Lipids and Fatty Acids
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary related to lipids, fatty acids, and their functions in the body for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Lipids
Macronutrients that include fats and oils, which are substances that are insoluble in water.
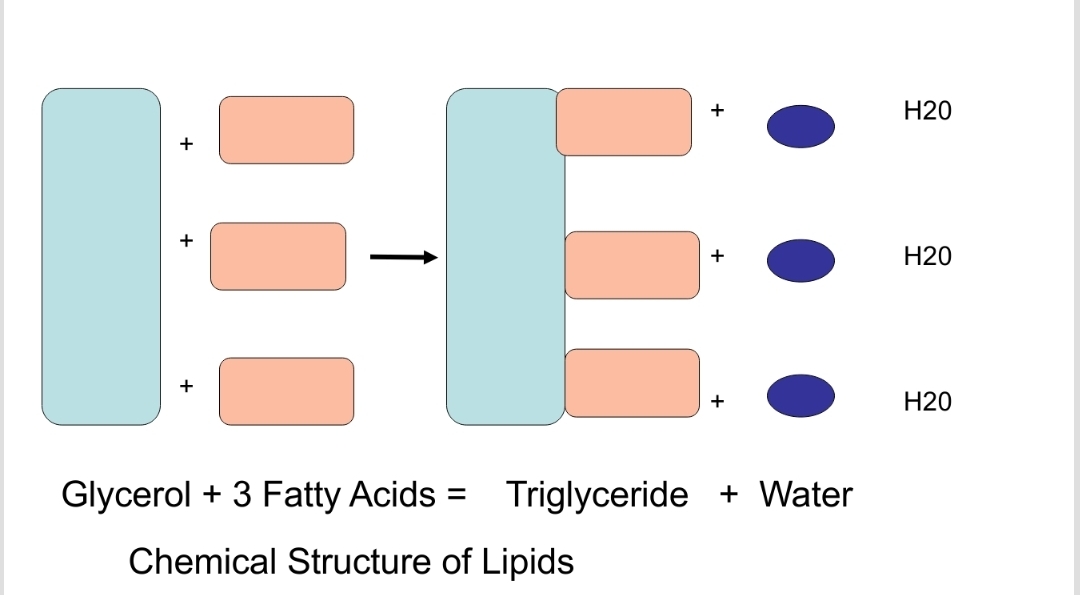
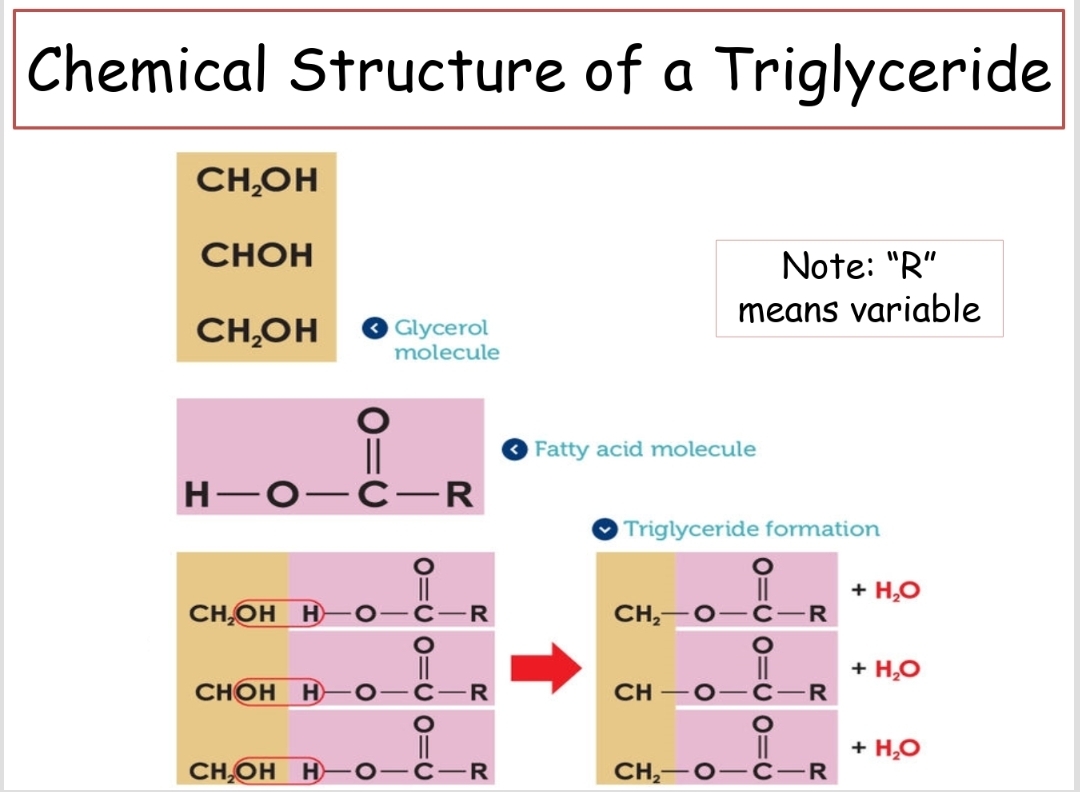
Triglyceride
A type of fat formed from one glycerol molecule joined with three fatty acids.
