N236: Viral Infections of Humans
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Chickenpox pathogen
Varicella zoster virus
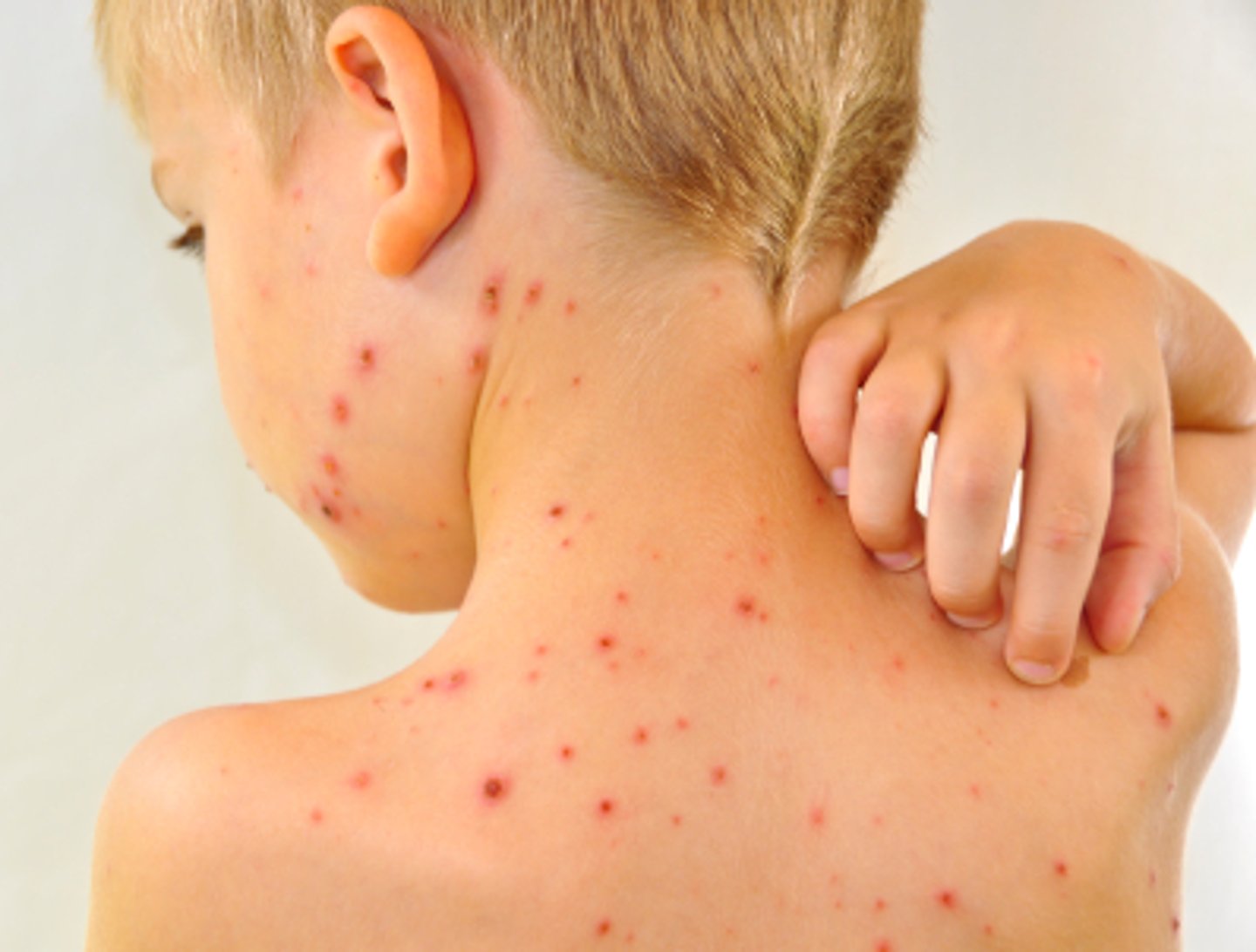
Chickenpox (Varicella) mode of transmission
Direct contact, or inhaling aerosols from vesicular fluid
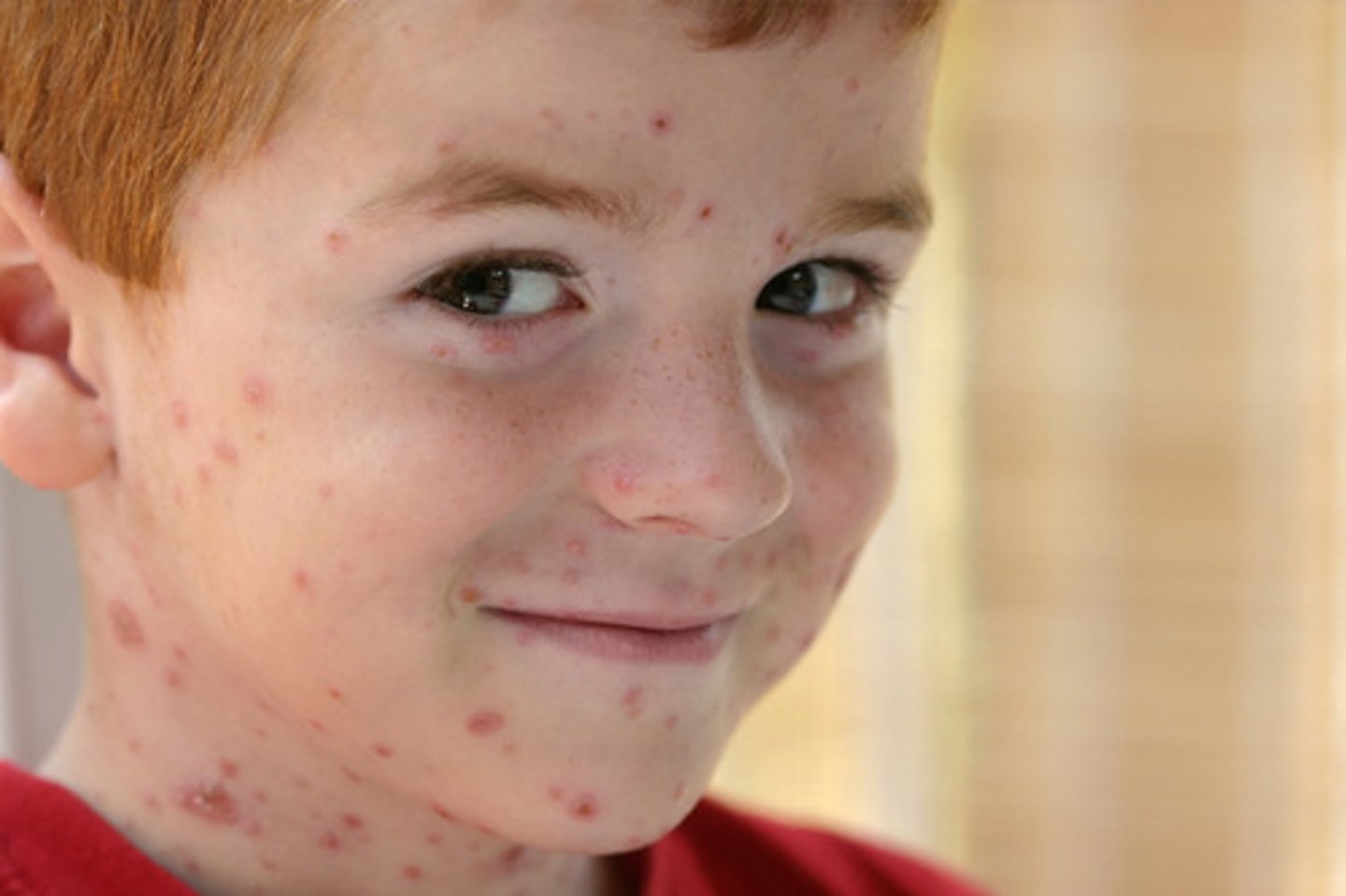
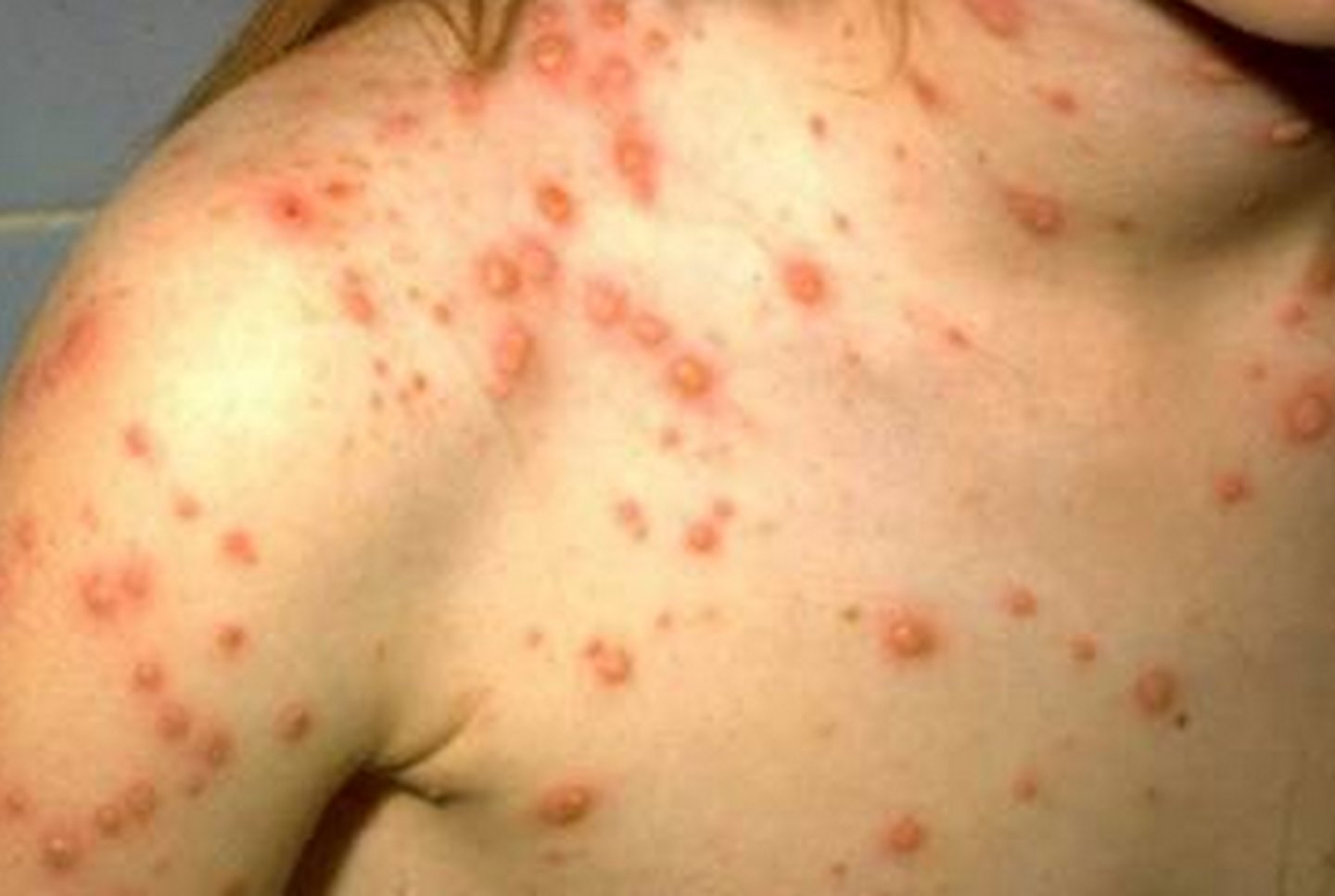
Chickenpox (Varicella) S+S
Fever, malaise, rash on chest that spreads to limbs, macular --> papular --> vesicular --> crust
Chickenpox (Varicella) prevention
Varicella vaccine
Dose 1 at 12-15 months, dose 2 at 4-6 yrs
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) pathogen
Varicella zoster virus
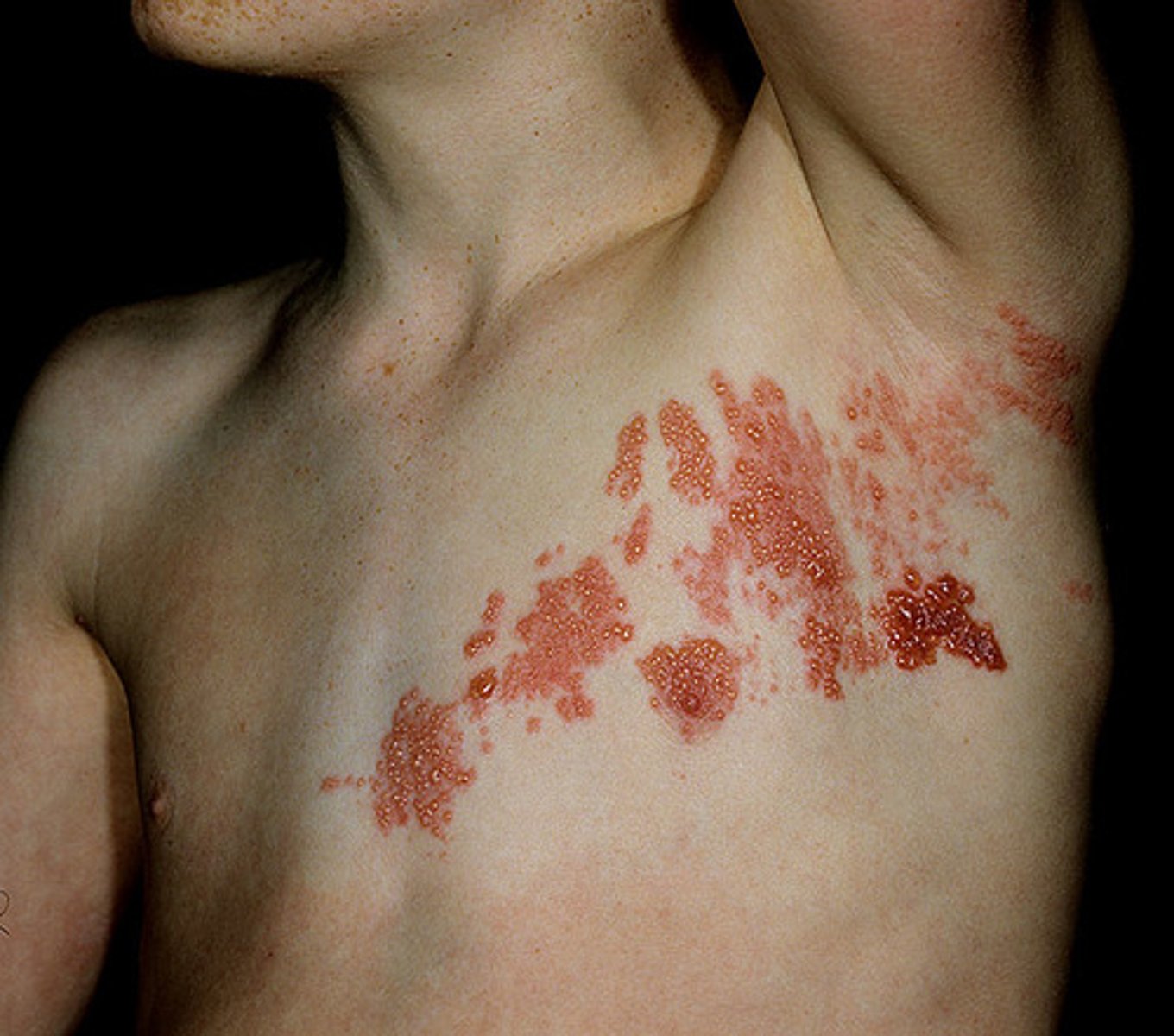
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) S+S
Tingling/burning/stinging → one sided vesicular rash on neck or chest, pain can persist for months-years after rash clears (post herpetic neuralgia)
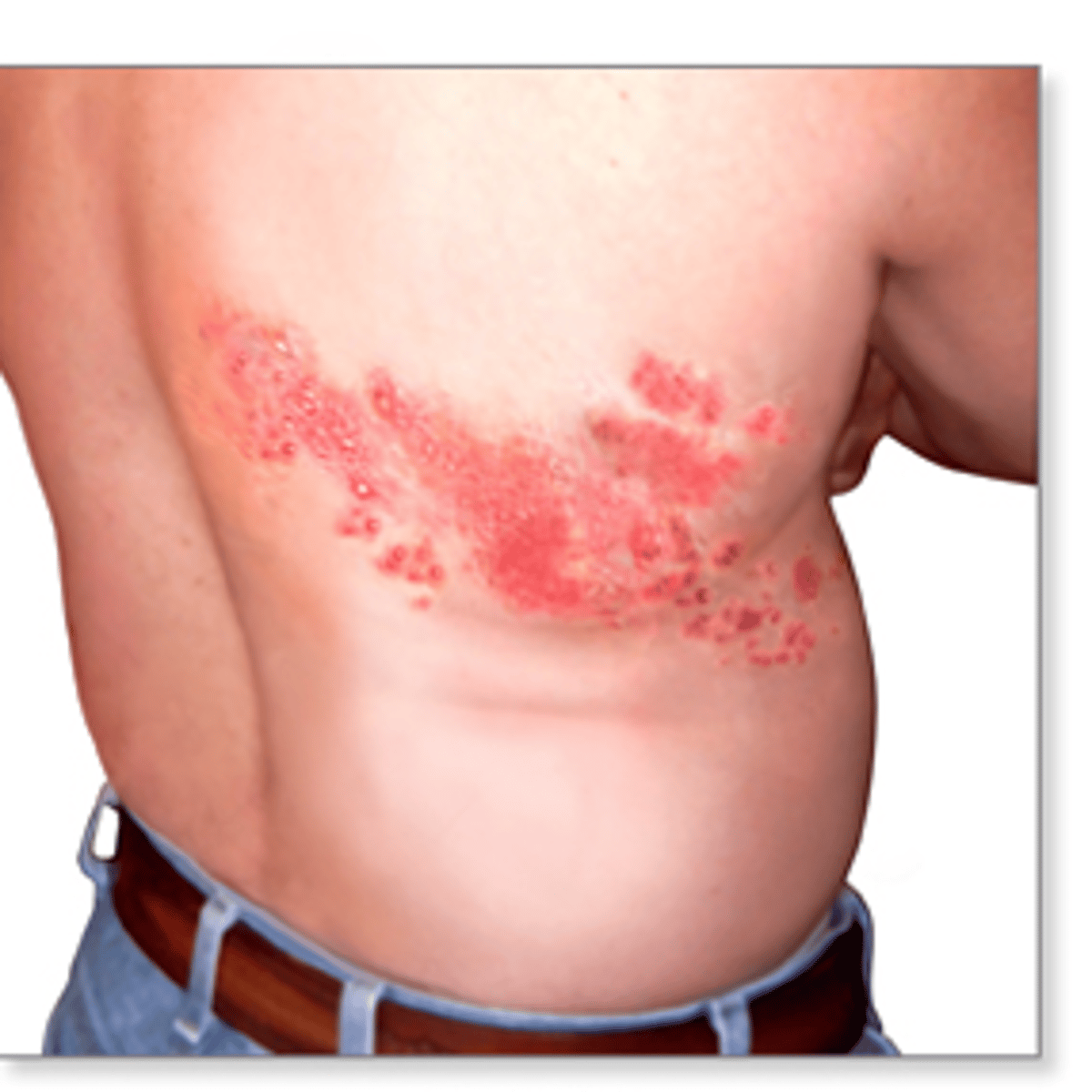
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) prevention
Shingrix vaccine
2 doses 2-6 mos apart in people > 50 yo

