Opportunity Cost & Production Possibilities Curve
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
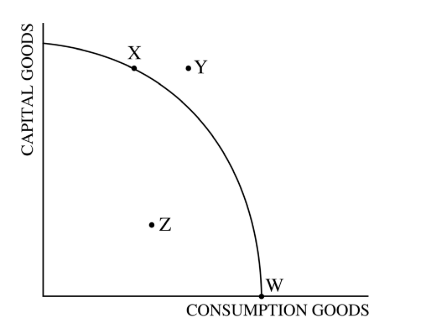
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for an economy that produces only consumption and
capital goods. All of the following statements about this economy are true EXCEPT:
E) Point X represents the most efficient combination of the two goods that can be produced by this economy.
Any point inside a production possibilities curve is
(C) associated with inefficient use or unemployment of some resources
A production possibilities curve that is concave to the origin (bowed out) implies that as more of a good is produced, the opportunity cost
(D) increases
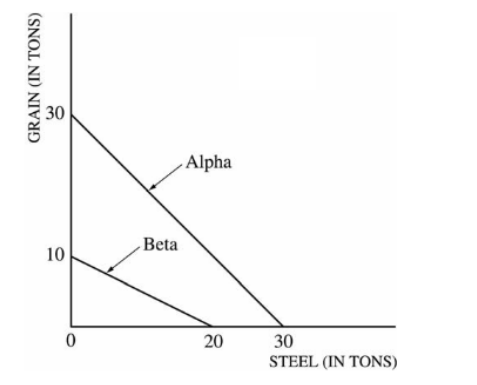
Before specialization and trade, the domestic opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of grain in Alpha and in Beta is which of the following?
B)
Alpha- 1 ton of steel
Beta- 2 tons of steel
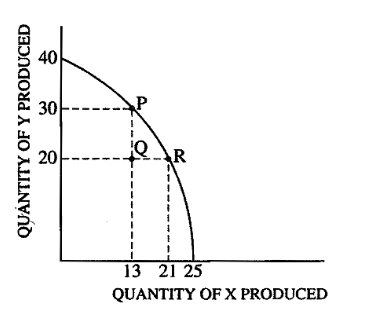
On the basis of the diagram above showing an economy's production possibilities curve for two goods, which of the following statements must be true?
I. The opportunity cost of moving from point P to point R is 10 units of Y.
II. The opportunity cost of moving from point R to point P is 8 units of X.
III. The opportunity cost of moving from point Q to point R is 0 units of Y.
(E) I, II, and III
When an economy operates inside its production possibilities curve, it can increase production of one good
(A) at zero opportunity cost in terms of the other good
If a certain combination of goods or services lies outside the production possibilities curve of an economy, which of the following is true?
(C) Resources are not available to achieve that combination of goods or services.
All of the following concepts can be illustrated using the production possibilities curve model EXCEPT
(B) inflation
Which of the following concepts can be illustrated using the production possibilities curve?
I. Choice
II. Scarcity
III. Price level
IV. Opportunity cost
(D) I, II, and IV only
Assume an economy produces two goods, capital goods and consumer goods. If the production of capital goods increases in the current period, which of the following will occur for the current and future production possibilities curve (PPC) for consumer goods and capital goods?
B) A movement along the current PPC and a rightward shift of the future PPC
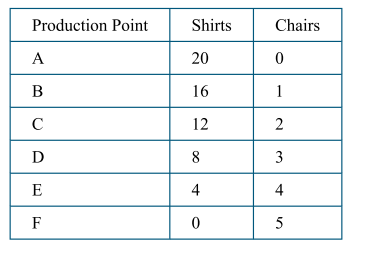
The opportunity cost of producing one additional chair is
(B) constant
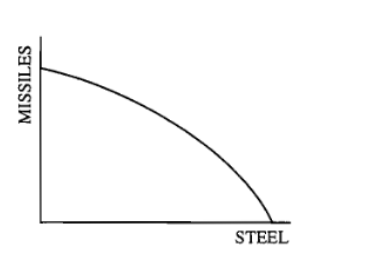
Which of the following would cause the production possibilities curve shown above to shift outward?
