenal cortex
Beta cells produced by the pancreas secrete which hormone?
insulin
glucagon
calcium
cortisol
insulin
Delta cells secreted by the pancreas secrete which hormone?
insulin
glucagon
somatostatin
glycogen
somatostatin
Which hormone INCREASES calcium blood levels by targeting bone and kidneys?
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
insulin
glucagon
parathyroid hormone
Which hormone stimulates strong uterine contractions that trigger labor during childbirth?
oxytocin
prolactin
estrogen
testosterone
oxytocin
Endocrine glands are ductless glands that are formed by secretory or endocrine cells that release BLANK into...
protein
blood
hormones
enzymes
nutrients
hormones
Alpha cells secreted by the pancreas secrete which hormone?
insulin
glucagon
somatostatin
calcium
calcitonin
glucagon
Which hormone stimulates milk production by the breast and promotes mammary gland development in females?
oxytocin
prolactin
estrogen
progesterone
prolactin
Where are platelets primarily found in the body?
in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow
teeth and bones
in the lymph nodes and thymus
in the skin and muscles
in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow
Plasma is primarily composed of which of the following?
formed elements
water and solutes
platelets and proteins
hemoglobin and oxygen
water and solutes
All of the following are true of red blood cells except?
they primarily contain hemoglobin, which transports oxygen.
they transport 20% of carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs.
they use aerobic respiration to generate energy.
they obtain glucose from plasma for anaerobic respiration.
they use aerobic respiration to generate energy
What is the role of antigens in blood cells?
they trigger an immune response and help determine blood type
they transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
they produce antibodies to fight infections
they dissolve in plasma to regulate blood pH
they trigger an immune response and help determine blood type
Which of the following is a primary function of eosinophils?
generating energy through glycolysis
transporting oxygen to tissues
defending the body against parasitic worms and flukes
producing antibodies
defending the body against parasitic worms and flukes
Which white blood cell contains granules that release histamine, a vasodilator, and heparin, an anticoagulant?
neutrophils
monocytes
B-cells
basophils
basophils
Which of the following blood types is lacking both A and B surface antigens?
A
B
AB
O
O
What is the condition called when there is a high count of platelets in the blood?
thrombocytopenia
thrombocytosis
anemia
leukopenia
thrombocytosis
Which of the following components make up approximately 45% of whole blood?
plasma
formed elements
water and solutes
hormones and waste
formed elements
What triggers an increase in the number of eosinophils?
allergic reactions
infection by bacteria
high blood pressure
oxygen deficiency
allergic reactions
Which of the following determines a person's blood type?
the number of red blood cells in circulation
the type of antibodies found in plasma
the amount of hemoglobin in the blood
the presence or absence of specific surface antigens on red blood cells
the presence or absence of specific surface antigens on red blood cells
Which type of lymphocytes are responsible for humoral immunity by producing plasma cells that generate antibodies?
B-cells
T-cells
basophils
monocytes
B-cells
What toxic compound do eosinophils expel to kill their targets?
oxygen
histamine
hydrogen peroxide
nitric oxide
hydrogen peroxide
Which type of white blood cell is the first to arrive at the injury site?
neutrophils
eosinophils
B- cells
T-cells
neutrophils
Why is atrial repolarization not visible on an ECG?
it is hidden by the large R wave of the QRS complex
it occurs after the T wave
it is too small to detect
it is part of the P wave
it is hidden by the large R wave of the QRS complex
Which of the following structures is contained within the myocardium of the ventricles?
superficial muscle layers only
deeper muscle layers that spiral between the ventricles
cardiac nerves only
endothelium
deeper muscle layers that spiral between the ventricles
What happens when antibodies in blood plasma attack foreign red blood cells with different surface antigens?
agglutination occurs, forming clumps
the red blood cells dissolve immediately
the red blood cells produce new antigens
the immune system ignores the foreign cells
agglutination occurs, forming clumps
Which part of the electrocardiogram represents ventricular depolarization?
P wave
QRS complex
T wave
R wave
QRS complex
Which white blood cell contains granules with histamine and heparin?
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
monocytes
basophils
How do white blood cells (WBC's) cells contribute to the body's defense system?
by producing hemoglobin for oxygen transport
by participating in inflammatory and immune responses
by carrying nutrients to tissues
by generating energy through anaerobic respiration
by participating in inflammatory and immune responses
What remains in place after the foramen ovale closes 48 hours after birth?
aortic arch
fossa ovalis
pulmonary valve
coronary sulcus
fossa ovalis
The deep groove that separates the atria from the ventricles is called the:
coronary sulcus
anterior interventricular sulcus
posterior interventricular sulcus
auricle
coronary sulcus
What is the primary function of intercalated discs in contractile cardiac muscle cells?
to provide structural support to the heart
to allow transfer of contractile forces and propagation of the action potential
to increase the size of the cardiac muscle cells
to store calcium for muscle contraction
to allow transfer of contractile forces and propagation of the action potential
Which of the following is the term for the ear-like extension of the atria when empty?
apex
auricle
coronary sulcus
ventricles
auricle
What produces the first (lubb) sound in the heart?
the closing of the AV valves
the opening of the AV valves
blood flowing into the ventricles
atrial contraction
the closing of the AV valves
What does the endocardium line?
the outer layer of the heart
the inside of the heart, including the heart valves
the muscle tissue of the ventricles
the inside of the heart, including the heart valves
the inside of the heart, including the heart valves
Which layer forms the bulk of the heart and is composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue?
epicardium (visceral pericardium)
myocardium
endocardium
pericardial sac
myocardium
Which part of the heart receives blood returning from the general circulation through the superior and inferior vena cava?
right atrium
left atrium
left ventricle
right ventricle
right atrium
What is the function of the ductus venosus in the fetus?
to bypass the immature lungs
to bypass the immature fetal liver
to circulate oxygenated blood from the placenta
to allow blood flow from the right atrium to the left atrium
to bypass the immature fetal liver
Which heart chamber has the largest and thickest walls?
right atrium
left atrium
right ventricle
left ventricle
left ventricle
Which structure allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium, bypassing the lungs in the fetus?
coronary sinus
pulmonary valve
aortic arch
foramen ovale
foramen ovale
Which heart sounds are typically very faint and mostly undetectable?
the first and second sounds
the first and third sounds
the second and third sounds
the third and fourth sounds
the third and fourth sounds
What does the P wave represent in an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
atrial depolarization
ventricular depolarization
atrial repolarization
ventricular repolarization
atrial depolarization
What is the function of the pulmonary semilunar valve?
to prevent backflow of blood from the left atrium into the right atrium
to facilitate the flow of oxygenated blood into the body
to regulate blood flow from the right ventricle to the left ventricle
to prevent backflow of blood from the pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle
to prevent backflow of blood from the pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle
What structures are found sitting on the superior border of each kidney and are attached by a fibrous capsule?
adrenal glands
adrenal cortex
adrenal Medulla
pancreas
adrenal glands
BLANK is released in response to high blood glucose levels.
insulin
glucagon
cortisol
epinephrine
insulin
Where is the tricuspid valve located in the heart?
between the right atrium and right ventricle
between the left atrium and left ventricle
between the right atrium and left atrium
between the left ventricle and aorta
between the right atrium and right ventricle
The second heart sound (dupp) is created by the closing of BLANK valve.
AV valve
tricuspid valve
semilunar valve
tricuspid valve
semilunar valve
Which zone of the adrenal cortex is responsible for producing androgens, the sex hormones?
zona glomerulosa
zona fasciculata
zona reticulata
zona medullaris
zona reticulata
BLANK causes peripheral vasodilation, which decreases blood pressure?
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
angiotensin II
aldosterone
norepinephrine
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Which hormone of the kidney causes an increase in red blood cell production and maturation, which results in...
renin
erythropoietin
aldosterone
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
erythropoietin
Which organ of the endocrine system is a butterfly-shaped gland that is located in the anterior part of the throat, just...
thyroid gland
thymus gland
parathyroid gland
adrenal gland
thyroid gland
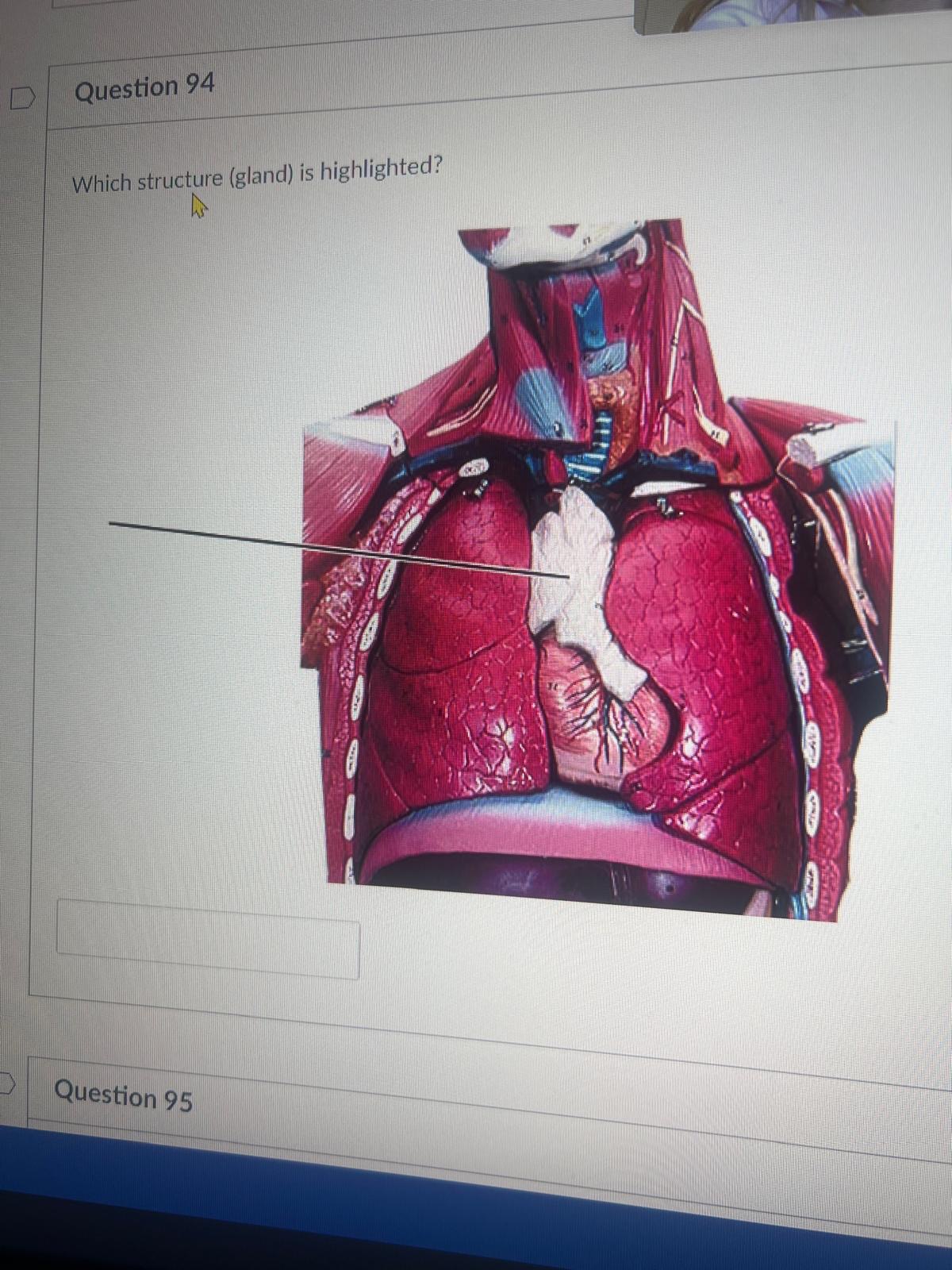
Which structure (gland) is highlighted?