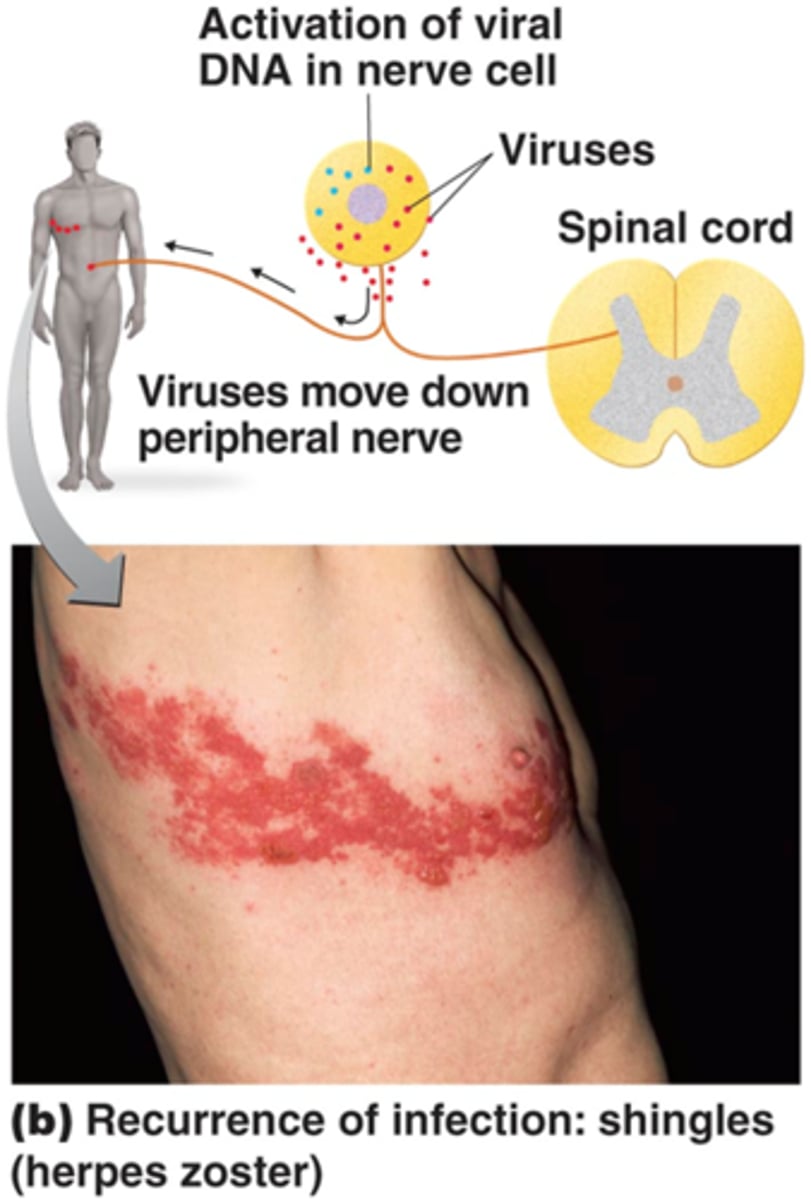
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) recurrence
Latent lives in the dorsal root ganglia neurons of the cervical/thoracic spinal nerves
Smallpox pathogen
Variola virus
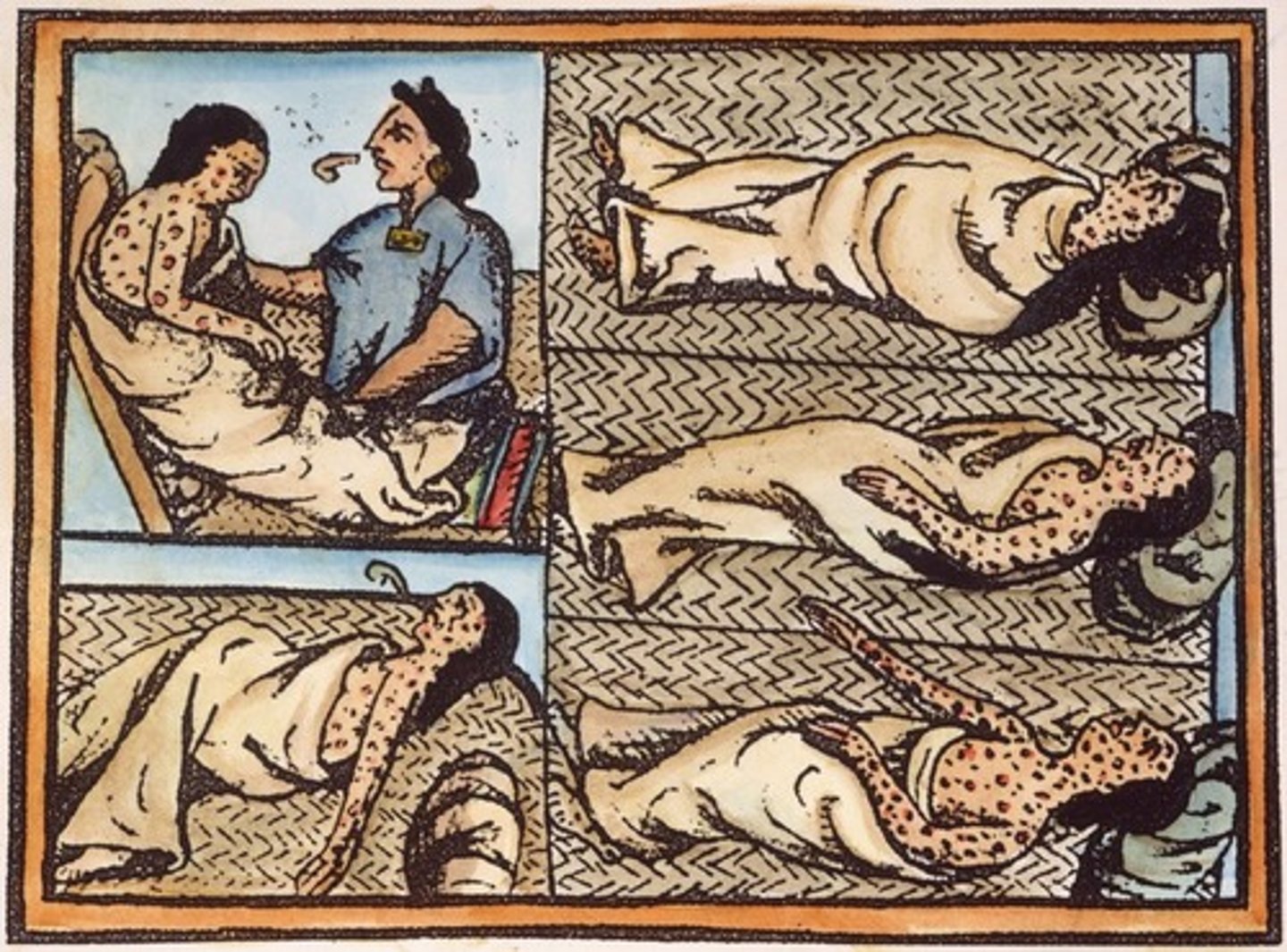
Smallpox (Variola) S+S
High fever, exhaustion, widespread rash that leaves permanent scars (macular --> papules --> vesicles --> crust)
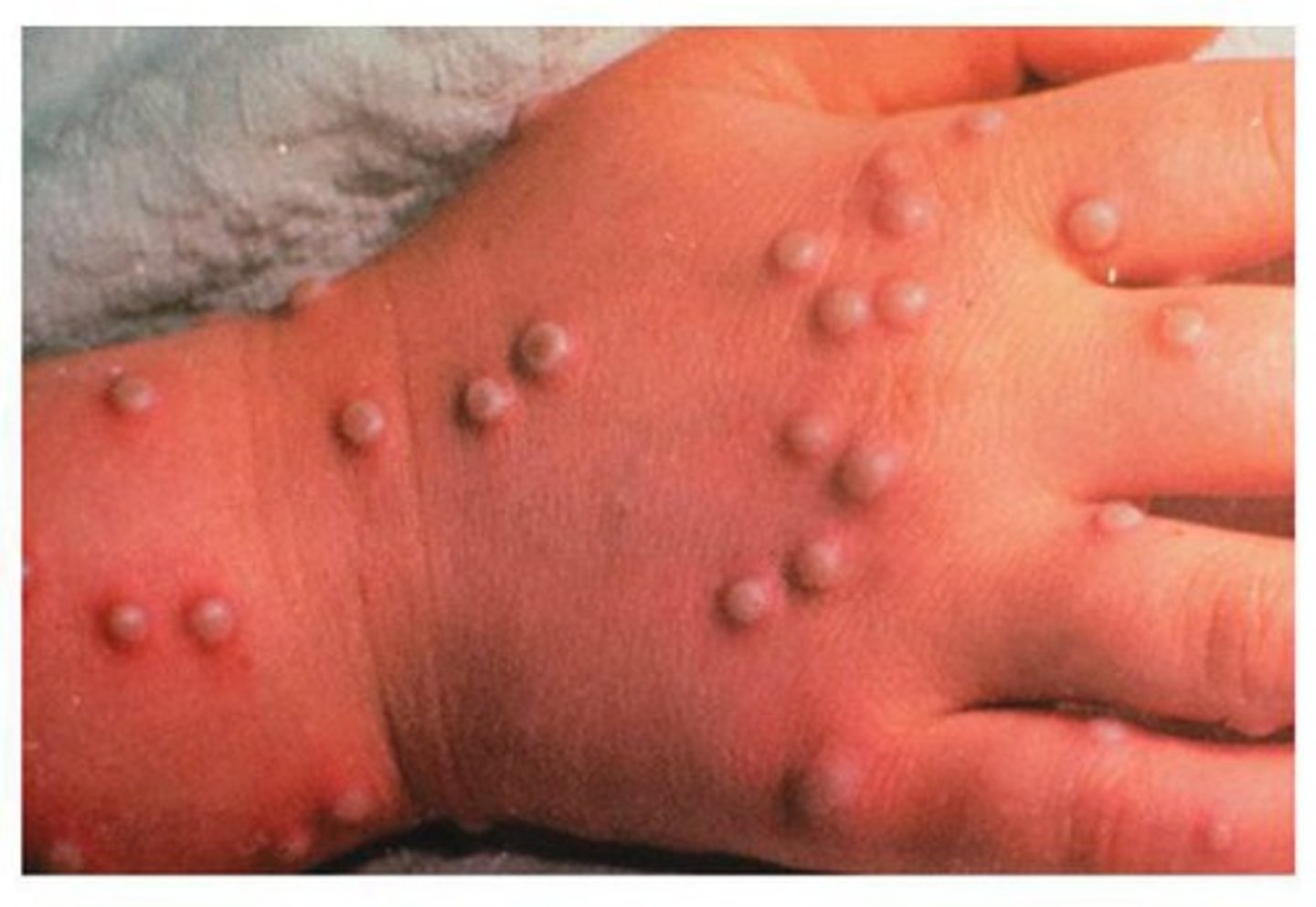
Smallpox (Variola) transmission
Direct contact, inhalation of vesicular secretions
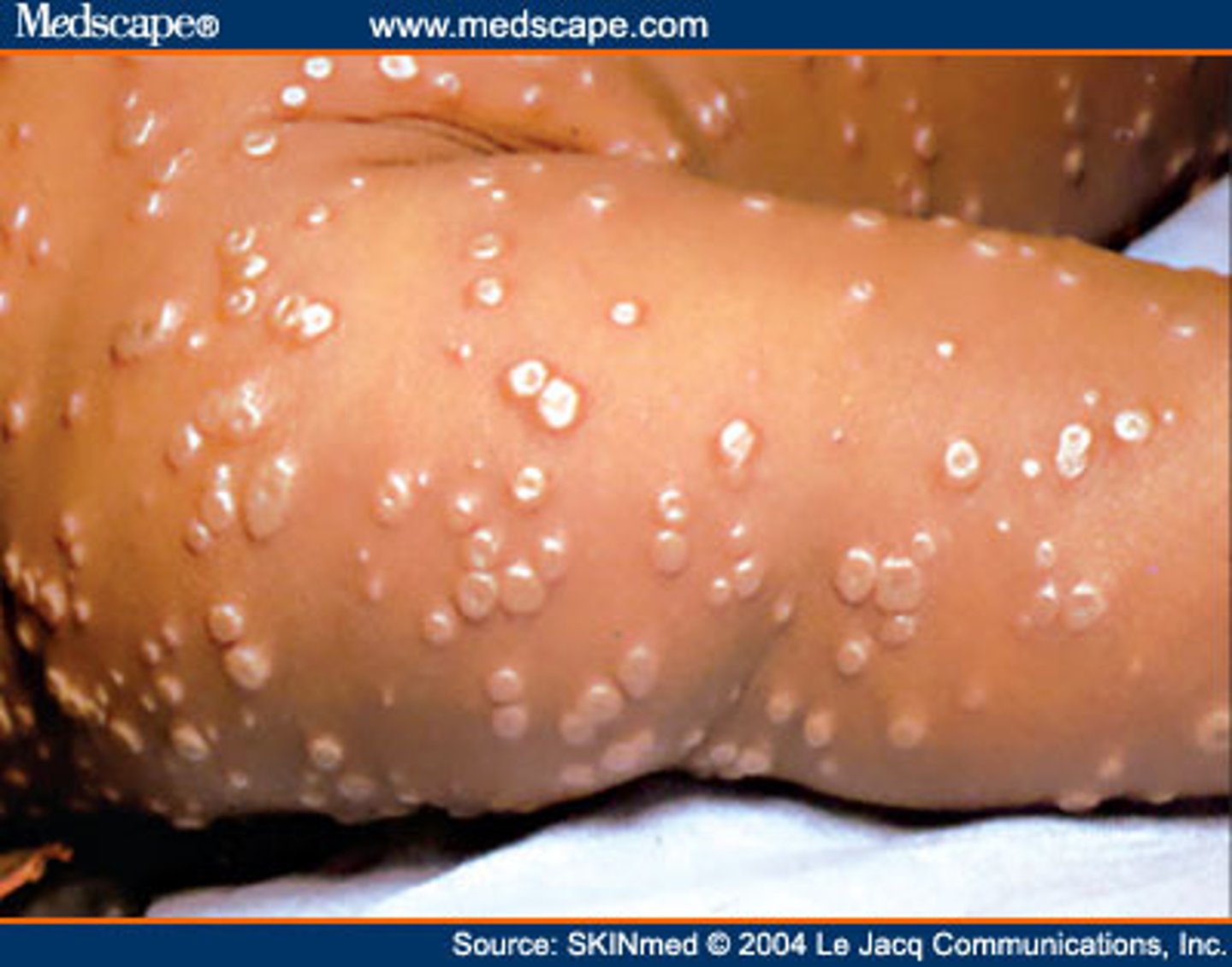
