Heart - McKee Unit 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
apex
lower tip of the heart
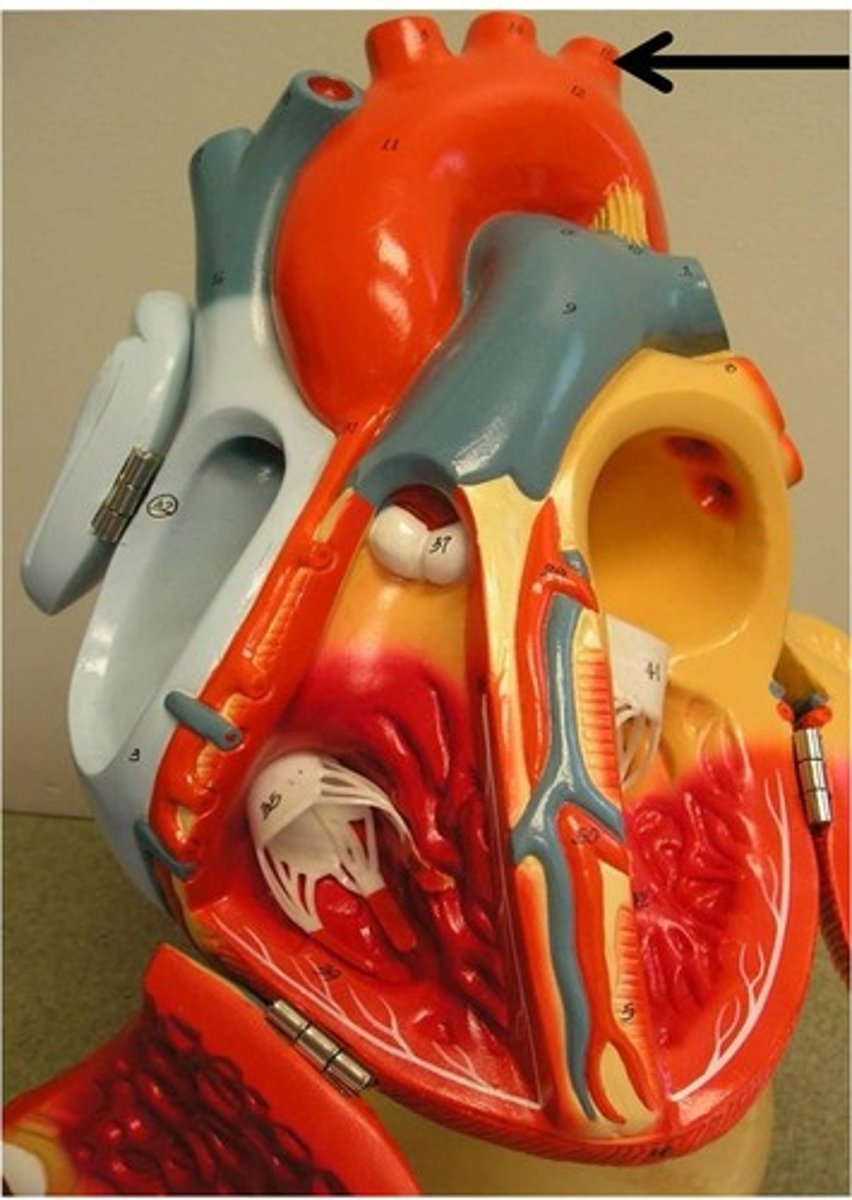
base
on top of the heart; where great vessels located
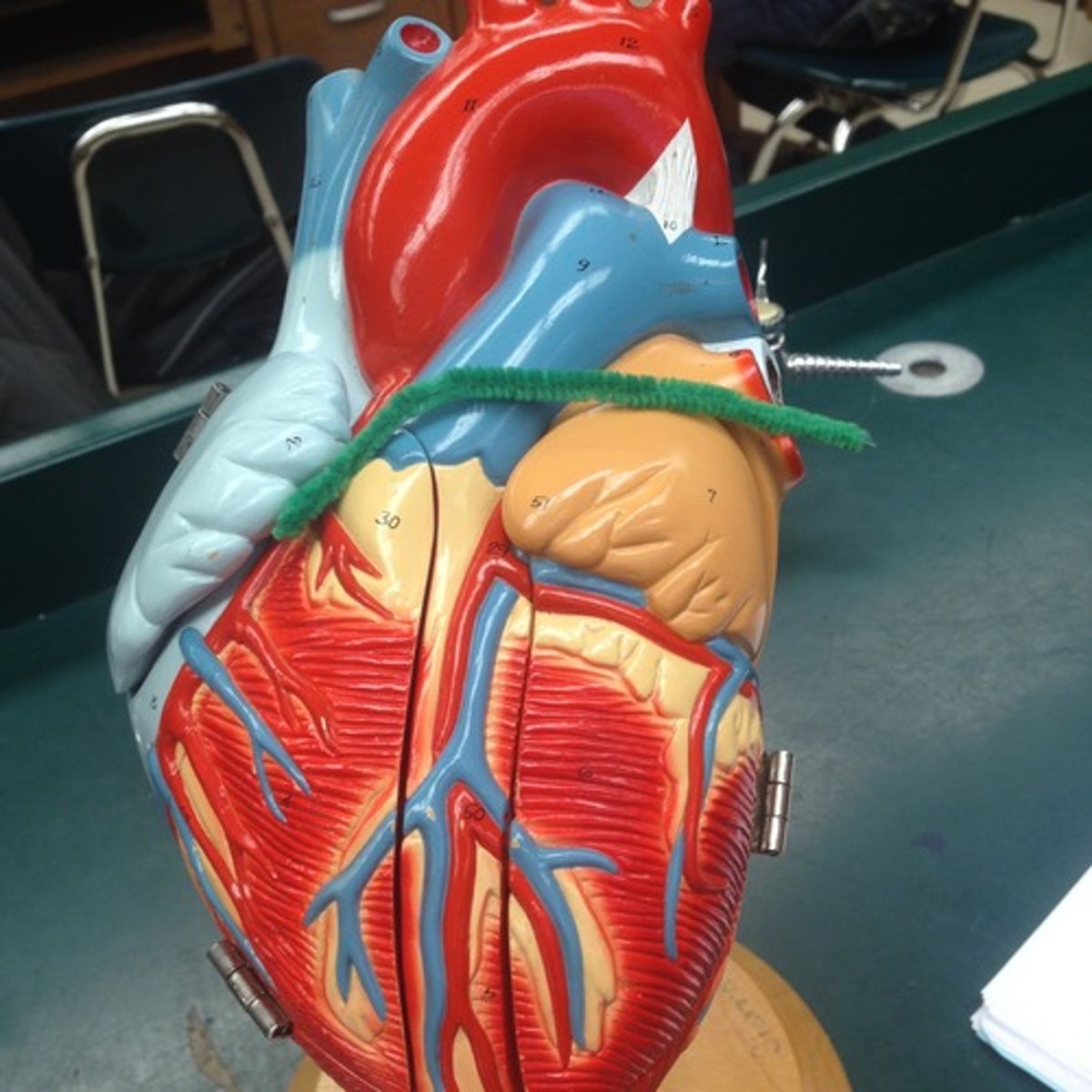
epicardium (visceral pericardium)
Function: proctecion from friction
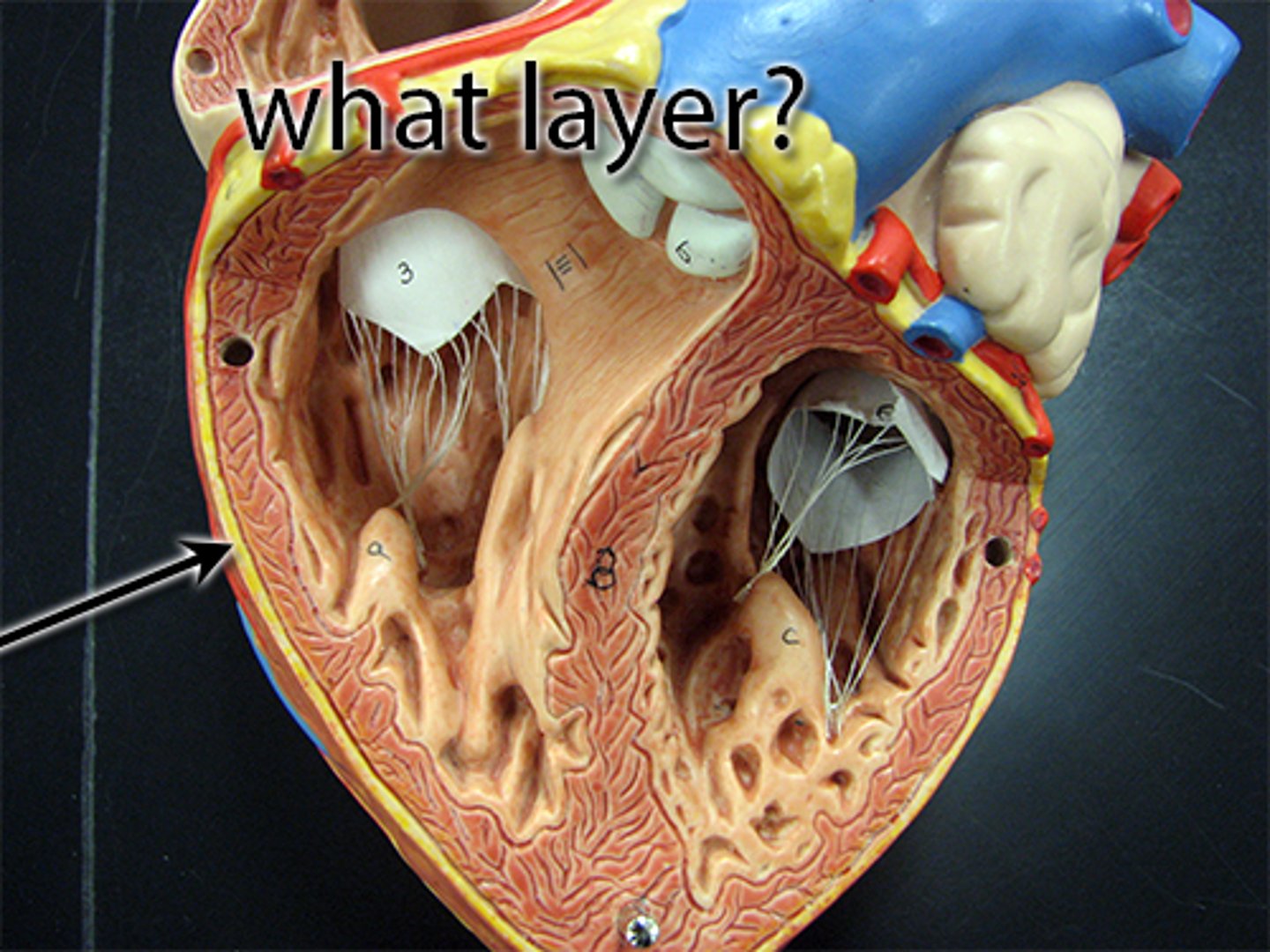
endocardium
Function: protection
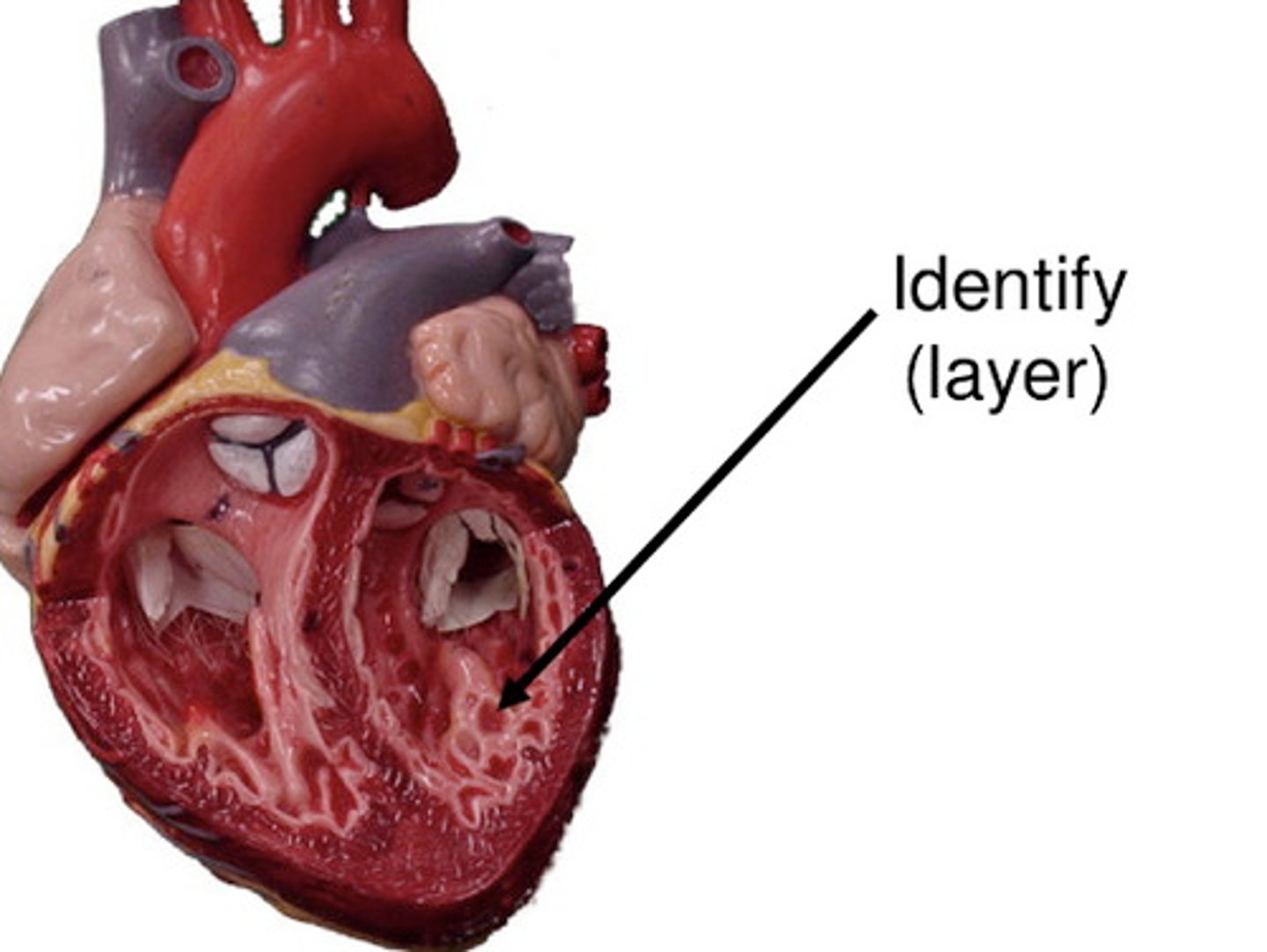
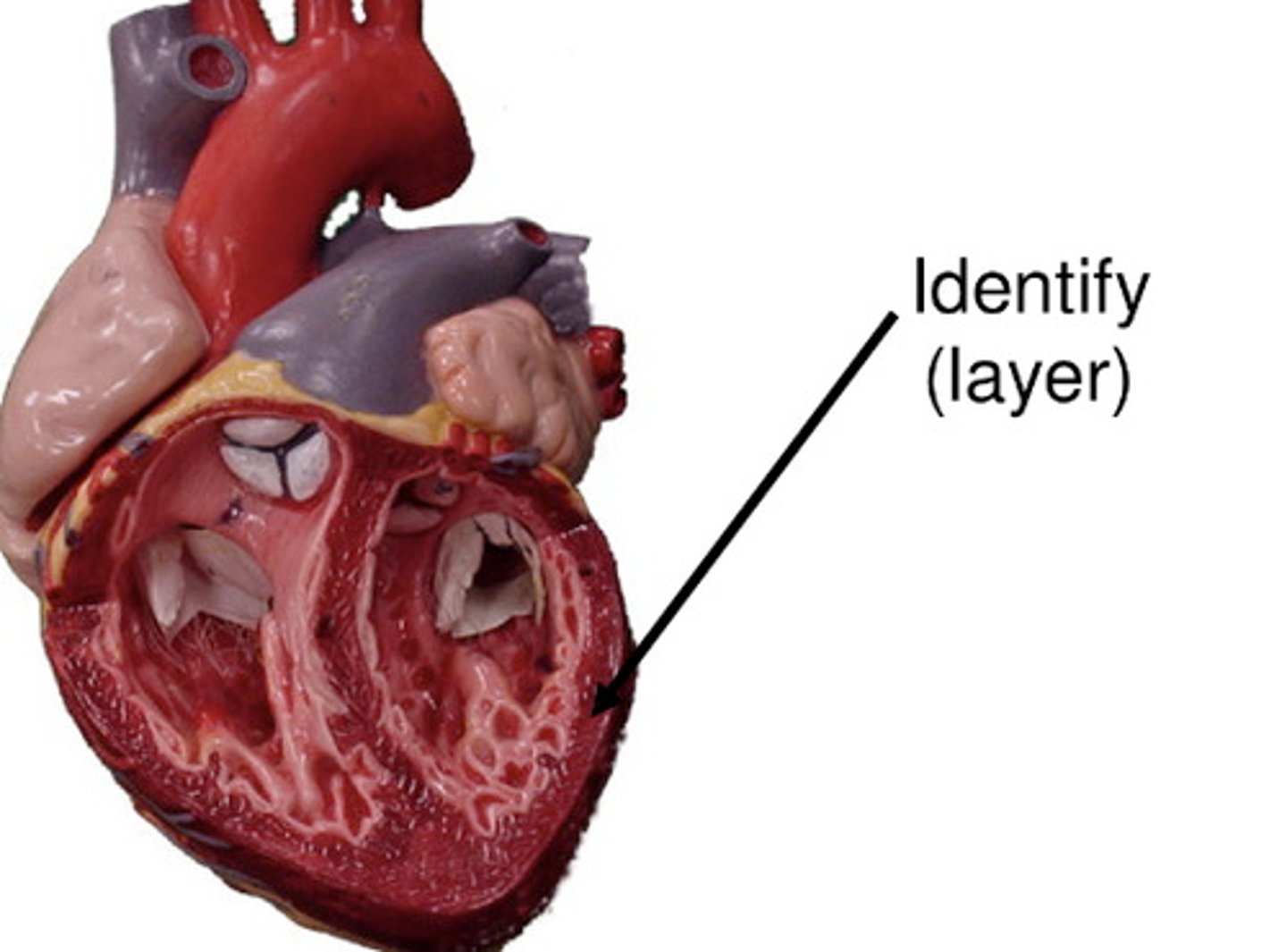
myocardium
Function: contract to pump blood
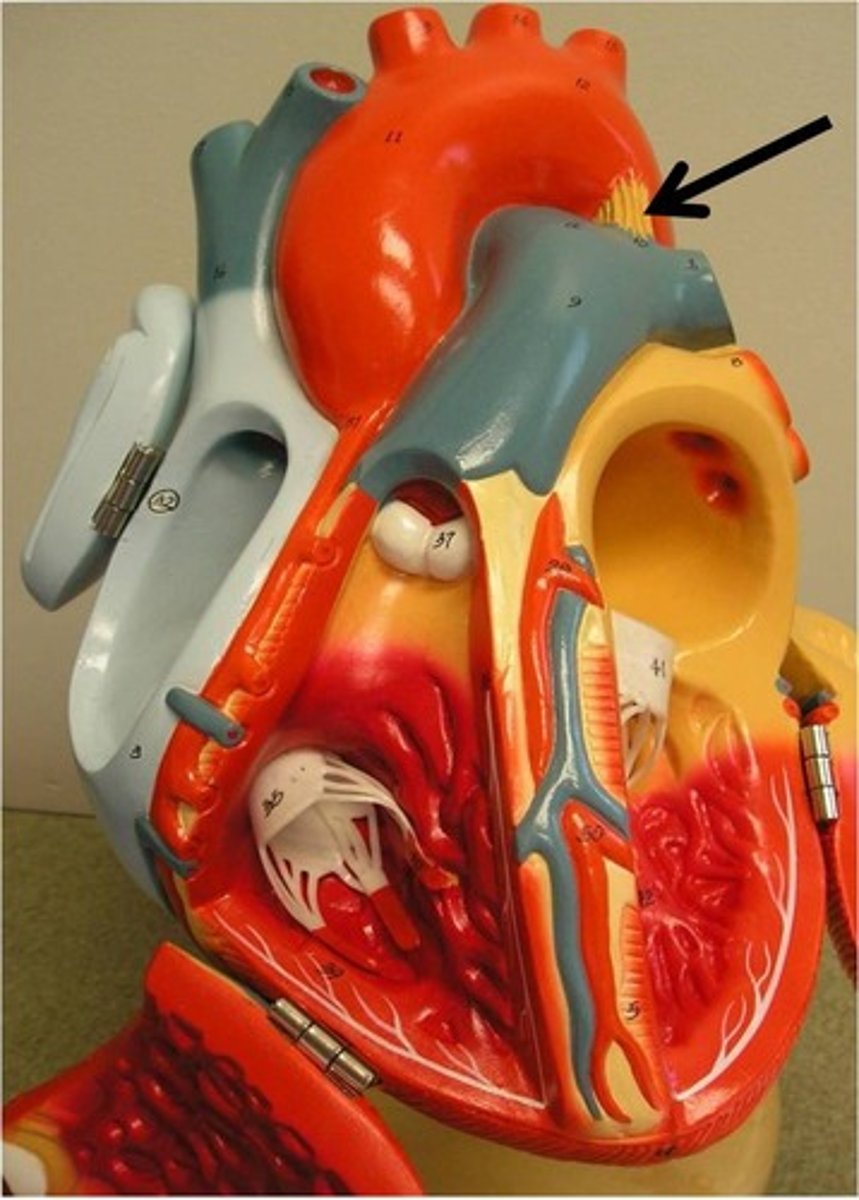
ligamentum arteriosum
remnant of ductus arteriosus in adults, no function in adults
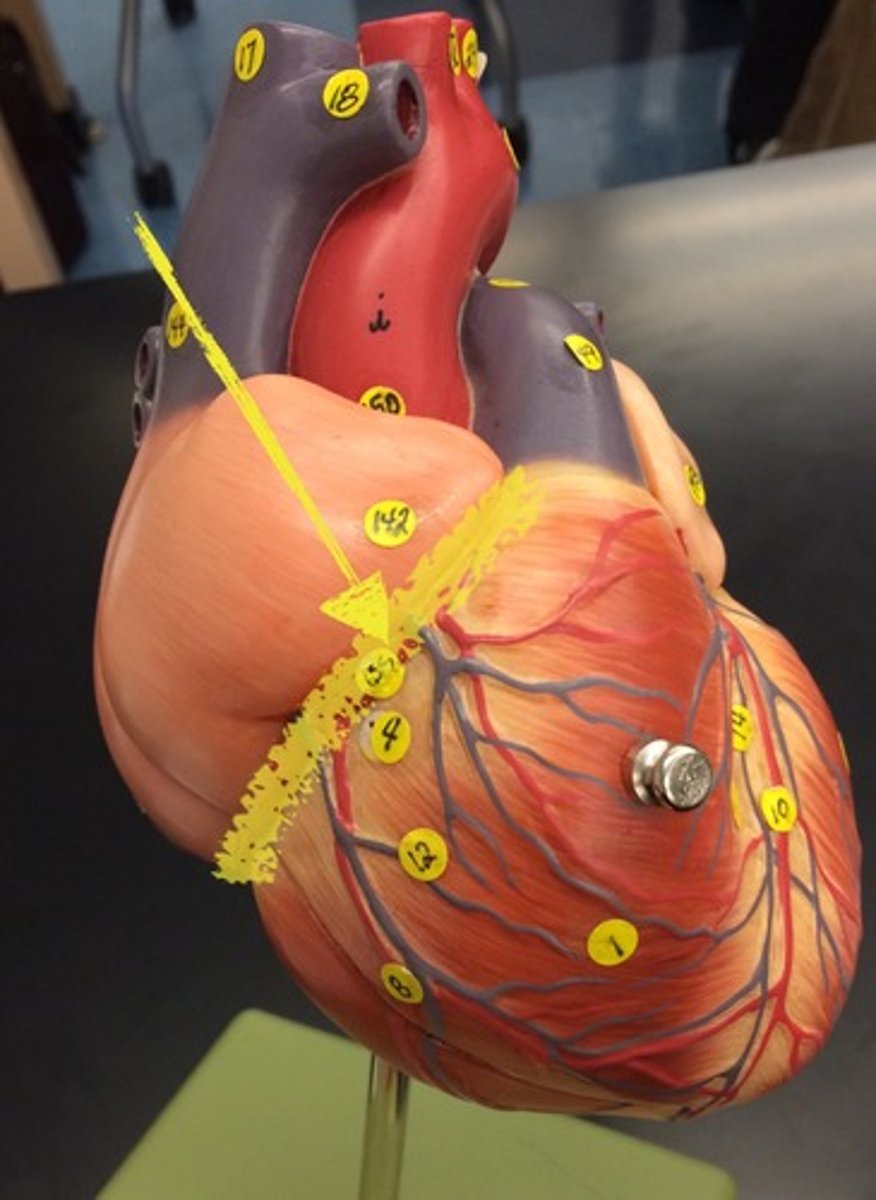
coronary sulcus