thymus

What structure is this? Hint- it is a gland
thyroid
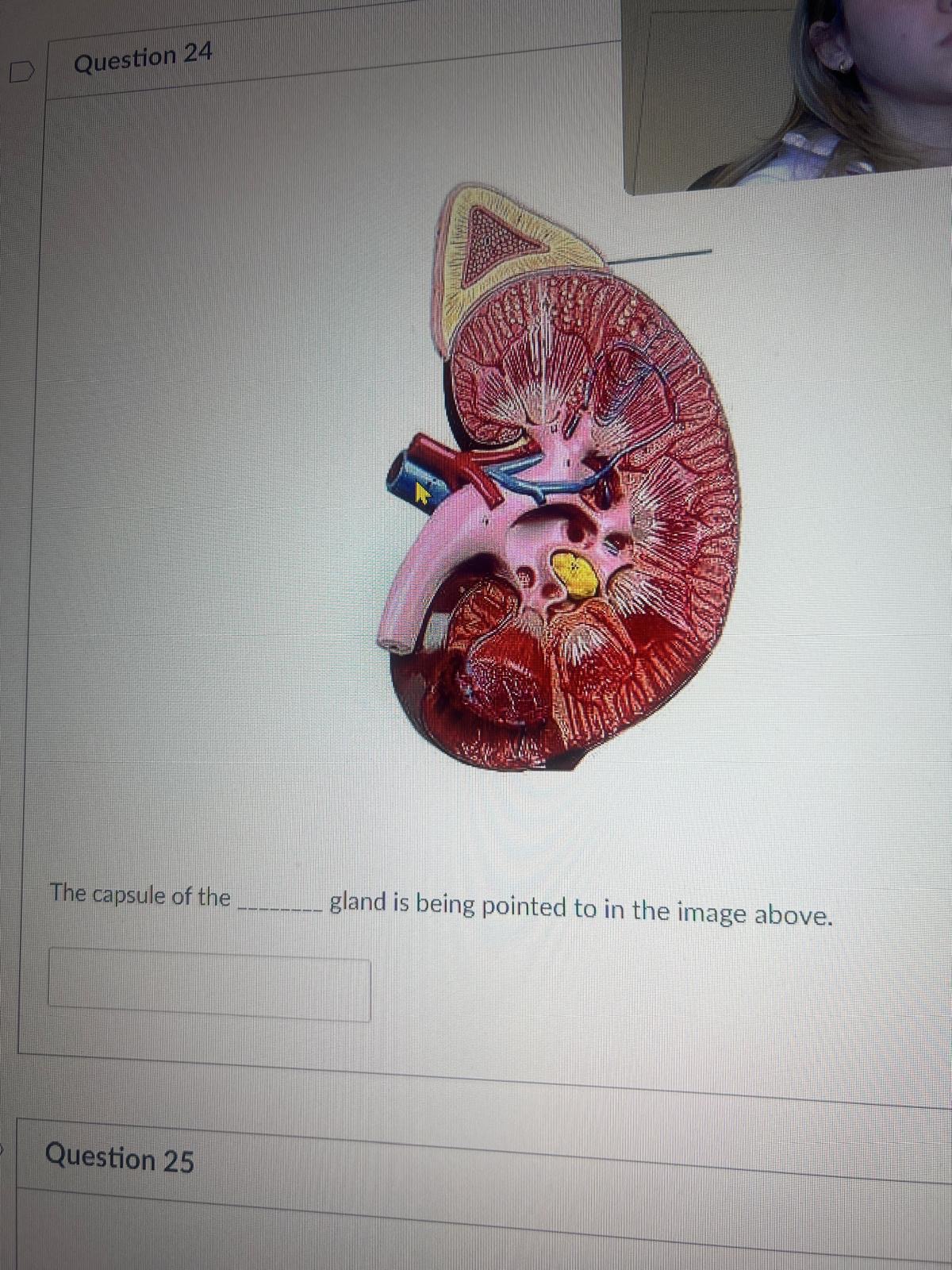
The capsule of the BLANK gland is being pointed to in the image above.
adrenal
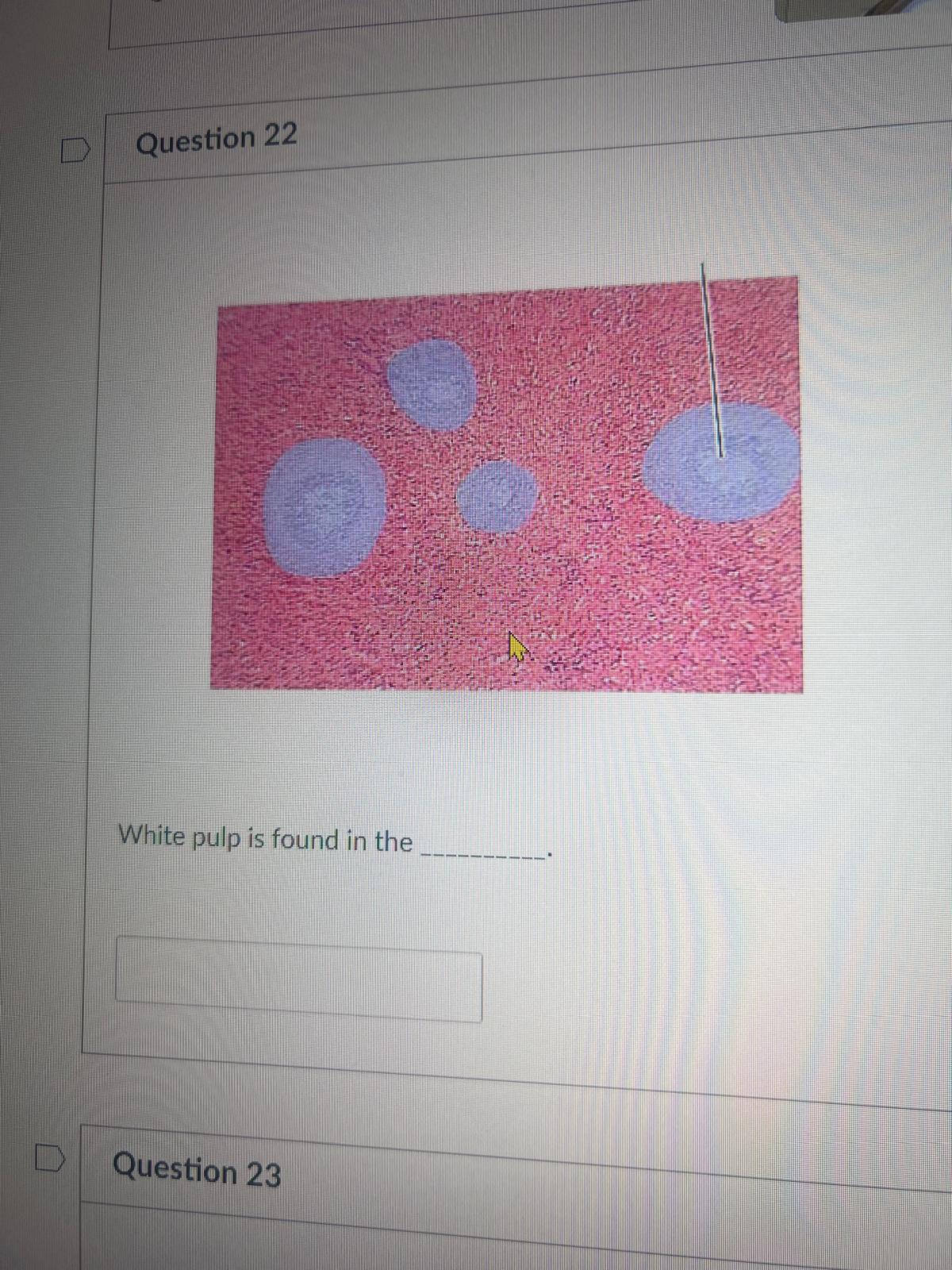
White pulp is found in the BLANK
spleen
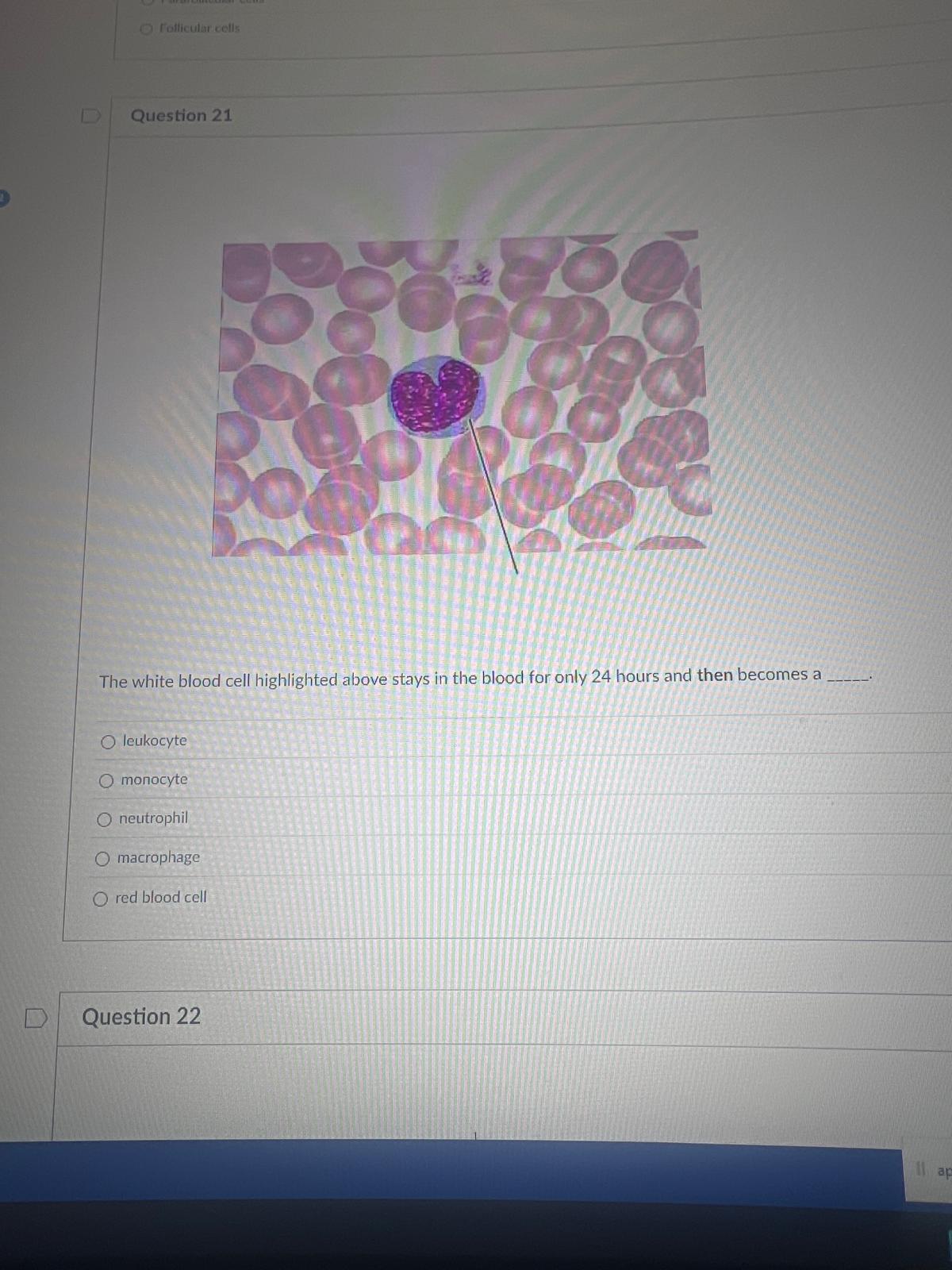
The white blood cell highlighted above stays in the blood for only 24 hours and then becomes a BLANK.
leukocyte
monocyte
neutrophil
macrophage
red blood cell
monocyte
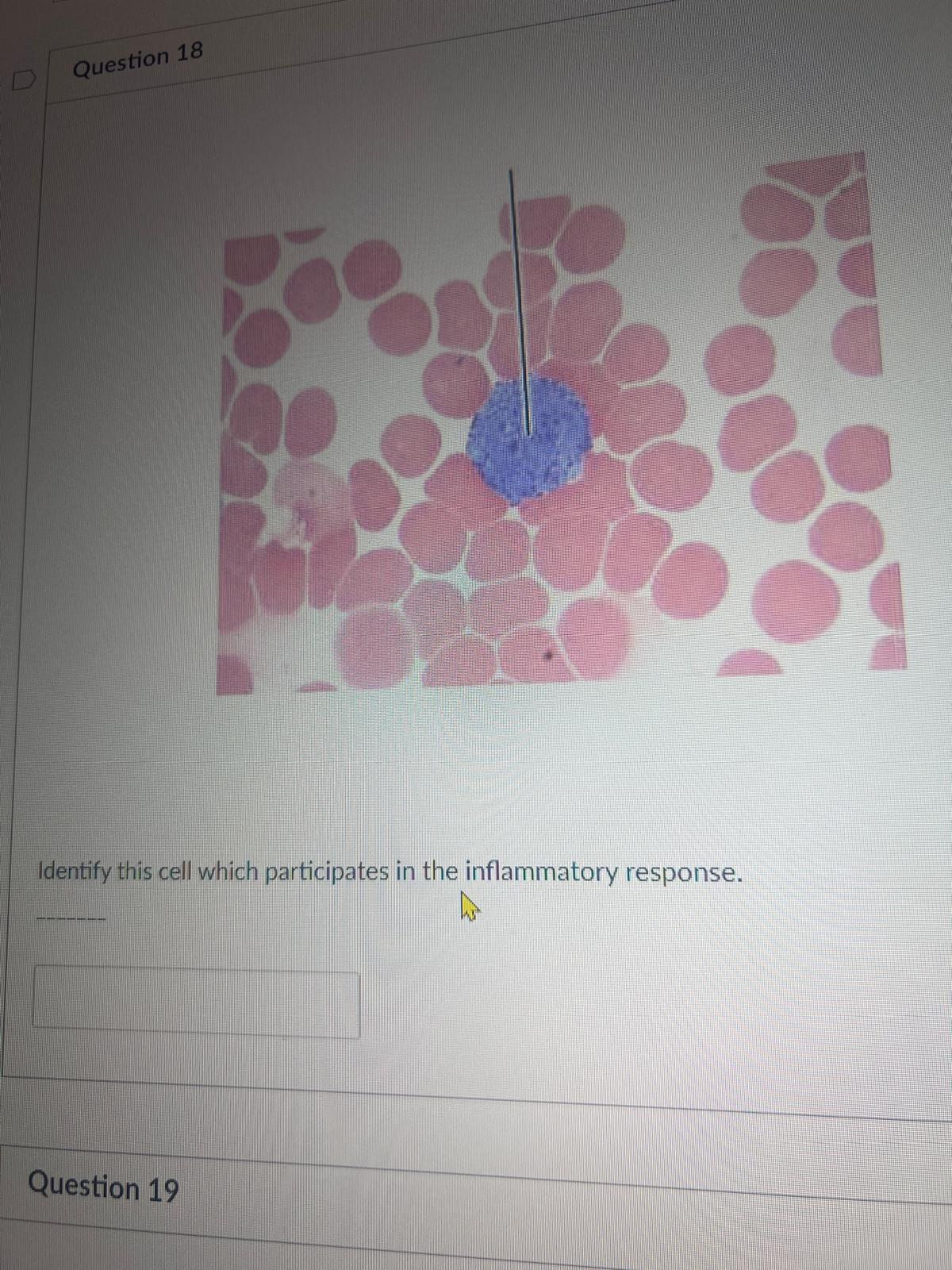
Identify this cell which participates in the inflammatory response.