Measles pathogen
Rubeola virus
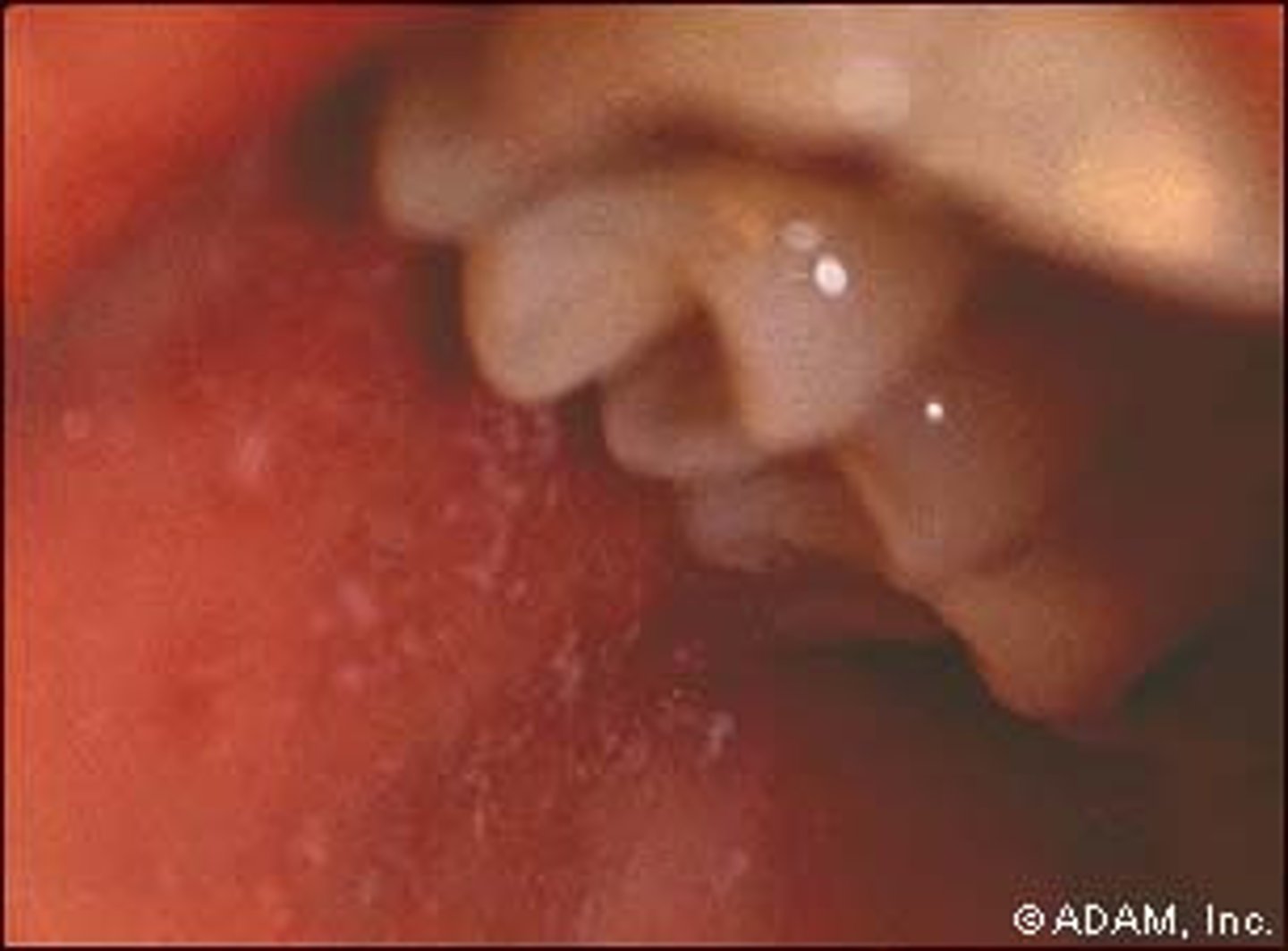
Measles (Rubeola) S+S
Fever, runny nose, cough, conjunctivitis, photosensitivity, Koplik spots in the mouth, skin rash on the face that spreads
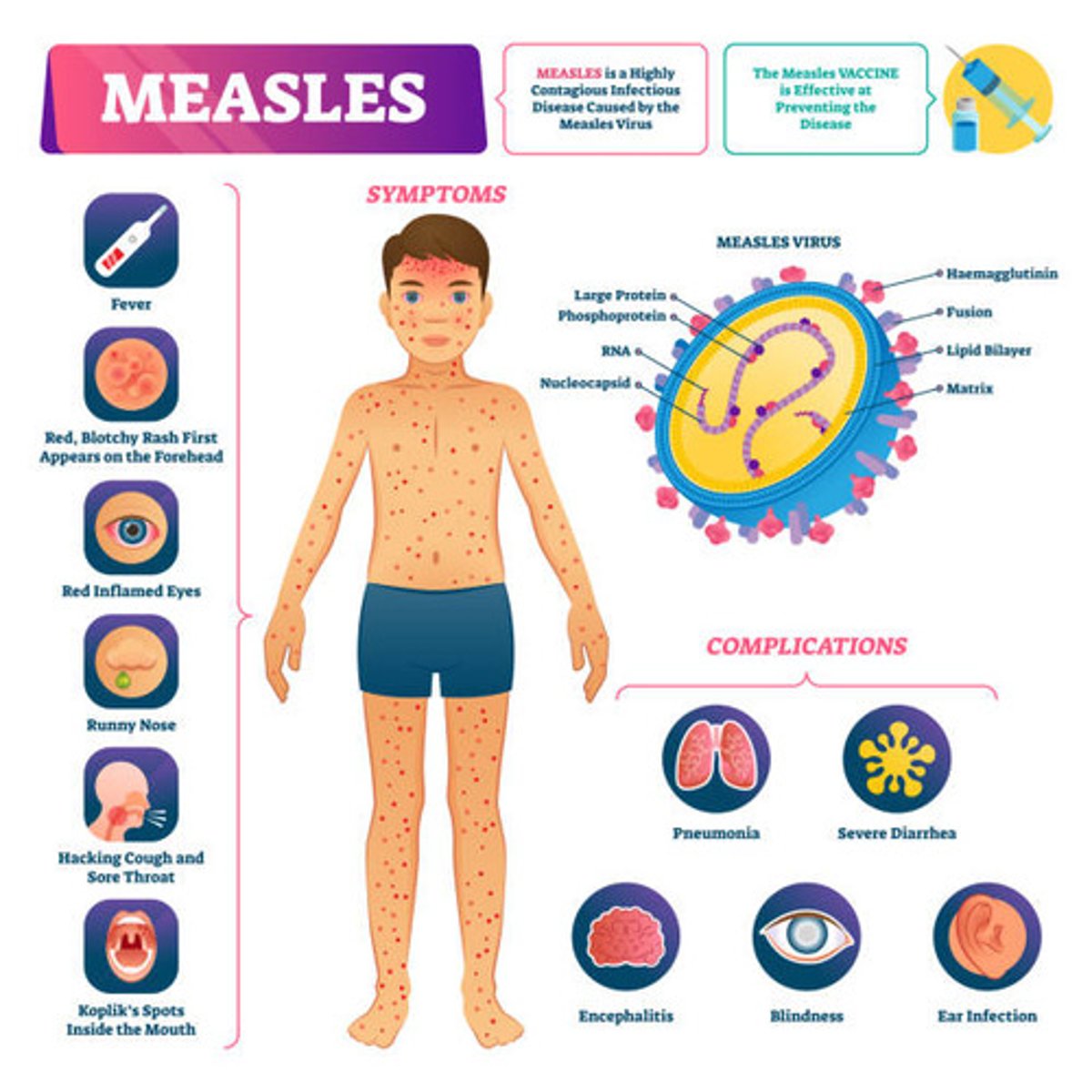
Measles (Rubeola) transmission
Inhalation or contact w/ oropharyngeal or respiratory secretions
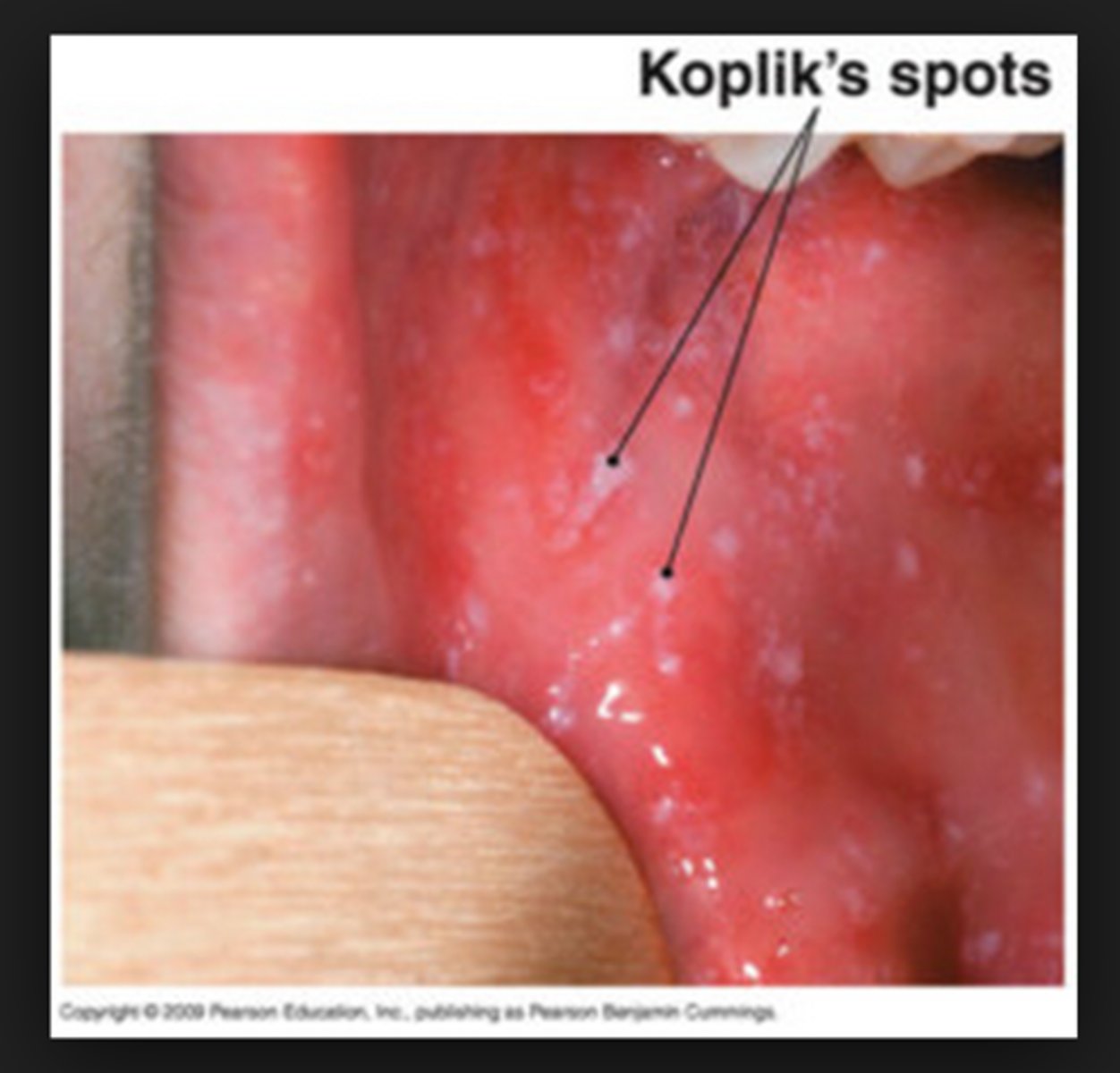
Measles (Rubeola) prevention
MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, and rubella)
Doses at 12-15 months and 4-6 years
German Measles pathogen