(E) Developing a more efficient steelmaking process
An economy is operating at a point inside its production possibilities curve (PPC) most likely cause the economy to move toward the current PPC. Which of the following will in the short run?
(D) An increase in employment
For an economy that is operating inside its production possibilities curve, which of the following is true?
(A) It can increase the production of both goods.
Which of the following is always true of an economy operating on its production possibilities frontier?
(A) Its resources are fully employed.
If producing each additional unit of good X required giving up ever-increasing amounts of good Y, the production possibilities curve between X and Y would be
(A) bowed outward
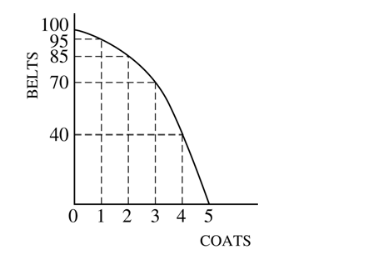
If two coats are currently being produced, the opportunity cost of producing the third coat is
(D) 15 belts
The best combination of belts and coats for this economy to produce is
(E) indeterminate with the available information
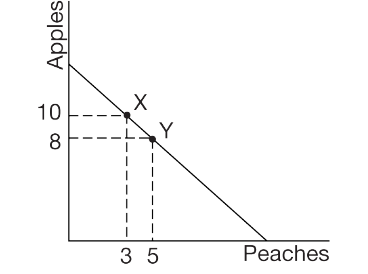
The production possibilities curve illustrates which of the following relationships?
(D) Fruitland cannot produce a combination of 5 units of peaches and 10 units of apples.
Between point X and Y on the PPC, the opportunity cost of one unit of peaches is which of the following?
(B) 1 unit of apples
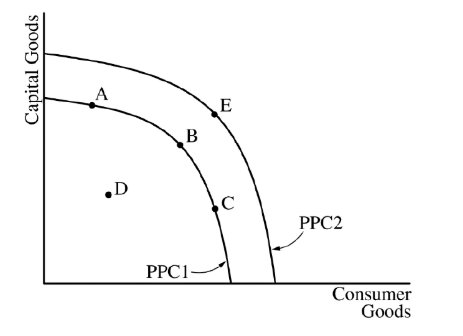
The concept of opportunity cost is best represented by which of the following?
(C) A movement from point B to point C
When an economy producing two goods is operating efficiently and at full employment, increasing the production of one good will result in
(C) a decrease in the amount of the other good that can be produced
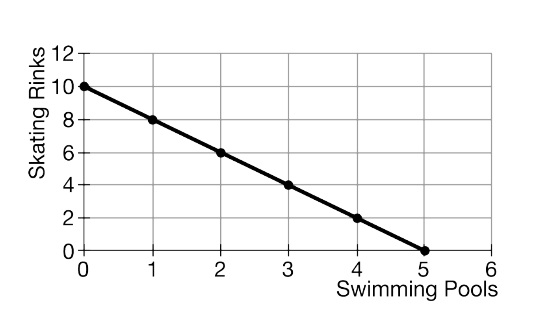
A city government received a $1 million grant to build swimming pools and skating rinks for youth. Based on the data provided in the graph, what is the opportunity cost of building one swimming pool?
C) 2 skating rinks
The opportunity cost of an activity is
(C) the value of the forgone benefit of the next best alternative
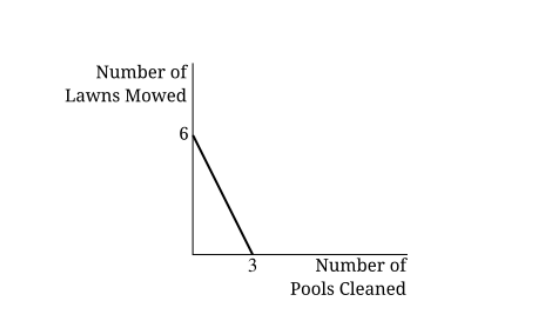
Peter runs a small business mowing lawns and cleaning pools. The production possibilities curve provided shows the combinations of lawns mowed and/or pools cleaned that Peter can complete in a day. Which of the following is true concerning Peter’s production possibilities curve?