basophil
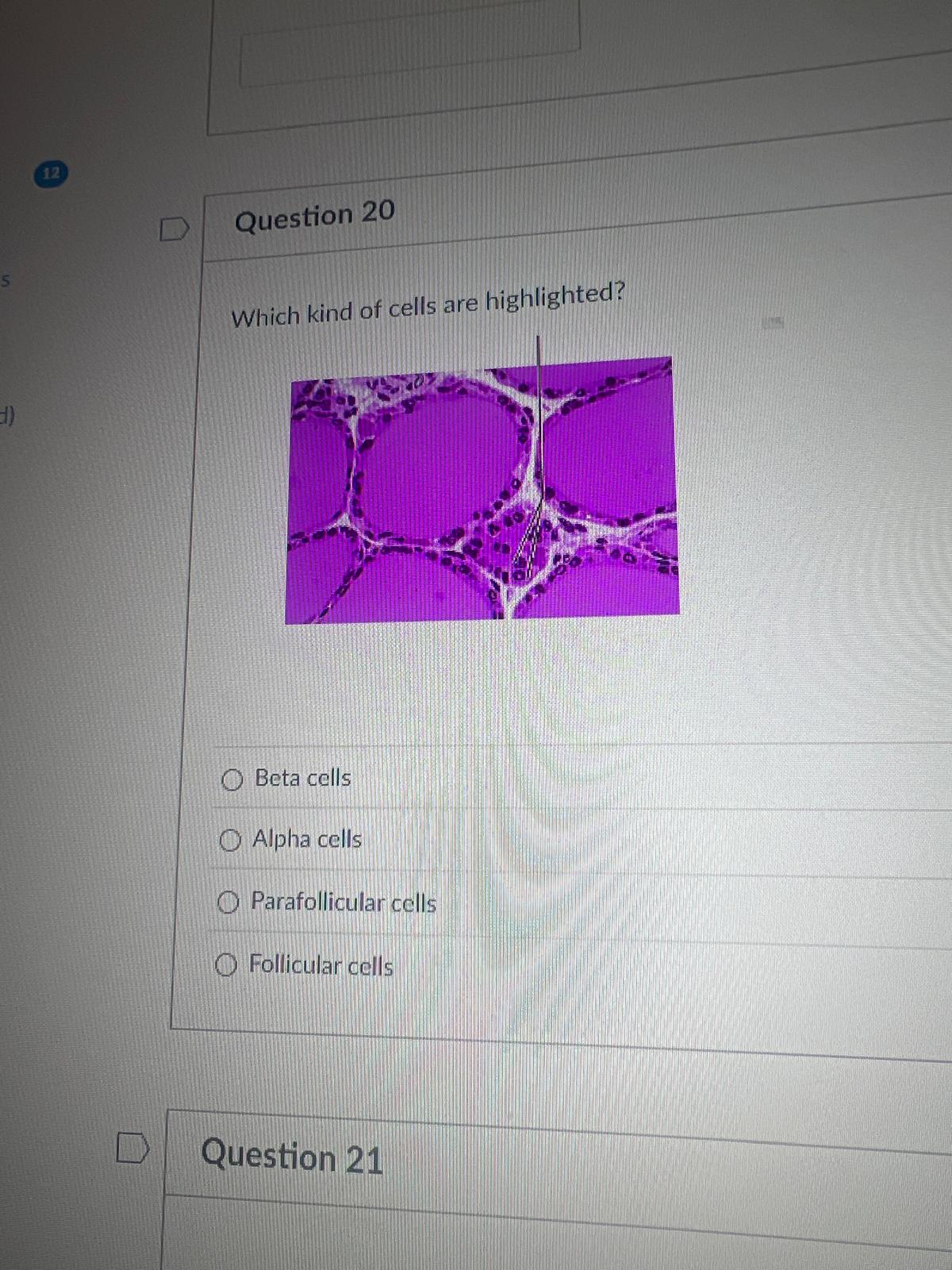
Which kind of cells are highlighted?
Beta cells
Alpha cells
Parafollicular cells
Follicular cells
Parafollicular cells
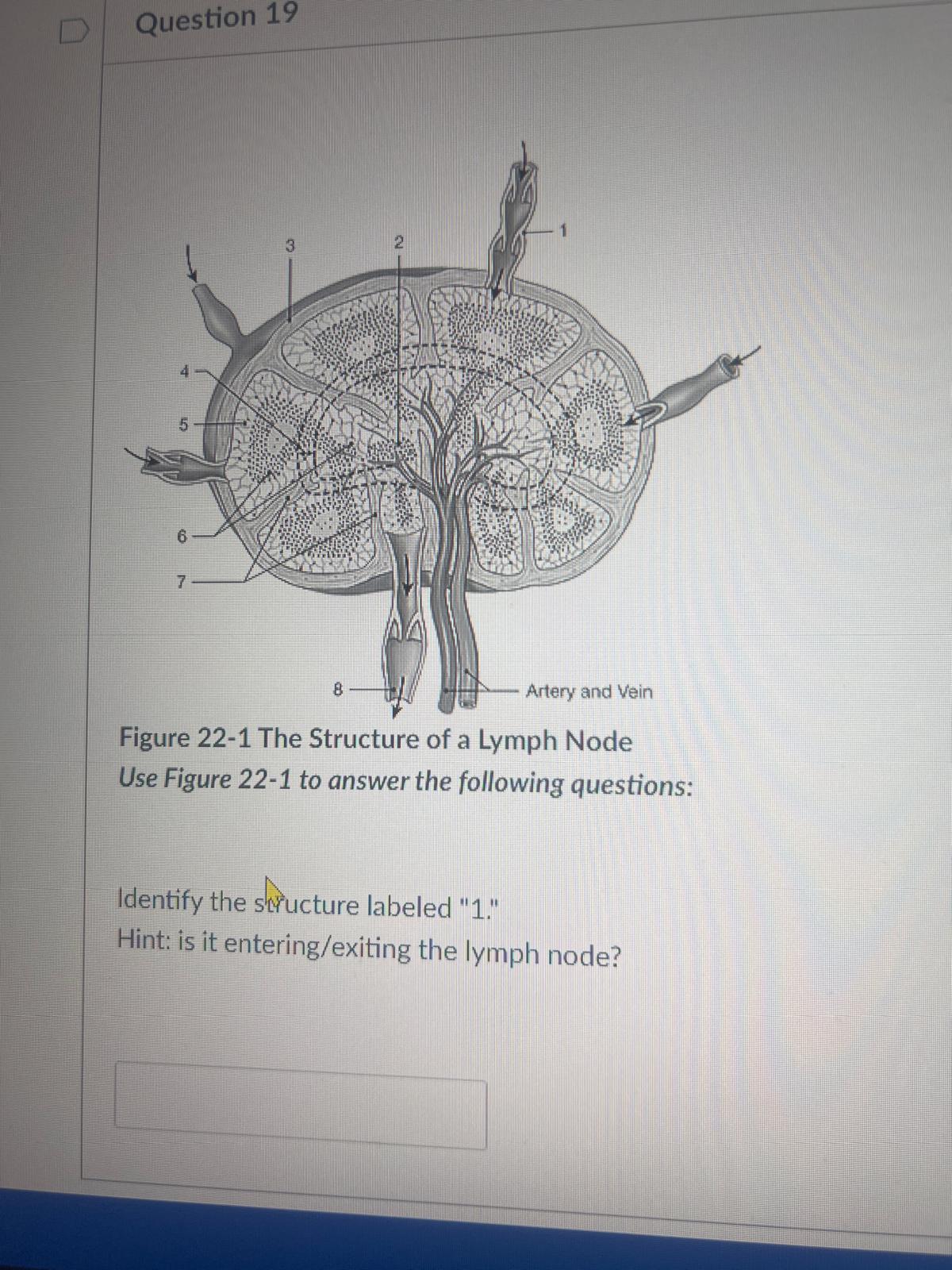
Identify the structure labeled "1." Hint: is it entering/exiting the lymph node?
afferent lymphatic vessel
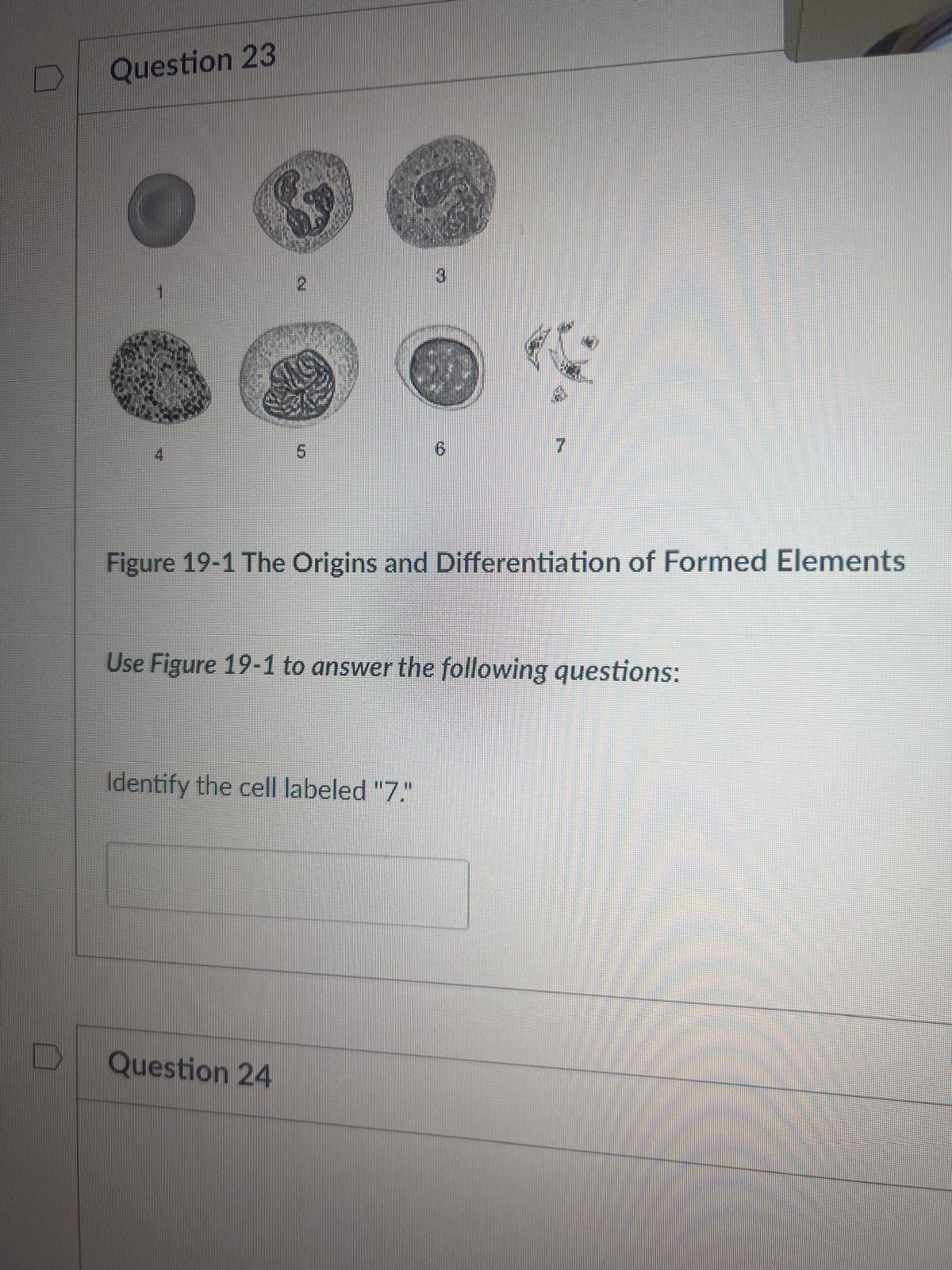
Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions: Identify the cell labeled "7."