Function: pathway for coronary arteries
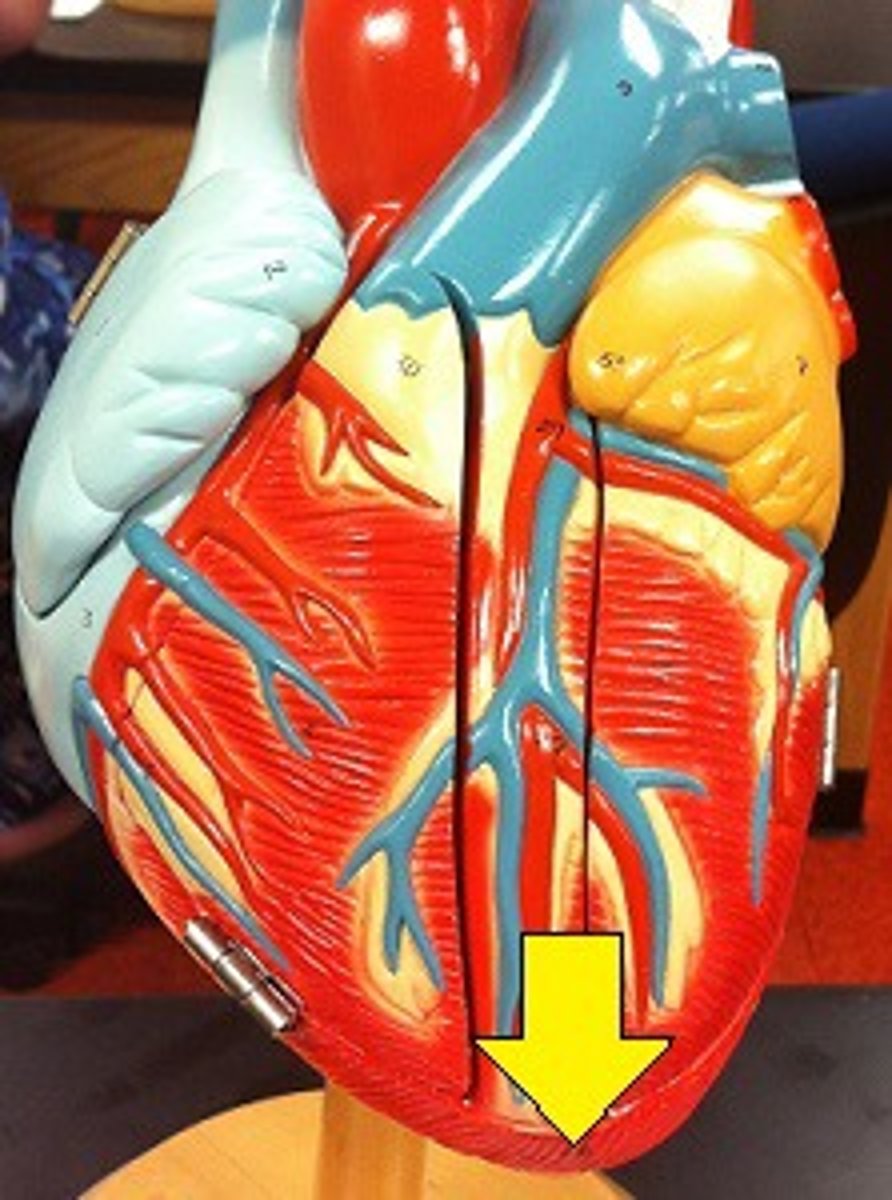
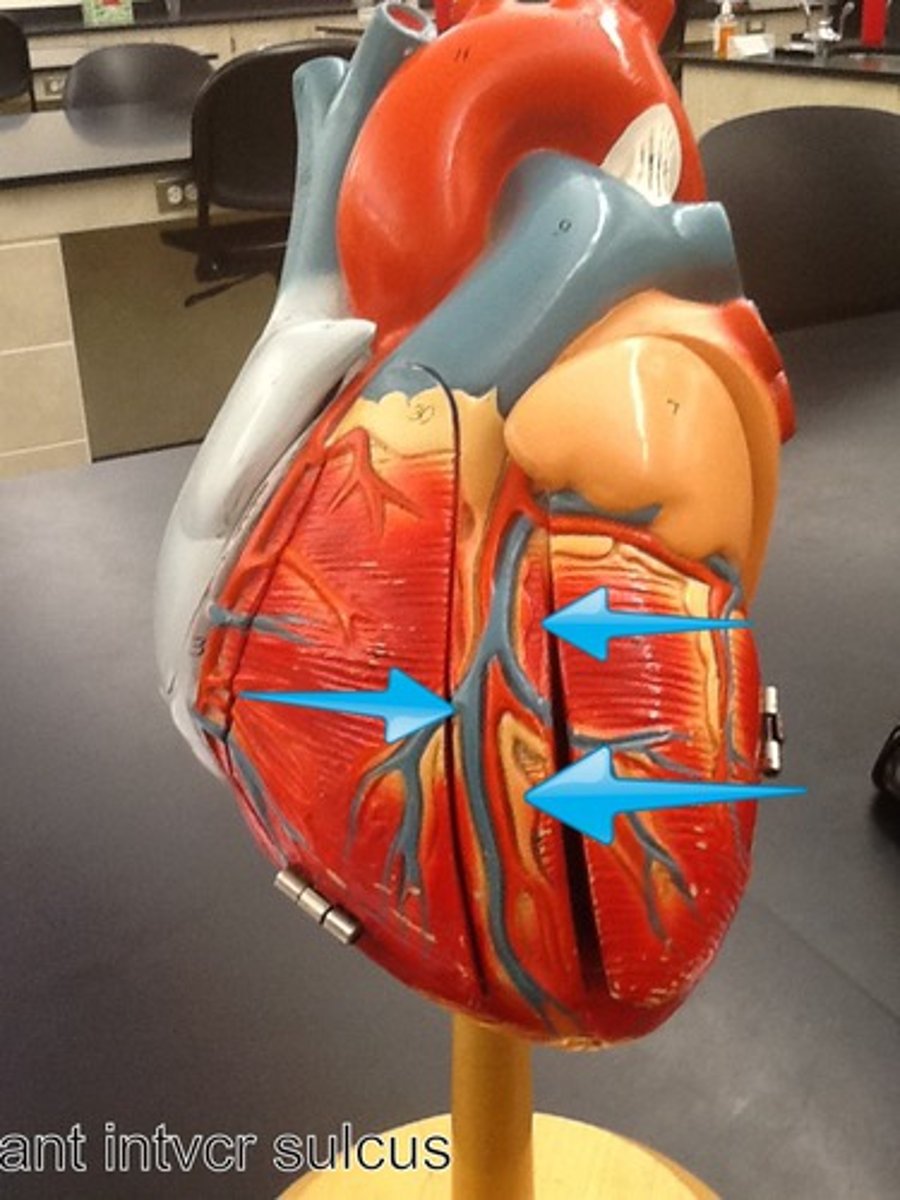
anterior interventricular sulcus
marks the boundary between the ventricles anteriorly
Function: pathway anterior interventricular blood vessels
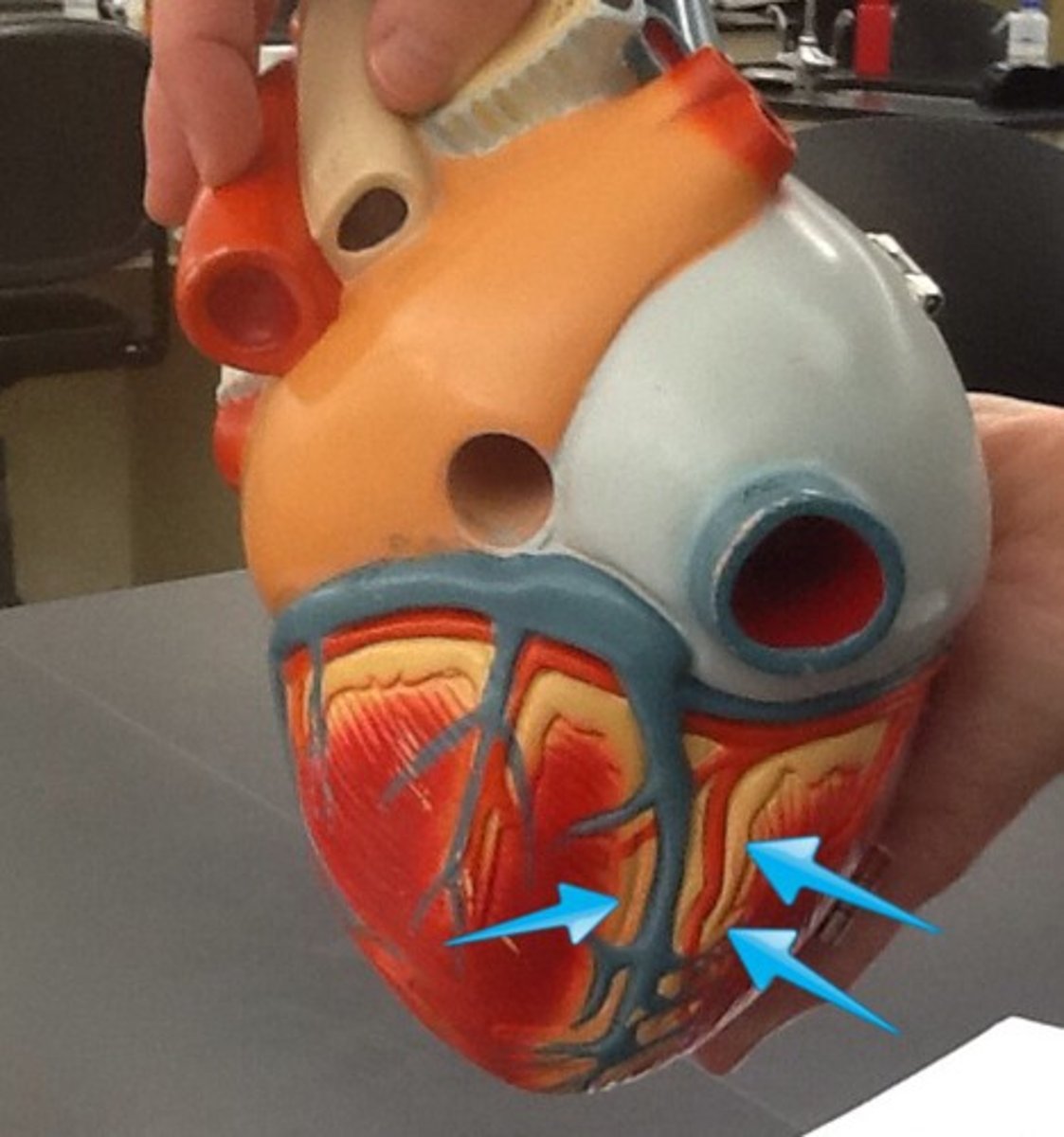
posterior interventricular sulcus
marks the boundary between the ventricles posteriorly
Function: pathway posterior interventricular blood vessels
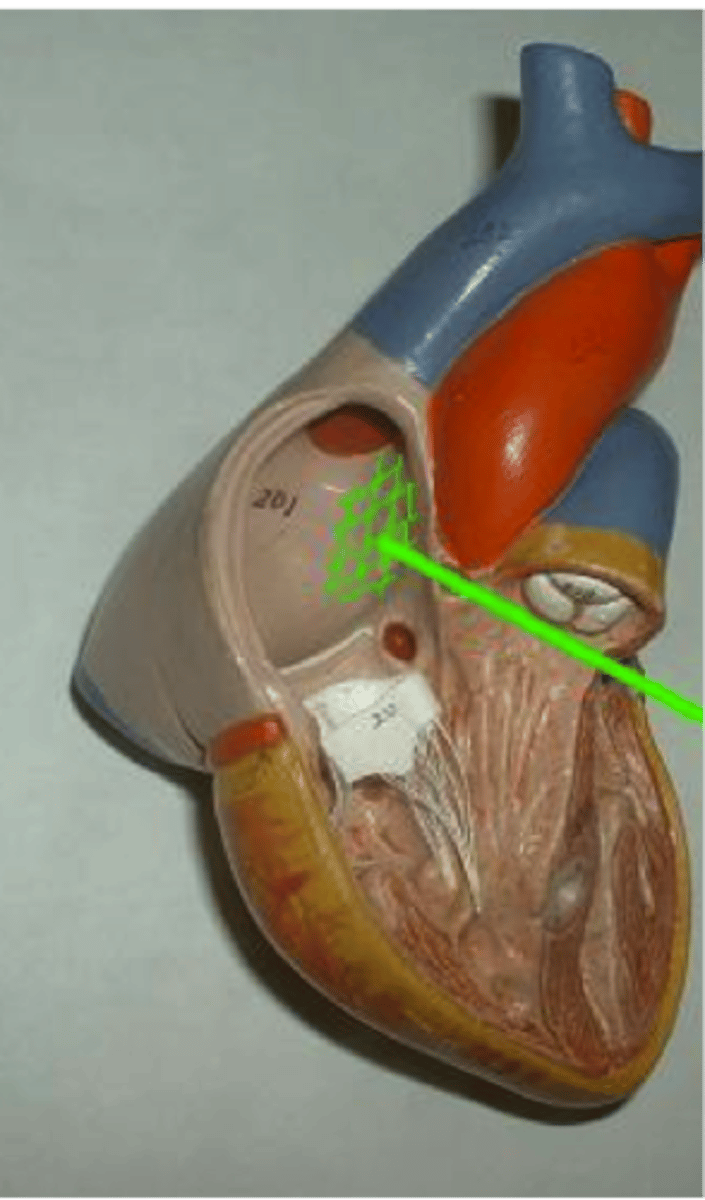
interatrial septum
Function: separate left and right atria
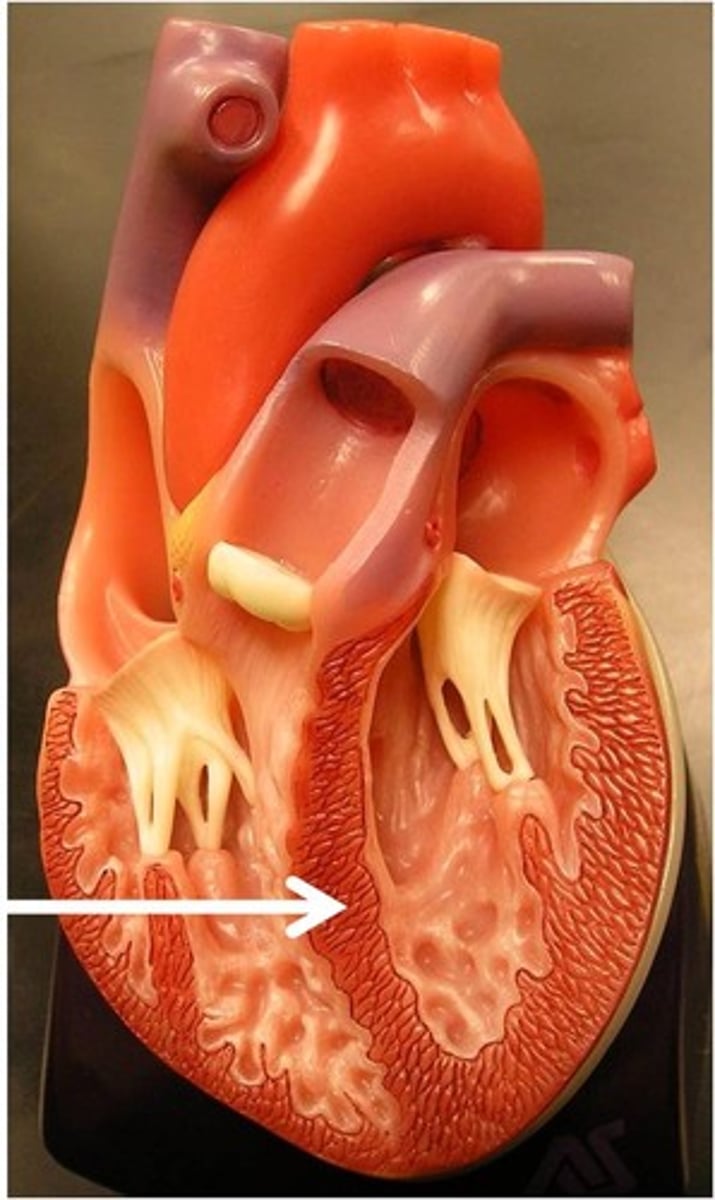
interventricular septum
Function: separate right and left ventricles
right coronary artery