Rubella virus
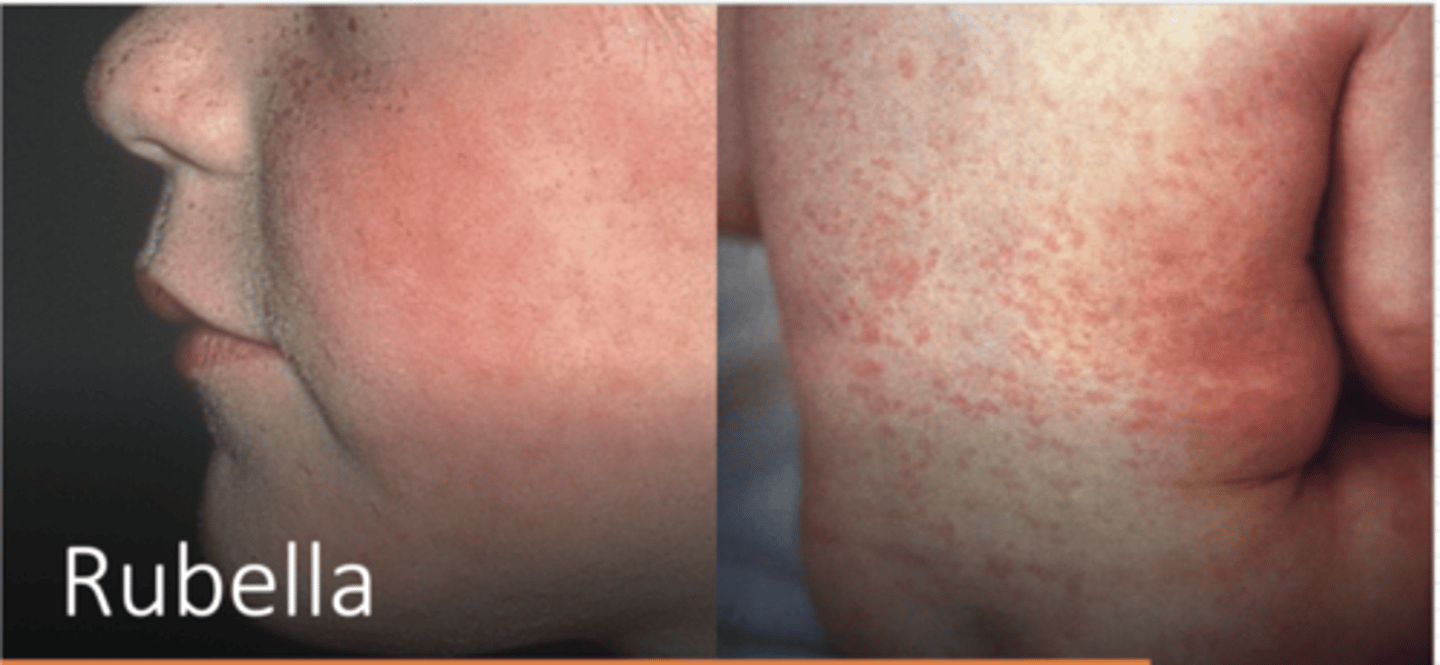
German Measles (Rubella) S+S
Mild fever, malaise, followed by maculopapular skin rash (face → body), milder than measles, resolves in 3 days
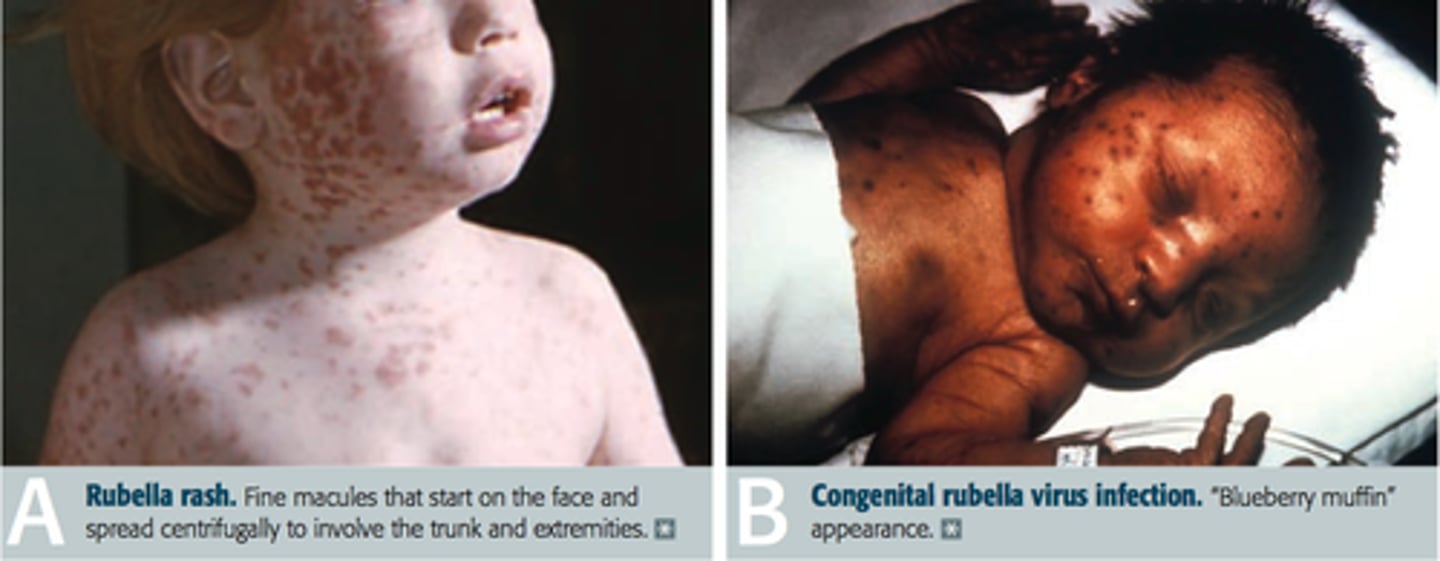
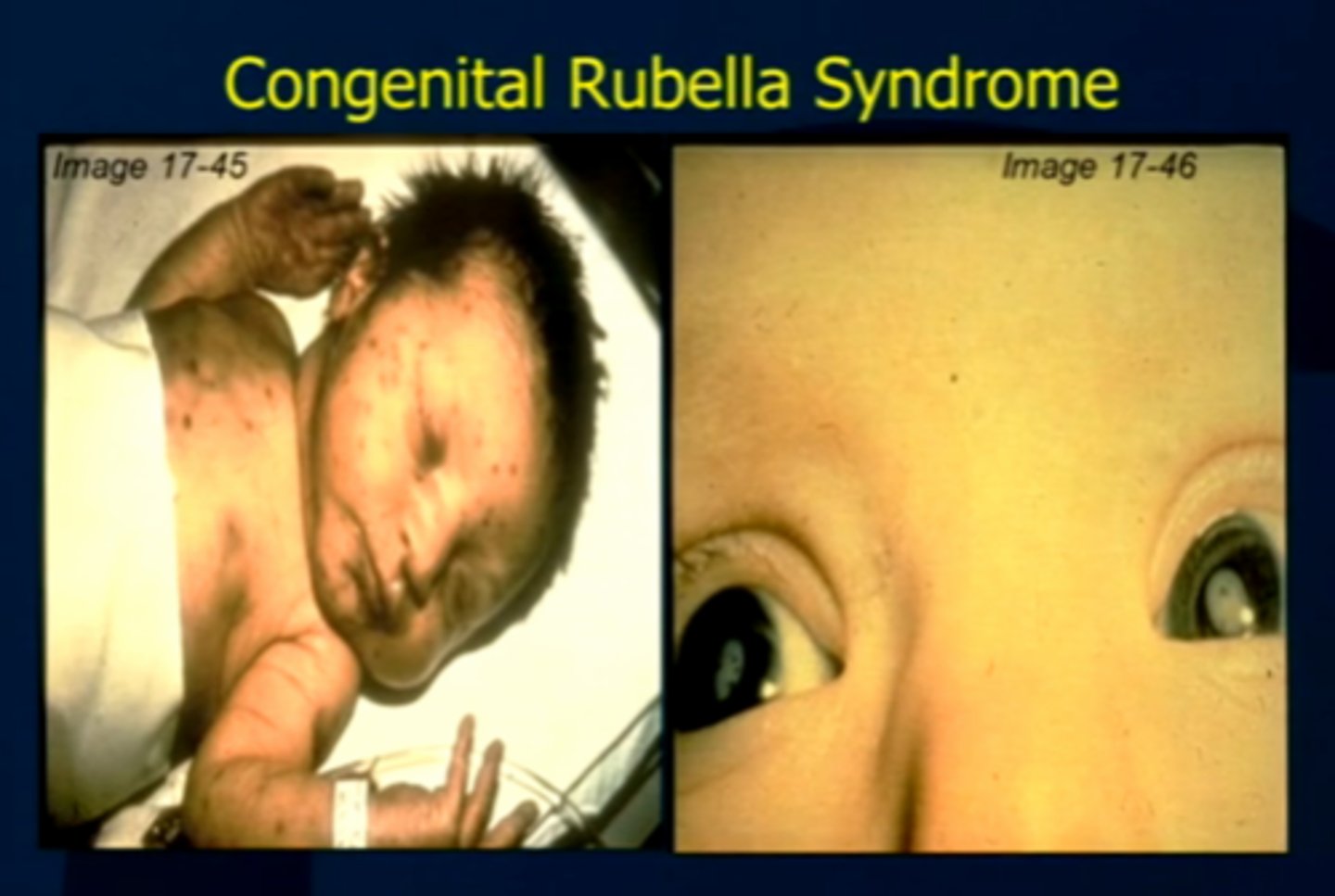
Congenital rubella syndrome
A birth defect that occurs when the mother becomes infected with the rubella virus in her first trimester
Hearing loss, heart defects, eye anomalies
German Measles (Rubella) transmission
Inhalation or contact w/ oropharyngeal or respiratory secretions