platelet
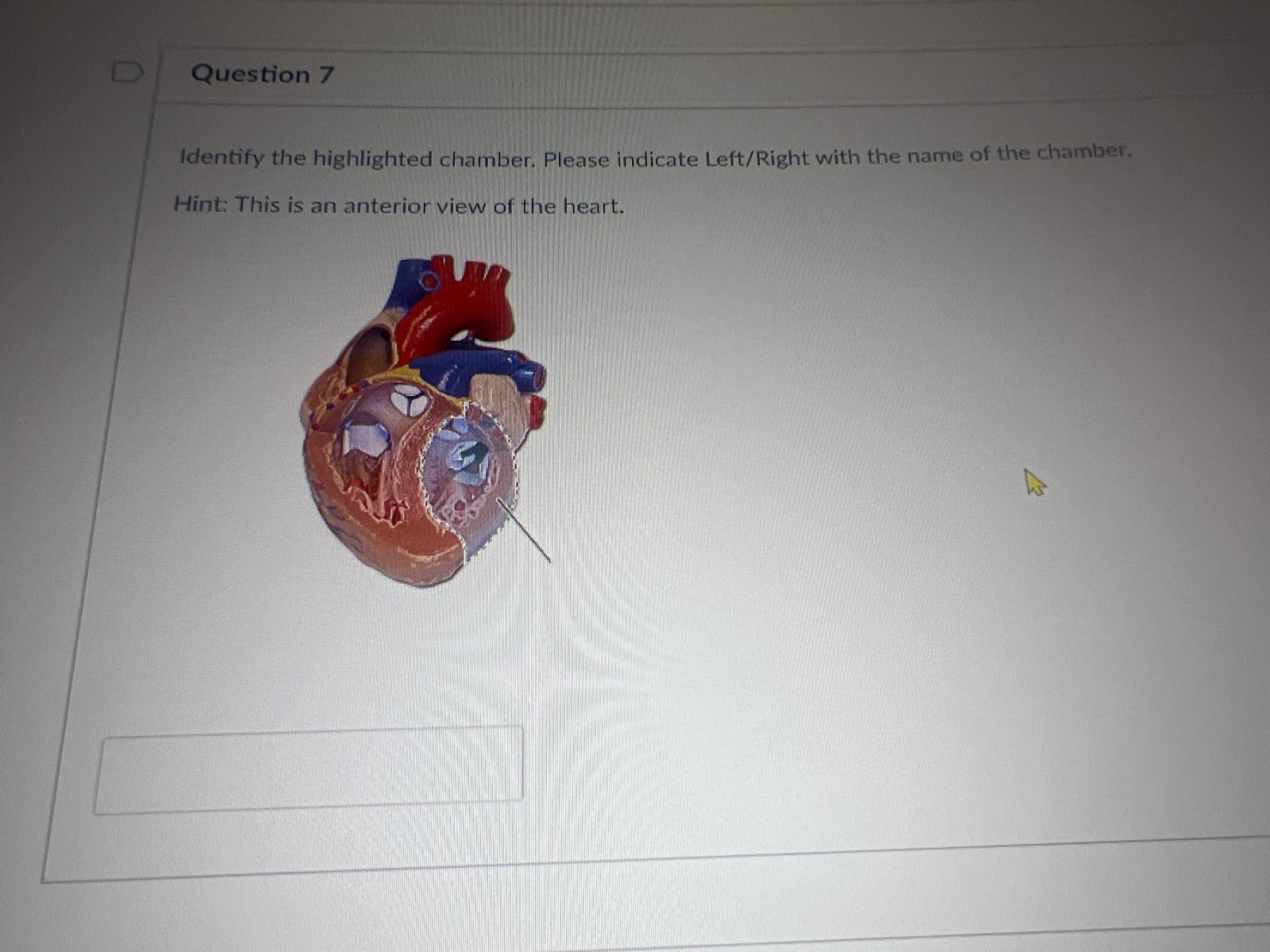
Identify the highlighted chamber. Please indicate Left/Right with the name of the chamber. Hint: This is an anterior view of the heart.
left ventricle
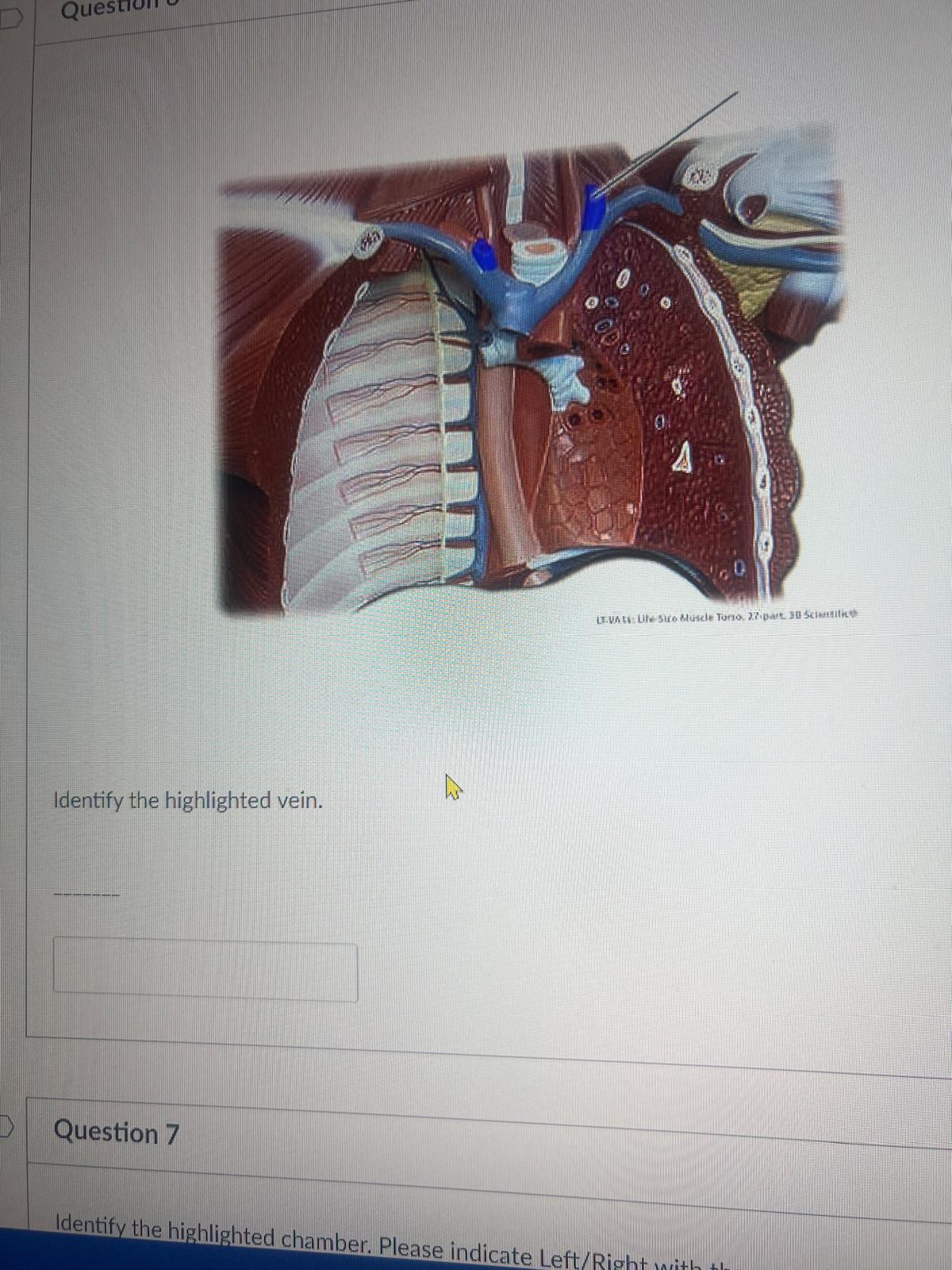
Identify the highlighted vein.
left subclavian
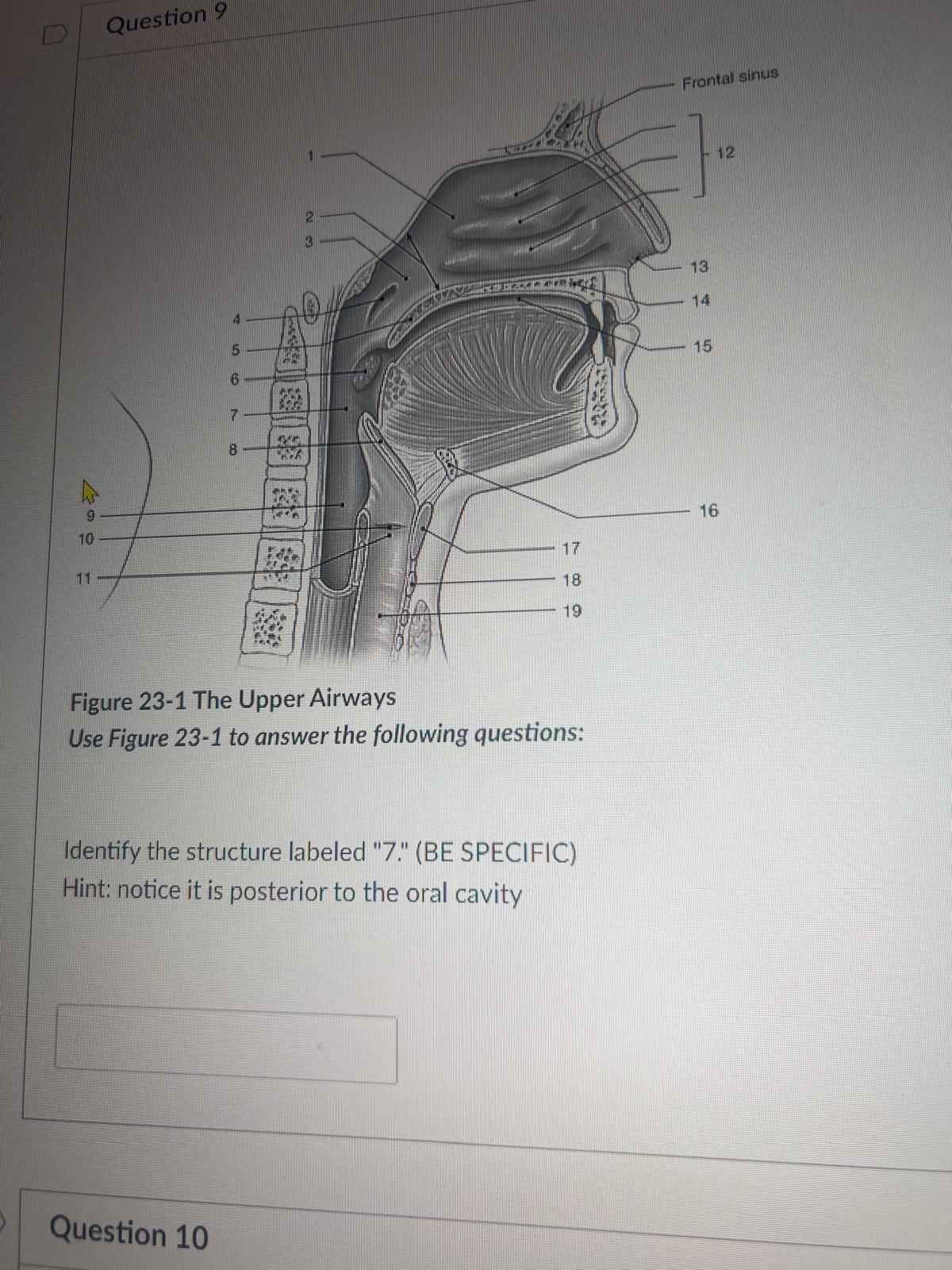
Identify the structure labeled "7." (BE SPECIFIC) Hint: notice it is posterior to the oral cavity
oropharynx
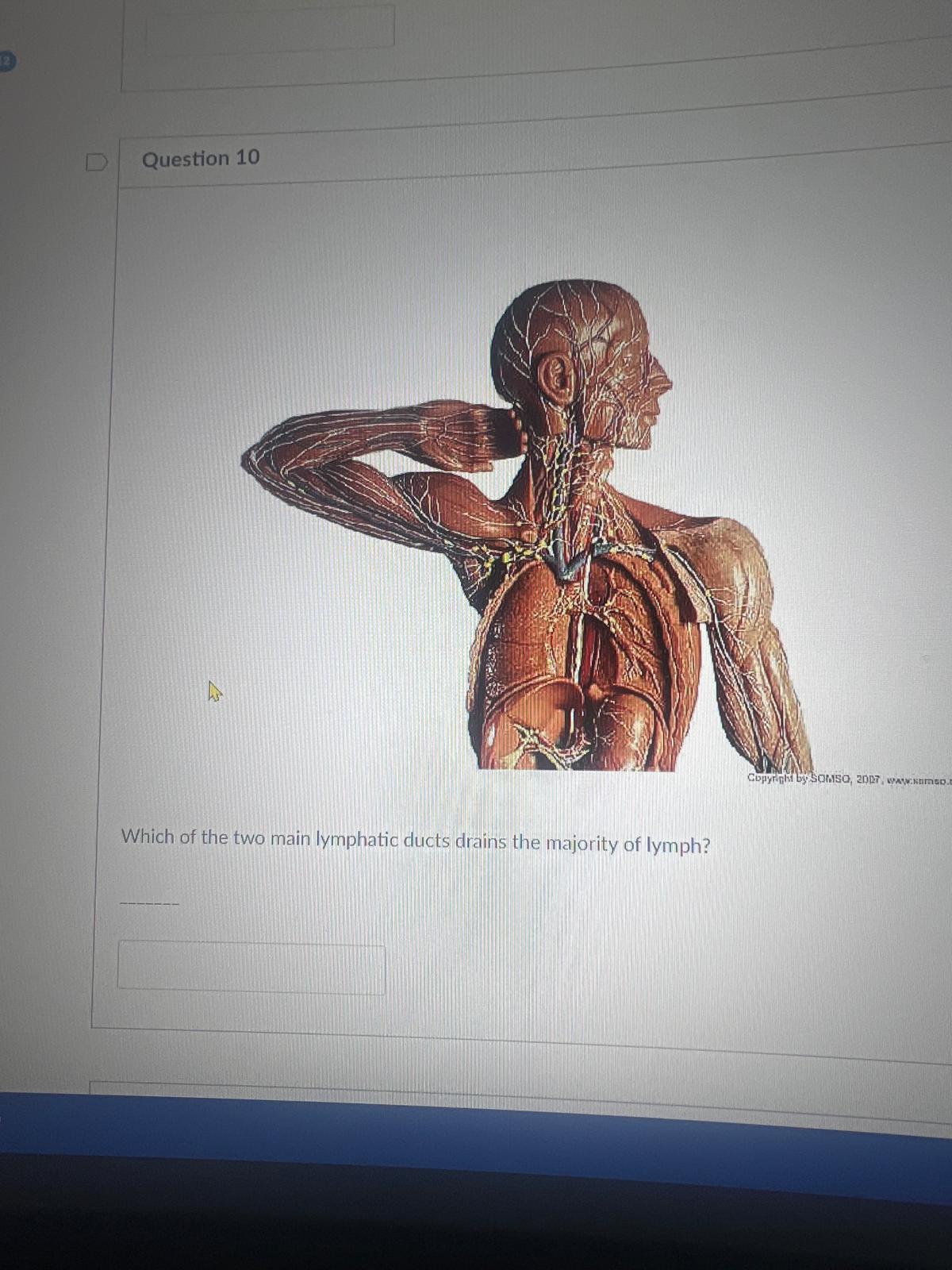
Which of the two main lymphatic ducts drains the majority of lymph?
