Torques and Levers
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
internal force
- produced from structures within the body
active force= muscle contraction
passive force= joint capsule or ligament limiting movement
external forces
produced by something outside the body
ex: gravity
stress strain curve measures
the ability of connective tissue to tolerate a load
what does the stress-strain graph depict?
Changes in a connective tissues length as strain is applied (ligament)
Y axis (stress) is the internal resistance from the ligament as it resists deformation (strain, lengthening)
X axis (strain) is the change is ligament length relative to its resting length
toe/non-linear region
where the ligament is designed to function optimally; when the ligament is becoming taught before excessive tension is applied to the ligament (use TB as an example here)
part of elastic region
linear region
load beyond what the ligament is designed to resist, deformation is occurring, ligament is still intact; Linear relationship between stress and strain
part of elastic region
stress-strain curve: plastic region
increased strain does not = increased stress to same degree or rate ; tissue has been overstretched and is beginning to fail - grade 1 and 2 injury occurs here before a complete failure of tissue at the ultimate failure point
Yield point = microscopic failure is occurring
Ultimate failure point = tissue loses its ability to hold shape - partial or complete tearing occurs
creep
describe this progressive slow strain of a tissue exposed to a constant load over time.
gravity
acts on all points of a body
Point of application of gravity = center of gravity (COG)
Hypothetical point at which all the mass appears to be concentrated
Line of gravity (LOG) acts from the COG