Function: supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes
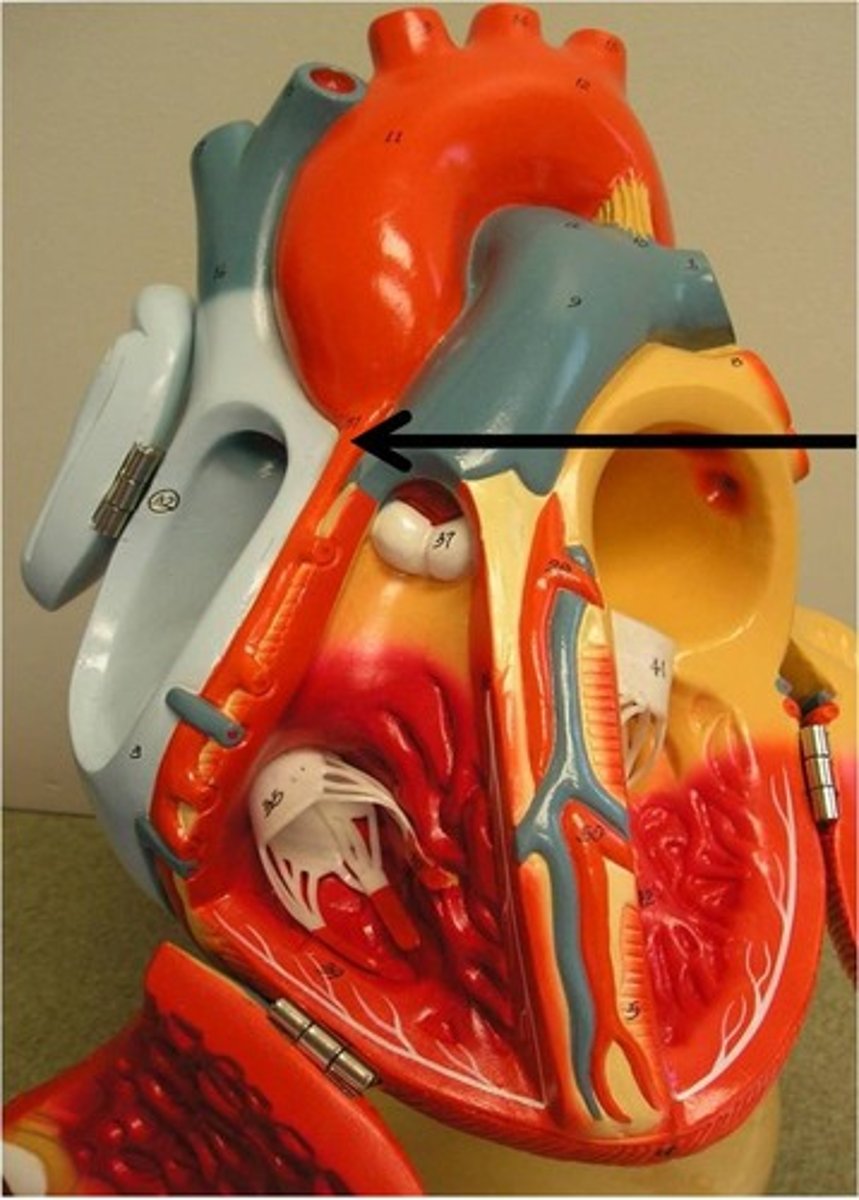
left coronary artery
Function: supplies blood to the left ventricle, left atrium, and interventricular septum
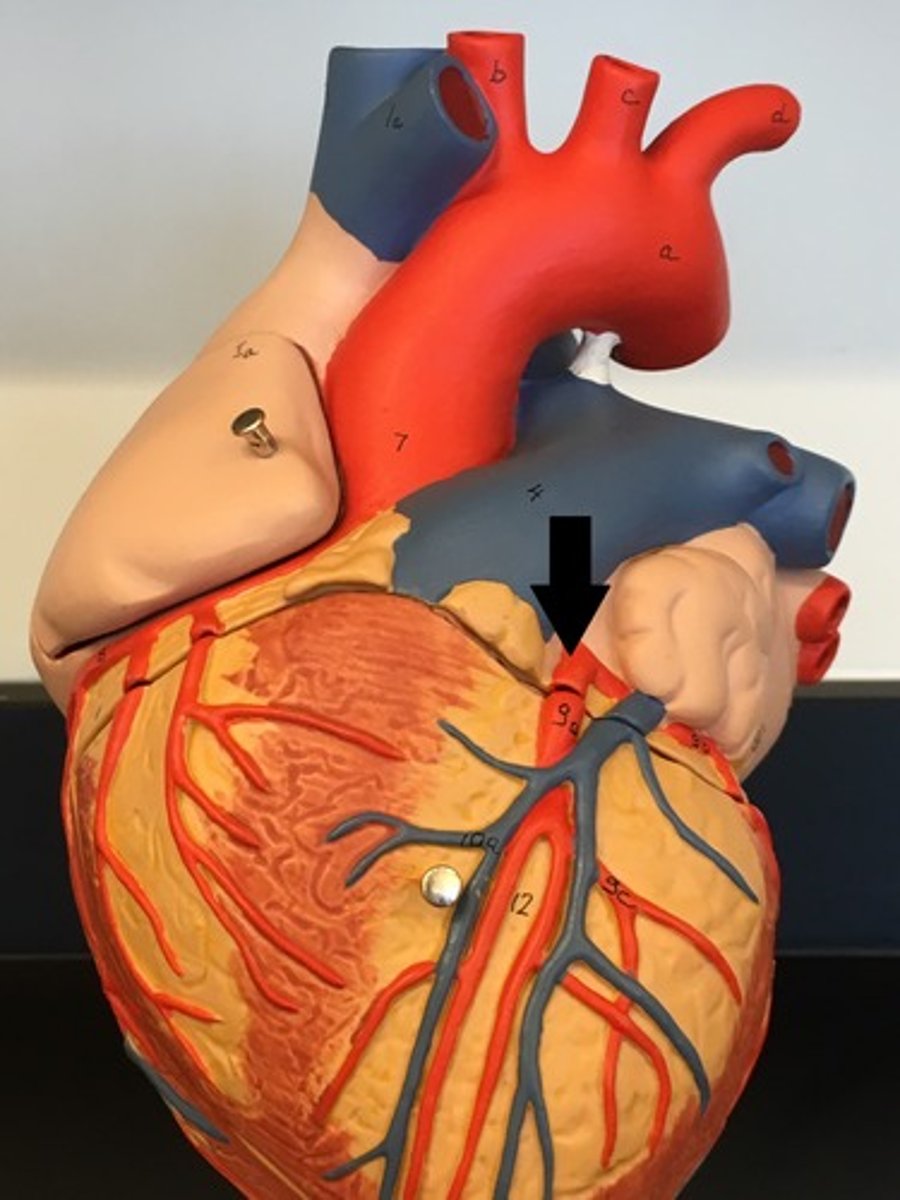
circumflex artery
Function: supplies the left atrium and the posterior walls of the left ventricle
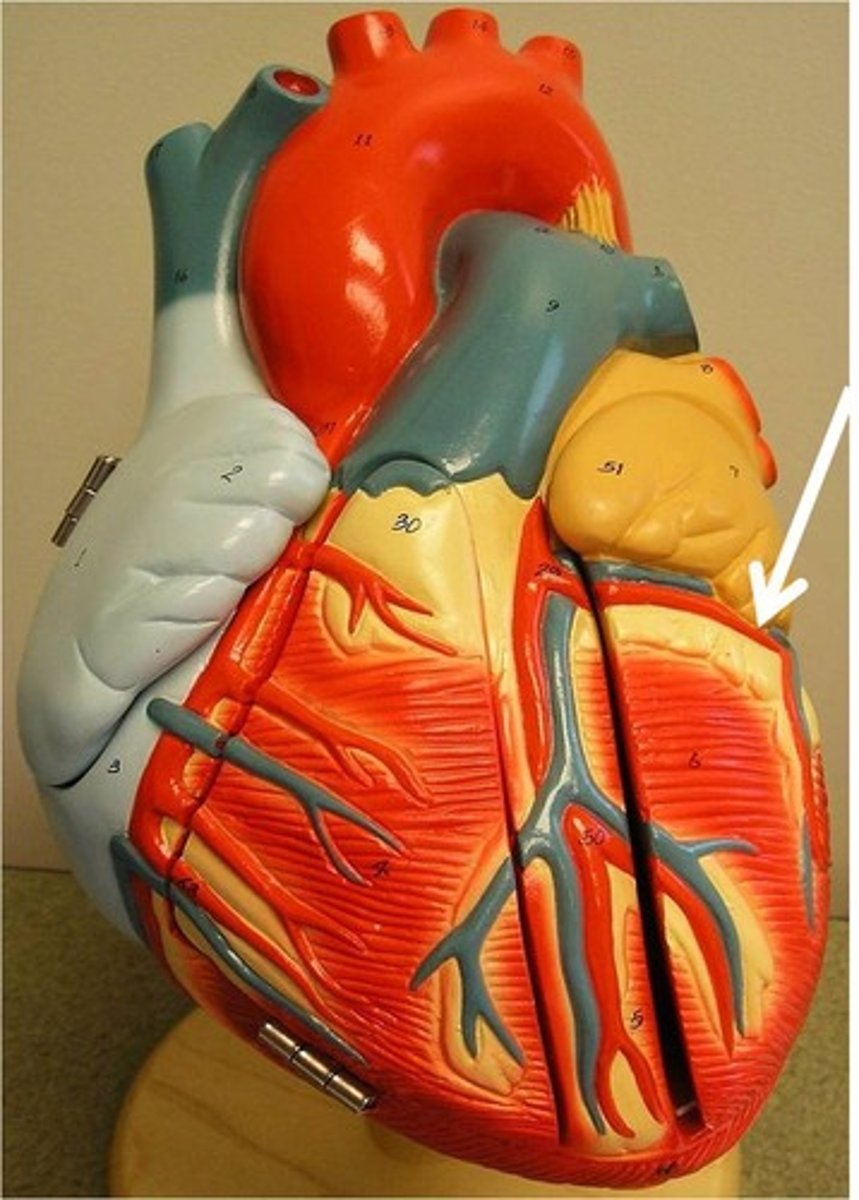
marginal artery
Function: supplies the right border of the heart
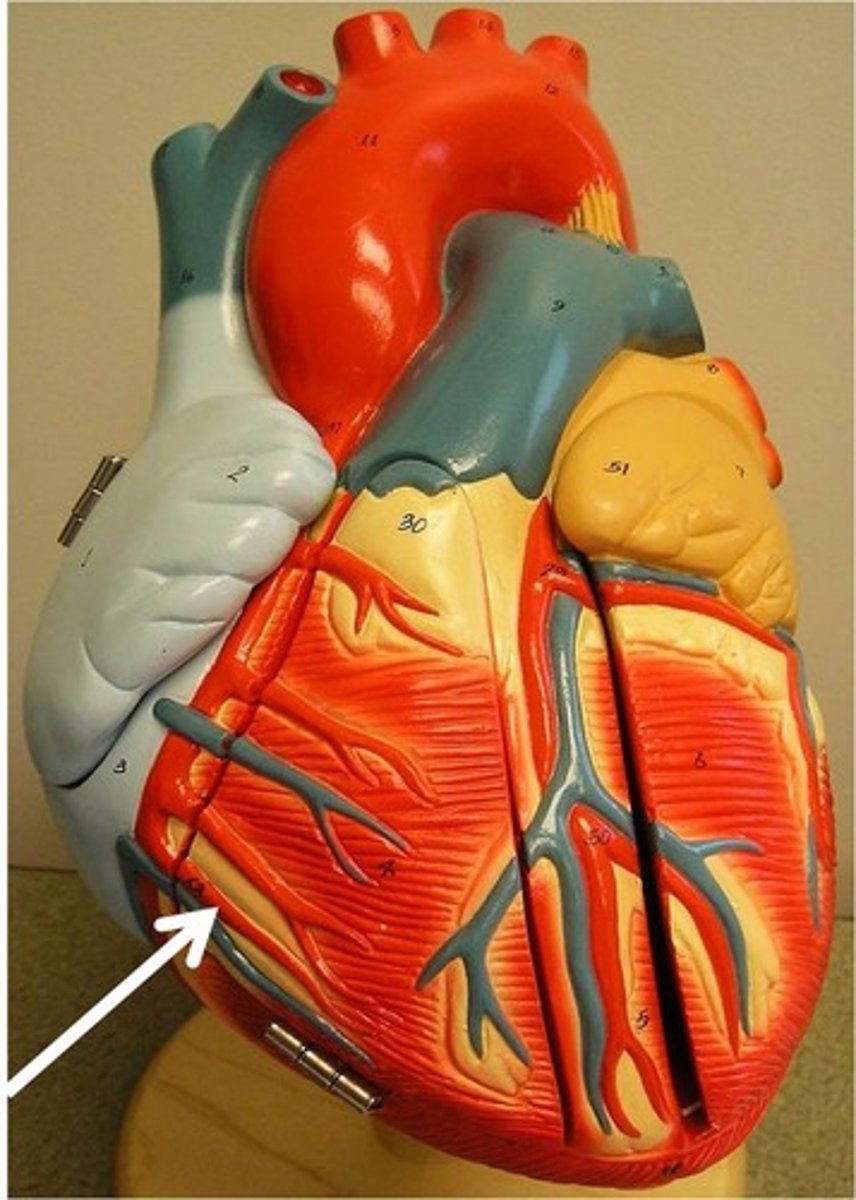
anterior interventricular artery
Function: supplies the anterior surface of both ventricles and most of the interventricular septum
also called the left anterior descending artery (LAD)