thoracic duct
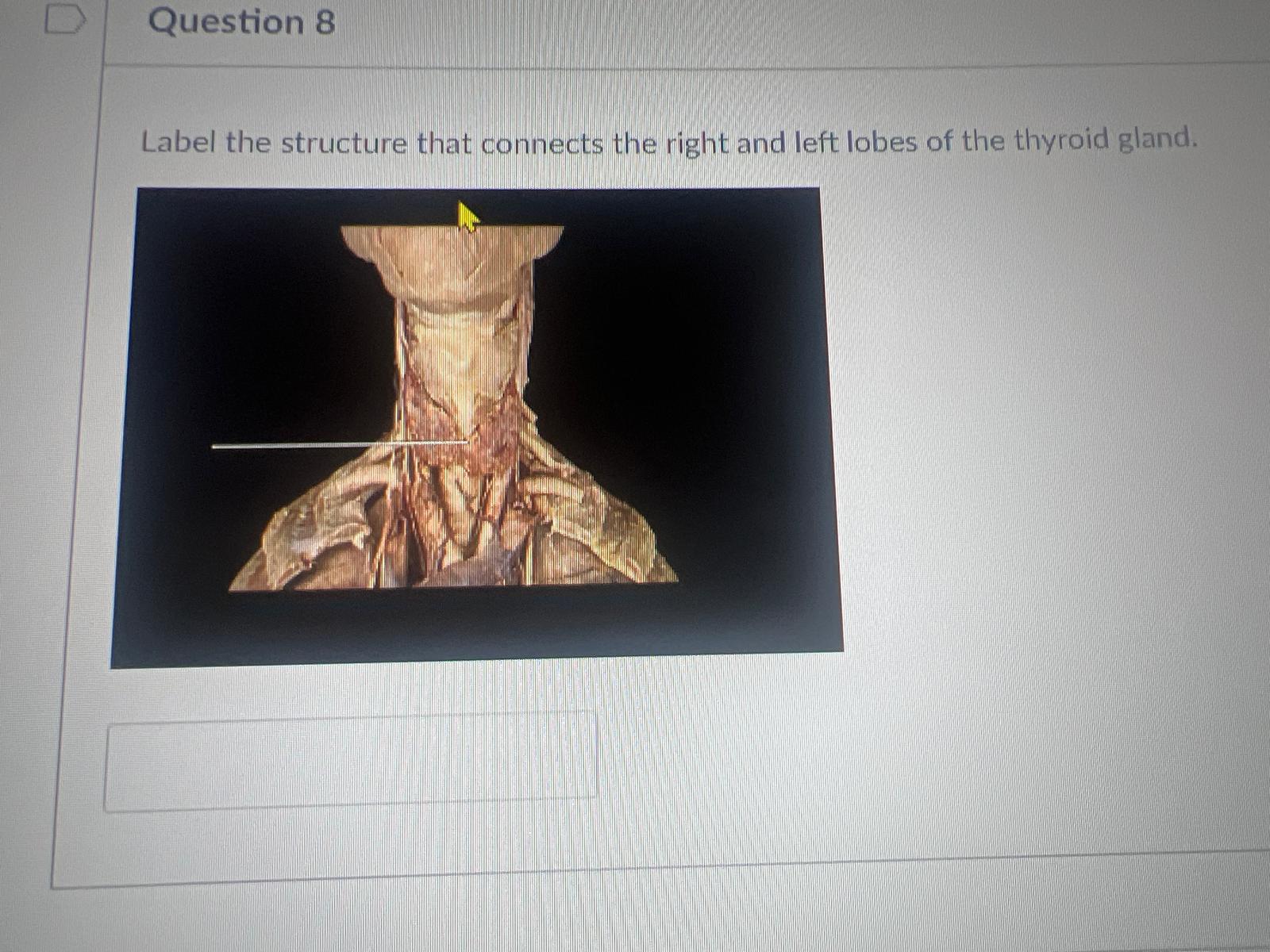
Label the structure that connects the right and left lobes of the thyroid gland.
isthmus
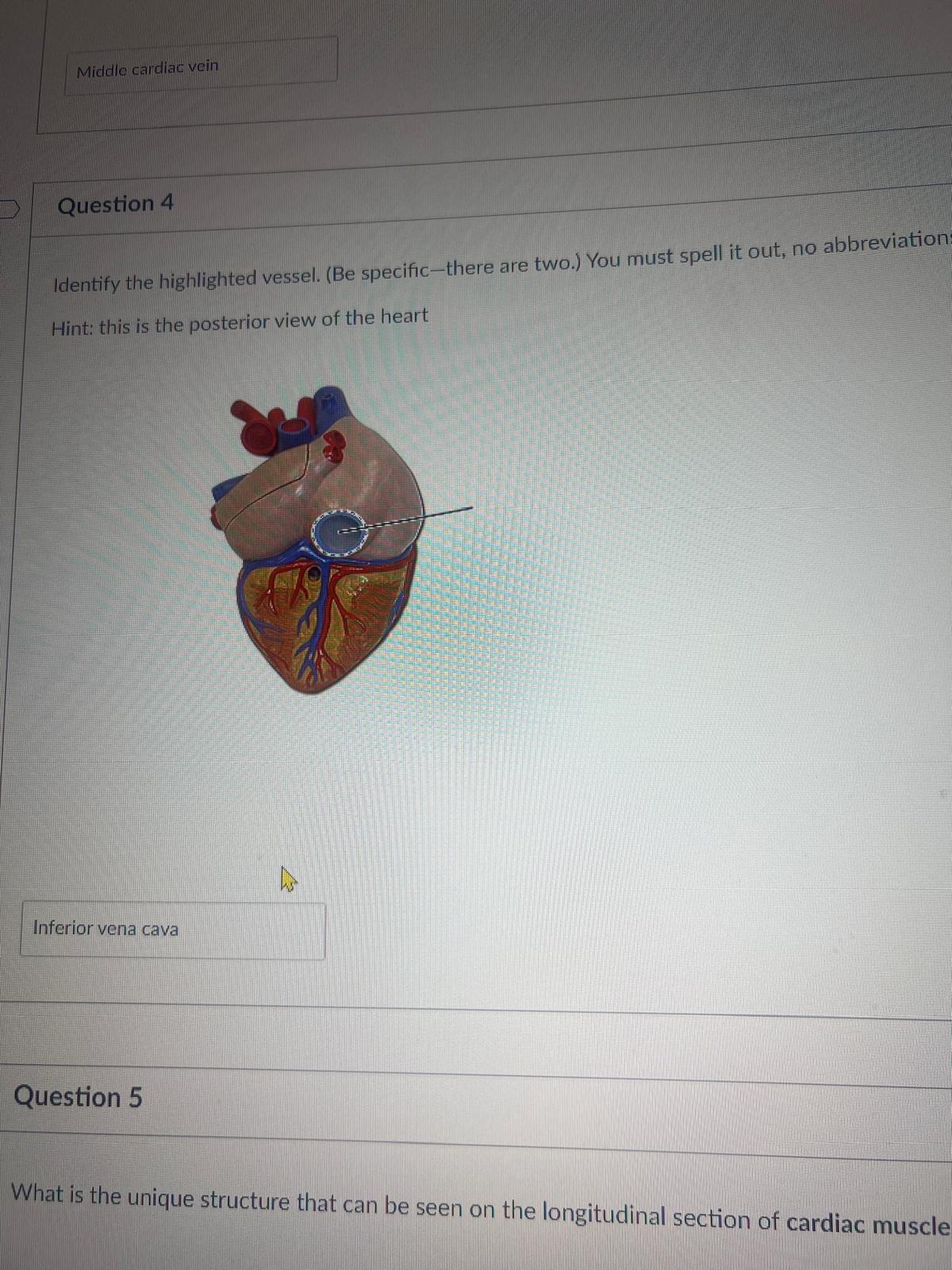
Identify the highlighted vessel. (Be specific-there are two.) You must spell it out, no abbreviation. Hint: this is the posterior view of the heart
inferior vena cava
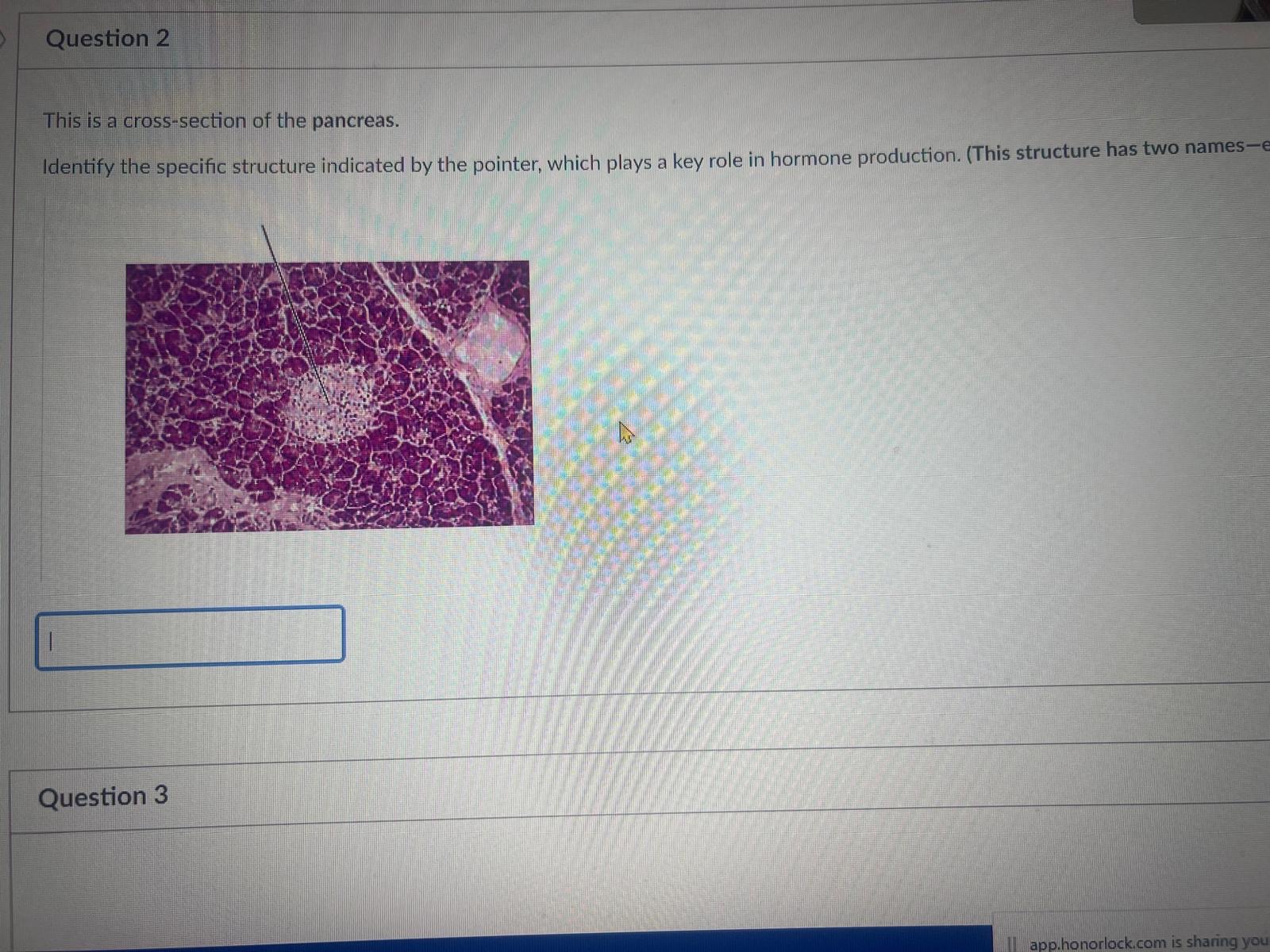
This is a cross-section of the pancreas.