vectors
arrow that depicts a forces magnitude and direction
ex: magnitude, spatial orientation, direction, point of application
magnitude
length of arrow
spatial orientation
position of the shaft of the arrows
direction
indicated by the arrowhead
point of application
where the force acts on the body (or segment)
angle of insertion
- angle formed between a tendon of a muscle and the long axis of the bone into which it inserts
- this changes as the joint moves through ROM, or muscle shortens or lengthens
- when it increases or decreases on a muscle, it changes the angle which then impacts how much force the muscle can produce
joint reaction force
- force generated within a joint in response to forces acting on a point
rotation
- when forces are applied some distance perpendicular to the axis of rotation
what is moment arm (lever arm)
- perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation of the joint and the force
force x moment arm = torque
- torque (motion around a joint in a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation)
internal torque
- internal force (muscles) x internal moment arm
external torque
- external force (gravity) x external moment arm
isometric muscle contraction
- static rotary equilibrium during isometric contractions
--> internal= external torque= no change in muscle length of joint angle
concentric muscle contraction
--> internal > external torque --> muscle shortens; muscle accelerates body or limb
eccentric muscle contraction
--> external > internal torque --> muscle lengthens; muscle decelerates body/limb
what are the 4 components of a lever
- a rigid beam (moving bone)
- a pivot or fulcrum (a joint)
- effort force (muscle work)
- resistance (the mass of the body part)
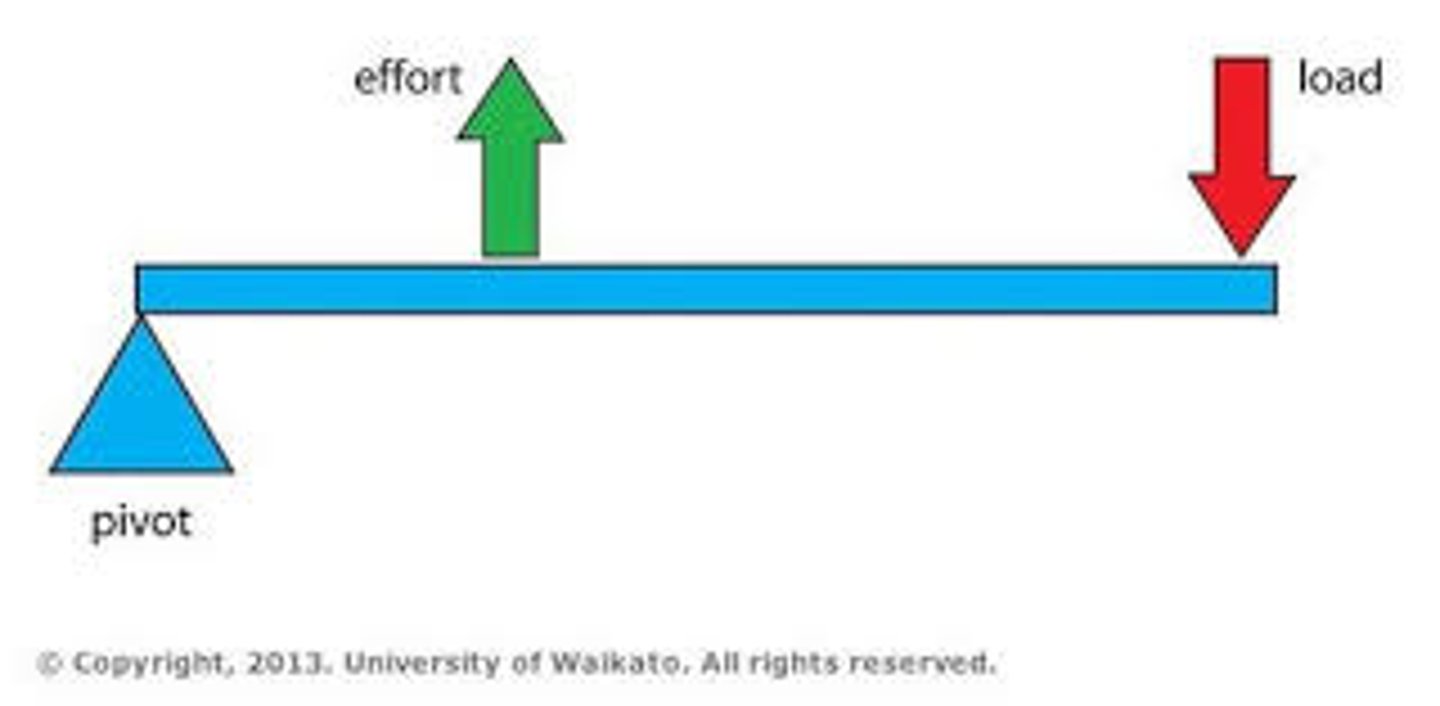