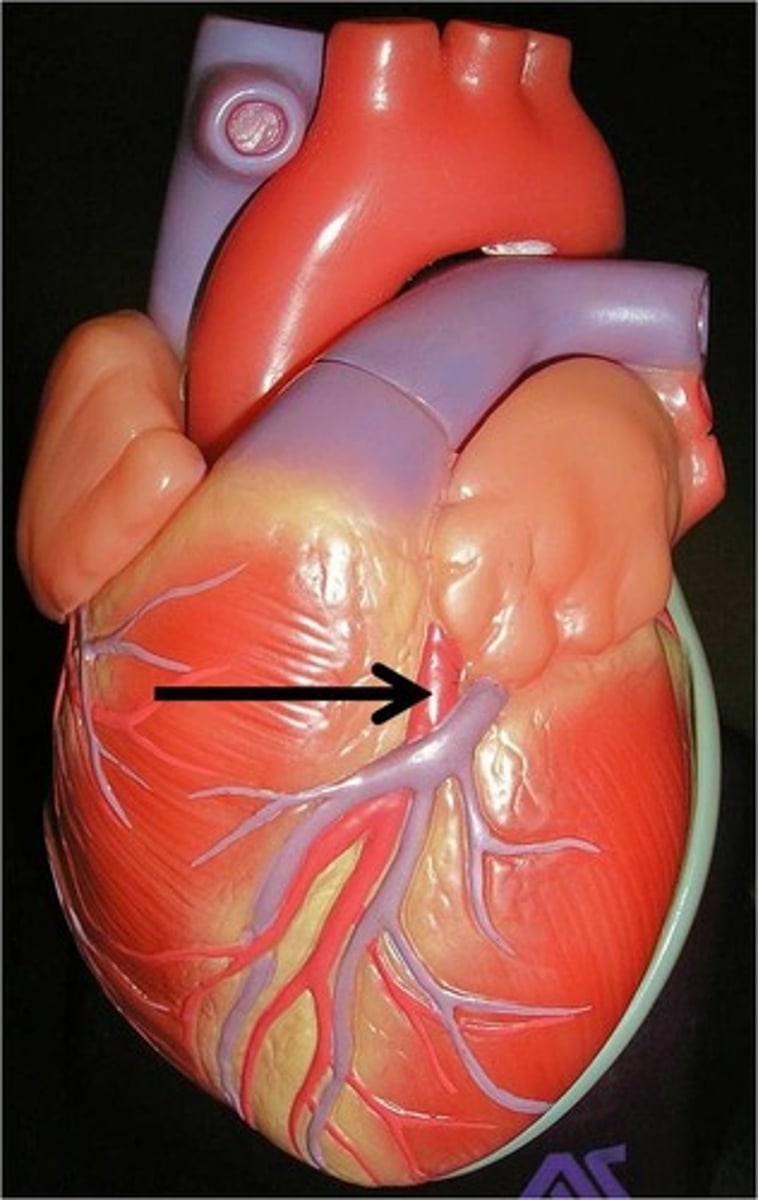
posterior interventricular artery
Function: supplies the posterior ventricular walls, runs to the heart apex
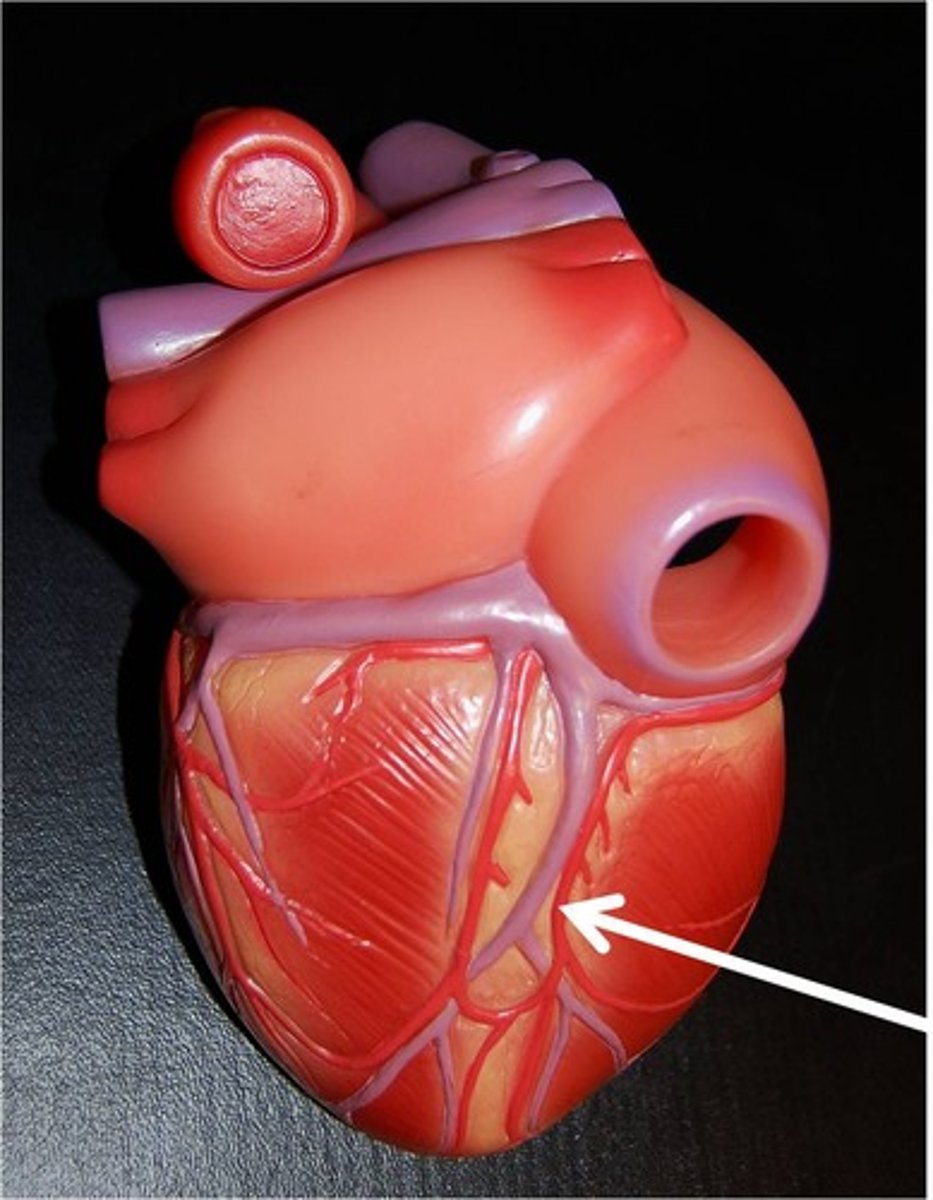
great cardiac vein
Function: drains the anterior surface of both ventricles and most of the interventricular septum;
runs alongside the anterior interventricular artery
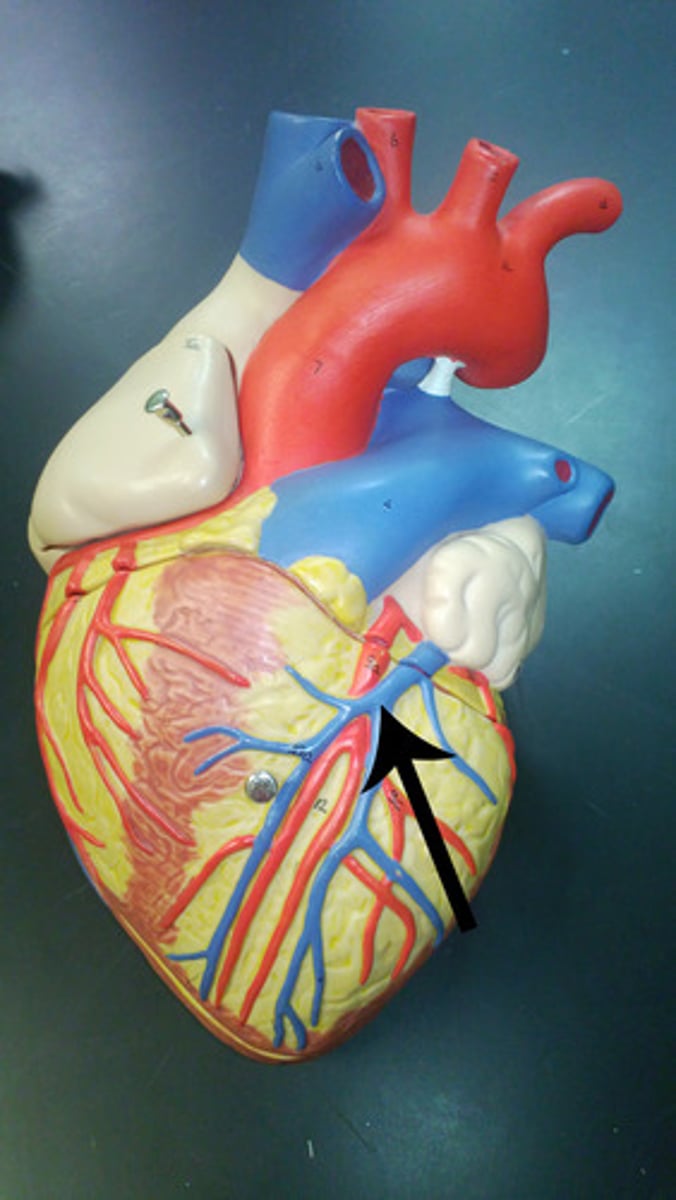
middle cardiac vein
Function: drains the posterior ventricular walls;
runs alongside the posterior interventricular artery
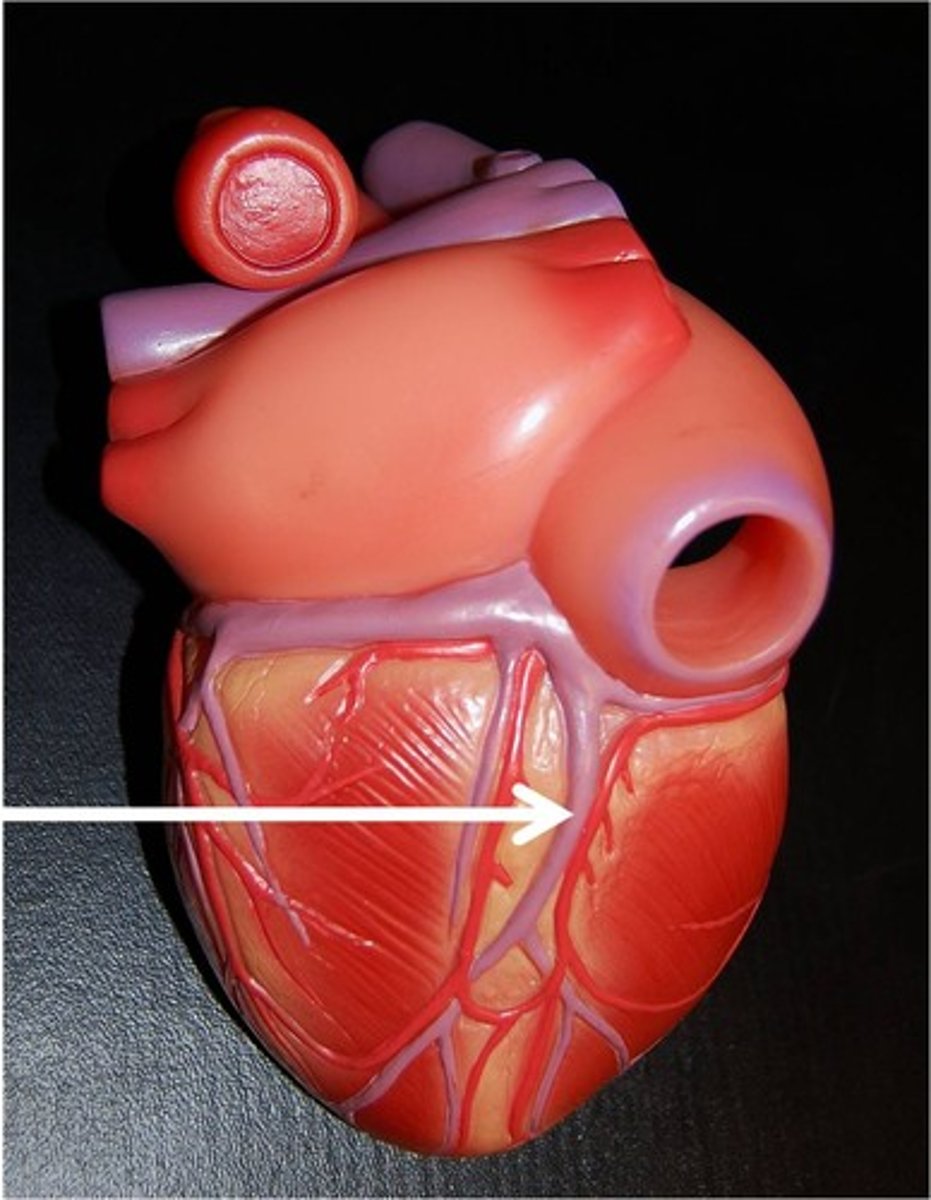
small cardiac vein
Function: drains the right border of the heart;
travels along side the right marginal artery.