Identify the specific structure indicated by the pointer, which plays a key role in hormone production. (This structure has two names)
pancreatic islets
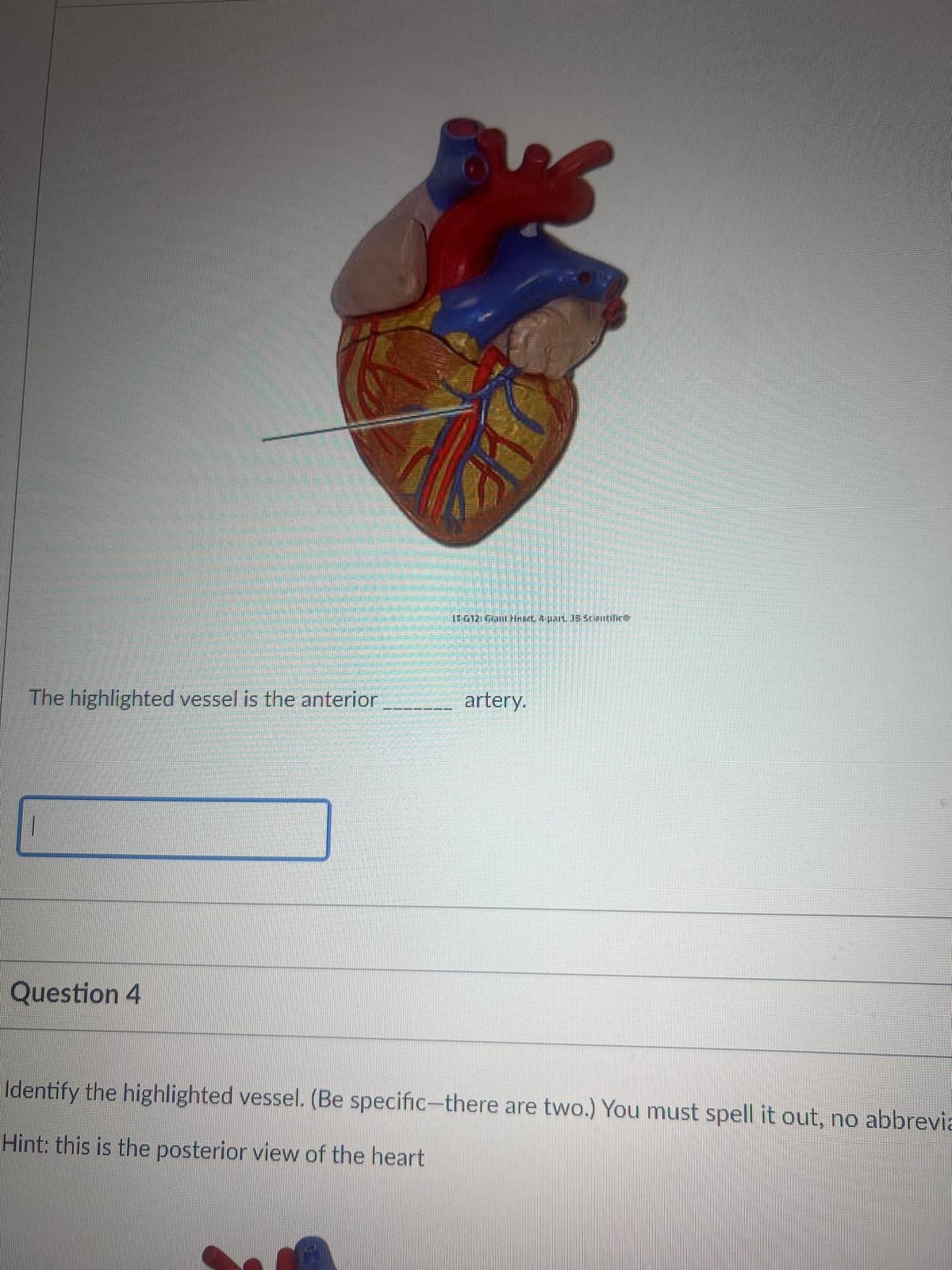
The highlighted vessel is the anterior BLANK artery.
interventricular
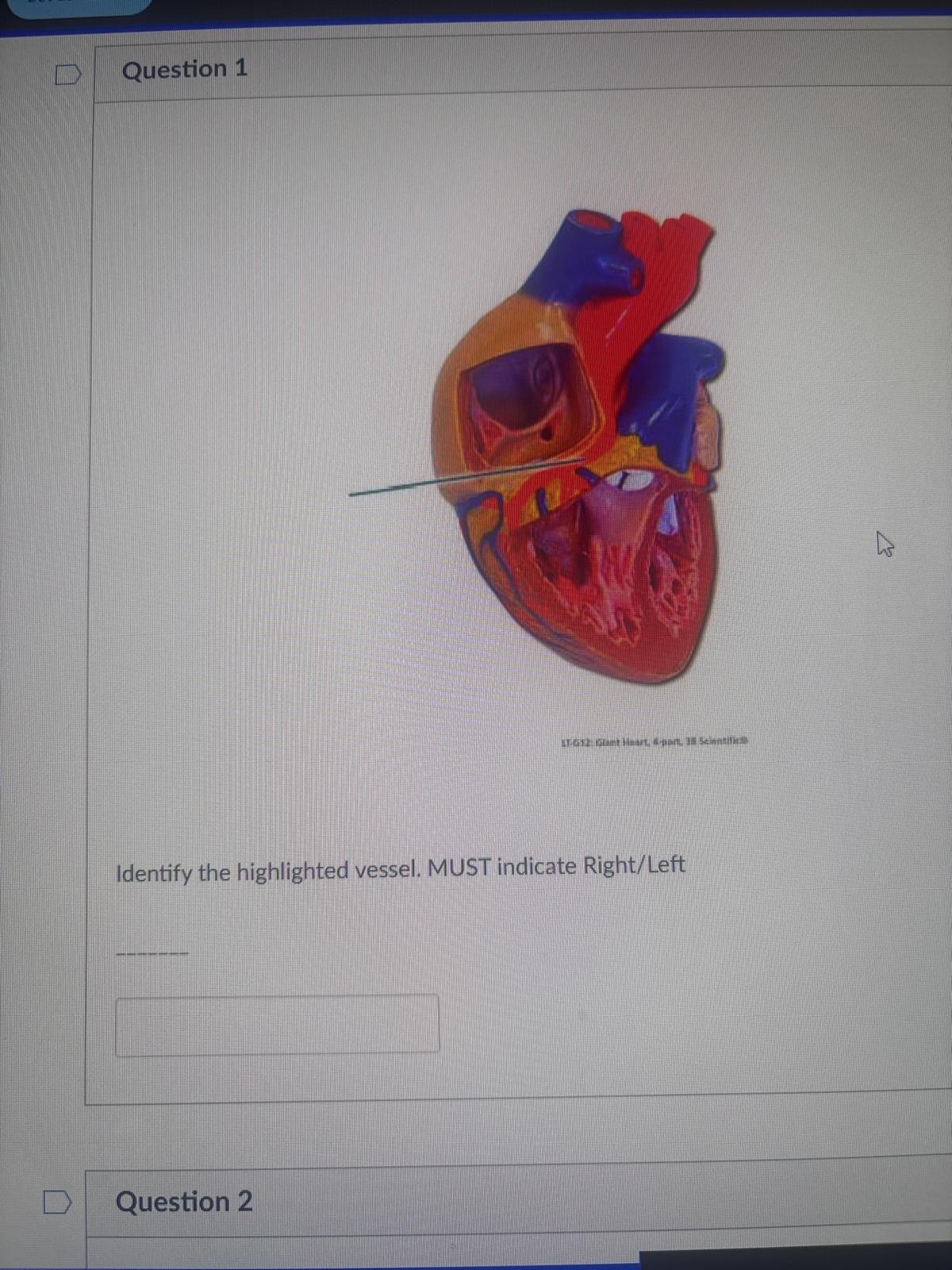
Identify the highlighted vessel. MUST indicate Right/Left
right coronary artery
What is the term for the lower tip of the heart?
Auricle
Atria
Apex
Ventricle
Apex
What is the ability of the heart to contract without neural or hormonal stimulation called?
Contractility
Autorhythmicity
Synchronization
Electroconductivity
Autorhythmicity
Which type of lymphocytes are responsible for cell-mediated immunity, defending the body against virus-infected cells, and coordinating the immune response?
B-cells
T-cells
Neutrophils
Basophils
T-cells
Which of the following veins carry oxygenated blood?
Pulmonary veins
Jugular veins
Carotid
Femoral veins
Pulmonary veins
Which blood vessels have thicker walls, with more smooth muscle, that allow them to resist pressure?
Arterioles
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Arteries
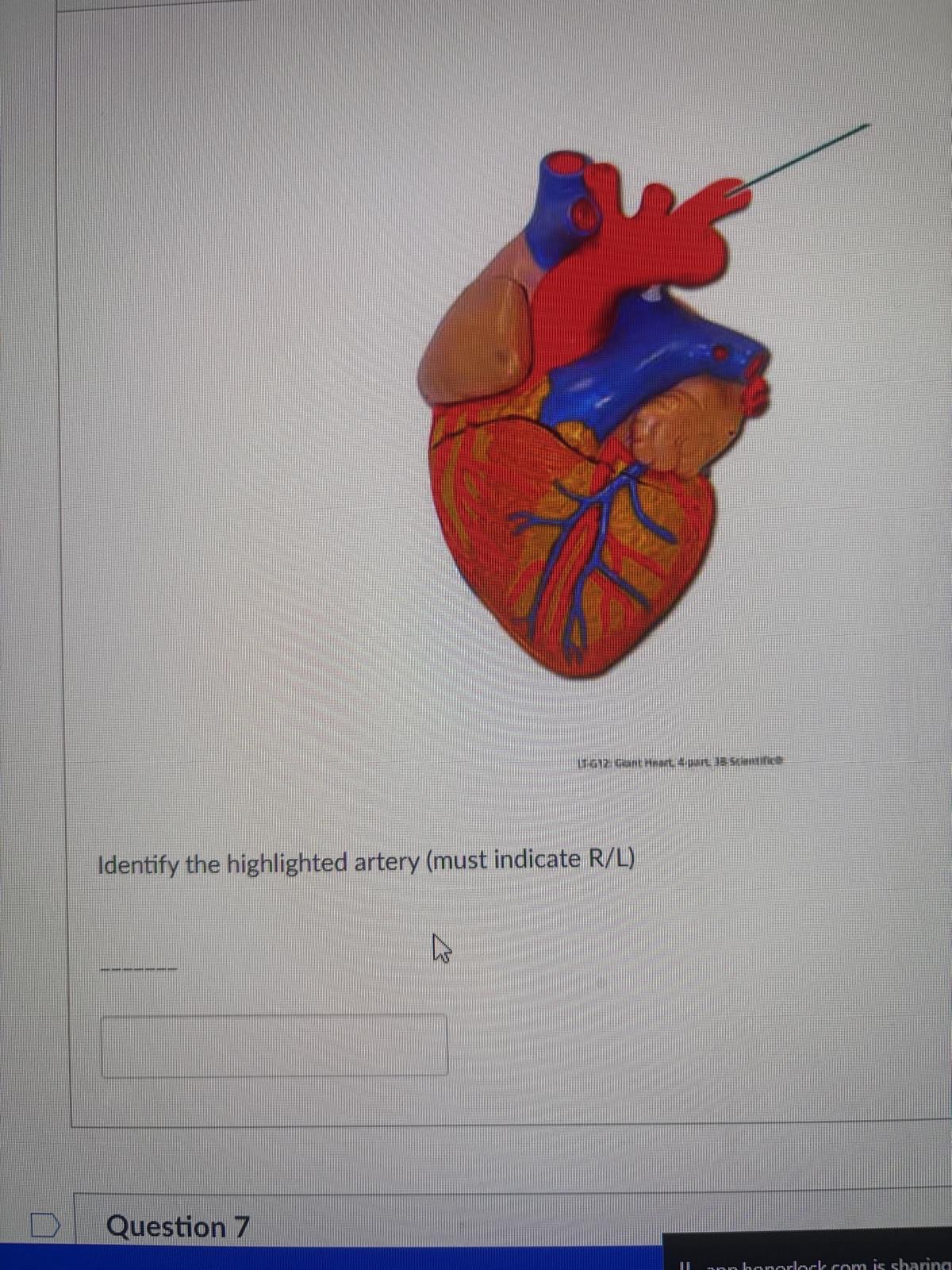
Identify the highlighted artery (must indicate R/L)
left subclavian
Which of the following structures is included in the upper respiratory system?