German Measles (Rubella) prevention
MMR vaccine
Doses at 12-15 months and 4-6 years
Acute Viral Rhinitis pathogen
160 types of rhinovirus

Acute Viral Rhinitis S+S
Malaise, inflammation of mucous membranes of URT (common cold symptoms)
Acute Viral Rhinitis transmission
Inhalation or contact with infected respiratory and oropharyngeal secretions

Acute Viral Rhinitis prevention
Handwashing, avoid people who are sick

Croup pathogen
Parainfluenza virus
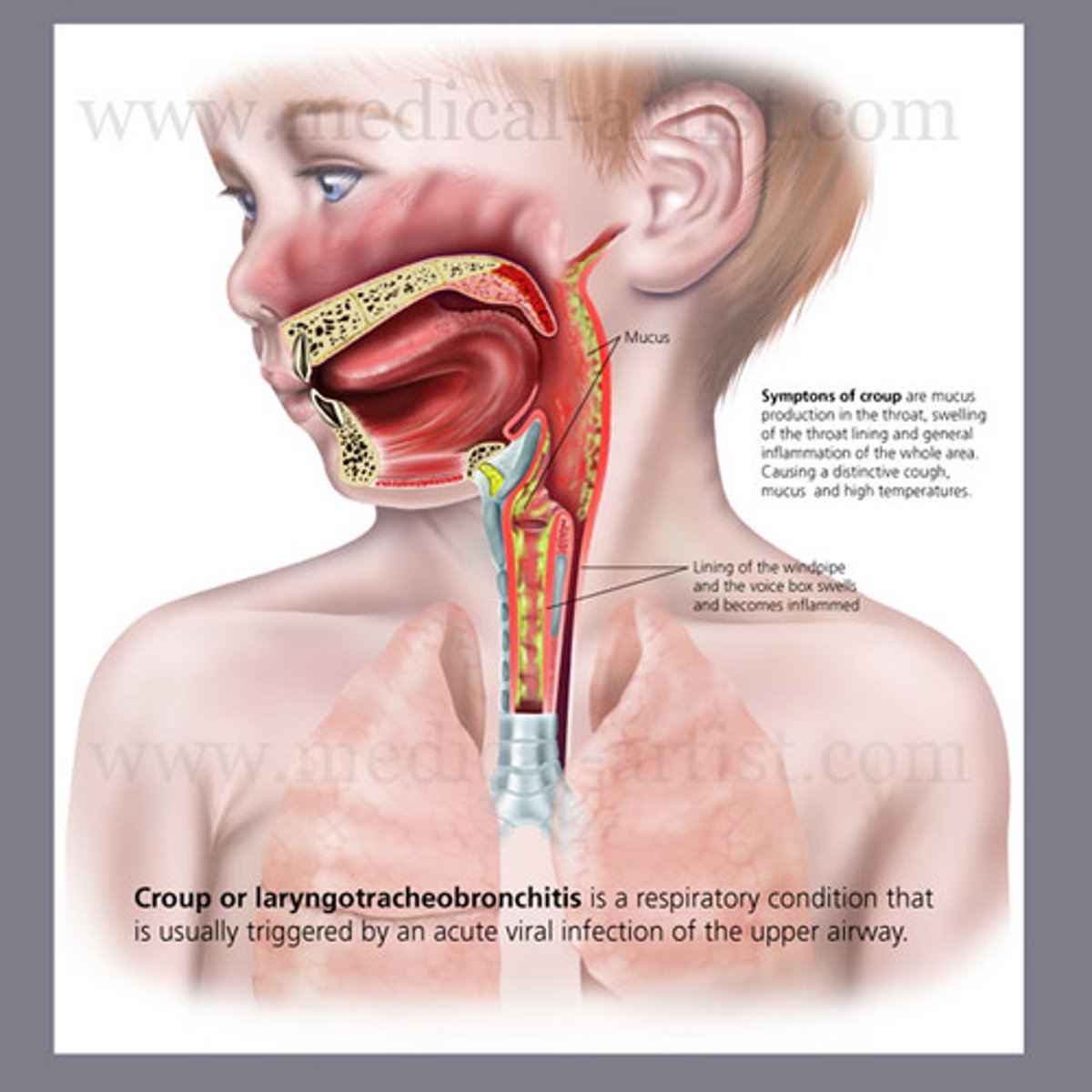
Croup alternate names
Laryngotracheitis, Laryngotracheobronchitis
Croup S+S
Begins as common cold, then within 24 hours, airways narrow and cause barking cough and stridor
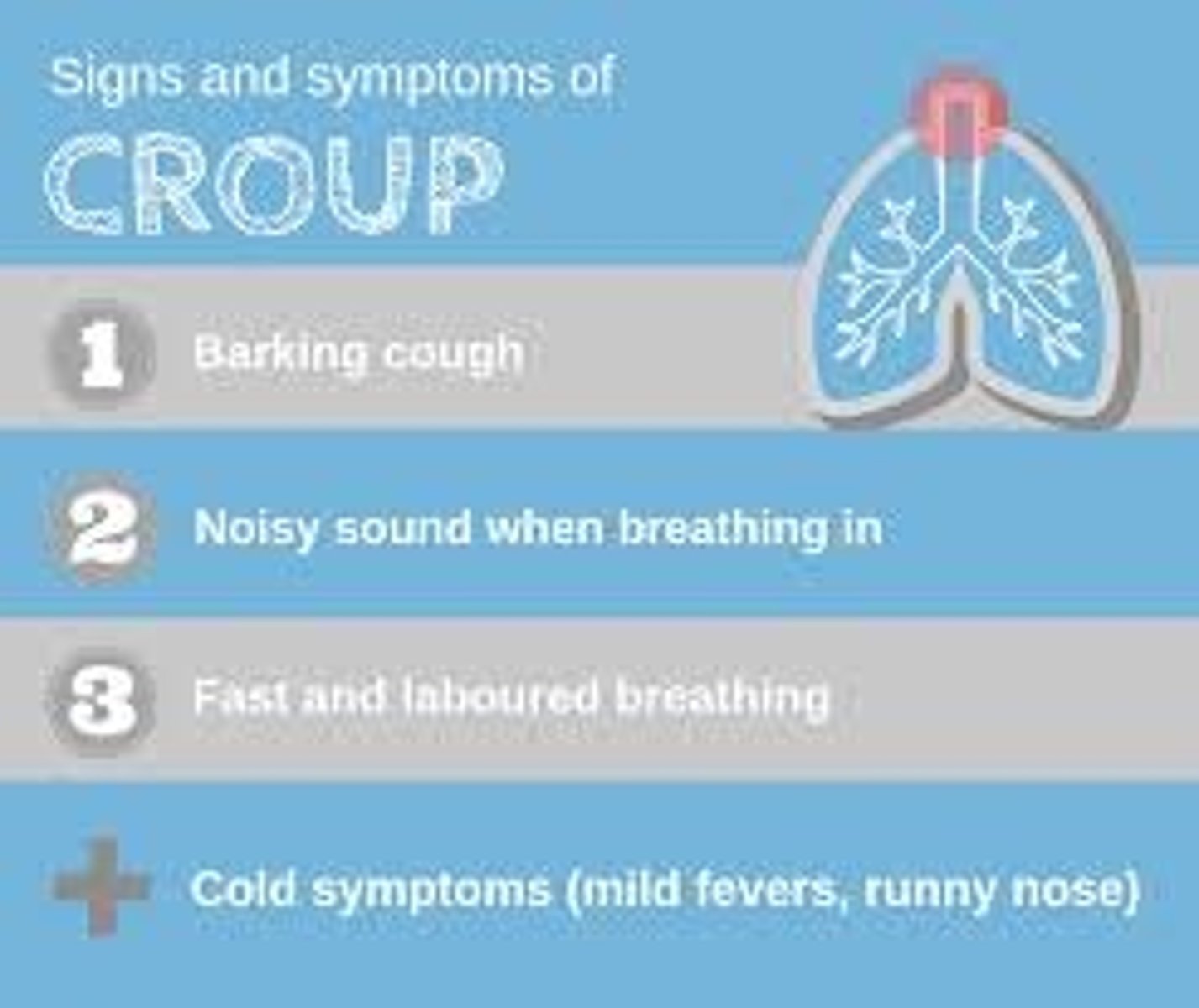
Croup transmission
Inhalation or contact with infected respiratory and oropharyngeal secretions

Croup prevention
Handwashing, no vaccine

Influenza (Flu) pathogen
Influenza viruses A, B, and C
Influenza (Flu) S+S
High fever, chills, dry cough, nasal congestion, aches and pains, pneumonia = serious complication

Influenza (Flu) transmission
Inhalation or contact with infected respiratory and oropharyngeal secretions
Influenza (Flu) prevention
Annual flu vaccine
What do H and N stand for?
Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase; different surface proteins of influenza viruses
Cute n fun vid:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z2Y0GMCFWq0&feature=share&si=ELPmzJkDCLju2KnD5oyZMQ
Bird Flu pathogen
Avian influenza virus
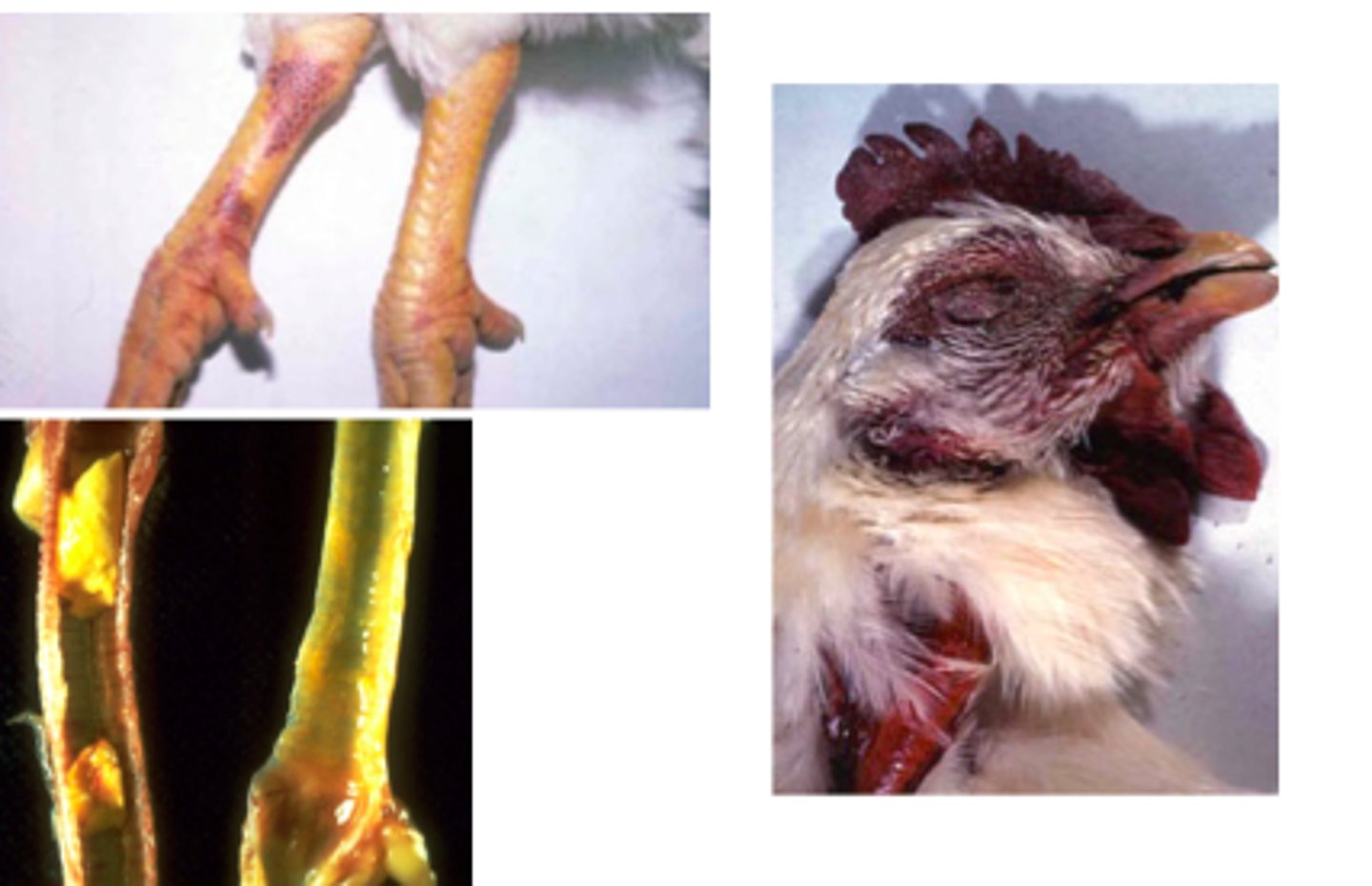
Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) S+S
High fever, chills, dry cough, nasal congestion, aches and pains, pneumonia = serious complication

Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) Reservoir
Infected wild and domesticated birds

Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) transmission
Contact with infected poultry or surfaces with excretions from infected birds

Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome pathogen
Hantavirus
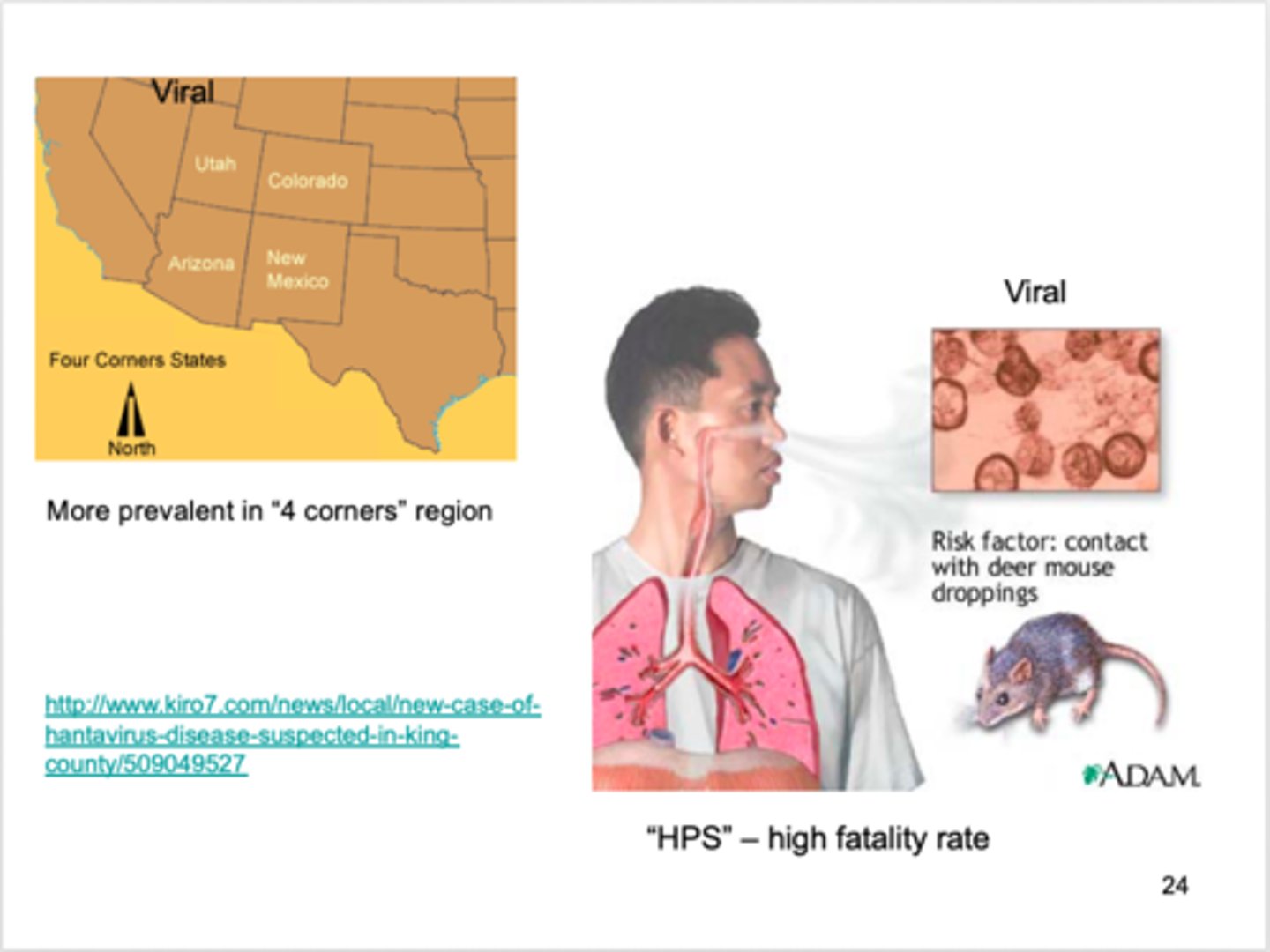
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome S+S
High fever, chills, headache, fatigue, hypotension, myalgia, SOB due to fluid in alveoli
"tight band around chest" or "pillow over face"

Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome Reservoirs
Infected rodents (deer mice, rice rats)

Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome transmission
Inhalation of rodent feces, urine, or saliva
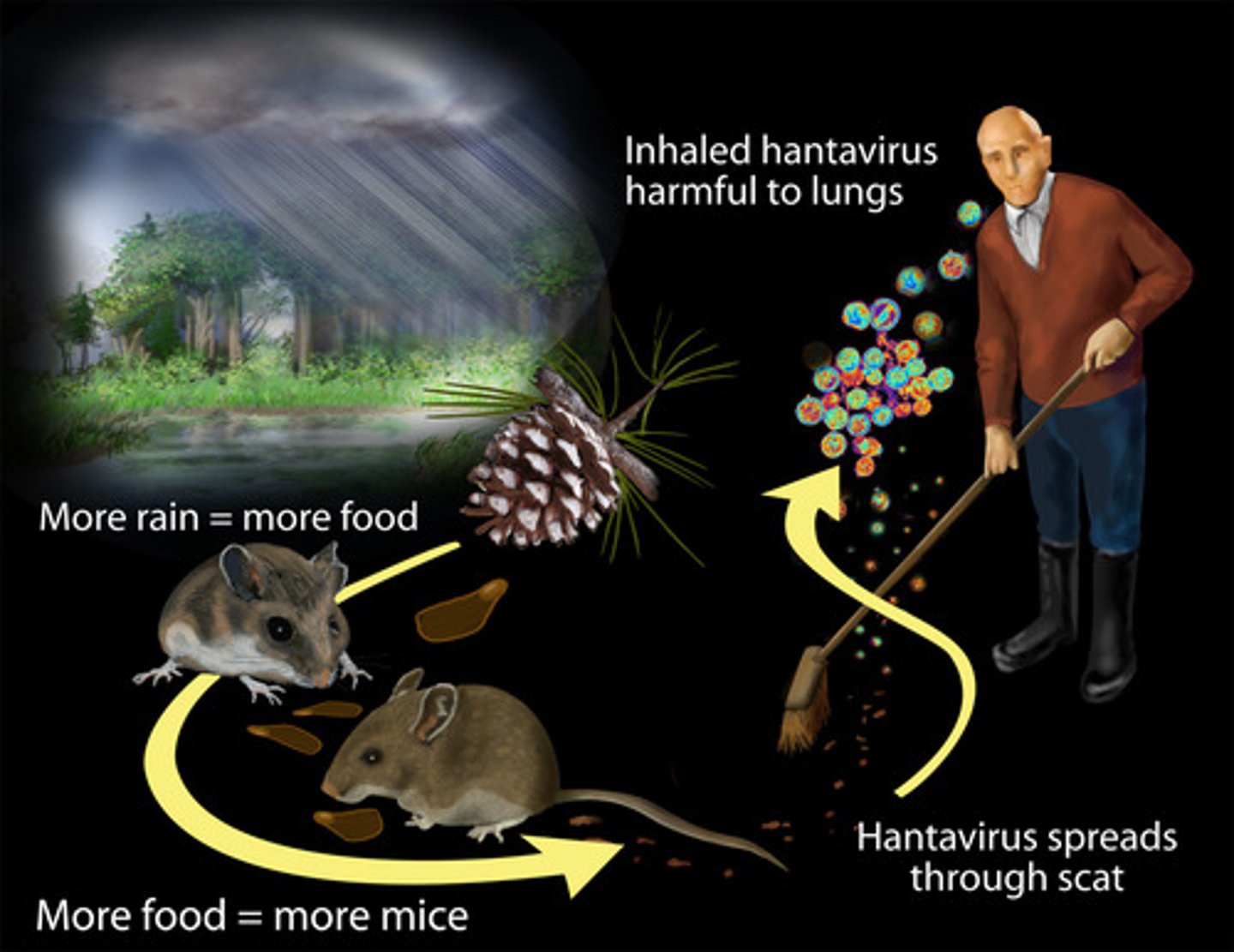
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome prevention
Stay AWAY from the rats

Coronavirus Infections
SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2
ranging from upper respiratory infection to bronchitis progressing to SARDS
SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome; Coronavirus
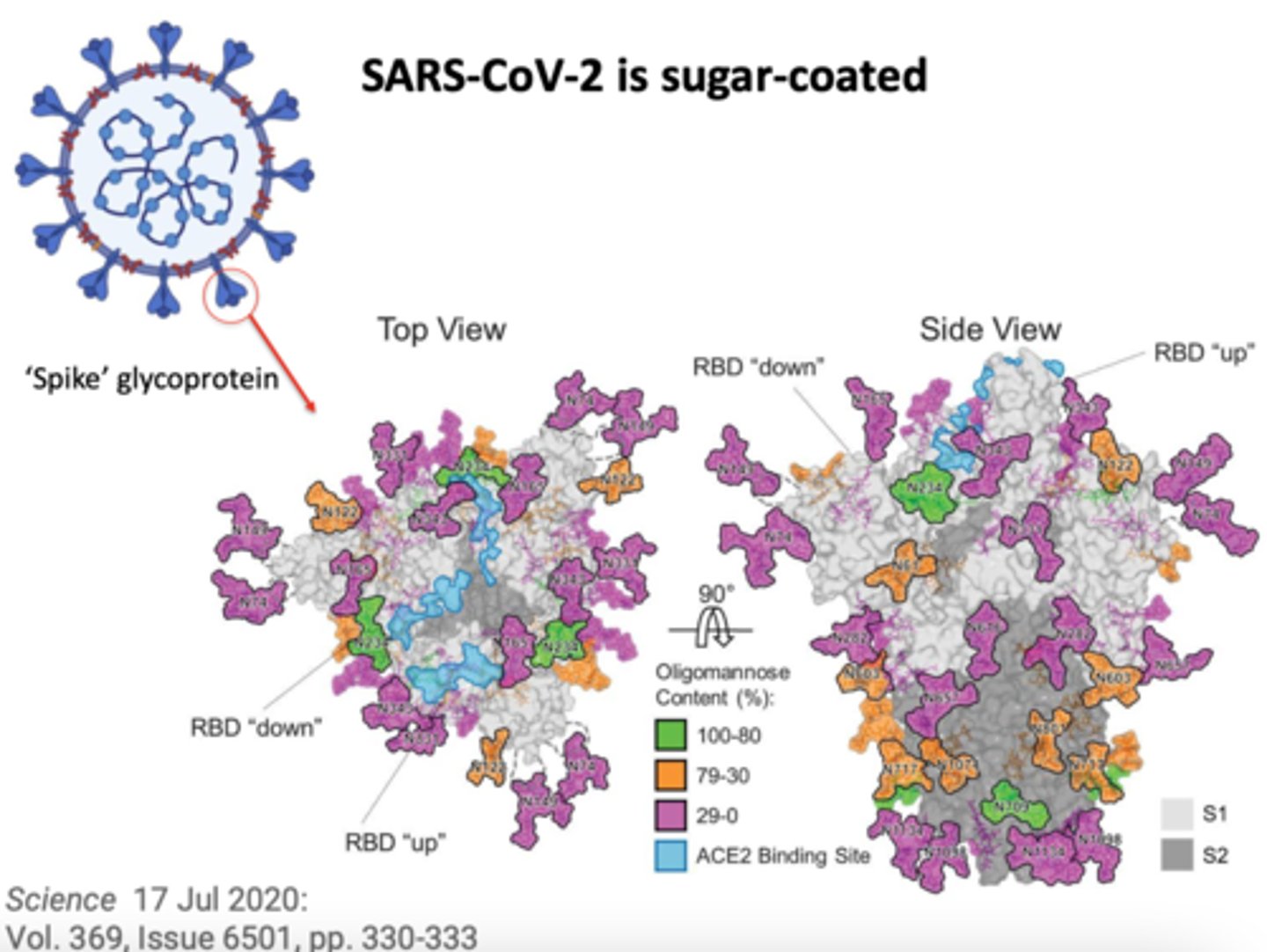
MERS-CoV
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome; Coronavirus
SARS-CoV-2
Coronavirus Disease 2019
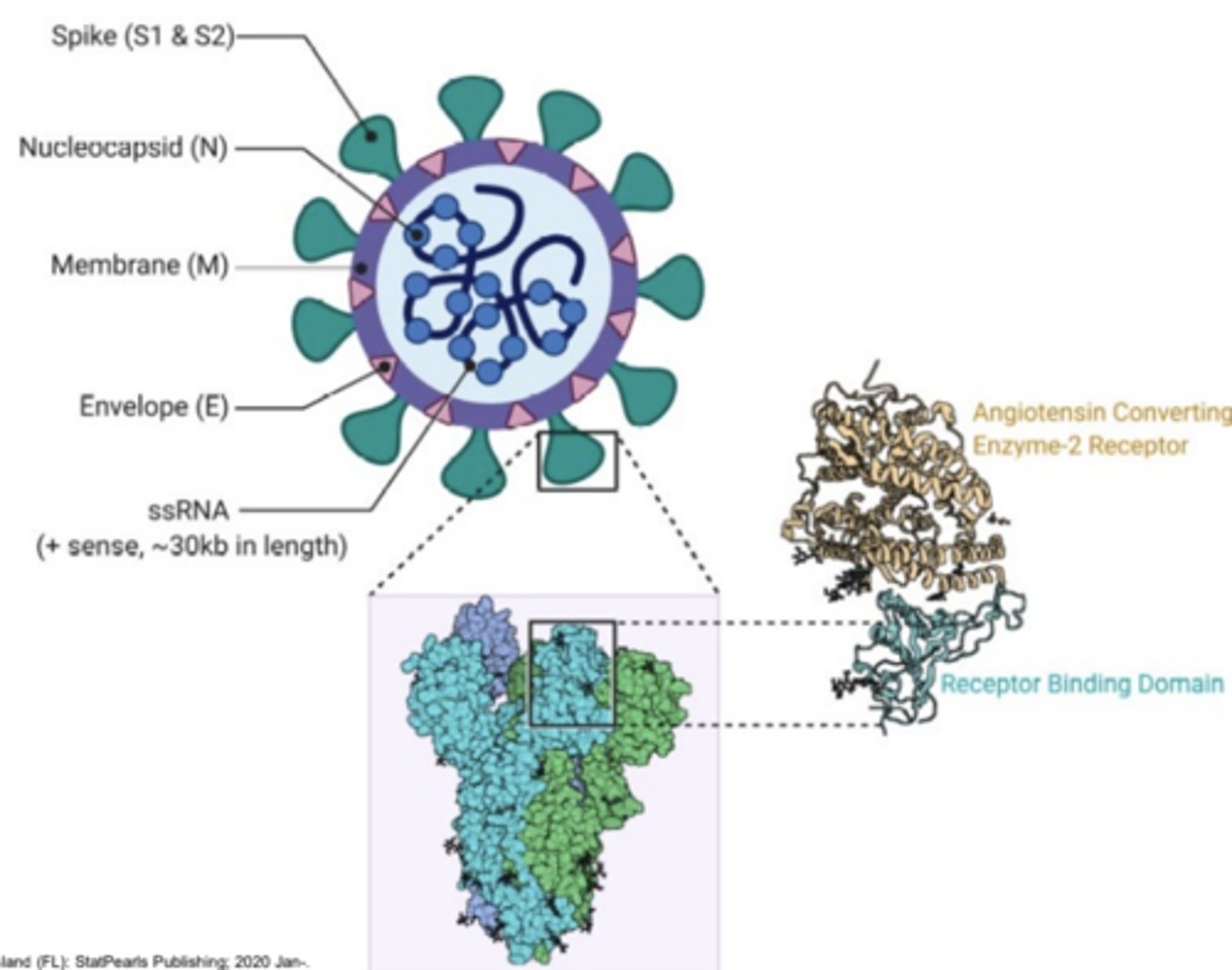
Coronavirus S+S
Fever, chills, cough, fatigue, headache, myalgia, malaise

Coronavirus Reservoirs
Bats (for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2) camels (for MERS-CoV)