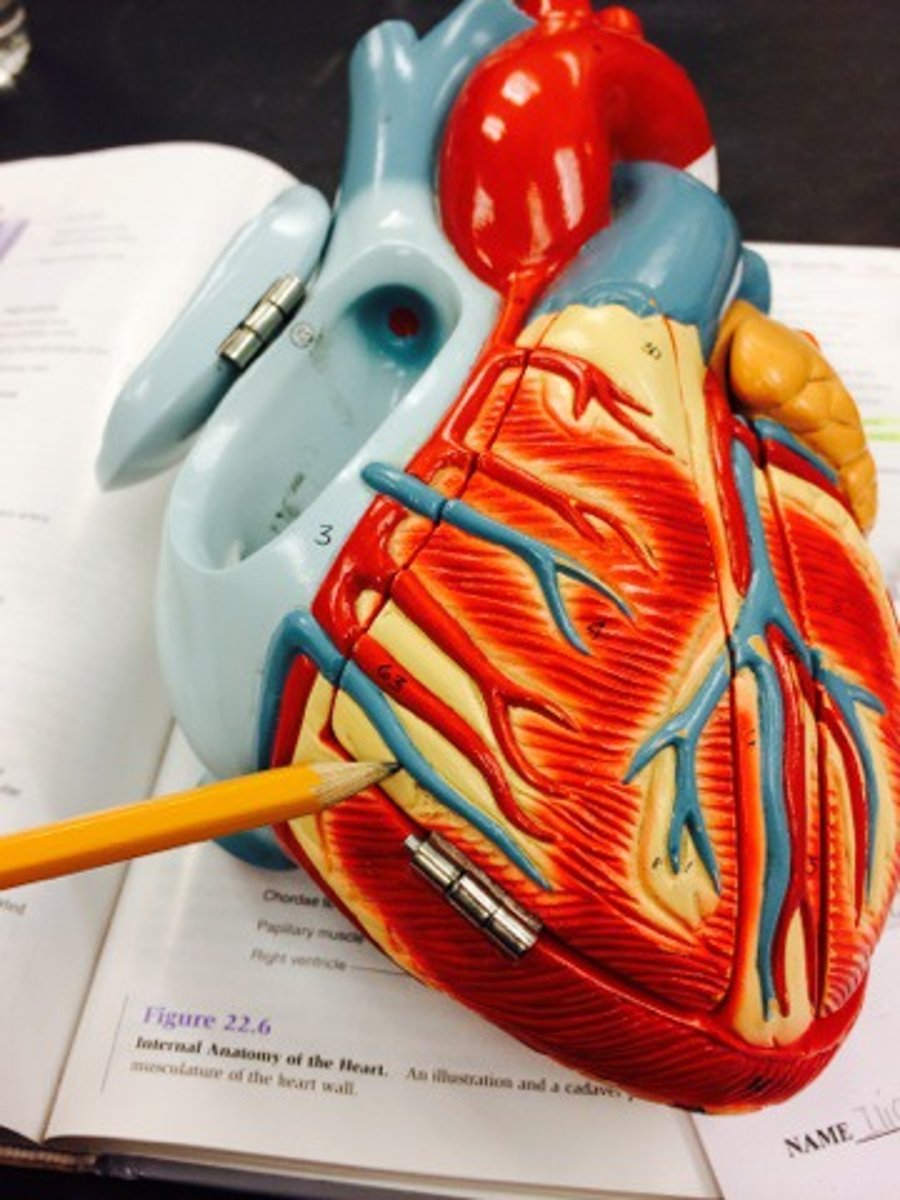
coronary sinus
Function: empties blood into the right atrium;
enlarged vein on the posterior aspect of the heart
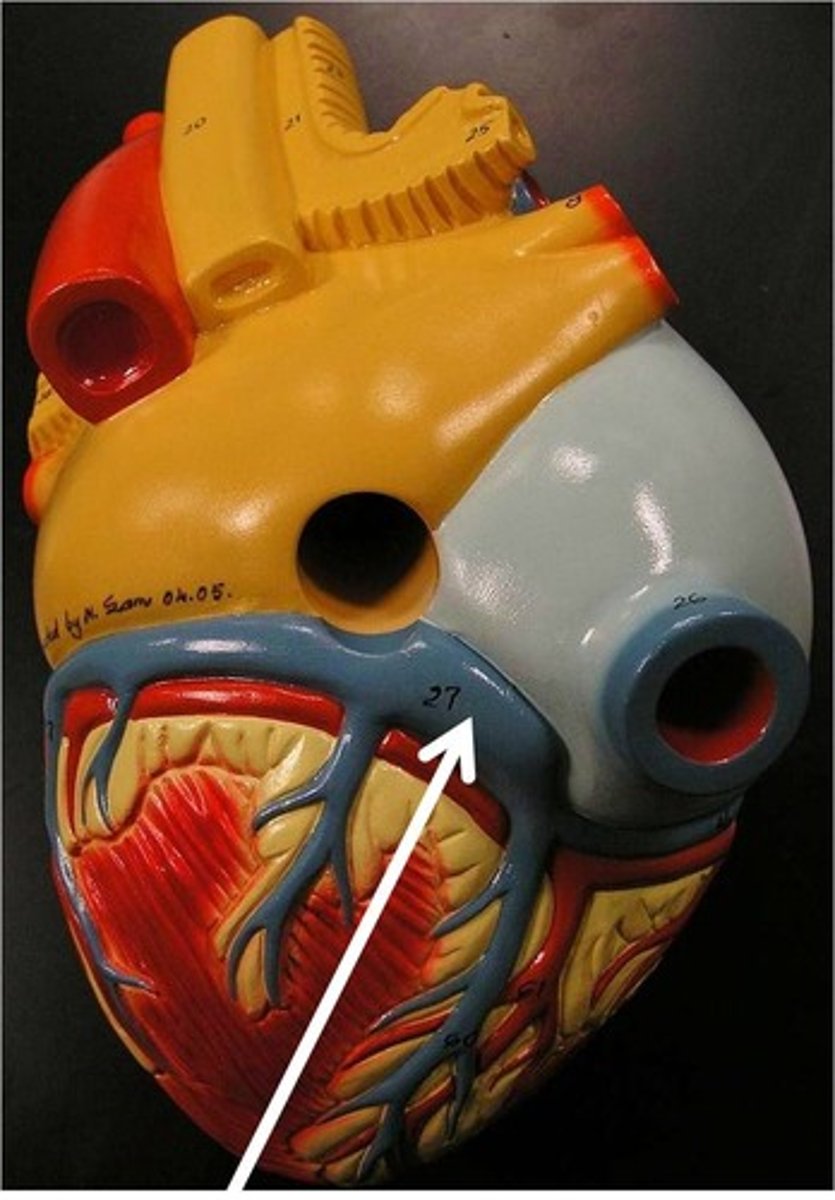
right atrium
Function: receives blood from the vena cava and coronary sinus
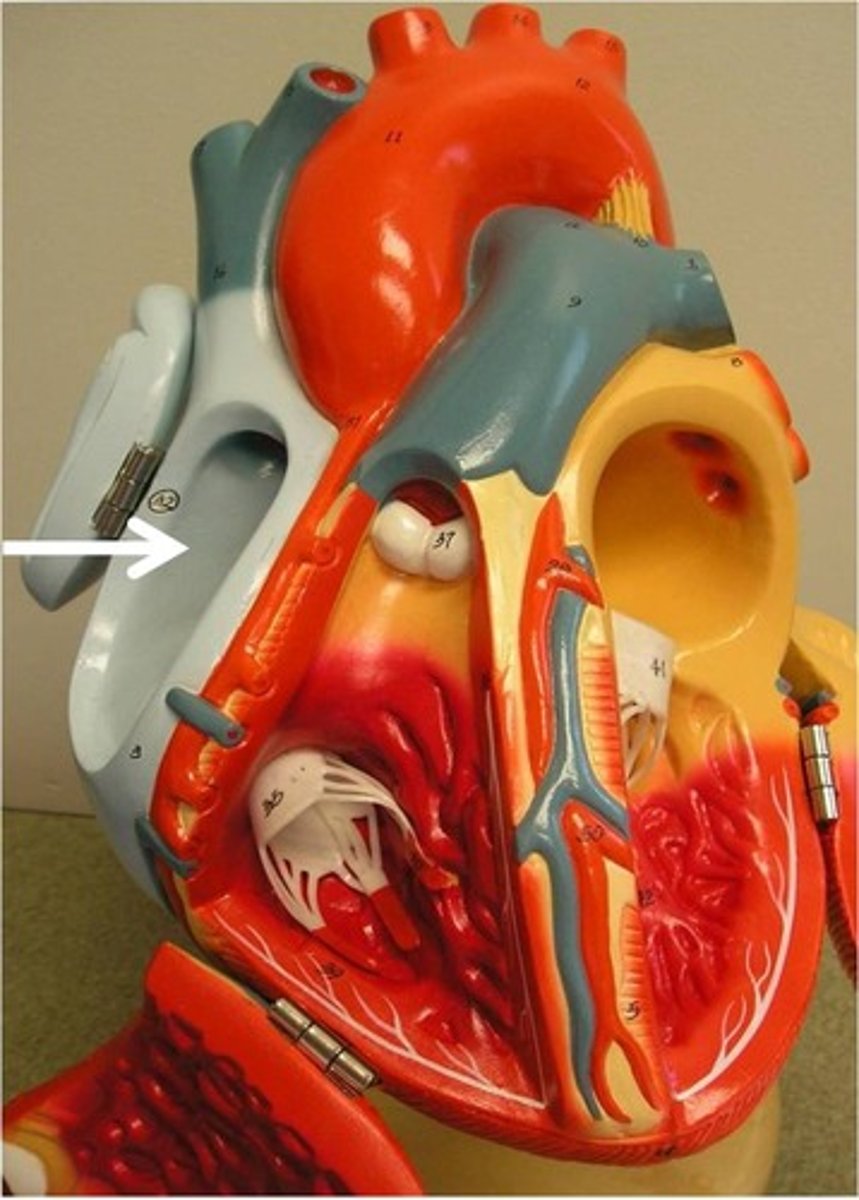
Auricles
Function: increase the volume of the atria
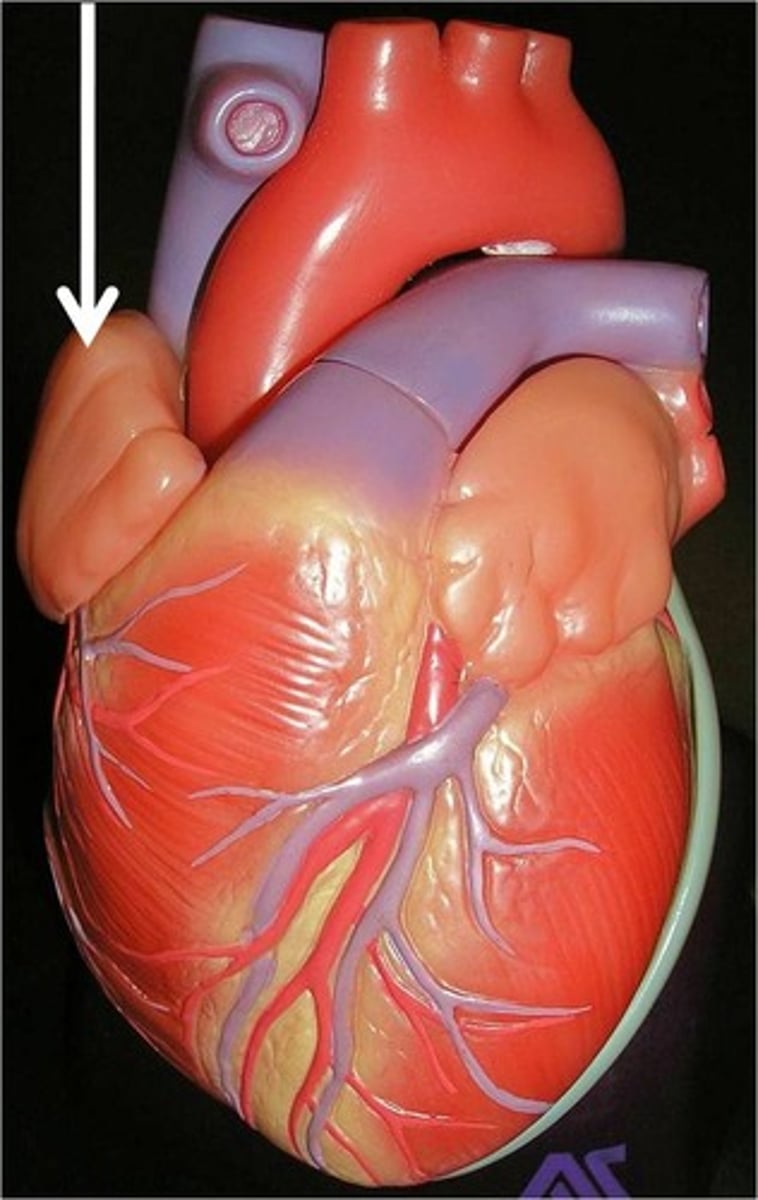
pectinate muscles
muscles located in the auricles
Function: increase power of atrial contaction
superior vena cava
Function: drains blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart
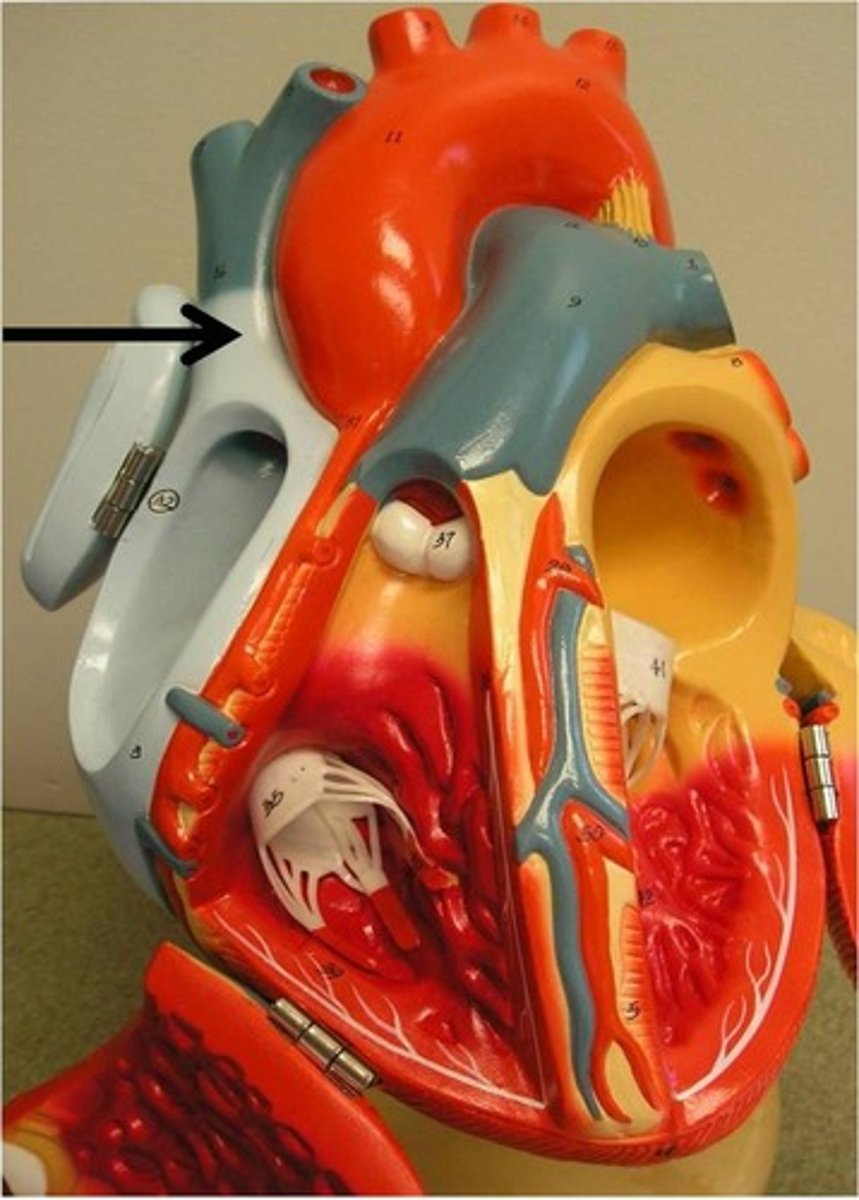
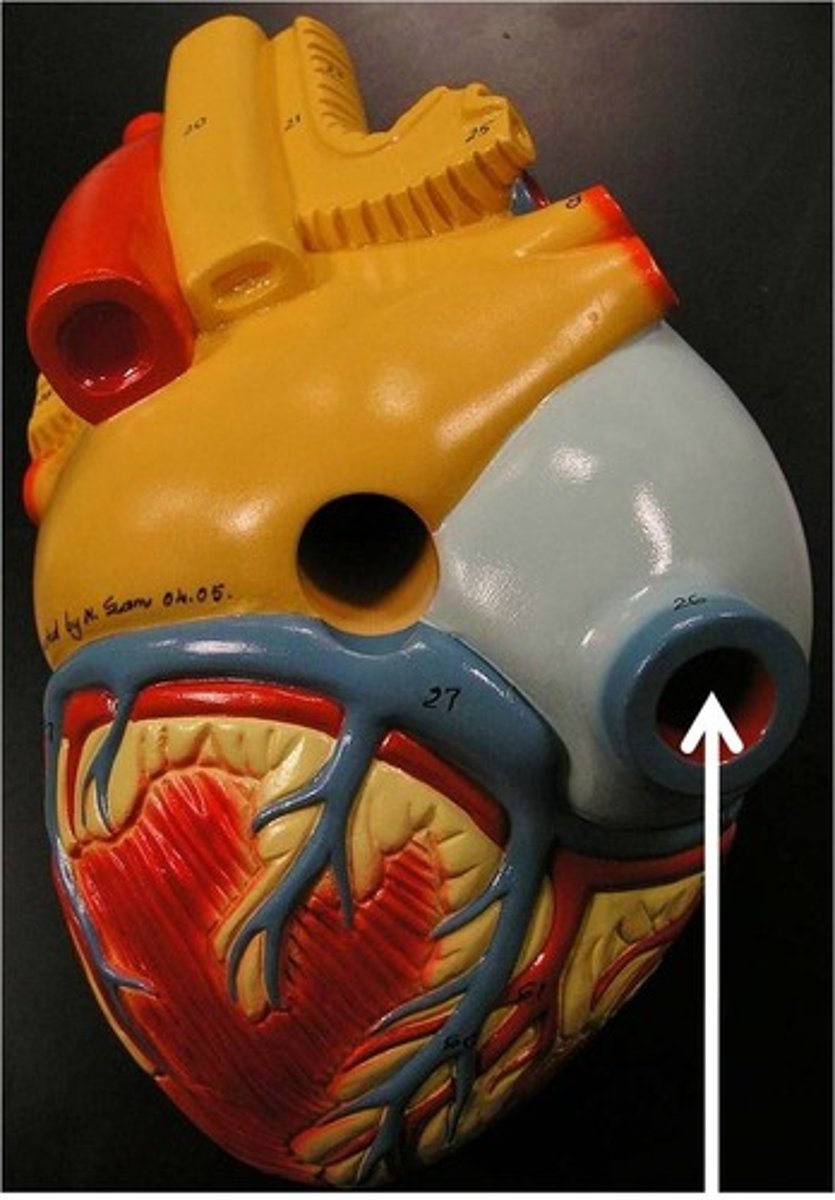
inferior vena cava
Function: carries blood from lower regions of the body to right atrium
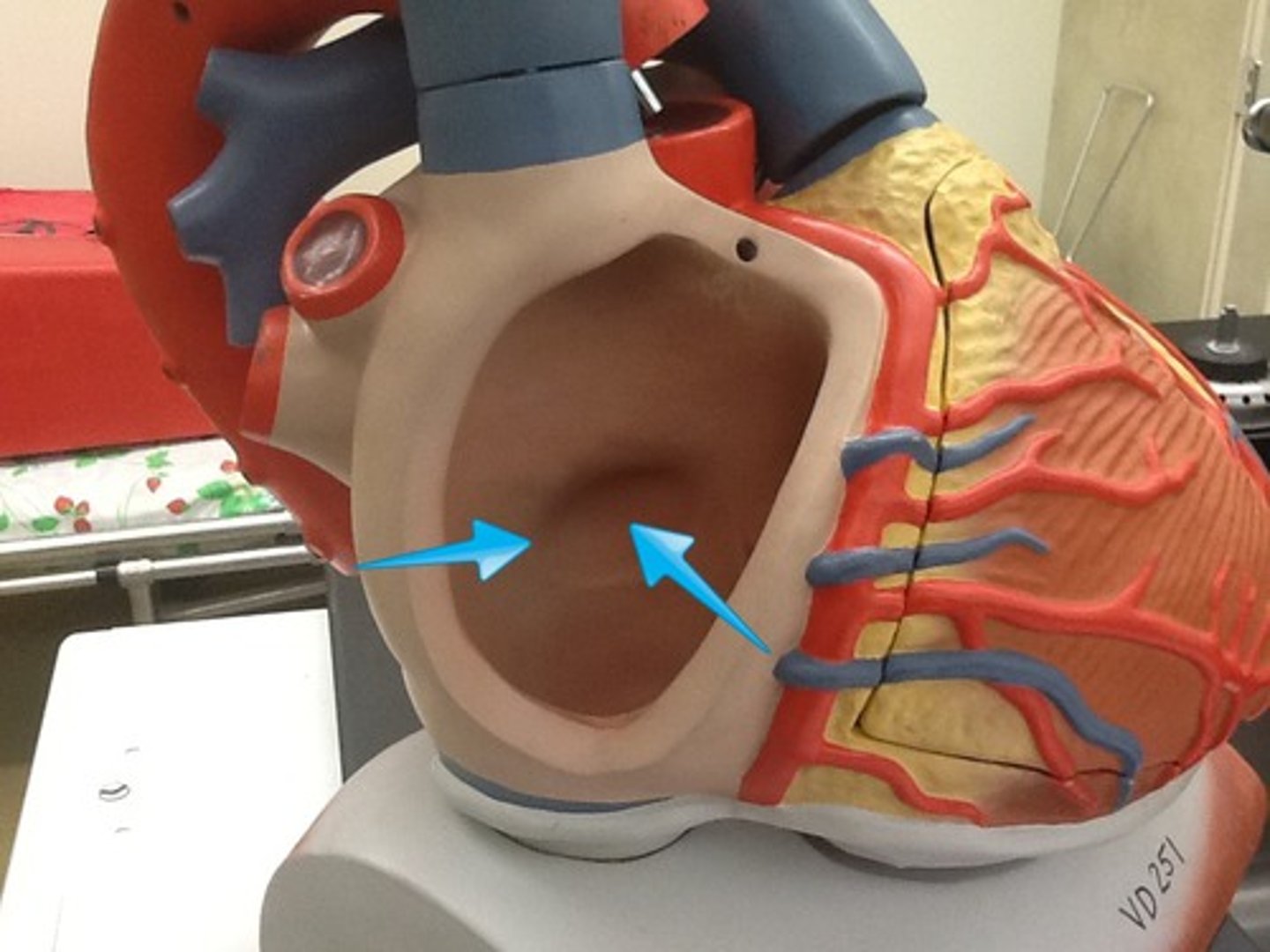
fossa ovalis
remnant of foramen ovale of fetal heart, no function in adults