Larynx
Trachea
Alveoli
Pharynx
Pharynx
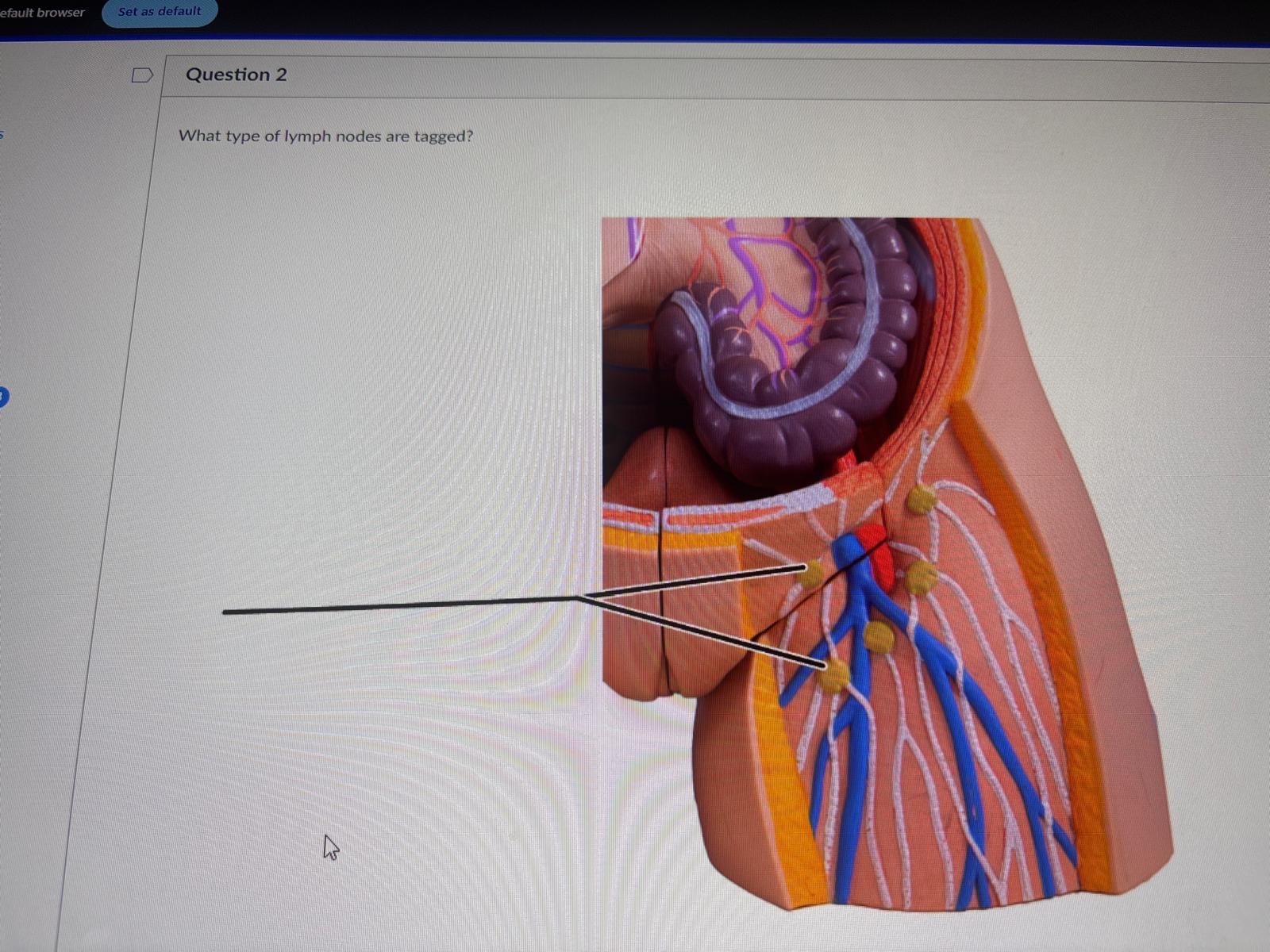
What type of lymph nodes are tagged?
inguinal
In children, this hormone stimulates bone growth and mineral deposition in the skeleton, while in adults it lowers blood calcium and phosphorus by decreasing the rate of removal of these minerals found within the bone.
Growth Hormone
Thyroxine
Parathyroid hormone
Calcitonin
Parathyroid hormone
What does the tunica media primarily consist of?
Circular smooth muscle sheets and loose connective tissue
Elastic fibers and collagen
overlaying connective tissue
endothelium
Circular smooth muscle sheets and loose connective tissue
Most veins carry blood toward the heart and most carry low oxygen blood except for the BLANK and BLANK veins.
Pulmonary, carotid
Umbilical, jugular
Pulmonary, aorta
Pulmonary, umbilical
Pulmonary, umbilical
Arteries: carry blood BLANK from the heart, and most carry highly oxygenated blood except for the pulmonary arteries and the umbilical arteries.
Toward
Away
Away
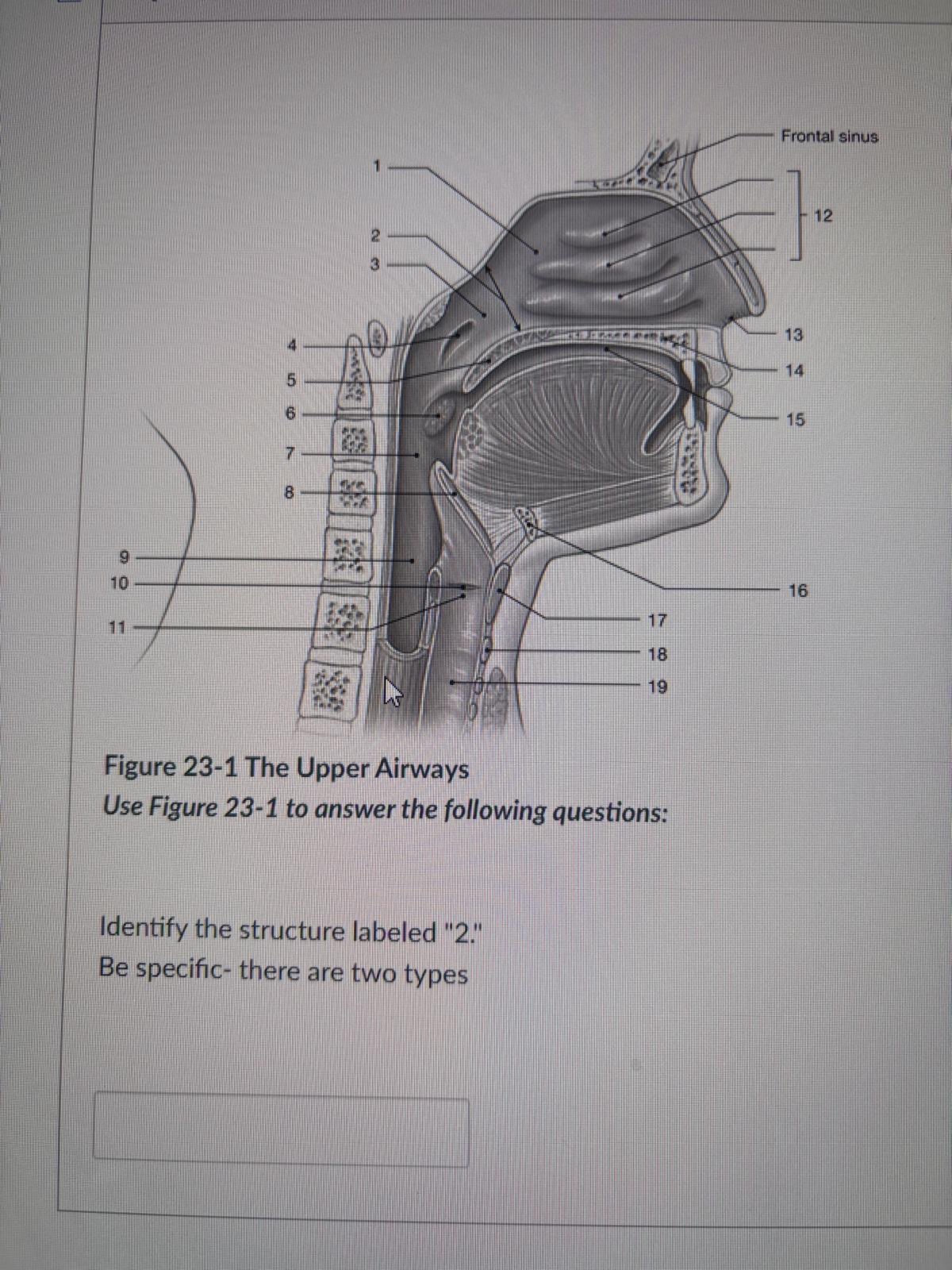
Identify the structure labeled "2." Be specific- there are two types
internal nares
Arteries contain an internal elastic membrane in the outer area of the BLANK.
Tunica externa
Tunica media
Tunica intima
Endothelium
Tunica intima
Generally, BLANK have valves that prevent backflow of blood.
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Lymphatic vessels
Veins
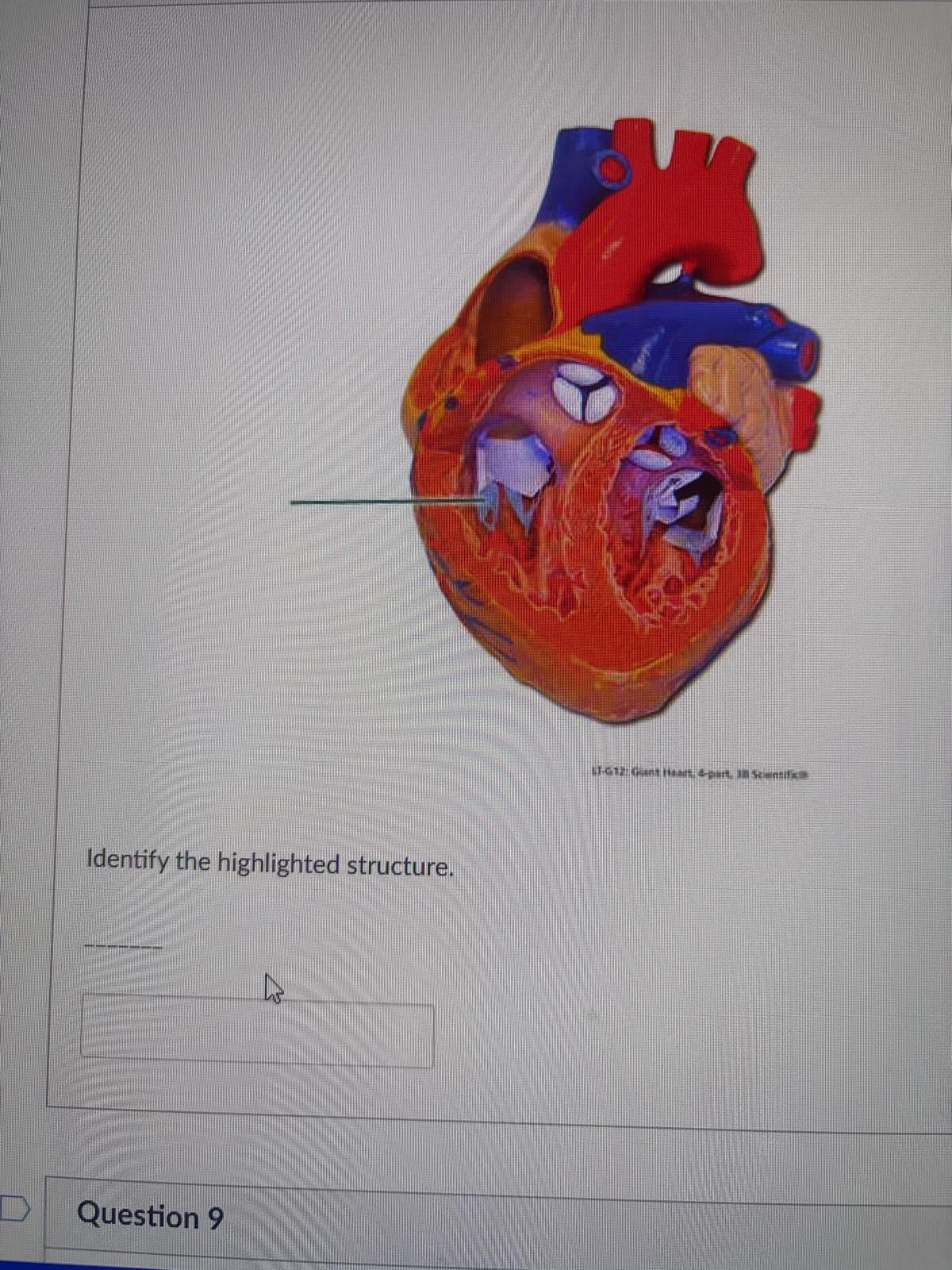
Identify the highlighted structure.
chordae tendineae
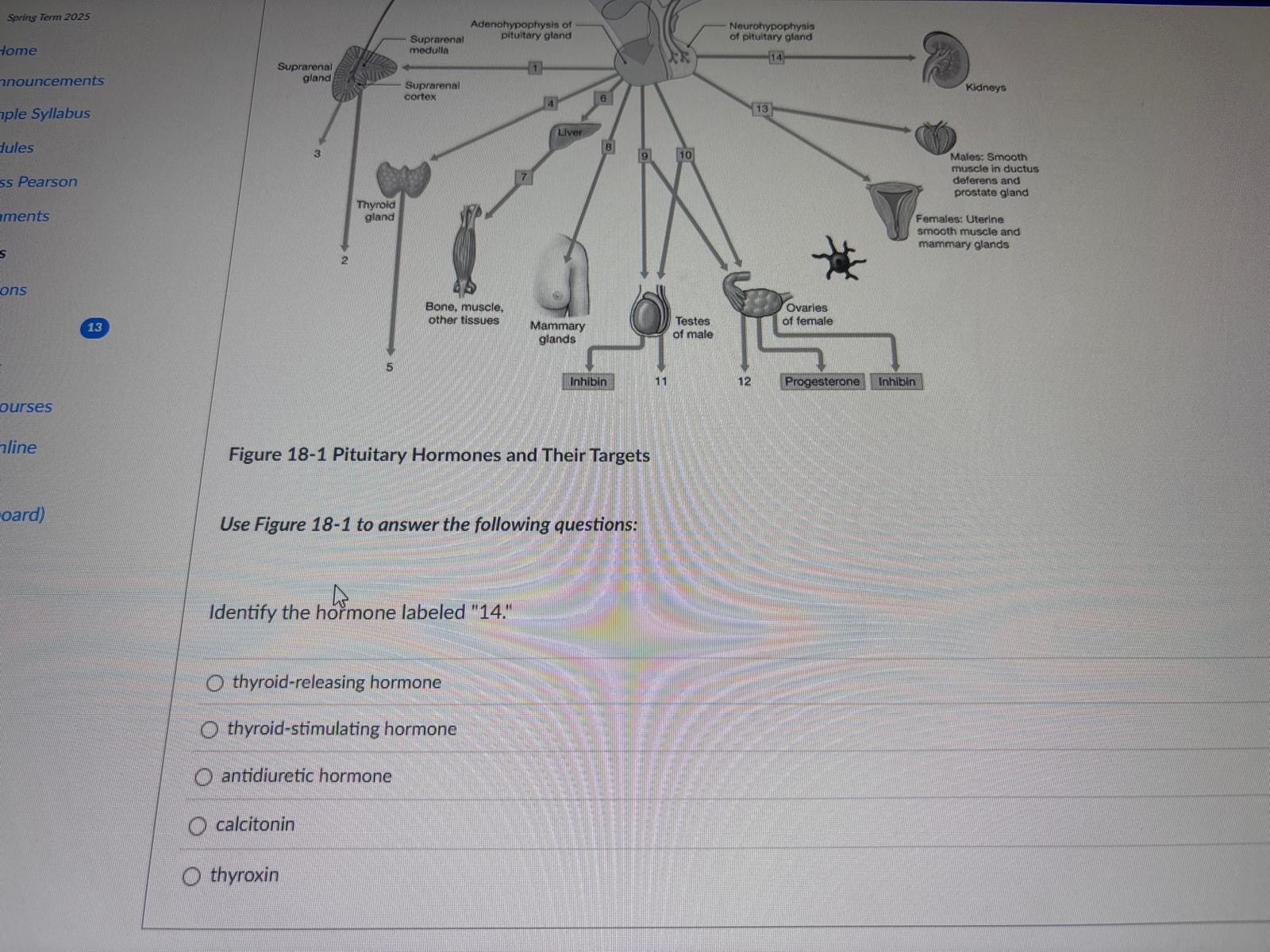
Identify the hormone labeled "14."