Coronavirus transmission
Contact or inhalation of respiratory secretions
Herpes Labialis pathogen
Herpes simplex virus (usually type 1)
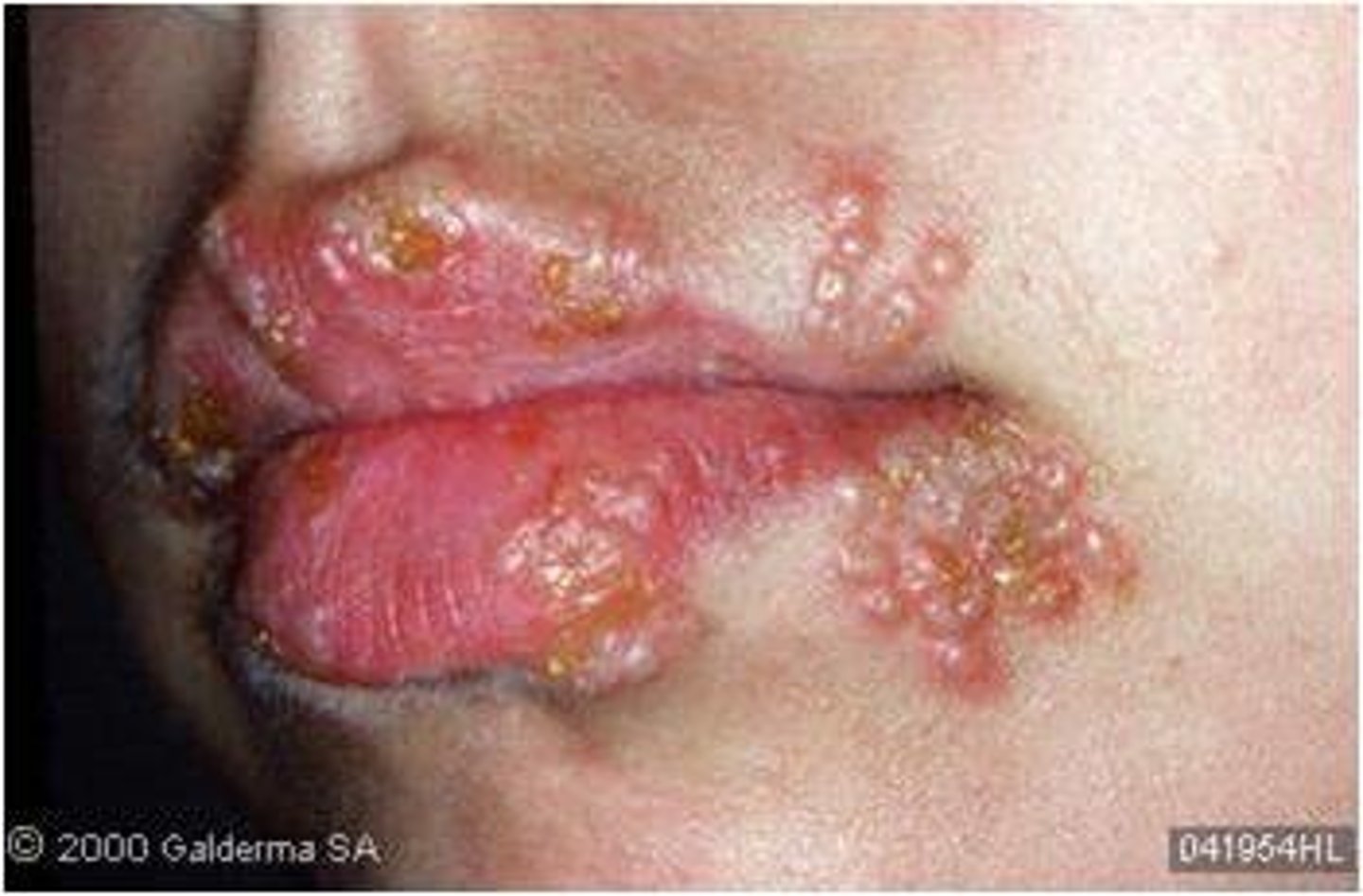
Herpes Labialis S+S
Burning pain, vesicles form around lips, blisters break, crust, and heal, no scarring
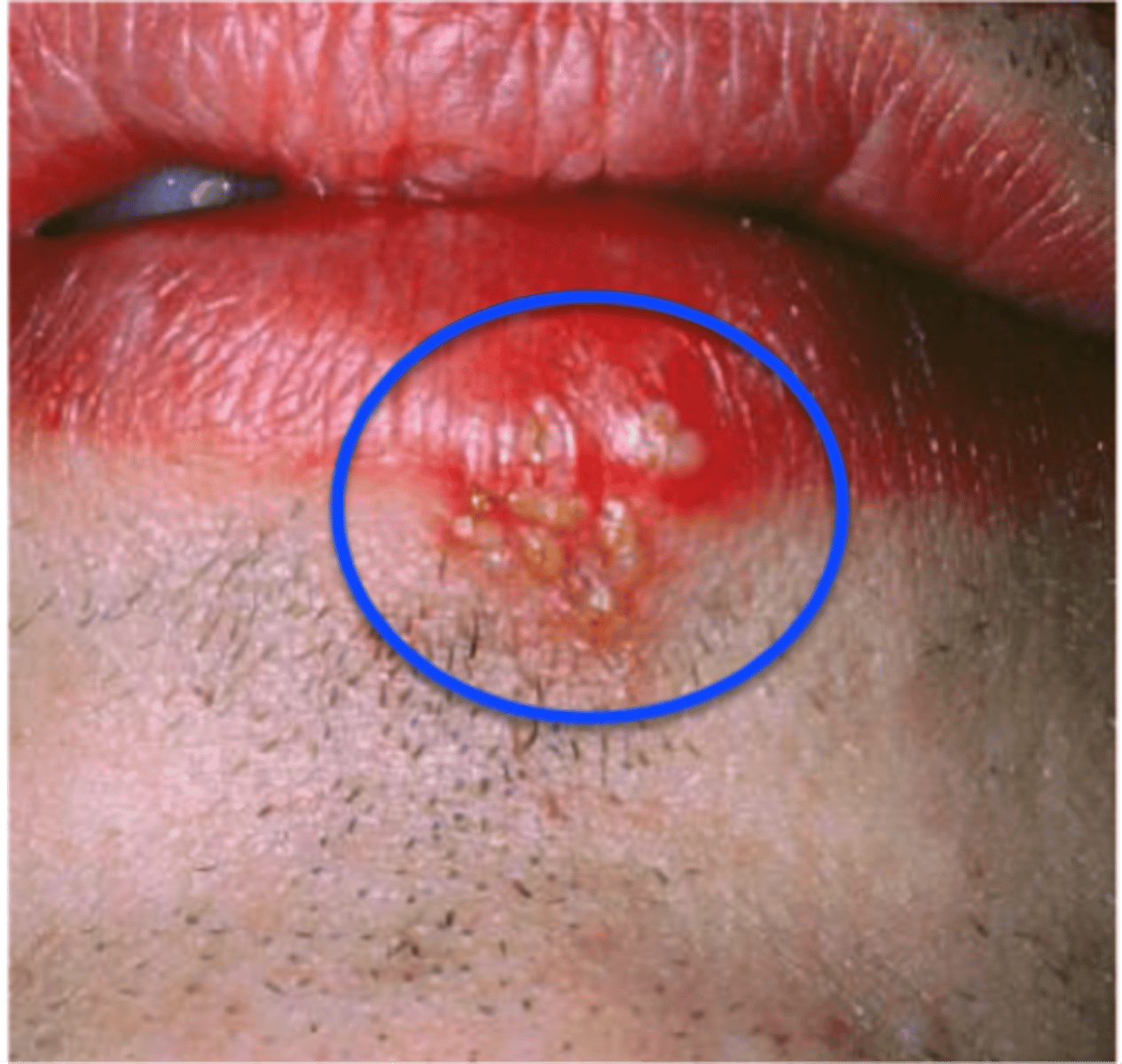
Herpes Labialis transmission
Direct contact with vesicle or vesicular fluid

Herpes Labialis prevention
Handwashing, avoiding kissing or oral sex during an active outbreak, no vaccine
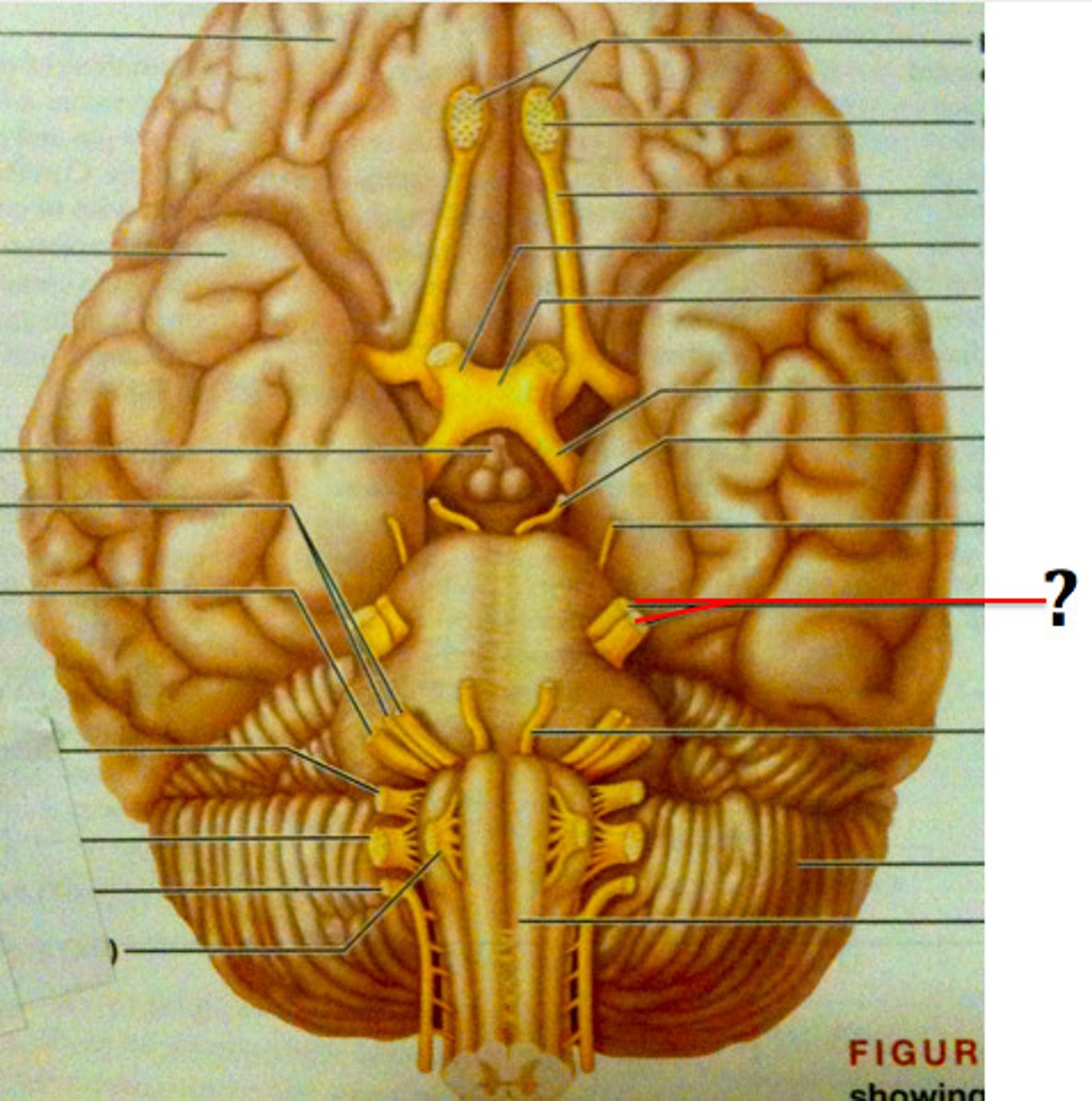
Herpes Labialis reoccurrence
Virus lives in the sensory neurons of the trigeminal (5th cranial nerve) ganglion (which relays sensory information from the face and head to the CNS)
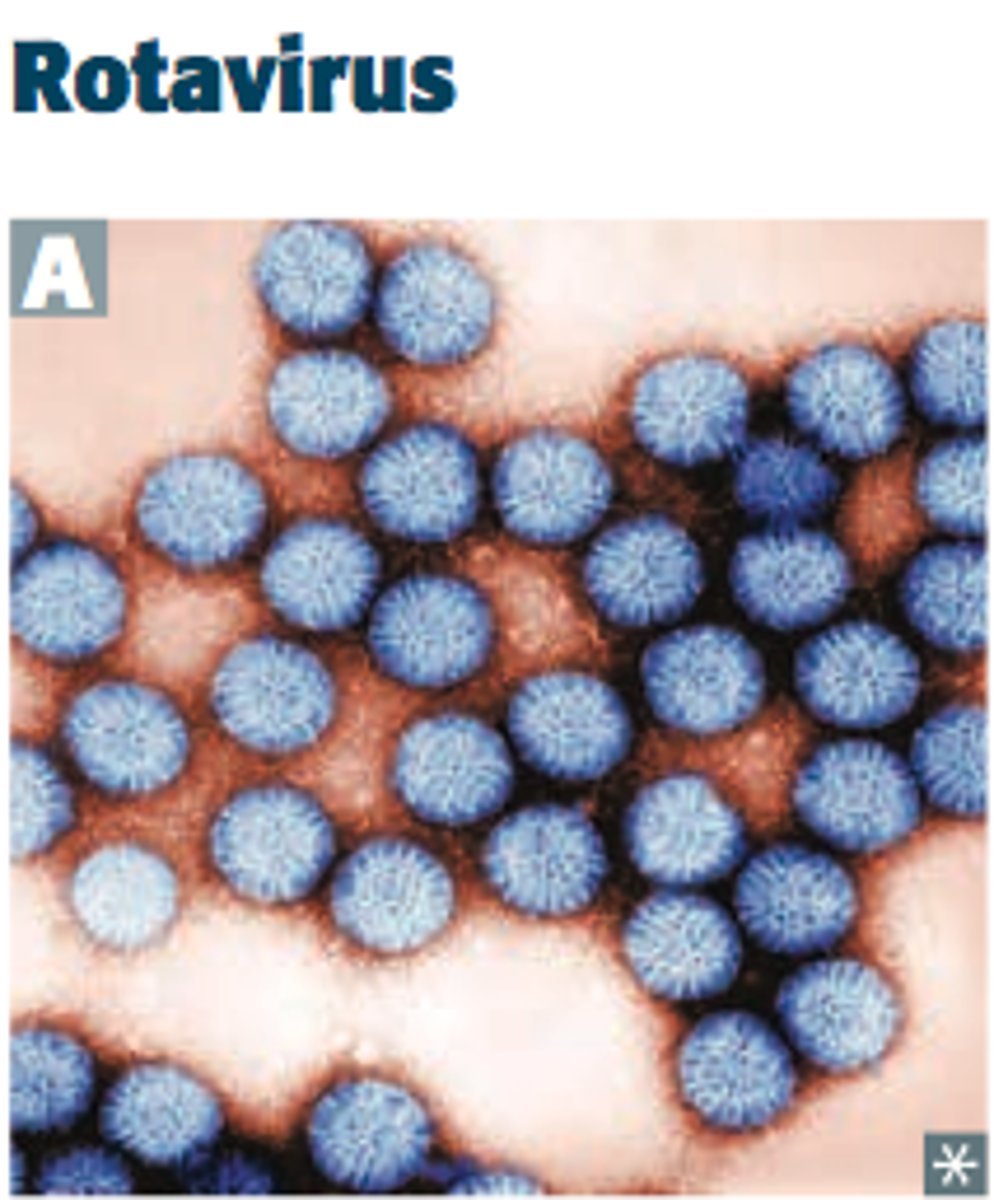
Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) pathogen
Rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus
Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) S+S
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dysentery, severe dehydration, fever; self-limiting lasting ≈ 48 hours

Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) transmission
Fecal-oral route, from infected humans or shellfish

Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) prevention
Handwashing, disinfecting surfaces (especially in the bathroom and kitchen), rotavirus vaccine

