Capital Budgeting Decision Tree Concepts
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to capital budgeting decision rules, project selection, and capital rationing strategies.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
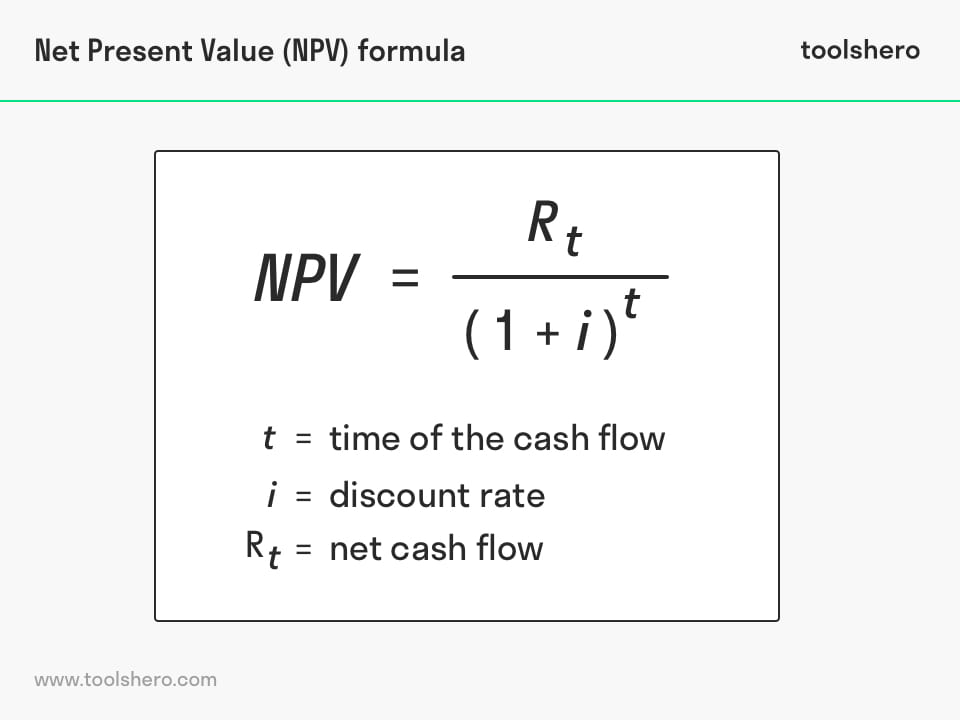
Net Present Value (NPV) formula
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The discount rate that makes a project’s NPV equal to zero
Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) Formula
PV benefits ÷ PV costs
Independent Projects
Projects whose cash flows do not affect one another, allowing each to be accepted or rejected on its own merit.
Mutually Exclusive Projects
Choosing one project prevents the selection of another.
Capital Rationing
most rewarding or necessary goals!
Maybe company is limited by budget
Equal Lives
A comparison condition where competing projects have the same economic lifespan, permitting direct NPV ranking.
Unequal Lives (Mutually Exclusive)
Rank By NPV over common investment horizon.
Use NPV IRR or BCR?
For Independent project, use largest “BCR” return!
No Fractional Projects
A capital-rationing constraint that requires accepting or rejecting entire projects; the optimal bundle is the combination with the…
accept highest total NPV within the budget.
Fractional Projects
Projects that can be partially accepted (divisible); when allowed, ranking by BCR is appropriate to allocate the budget efficiently.
Rank by NPV
When projects are:
1) mutually exclusive
2) Have equal lives
Rank projects by BCR when
Projects are divisible under capital rationing.
An investment horizon is
The period during which an investor expects to hold an investment before cashing out
projects with BCR > 1
create value
can be ranked by highest ratio when projects are divisible.
a project is acceptable if its IRR?
Exceeds the required return.
When BCR is < 1
Reject project.