AP Environmental Science Unit 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
community
Different species living together at the same time in a habitat
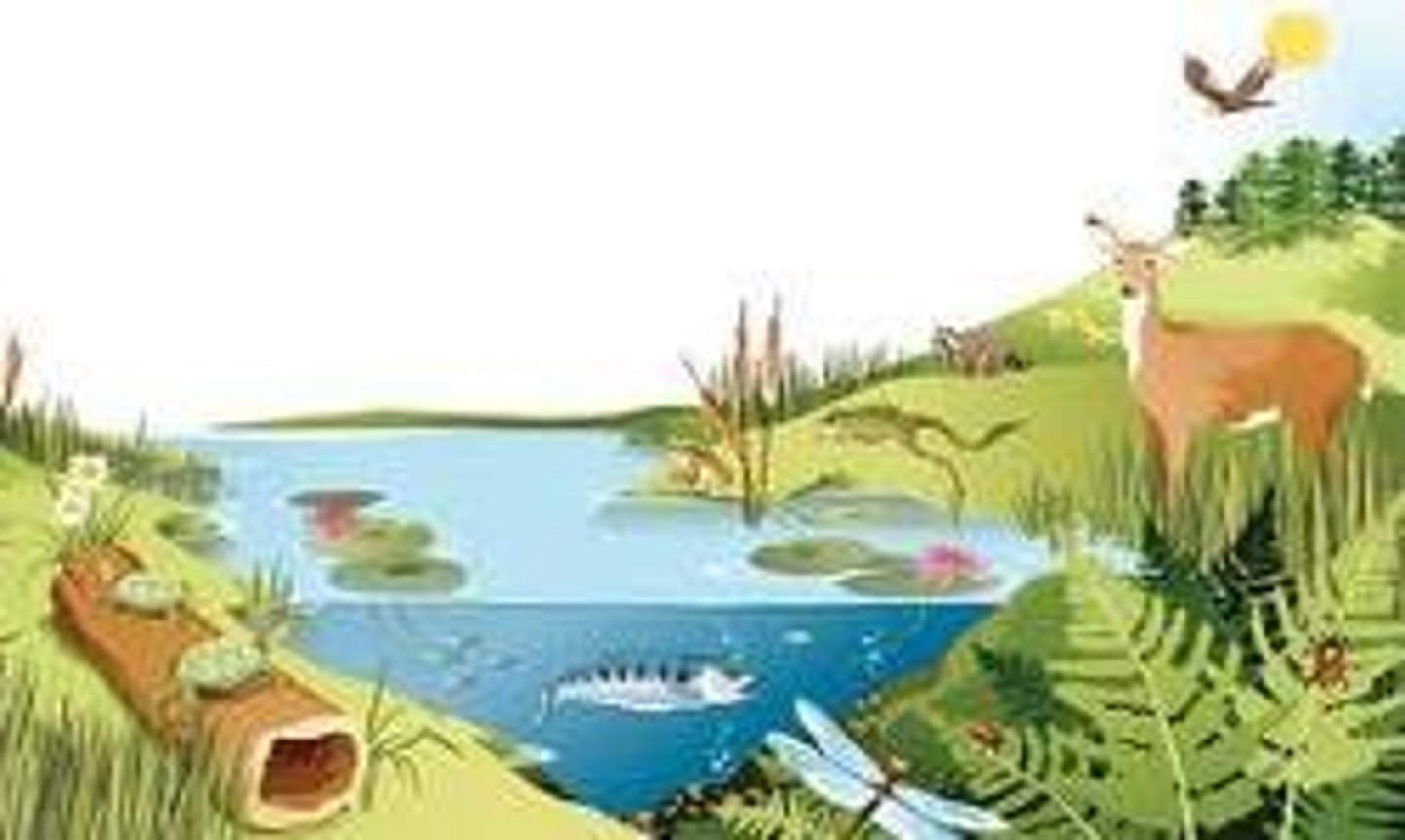

ecosystem
The interacting system of biotic and abitoic factors in an area
competition
The interaction among organisms that vie for the same resources in an ecosystem (such as food, living space, or other resources)
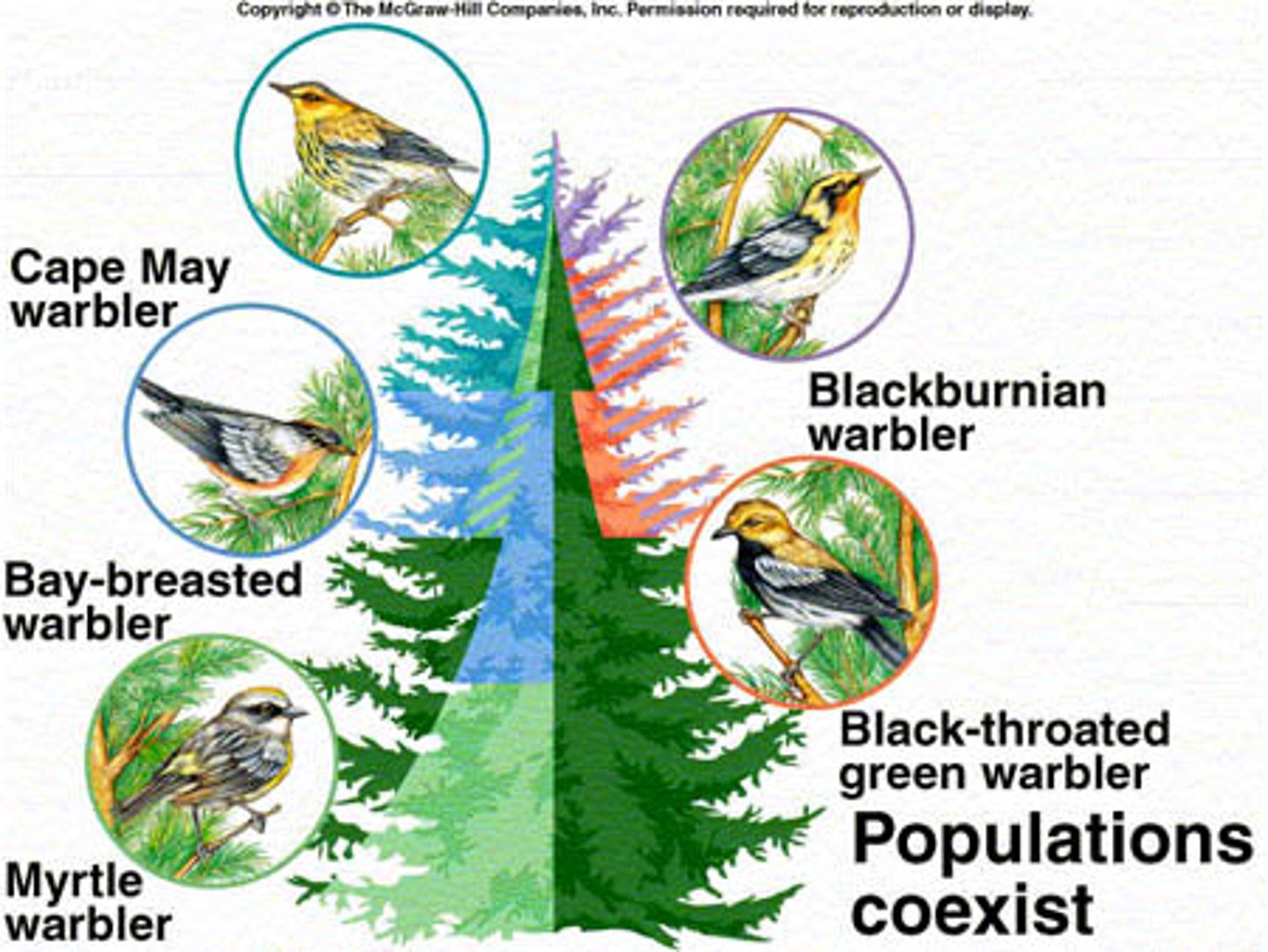
resource partitioning
the division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche
symbiosis
An intimate relationship between two or more organisms of different species
mutualism
A symbiotic relationship in which both partners benefit from the association
commensalism
A type of symbiosis in which one organism benefits and the other one is neither harmed nor helped
parisitism
A symbiotic relationship in which one member (the parasite) benefits and the other (the host) is adversely affected
biogeochemical cycle
Process by which matter cycles from the living world to the nonliving physical environment and back again. Examples of biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, phosphorus cycle, and sulfur cycle
photosynthesis
The biological process that captures light energy and transforms it into the chemical energy of organic molecules (such as glucose), which are manufactured from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis is performed by plants, algae, and several kinds of bacteria.