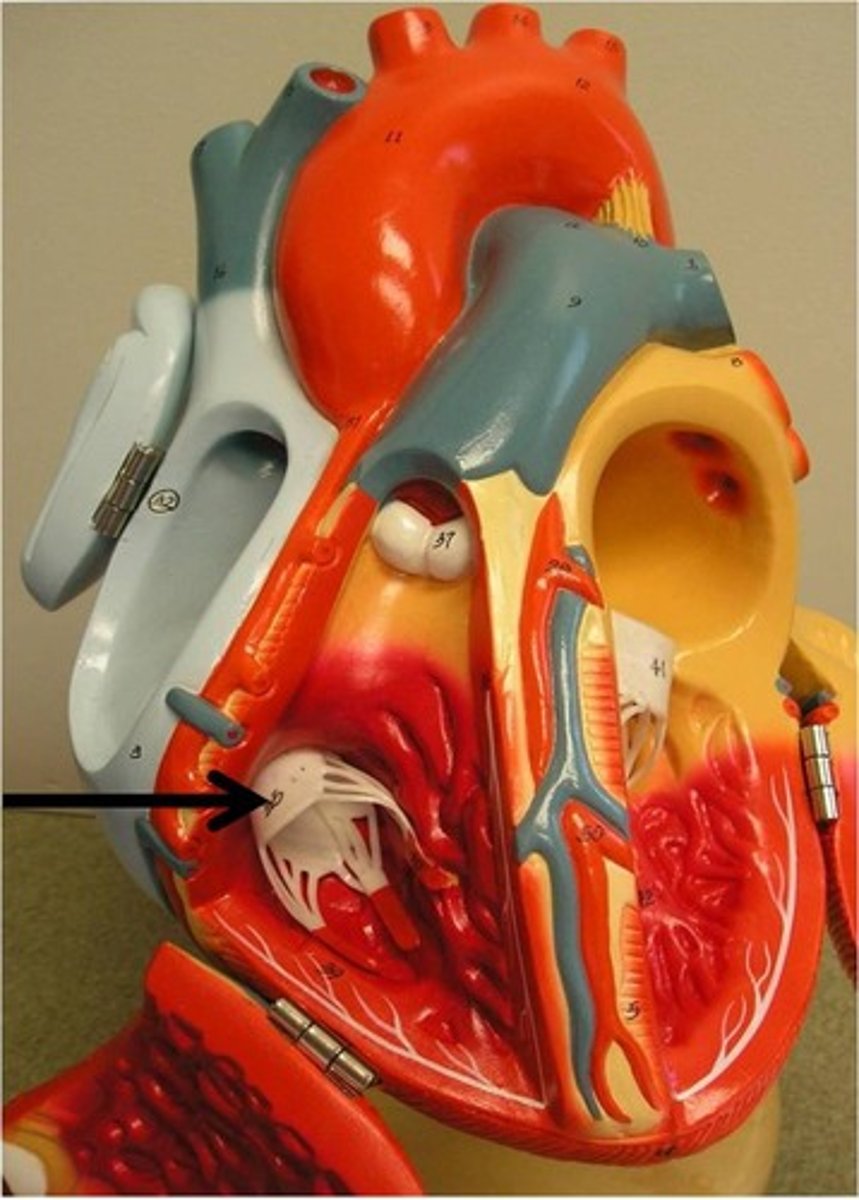
tricuspid valve (right AV valve)
Function: prevent back flow of blood between right ventricle and right atrium
right ventricle
Function: pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries
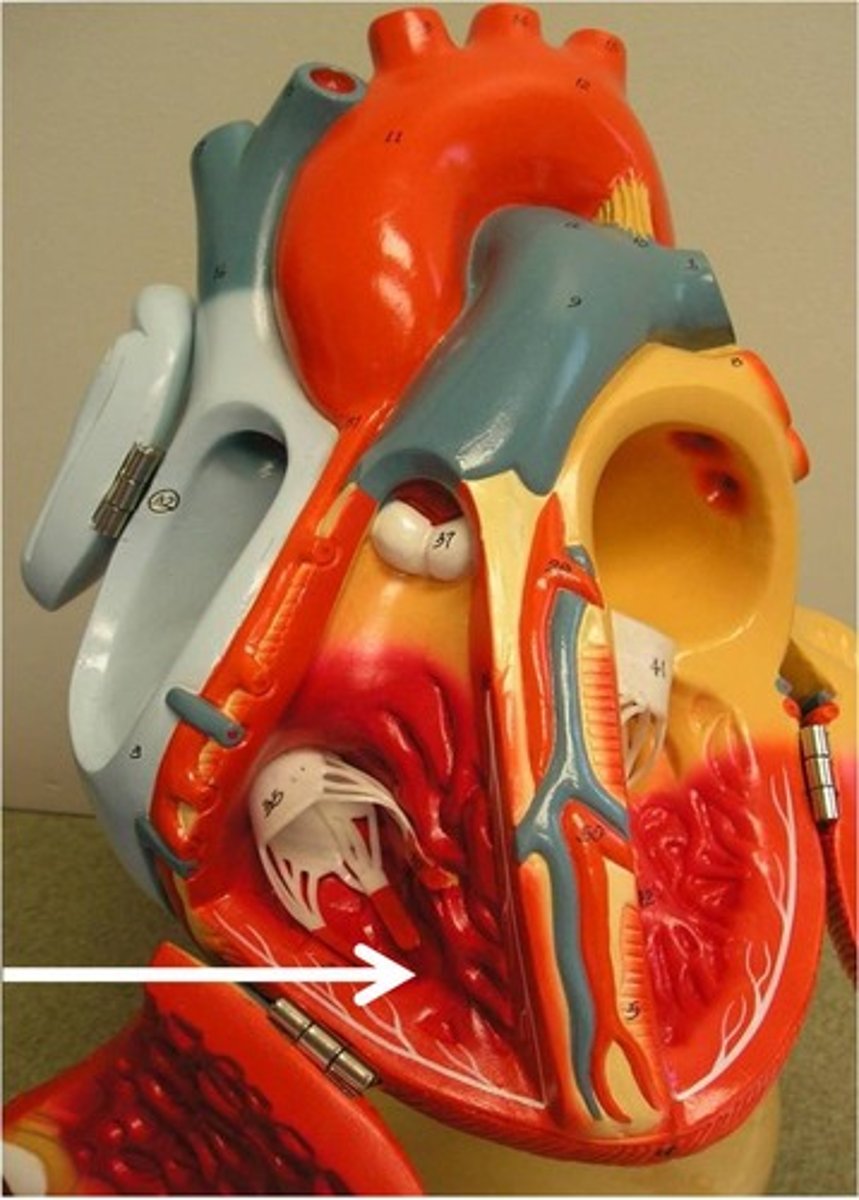
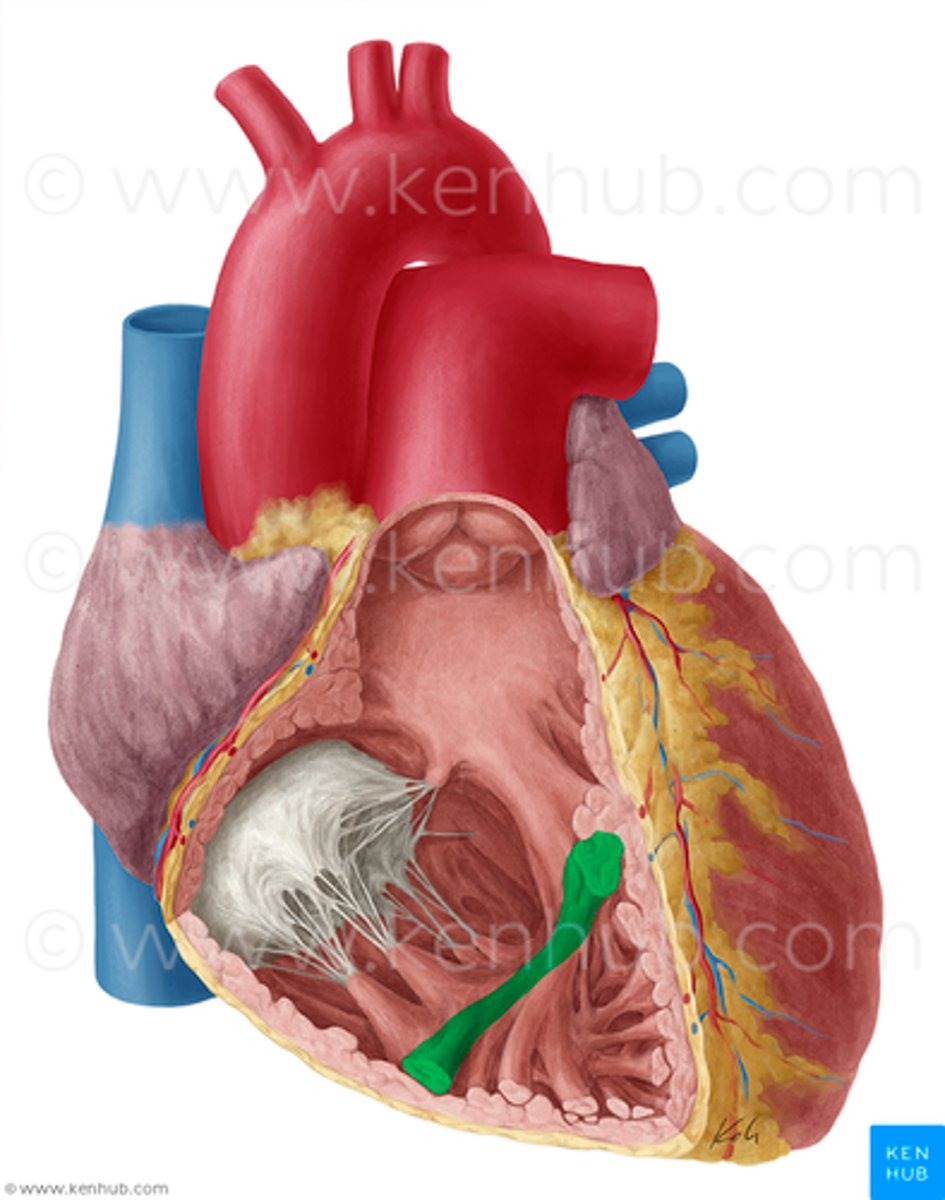
papillary muscles
Function: pull the atrioventricular valves closed by means of the chordae tendineae
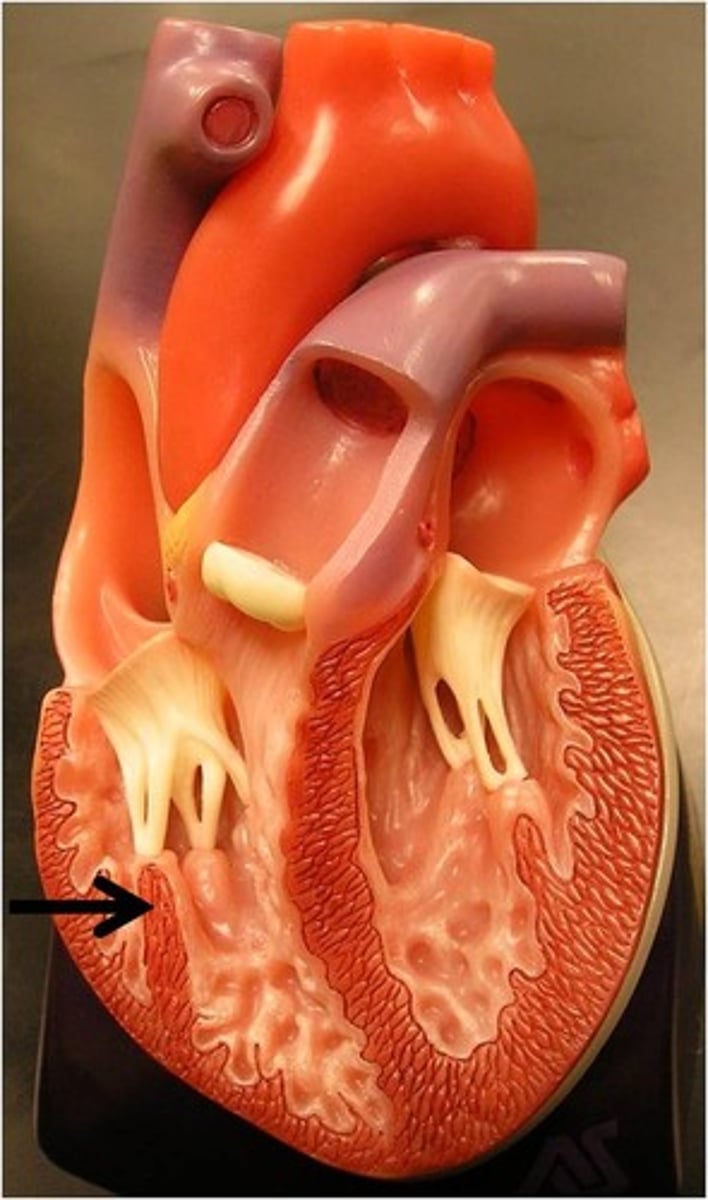
chordae tendineae
Function: attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
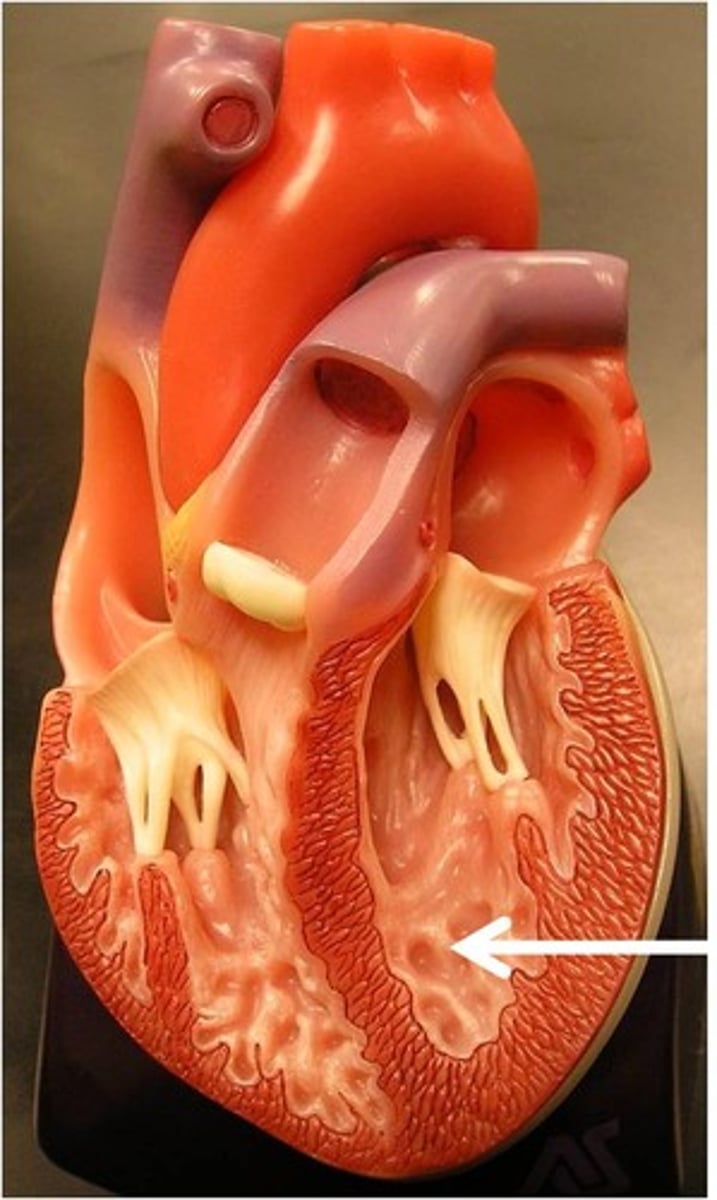
trabeculae carneae
Function: contraction prevents inversion of mitral and tricuspid valves
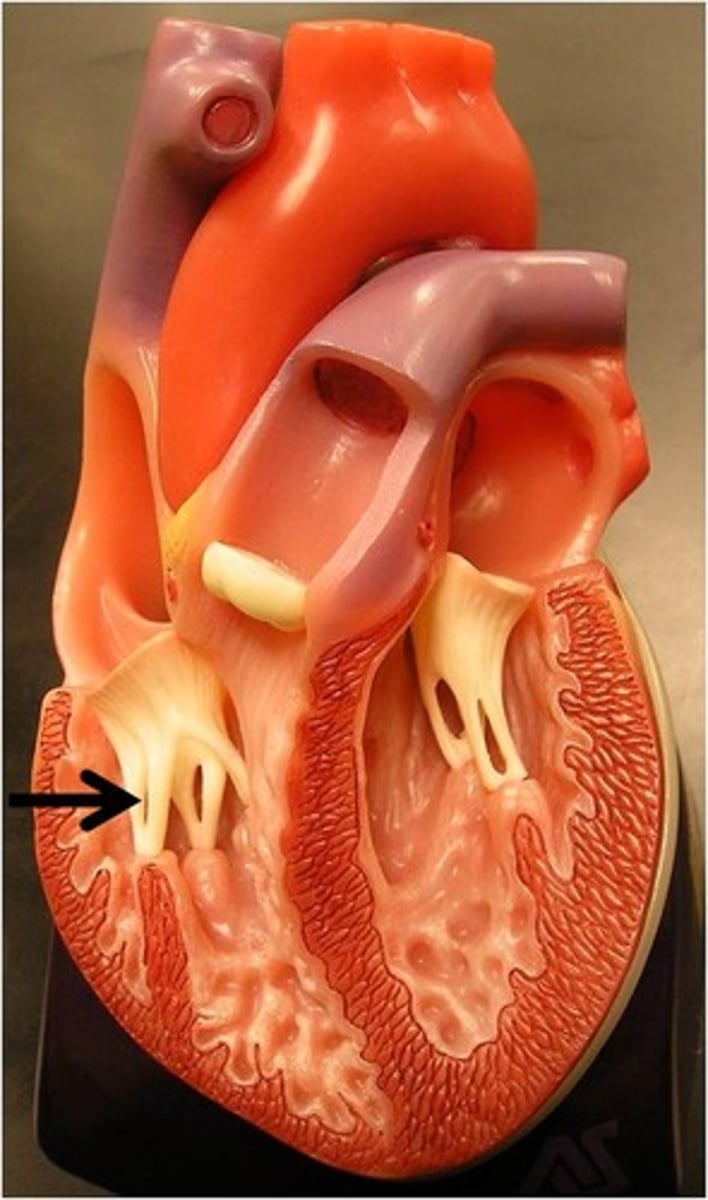
moderator band
Function: conducts impulses between right papillary muscle and interventricular septum, thereby coordinating the contraction of the cells;