thyroid-releasing hormone
thyroid-stimulating hormone
antidiuretic hormone
calcitonin
thyroxin
antidiuretic hormone
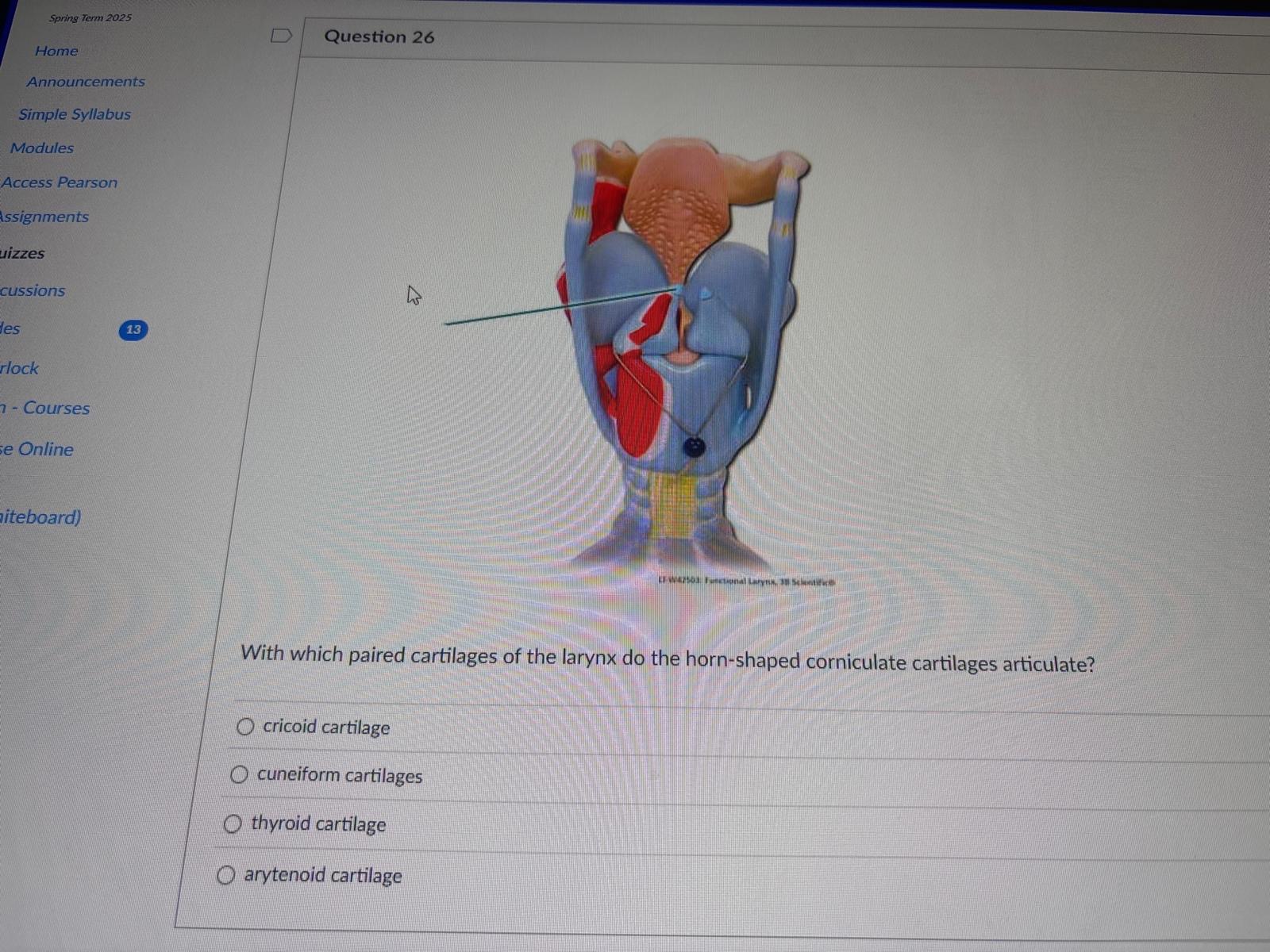
With which paired cartilages of the larynx do the horn-shaped corniculate cartilages articulate?
cricoid cartilage
cuneiform cartilages
thyroid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
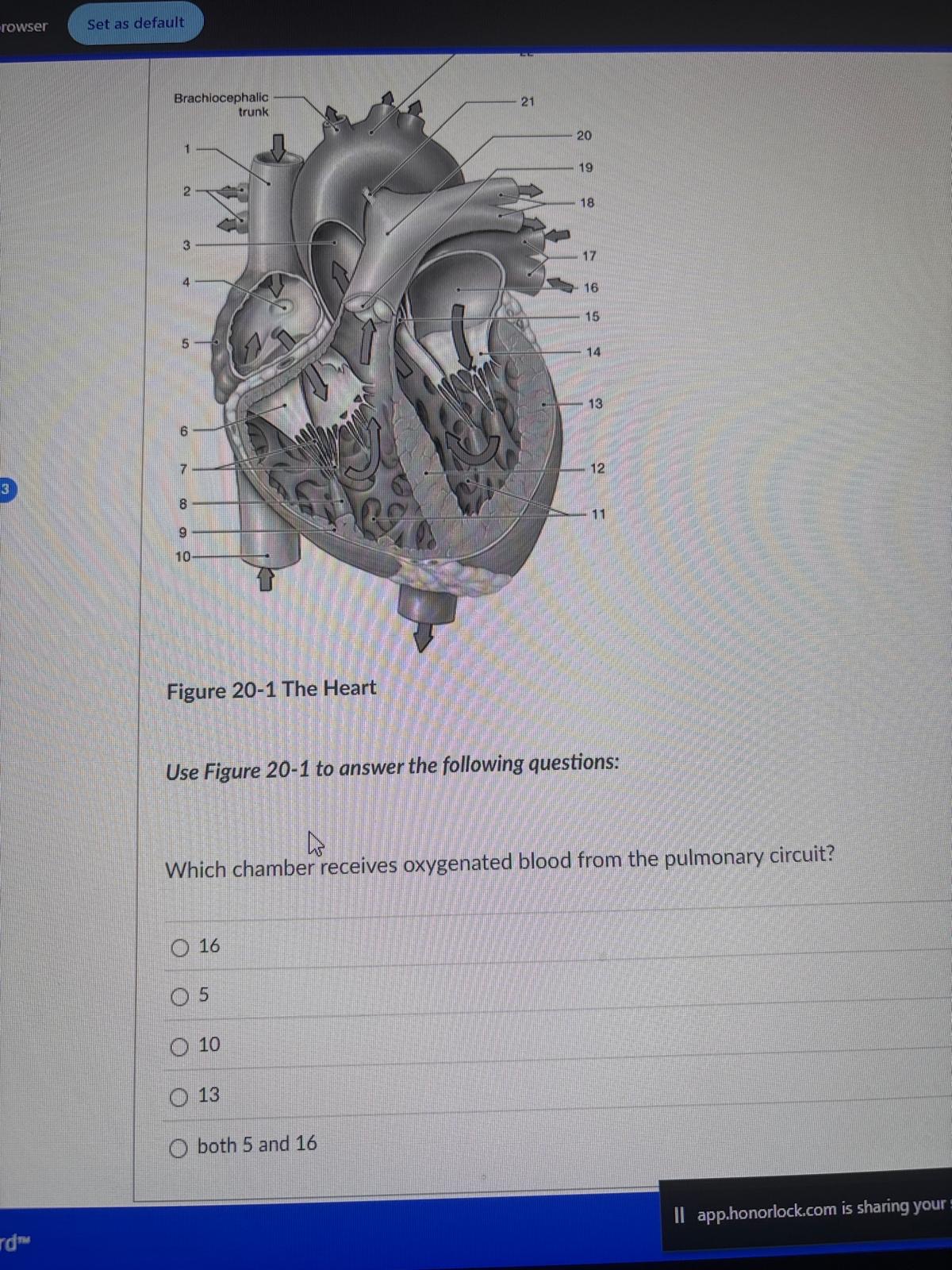
Which chamber receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circuit?
16
5
10
13
both 5 and 16
16
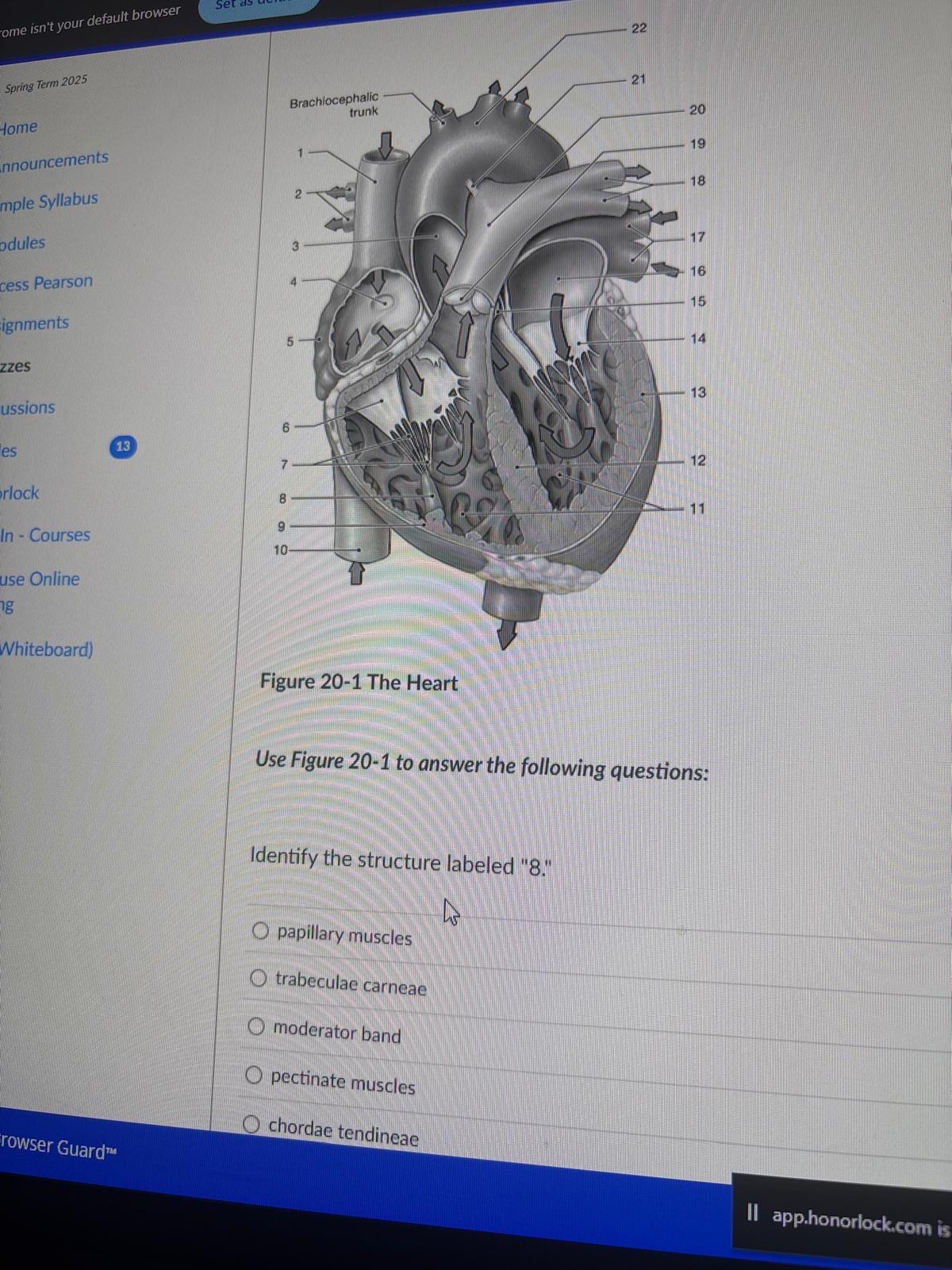
Identify the structure labeled "8."
papillary muscles
trabeculae carneae
moderator band
pectinate muscles
chordae tendineae
papillary muscles