Weight Management
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
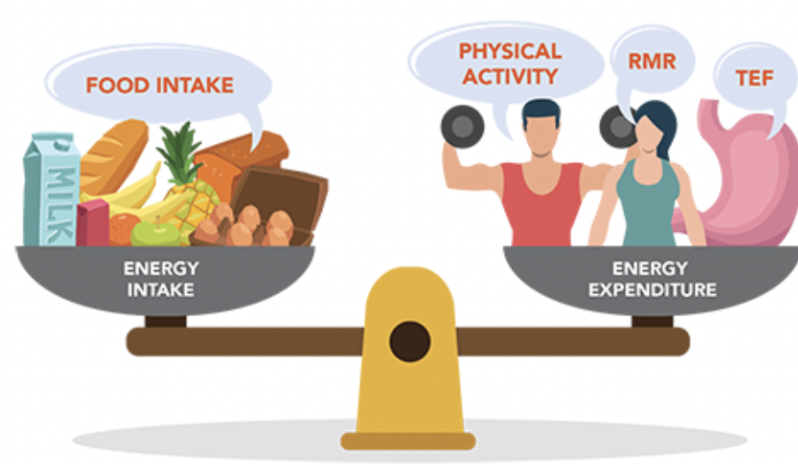
Energy Balance
Energy in EQUALS energy out
Effective Weight Management - Should include a combination of:
Reduced sedentary behaviour
Regular physical activity and exercise (including ressitane exercise)
Dietary modifications based on Canada’s Food Guide (what yuo can and can’t tell them - can’t tell them what to eat, can refer them to the food guide)
Benefits of Exercise in Weight Management
Increases energy expenditure
Helps create a negative energy balance for weight loss (more exepnding = weight goes down)
Promotes fat loss and preservation of lean body mass (muscle and bone)
Maintains or slows down FFM loss resulting from weight loss via diets only (maintain more muscle mass)
Helps maintain weight loss after dieting
Increases RMR (larger your muscles, larger the engine, more at a baseline consuming energy)
Dieting - Helping Clients Understand
Caloric restriction vs fad diets (being able to describe potential risks of diet, help facilitate their understanding)
Temporary vs. permanent weight loss (temporary = accomplished with a crash diet or sig dehydrateion - can not be safe/healthy)
Difference between fat loss and weight loss
Non-fat mass weighs more than fat
Yo-yo effect (if you don’t treat the underlying problems with any sort of long term eating issue (energy intake is larger than energy expenditure), when your are done the crash course, you will yo-yo back to your previous weight)
Instead of “deiting”, use food labels/tables and Food Guide to make client aware of their food intake
Effects of Severe Energy Restriction
Body thinking it is starving
Turns on backup mechanisms that help preserve the fuel you have remaining)
RMR may decrease by 15%
Lose muscle
Utliizing less energy
Body gets efficient at using energy (energy put in body will be put into storage)
Become lethargic usually = decrease in activity
Weight Loss Strategies - Dos vs. Don’ts
Do:
Exercise regularly
Foolow Canada’s Food Guide
Set realistic weight loss goals
Consume more fruits and veggies
Increase water consumption
Don’t:
Think there is a magic pill
Go on a severe low-calorie diet
Can yo-yo
Reduce physical activity
Longest long term low calorie diet has functioned for: 11-13%
Replace real food with a meal in a can
Establishing Weight Loss Goals
Goals should be modest as well as realistic and attainable
Health can be improved with relatively minor weight loss (i.e. as little as 2-3% of body weight)
Regular physical activity, even without weight loss, improves health risk
Healthy Weight Loss Basics
Maximum 1.0 kg/wk (in a short period of time)
Set realistic short term goals
Set re-appraisal date to monitor changes in BMI and WC
Weight loss may not occur as quickly as desired because:
Non-fat mass weighs more than fat
Muscle mass may increase with increased physical activity, but only if resistive in nature
Healthy Weight Loss
Weight loss of mo more than 0.5-1.0kg (~1-2 lb) per week
1 lb (~0.5 kg) of fat = 3500 kcal
Thereofore, to lose body weight
Decrease energy intake by 250 kcal/day
Increase physical activity by 250 kcal/day
Negative energy balance by 500 kcal
RESULT: 1 lb (~0.5 kg) of fat loss/week
Energy Expenditure Equations
Energy (kcal) burned with exercise depends on oxygen consumption (or MET level), body mass and duration
1lb of fat = 3500 kcal
memorize equations for midterm