also prevents over stretch of the ventricular wall
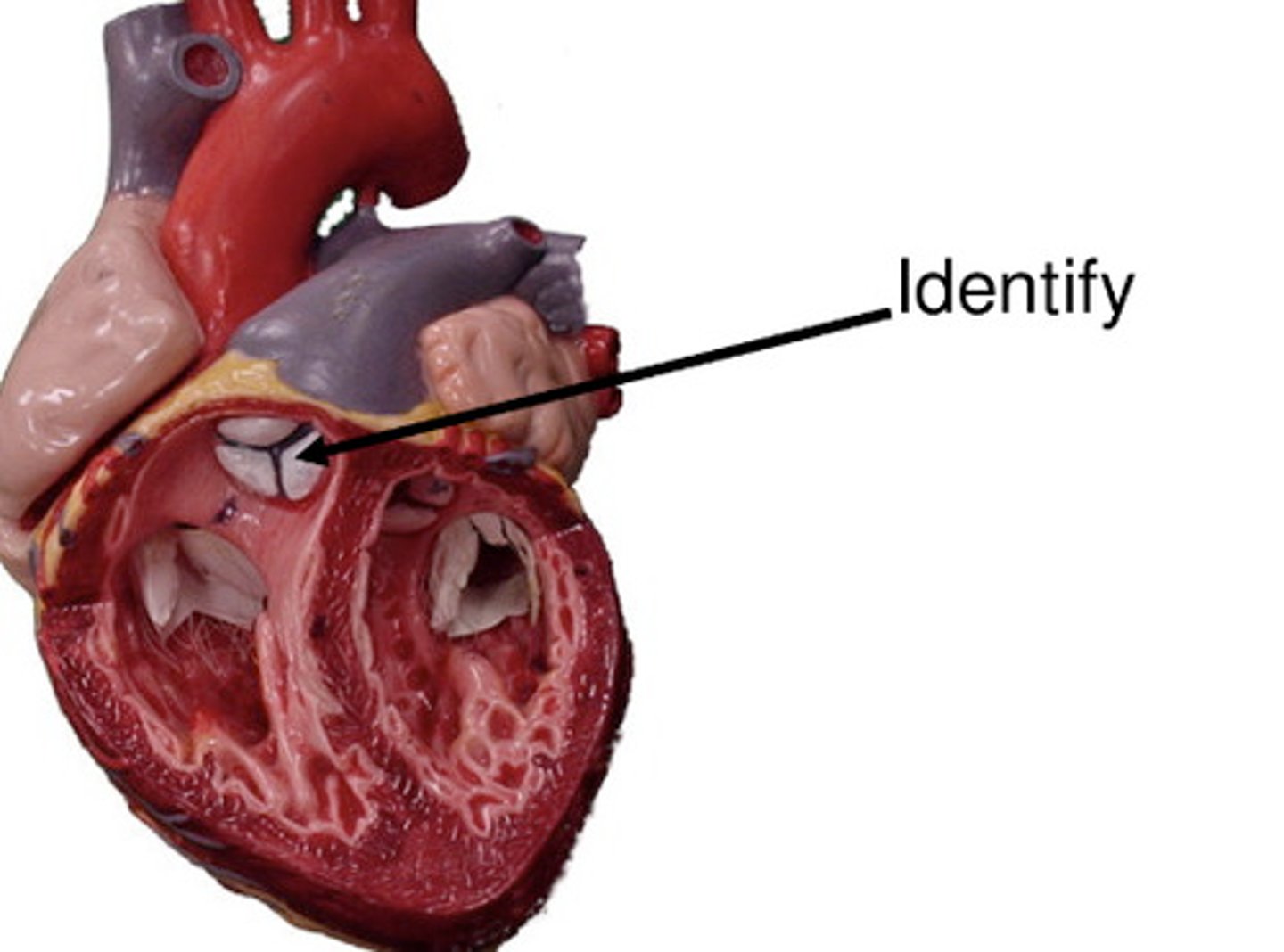
pulmonary valve
Function: prevent back flow of blood between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk
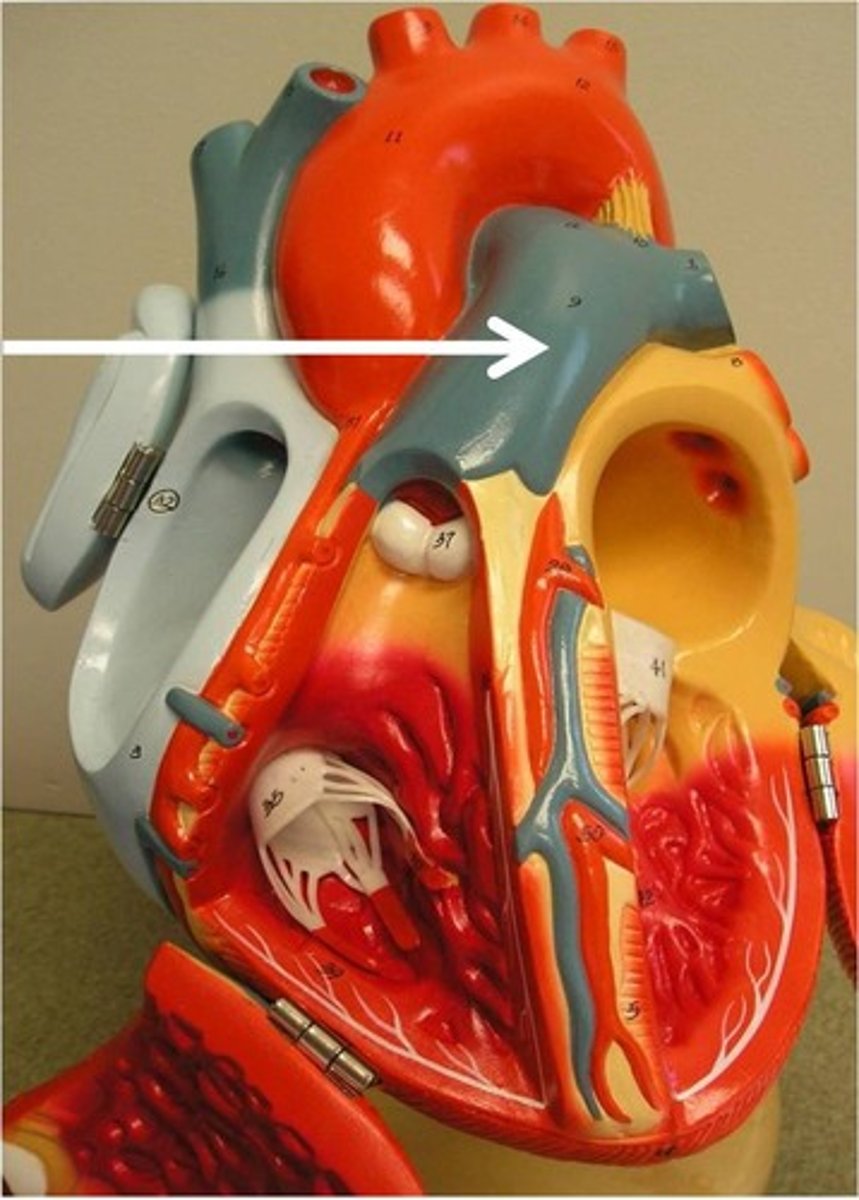
pulmonary trunk
Function: passage of blood out of right ventricle toward the lungs
pulmonary arteries (left & right)
Function: artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs
pulmonary veins (left & right)
Function: carry oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium
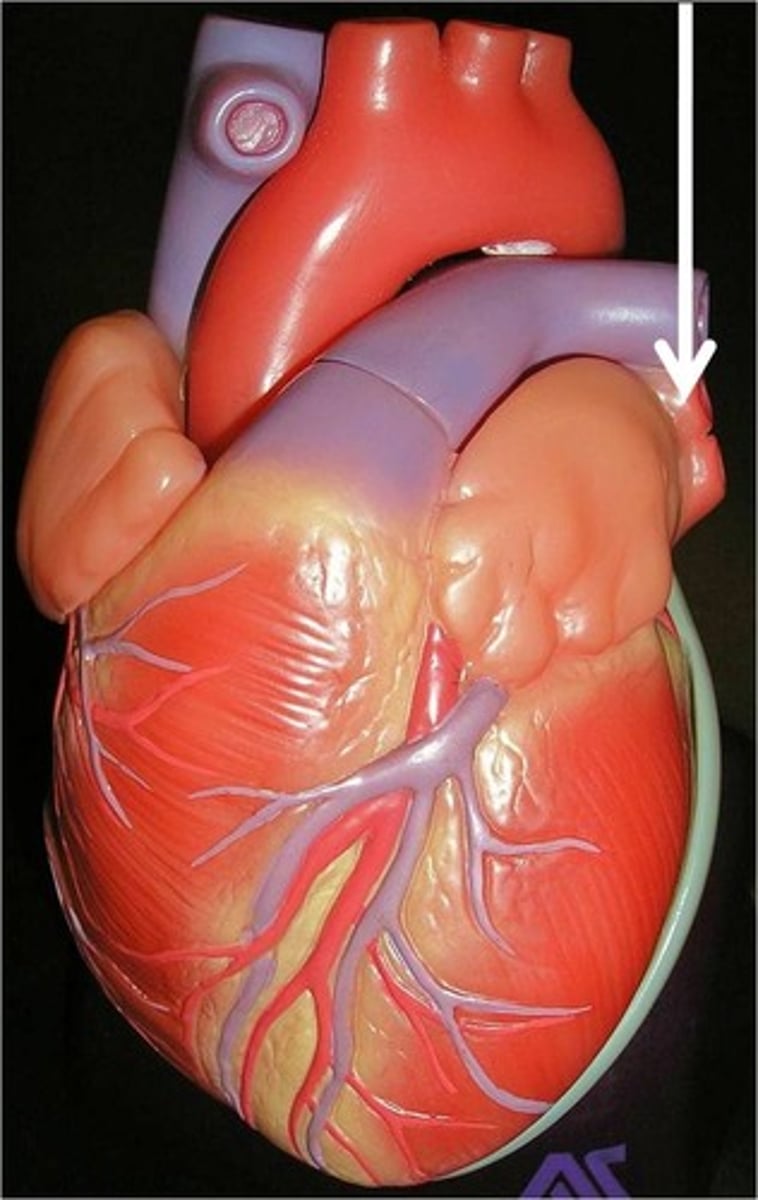
left atrium
Function: receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins
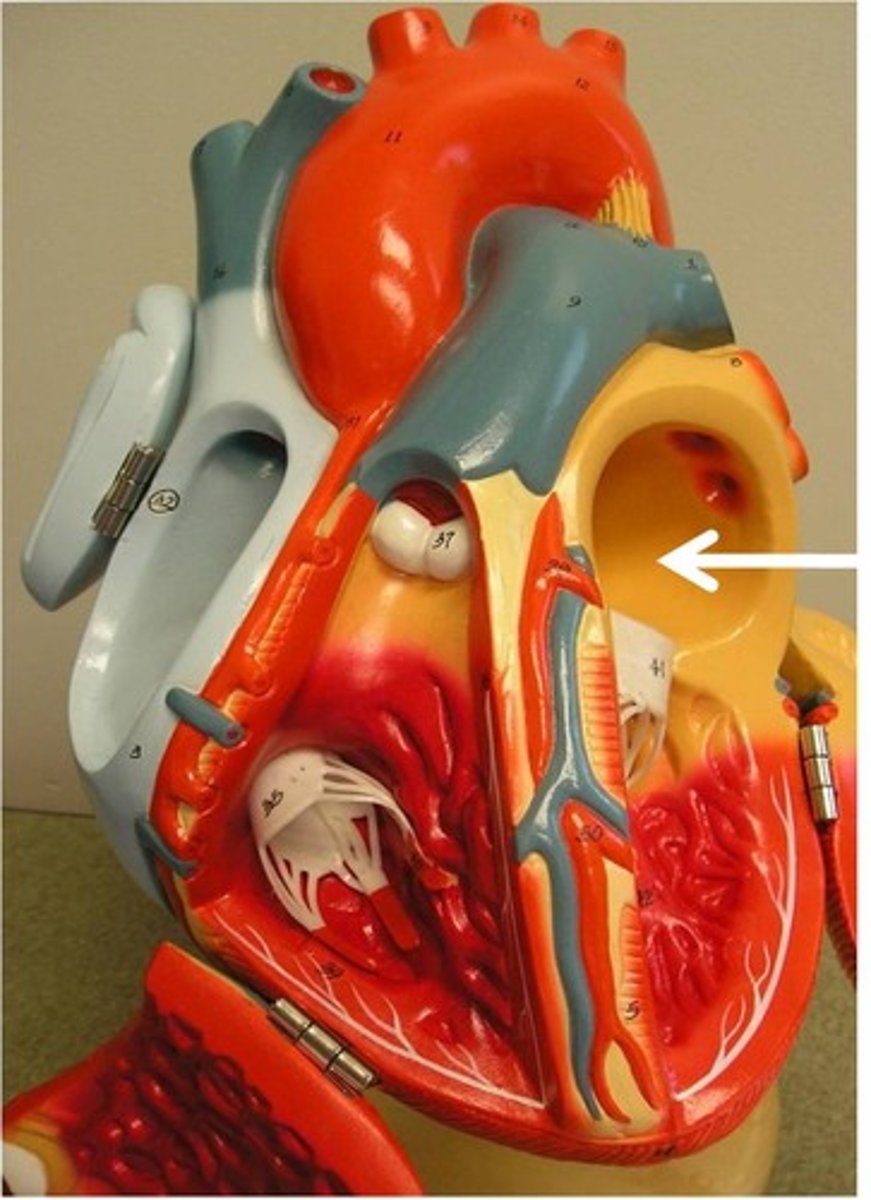
mitral valve (left AV valve)
Function: prevent back flow of blood between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