cellular respiration
A process in which the energy of organic molecules is released within cells
nitrogen fixation
The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) to ammonia (NH₃) by nitrogen fixing bacteria and cyanobacteria; part of the nitrogen cycle
biotic
Living
abiotic
nonliving
population
A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same geographic area at the same time
first law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although it can be transformed from one form into another
second law of thermodynamics
When energy is converted from one form to another, some of it is degraded into a lower quality, less useful form. Thus, with each successive energy transformation, less energy is available to do work
Producer/Autotroph
An organism (such as a chlorophyll containing plant) that manufactures complex organic molecules from simple inorganic substances. In most ecosystems, producers are photosynthetic organisms
food chain
The successive series of organisms through which energy flows in an ecosystem. Each organism in the series eats or decomposes the preceding organism in the chain
trophic level
Each level in a food chain. All producers belong to the first trophic level, all herbivores belong to the second trophic level, and so on
food web
A complex interconnection of all the food chains in an ecosystem
hydrologic cycle
The water cycle which includes evaporation, precipitation, and flow to the seas. The hydrologic cycle supplies terrestrial organisms with a continuous supply of fresh water. Also called water cycle
groundwater
The supply of fresh water under earths surface. Groundwater is stored in underground caverns and porous layers of underground rock called aquifers
10% rule
when energy is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next, only ten percent of the energy will be passed on
Ammonia (NH3)
A compound of nitrogen and hydrogen. This is the result of Nitrogen gas (N2) once it is "fixed."
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
Constants/Controlled Variables
The factors that are kept the same in an experiment.
Control Group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.
dimensional analysis
A way to analyze and solve problems using the units, or dimensions, of the measurements
Ecology
Scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
GPP
Gross Primary Productivity; The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
Histogram
a display of statistical information that uses rectangles to show the frequency of data items in successive numerical intervals of equal size;
Independent Variable (IV)
the variable that a researcher actively manipulates, and if the hypothesis is correct, will cause a change in the dependent variable
Dependent Variable (DV)
the research variable that is influenced by the independent variable, and the impact can be measured
NPP
(Net Primary Productivity): the energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
null hypothesis
A prediction that there is no difference between groups or conditions, or a statement or an idea that can be falsified, or proved wrong.
nutrient
a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life.
positive feedback loop
feedback loop that causes a system to change further in the same direction
negative feedback loop
A feedback loop in which a system responds to a change by returning to its original state, or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring.
primary productivity
rate at which organic matter is created by producers in an ecosystem
qualitative data
Information describing color, odor, shape, or some other physical characteristic
quantitative data
Any data from numerical source, such as measures of central tendency.
reservior
a large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply.
resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species
salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid
scatterplot
a graphical depiction of the relationship between two variables
sink
A reservoir that takes up a chemical element or compound from another part of its natural cycle.
source
Any process or activity through which a greenhouse gas is released into the atmosphere. Both natural processes and human activities release greenhouse gases.
System
A group of parts that work together as a whole
Tragedy of the Commons
The tendency of a shared, limited resource to become depleted because people act from self-interest for short-term gain
Turbidity
A measure of how clear water is.
uptake
The transfer of substances from the environment to plants, animals, and humans.