Fatty Acids
Long carbon chains with a methyl group (CH3) at one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) at the other.
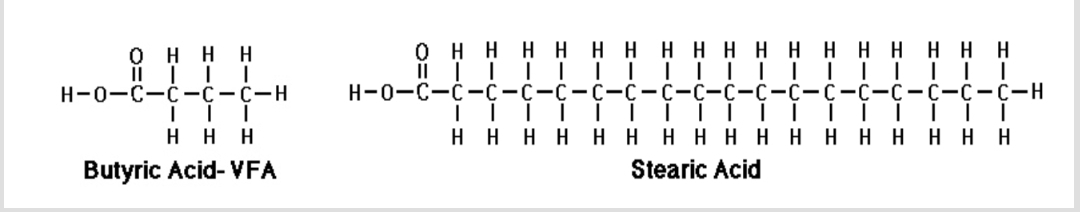

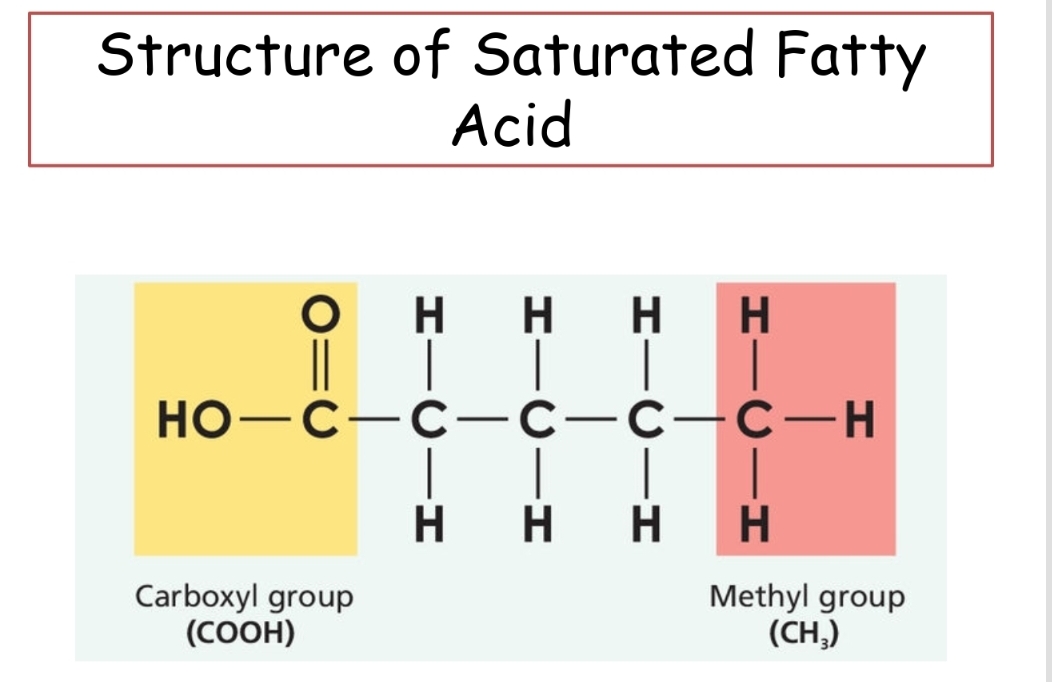
Saturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids where each carbon atom is saturated with hydrogen and contains no double bonds.