(B) Peter’s opportunity cost of mowing 1 lawn is ½ of a pool cleaned.
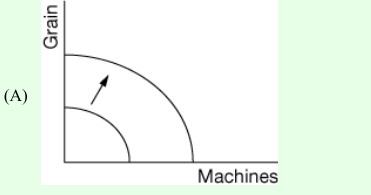
Machines are produced using capital and labor. Grain is produced using land and labor. Which of the following production possibilities curve graphs shows the effect of an increase in the amount of labor available?
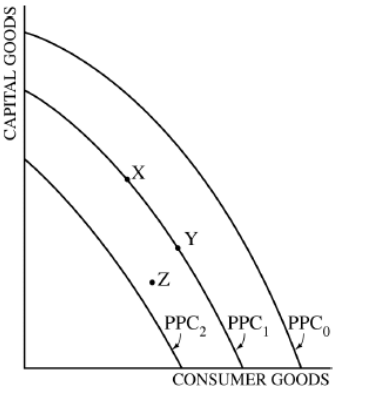
The diagram above shows three production possibilities curves (PPCs). If the current PPC is PPC1, which of the following changes indicates a recession?
(C) Movement from point Y to point Z
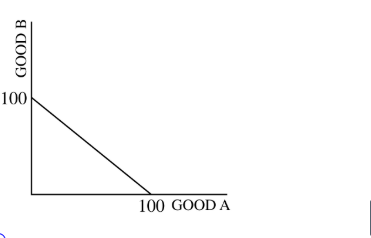
If the economy is currently producing 10 units of good A and 90 units of good B, the opportunity cost of increasing the production of good A from 10 units to 20 units is how many units of good B?
(D) 10
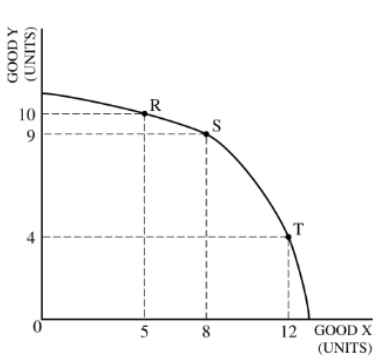
The opportunity cost of moving production from point R to point T is
(C) six units of Good Y
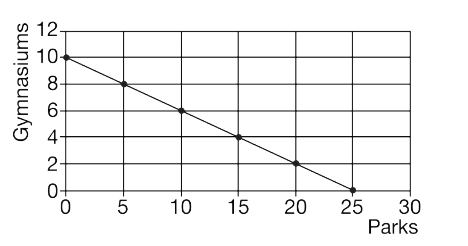
The graph above shows the production possibilities curve for a small township that is deciding to build parks and gymnasiums. Which of the following combinations of parks and gymnasiums is unattainable given the township's available resources?
(E) 20 parks and 4 gymnasiums
Which of the following illustrates the effect of a decrease in an economy’s resources using a production possibilities curve (PPC)?
A) The economy’s PPC will shift inward and to the left
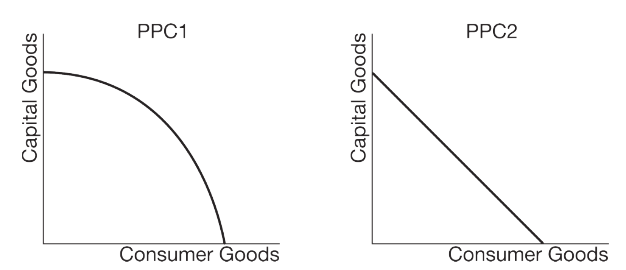
What type of opportunity costs do PPC1 and PPC2 illustrate?
D) PPC1 illustrates increasing opportunity costs and PPC2 illustrates constant opportunity costs.
Which of the following would shift a country’s production possibilities curve inward?
(C) A reduction in the size of the country’s labor force
Which of the following would best explain an inward shift of the production possibilities curve?
(D) A decrease in the quality of human capital