what is a 1st class lever
- fulcrum is in the middle
- mechanical advantage: = 1, >1 or <1
- mechanical advantage depends on how far the load and effort is from the fulcrum --> not most ideal for human movement
(ex. seesaw) (skull)
what is a 2nd class lever
- least common
- load is in the middle
- mechanical advantage: greater than 1
- (ex. wheelbarrow) (foot/calf)
what is a 3rd class lever
- most common
- effort is in the middle (the application of effort force is the insertion point)
- mechanical advantage: less than 1 (our body will overpower the load)
- (ex. fishing rod) (elbow curl)
what is a positive (uncompensated) trendelenburg sign
- if weak, load will overpower effort, hip will fall into adduction
- internal force < external force (pelvis will not be level, origin and insertion will be farther apart)
what is a (compensated) trendelenburg sign
- weak hip abductors can also cause a shift in the center a mass
- upper trunk leans toward weight- bearing side
example of tredelenburg sign (type 1 lever) (sls right side)
- rigid beam (line from hip bone to other hip bone)
- fulcrum (femoracetabular jt)
- effort (abductors)
- load (body weight/gravity)
example of type 1 lever
OA joint
seesaw
fulcrum in center
example of type 2 lever
calf raise
wheelbarrow
load in center
example of type 3 lever
bicep curl
fishing rod
effort in center
the nonlinear/toe region is where the ligament is designed to work
best
where will internal force be?
at point of muscle insertion
where does joint reaction force point?
into the joint creating compression
external force will change depending on
point of application
1st class lever image
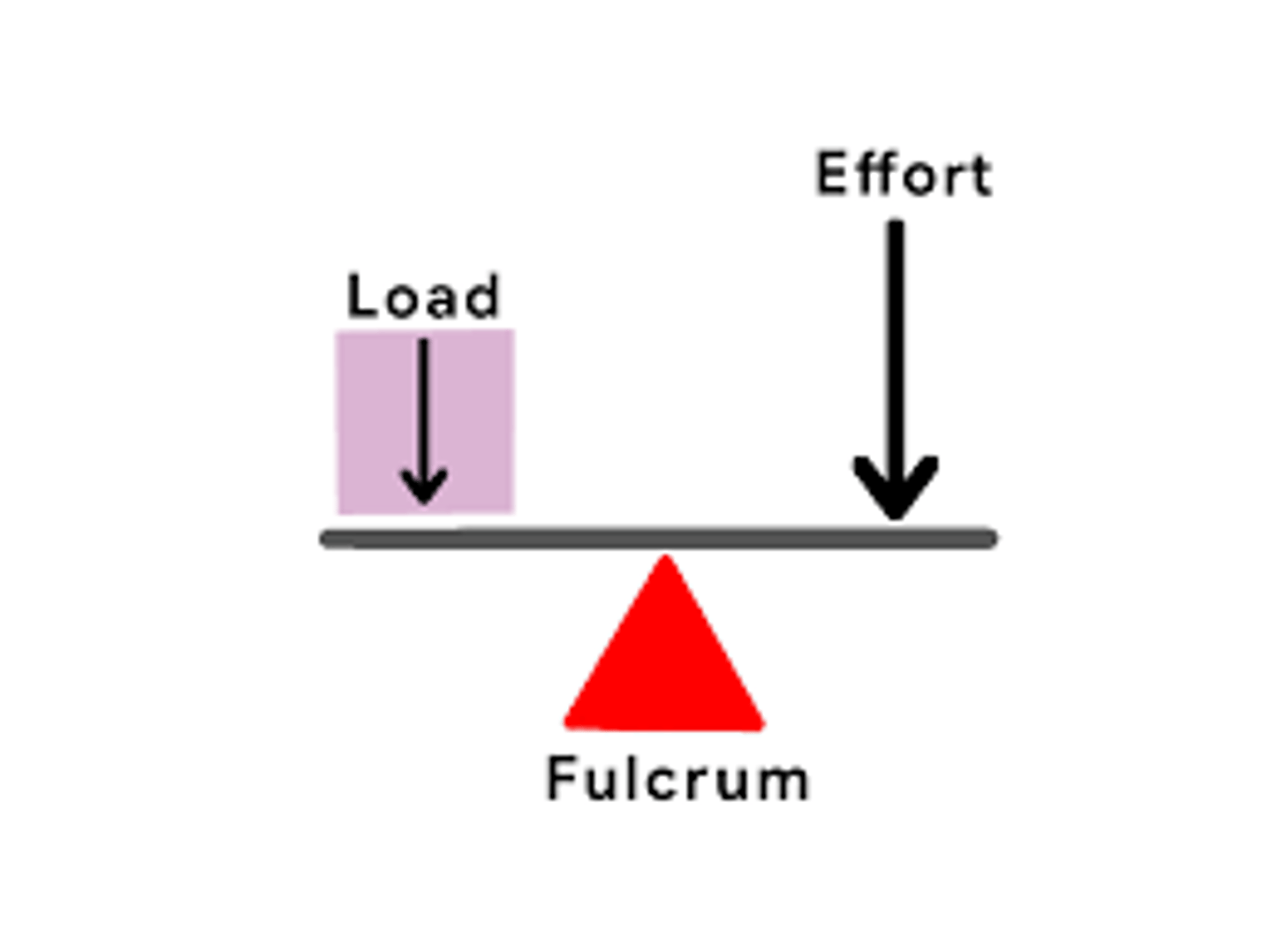
2nd class lever image
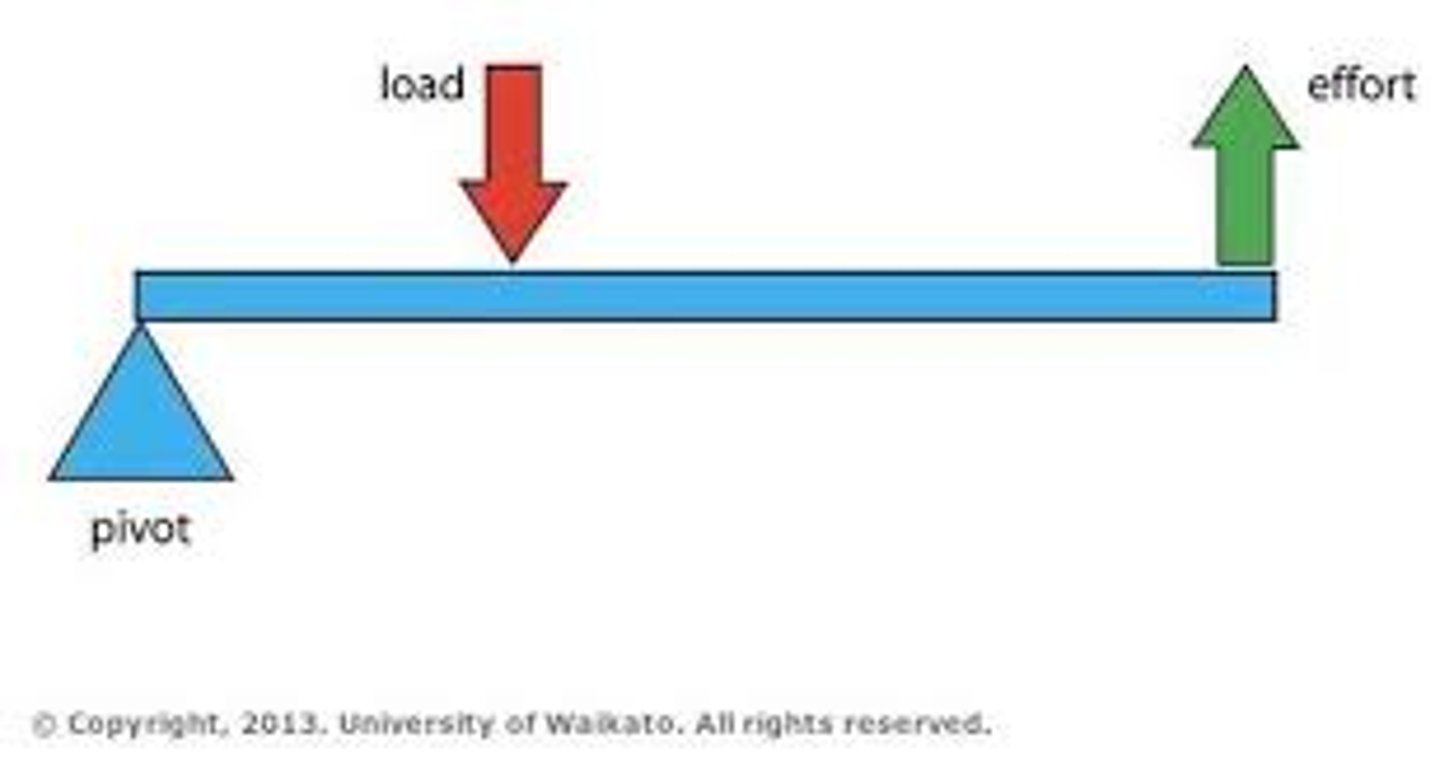
3rd class lever image