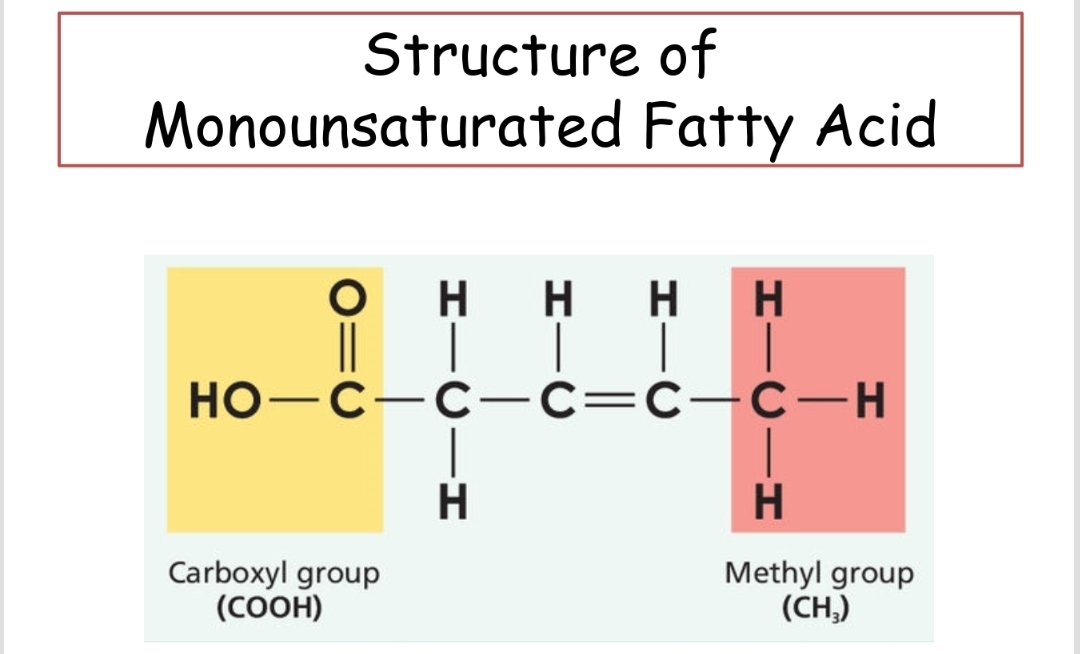
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
A fatty acid that contains one double bond and is usually liquid at room temperature.

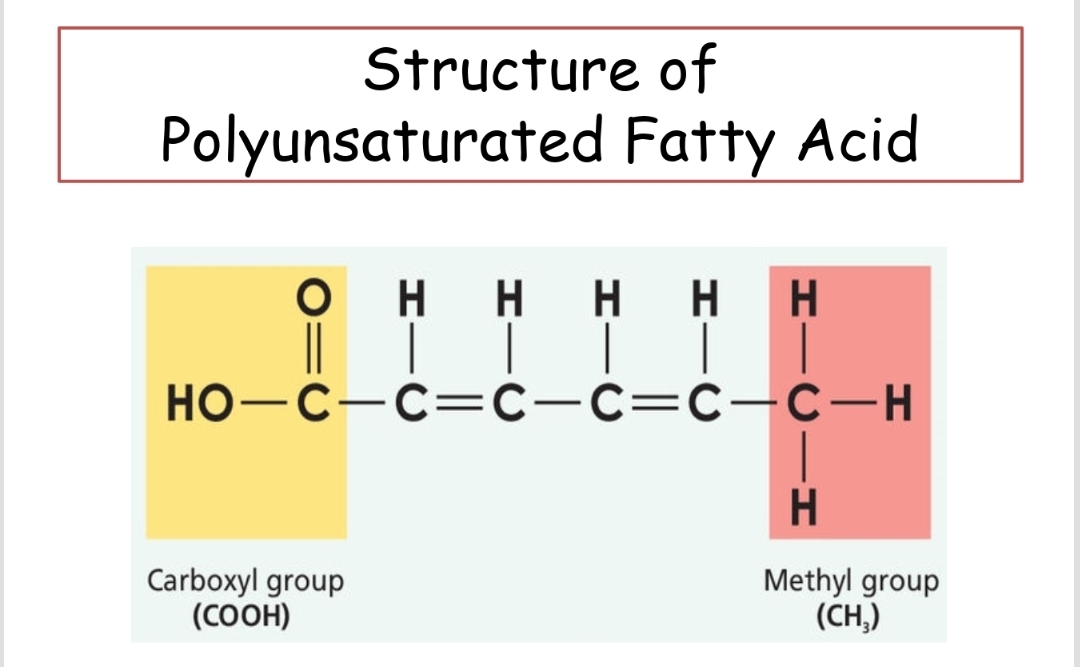
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
Fatty acids that contain two or more double bonds and are generally liquid at room temperature.