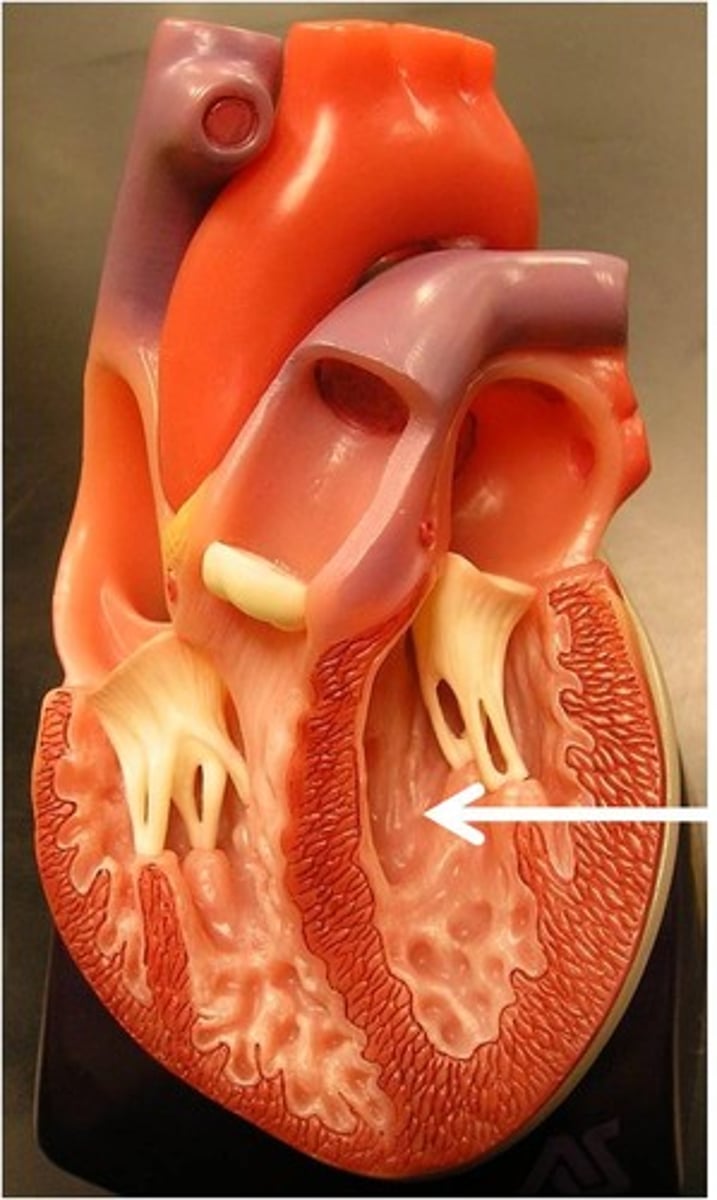
left ventricle
Function: pumps oxygenated blood to the body
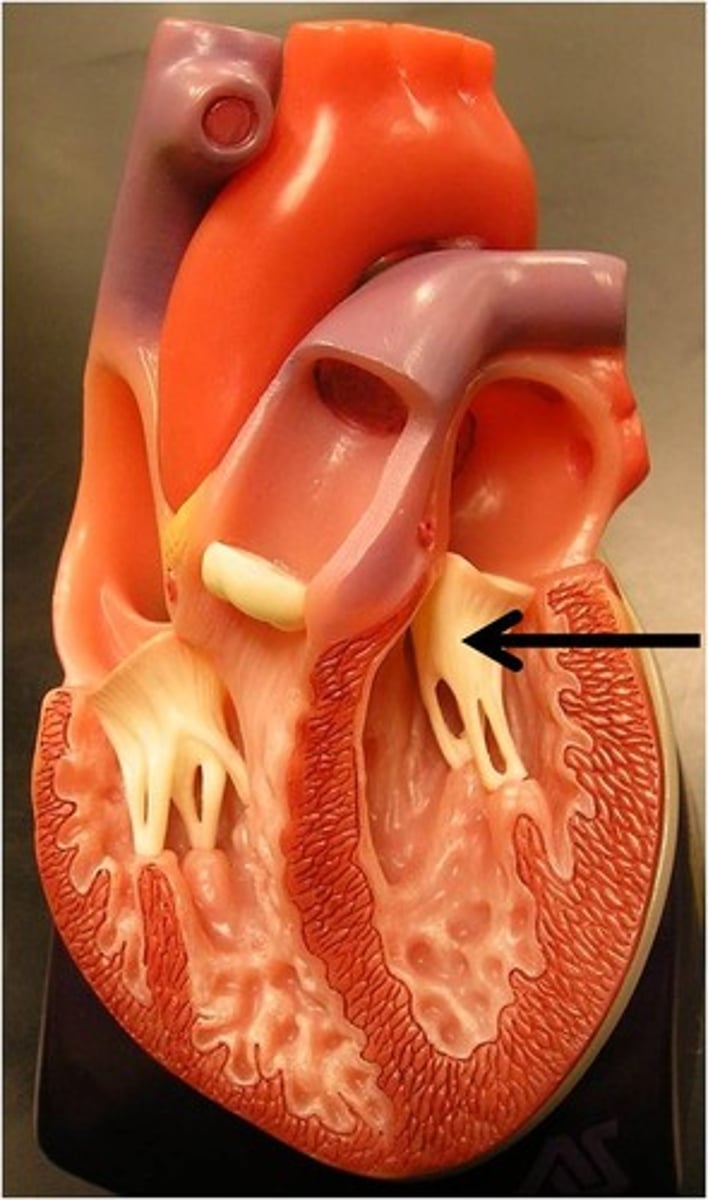
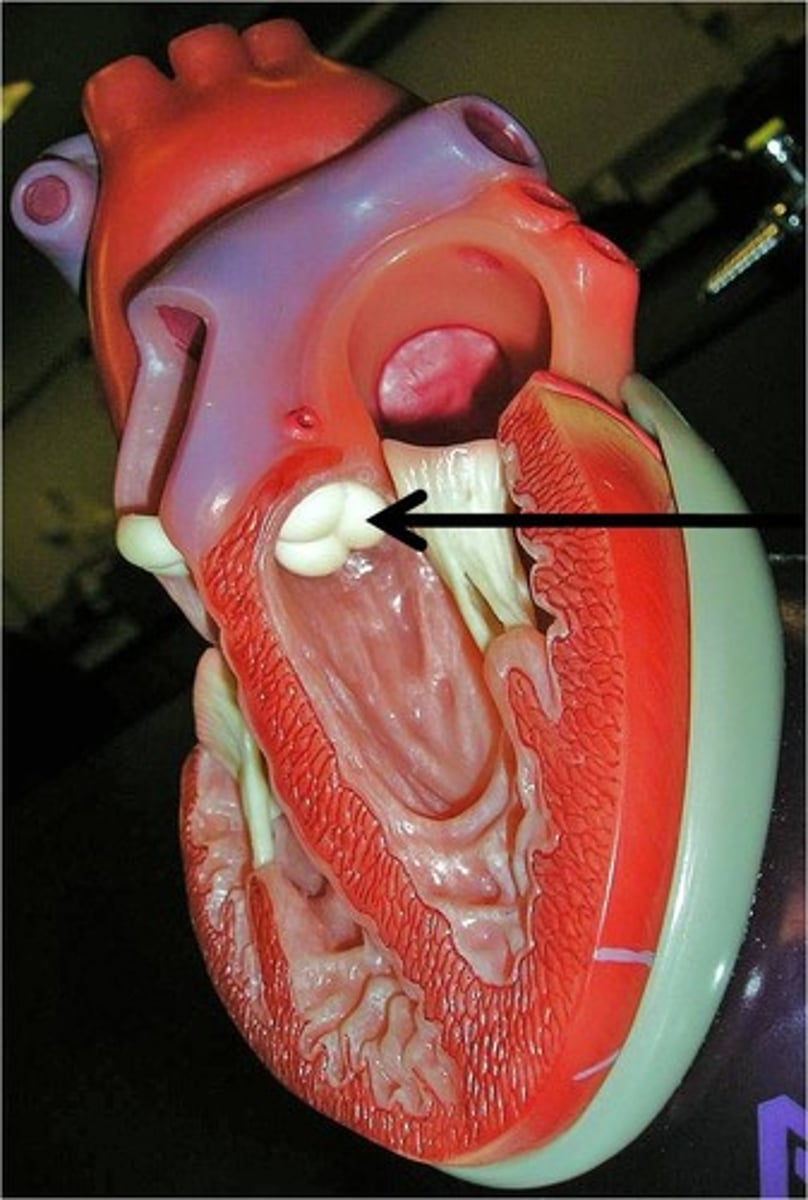
aortic valve
Function: prevents back flow of blood from aorta into the left ventricle; semilunar valve
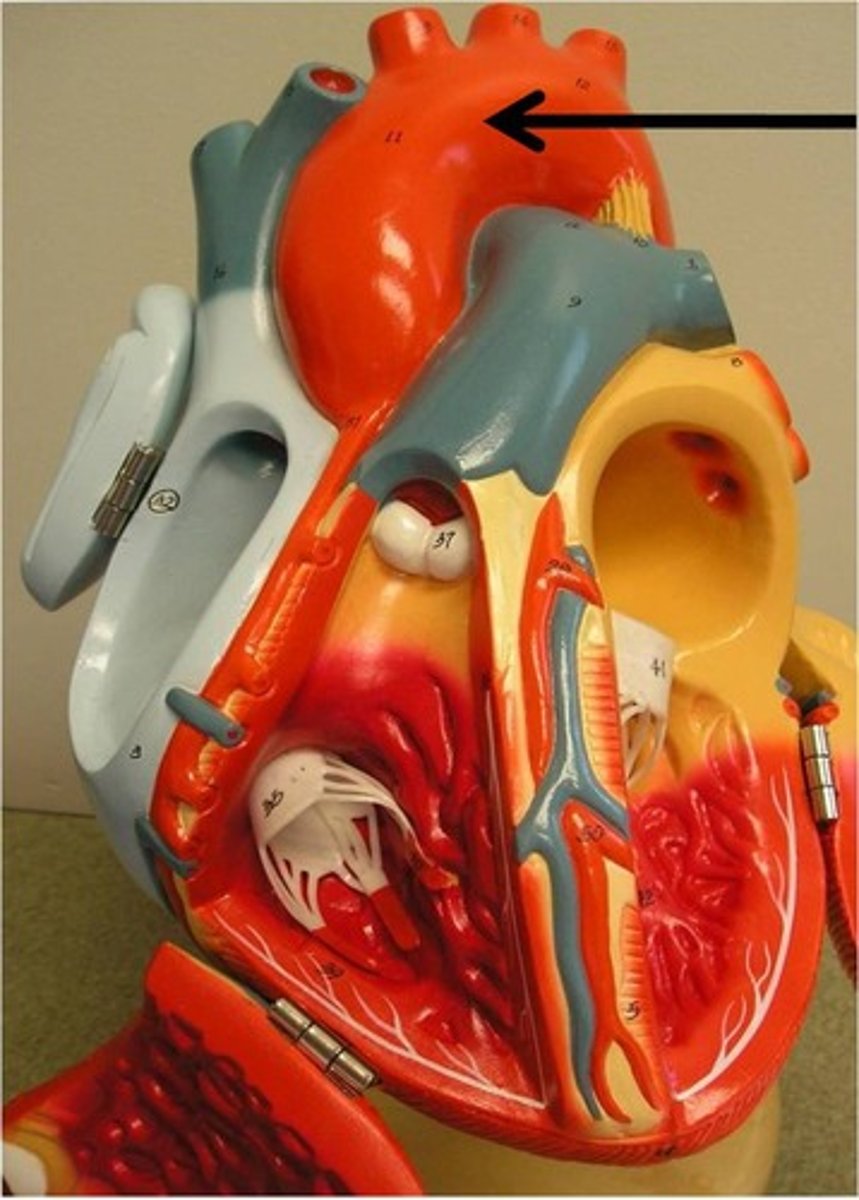
ascending aorta
Function: deliver oxygren rich blood to whole body
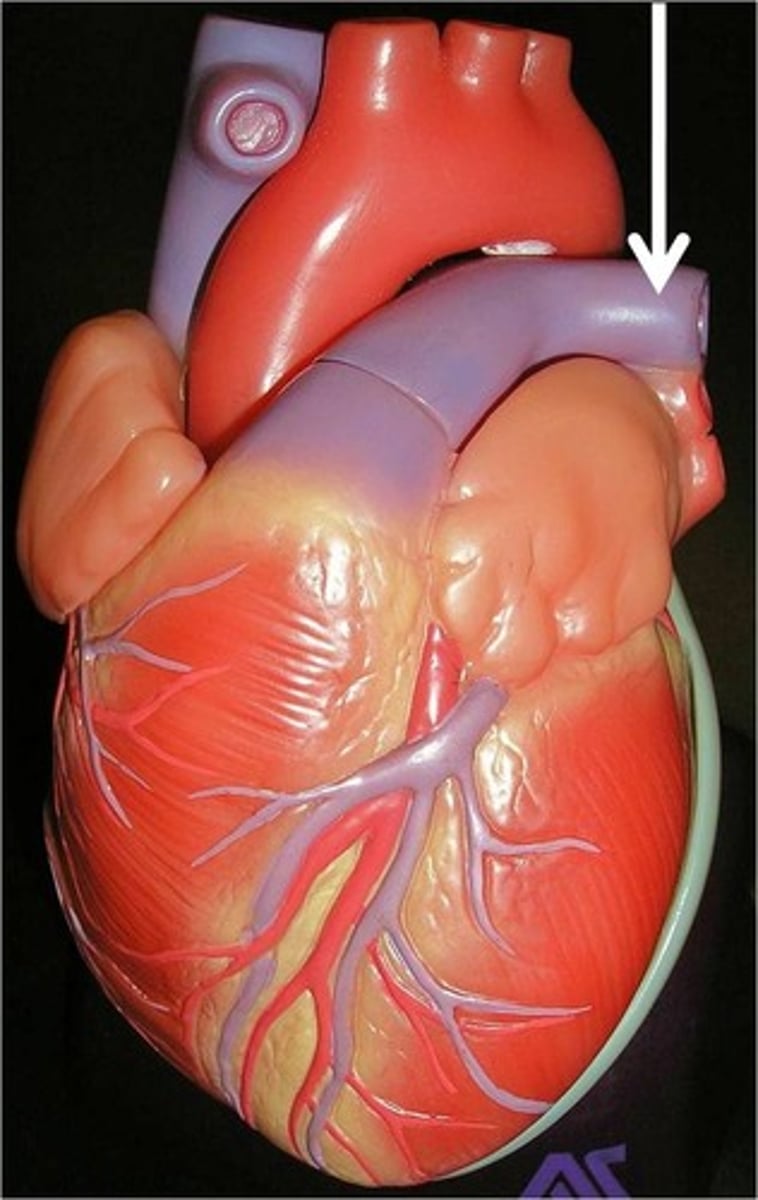
aortic arch
Function: deliver oxygren rich blood to whole body
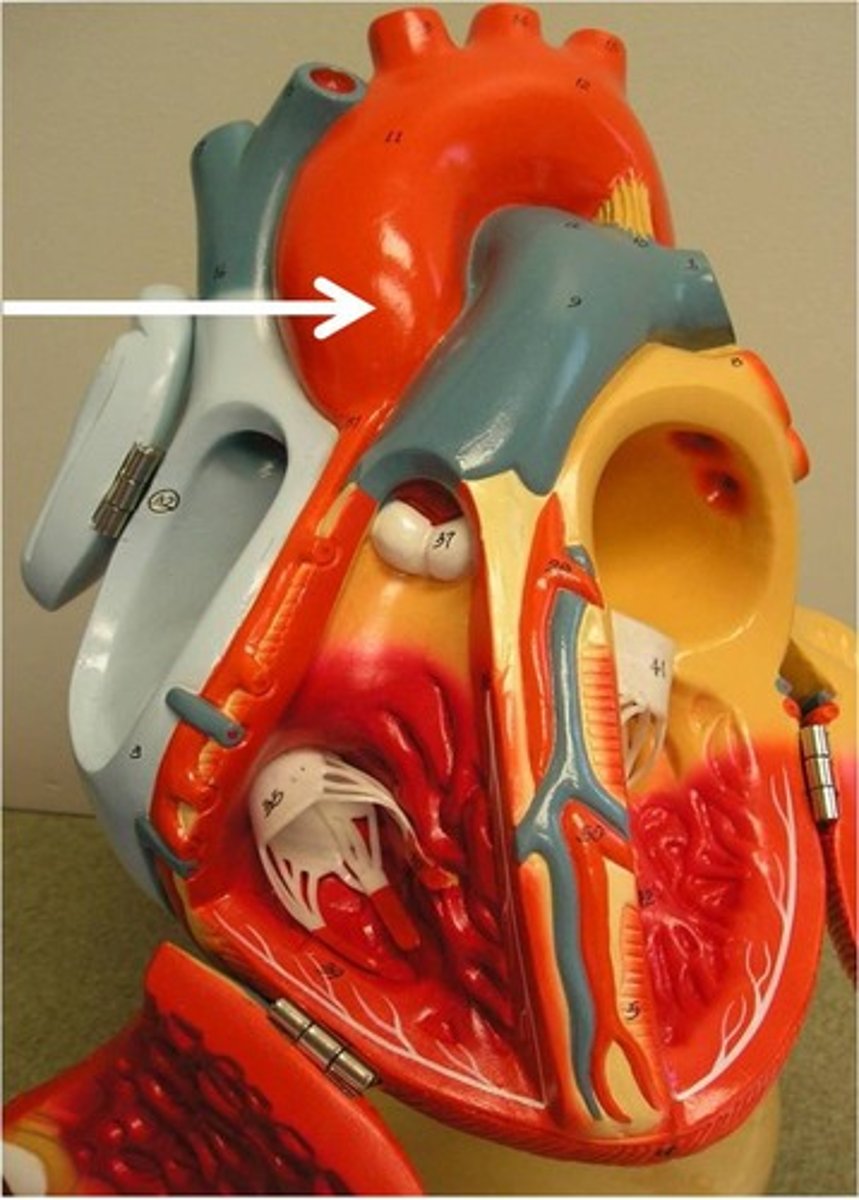
brachiocephalic trunk
Function: carries oxygenated blood to the neck, head, and right anterior limb
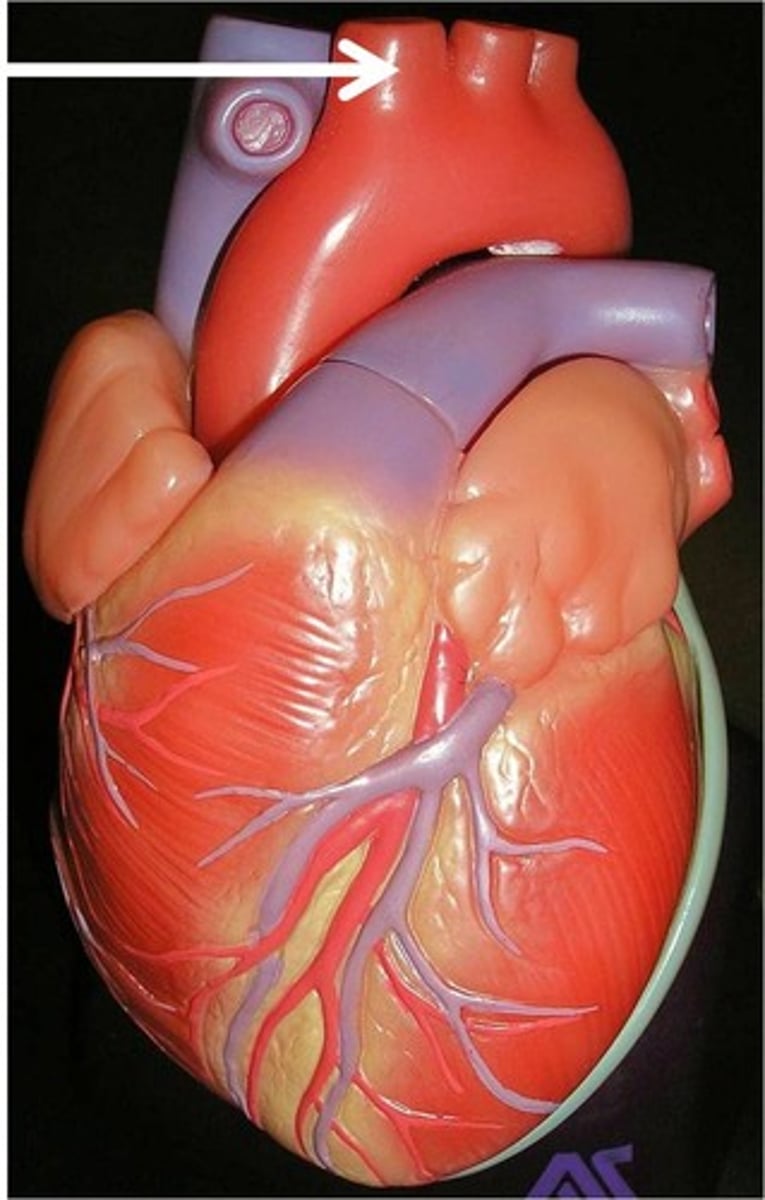
left common carotid artery
Function: provides blood to neck & head;
further divides into internal and external carotid arteries
left subclavian artery
Function: distributes blood to the left arm