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs)
Fatty acids that cannot be manufactured by the body and must be obtained through diet.
Three essential fatty acids
Linoleic Acid
Linolenic Acid
Arachidonic Acid
Source where Linoleic Acid is found?
Corn oil
Source of Linolenic Acid?
Vegetable oil
Source of Arachidonic Acid ?
Animal fat
Sources of essential fatty acids
Nuts
Seeds
Olive oil
Oily fish
Functions of essential fatty acids
Build the cell membrane
Counteract the hardening affect of cholesterol in the arteries
Help prevent CHD
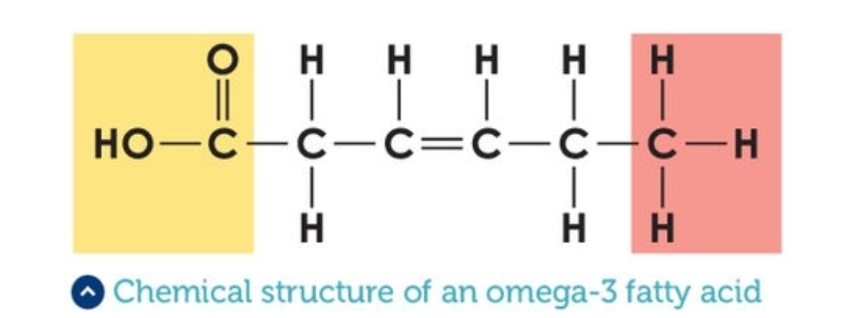
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Polyunsaturated fatty acids with a double bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms.
Omega 3 fatty acids are also known as?
EPA (eicosapentanoic acids)
DHA (docosahexaenoic acids)
EPA
Eicosapentanoic acids
DHA
Docosahexaenoic acids
Sources of Omega 3 fatty acids
Nuts
Oily fish
Seeds
Supplements
Soya beans
Functions of Omega 3 fatty acids
Reduces risk of heart attack, strokes, circulatory disease and formation of blood cloth
Increase HDL cholesterol levels
Healthy brain activity
Cis Fatty Acids
Fatty acids where hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond, generally beneficial to health.
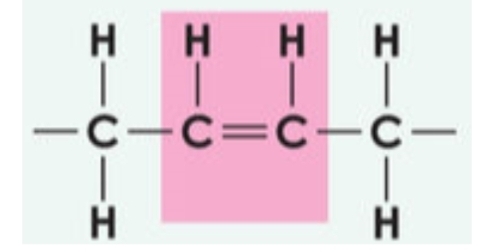
Trans Fatty Acids
Fatty acids where hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond, generally harmful to health.
Digestion of Lipids
The process involving the liver and pancreas that breaks down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids.
Absorption of Lipids
The process where digested lipids are absorbed into the lymph system and then into the bloodstream.
Utilisation of Lipids
The oxidation of lipids in the liver and muscles to produce heat, energy, and form cell membranes.
Caloric Value of Lipids
Lipids provide approximately 9 kilocalories per gram, making them a dense source of energy.
Carboxyl Group
The functional group (-COOH) found at the end of fatty acids.
Hydroxyl Group
The functional group (-OH) found in glycerol.