Viral Hepatitis pathogens
Hepatitis A virus (HAV)
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Hepatitis D virus (HDV)
Hepatitis E virus (HEV)
Acute viral hepatitis
HAV and HEV
Pre-icterus phase
Myalgia, arthralgia, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, elevated ALT and AST
Icterus phase
Abdominal pain, increased serum bilirubin
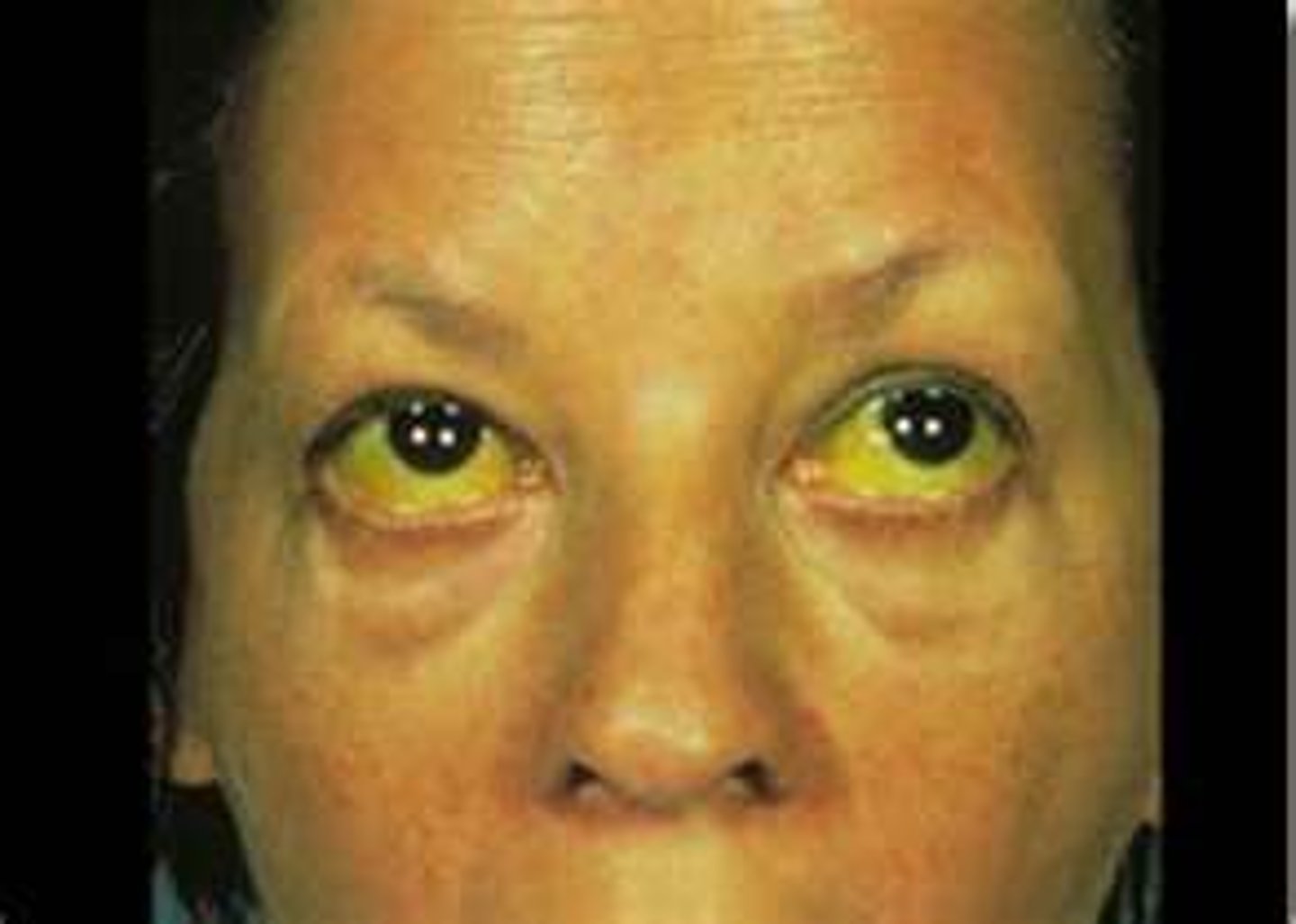
Convalescent phase
Increased sense of well-being, return of appetite, disappearance of jaundice

Chronic viral hepatitis
HBV, HCV, and HDV
Hepatitis A
Pathogen: HAV
Transmission: Fecal-oral route
Prognosis: Benign and self-limiting, does not cause chronic hepatitis or induce a carrier state
Prevention: HAV vaccine
Hepatitis B
Pathogen: HBV
Transmission: Unprotected sex, injected drug use
Prognosis: Serious, can cause chronic hepatitis or induce a carrier state
Prevention: HBV vaccine
Hepatitis C
Pathogen: HCV
Transmission: injection drug use
Prognosis: Serious, can cause chronic hepatitis or induce a carrier state
Prevention: NO VACCINE

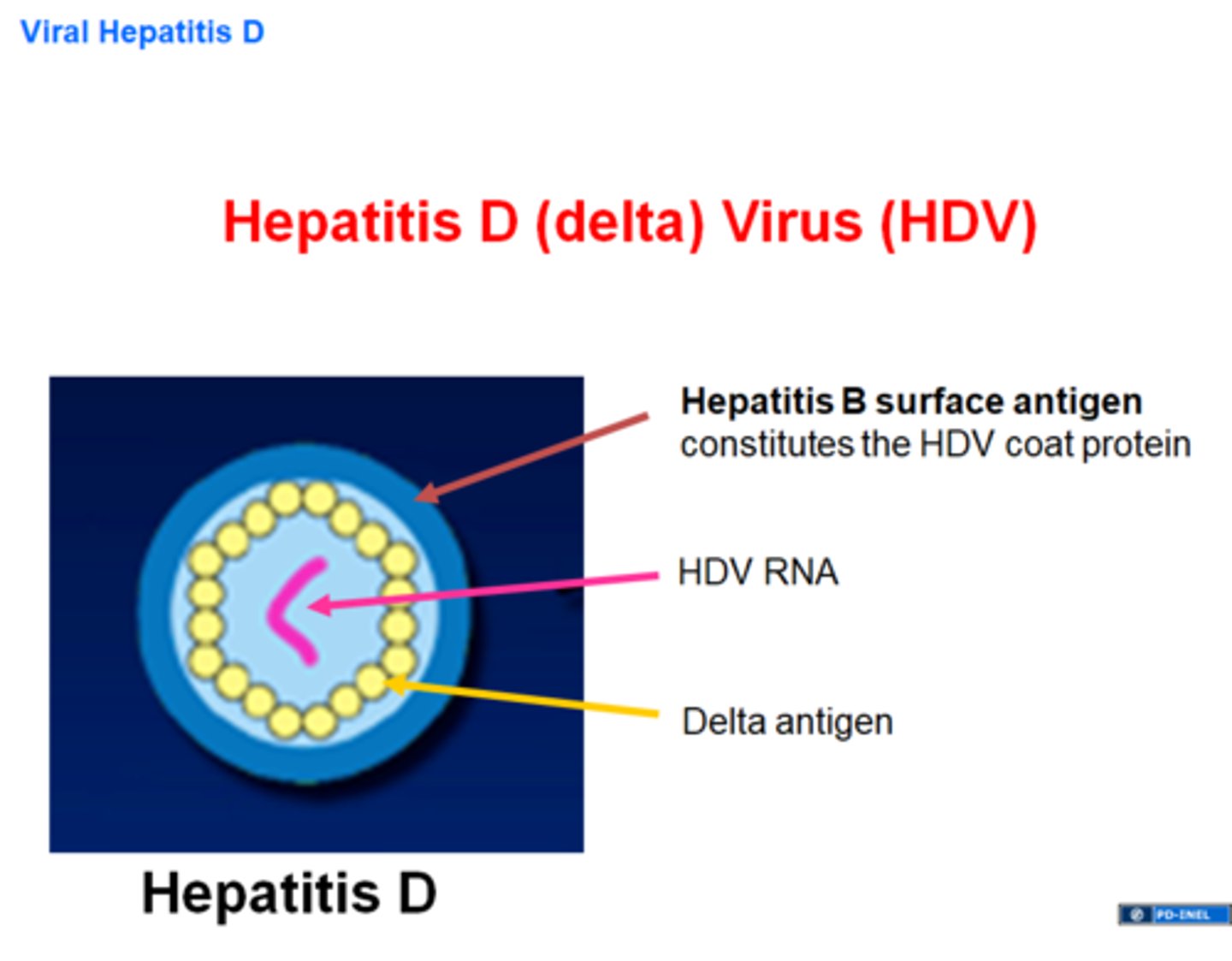
Hepatitis D
Pathogen: HDV
Transmission: Requires the presence of HBV for its replication, so it can only cause an infection in people who have an HBV infection
Prognosis: Serious, can cause chronic hepatitis or induce a carrier state
Prevention: HBV vaccine
Hepatitis E
Pathogen: HEV
Transmission: Fecal-oral route
Prognosis: Benign and self-limiting, does not cause chronic hepatitis or induce a carrier state
Prevention: HEV vaccine
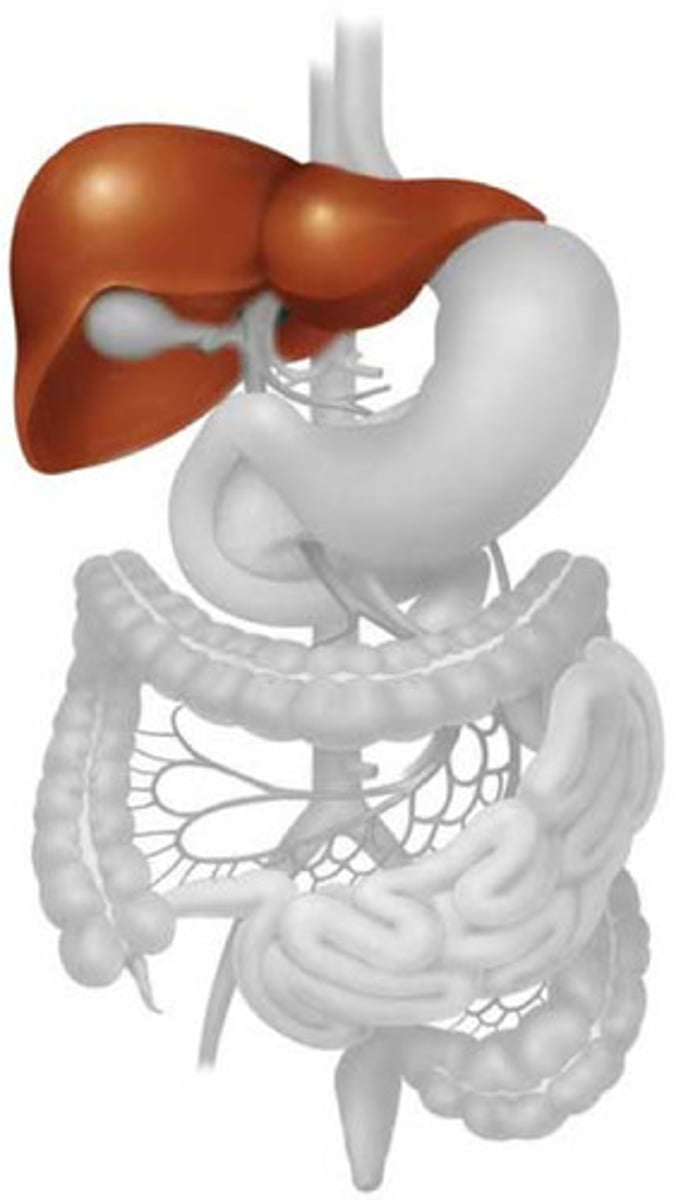
Herpes Genitalis (anogenital herpes) pathogen
Herpes simplex virus (usually type 2)
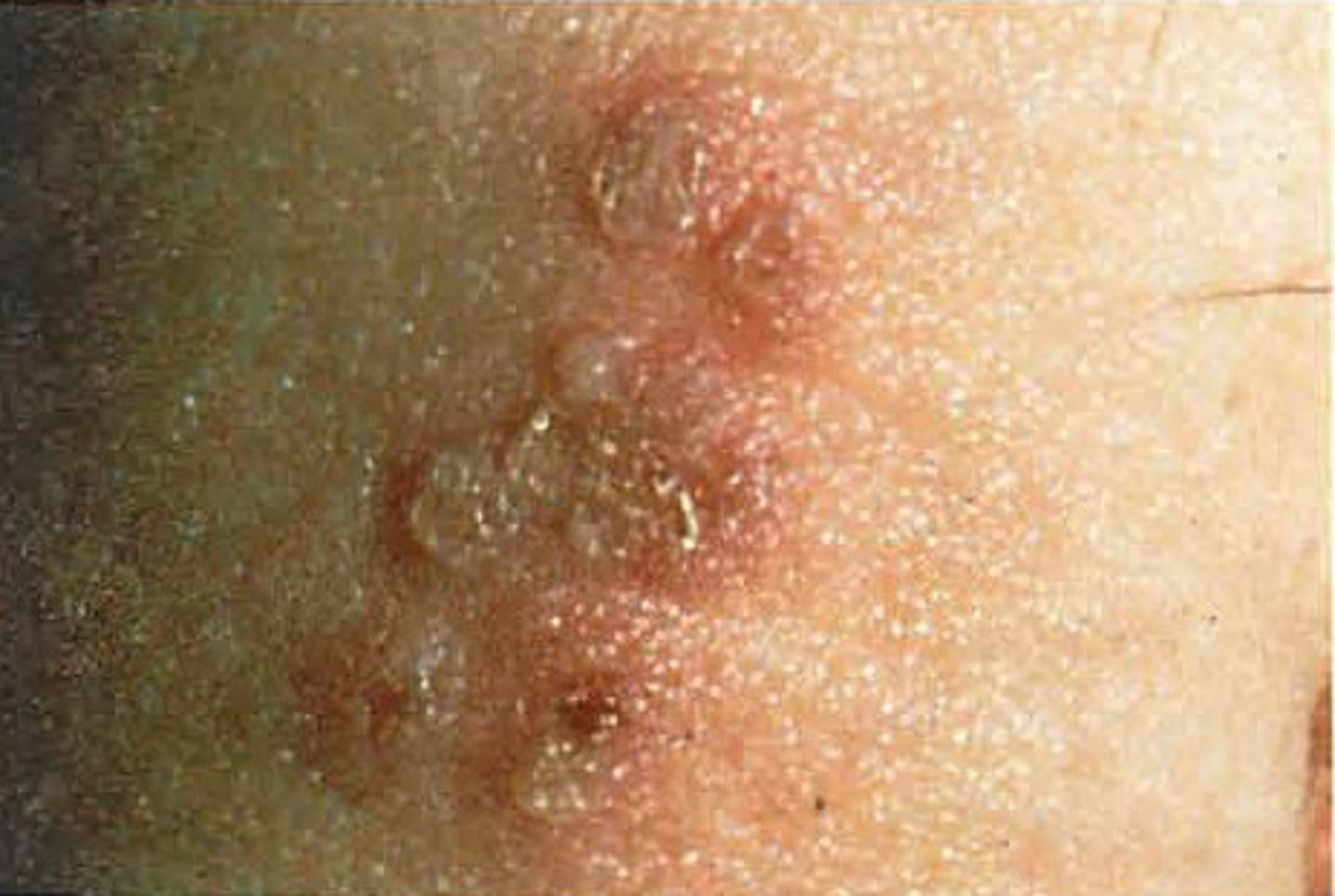
Herpes Genitalis S+S
Itching, then vesicular eruptions that break and crust, cause scarring
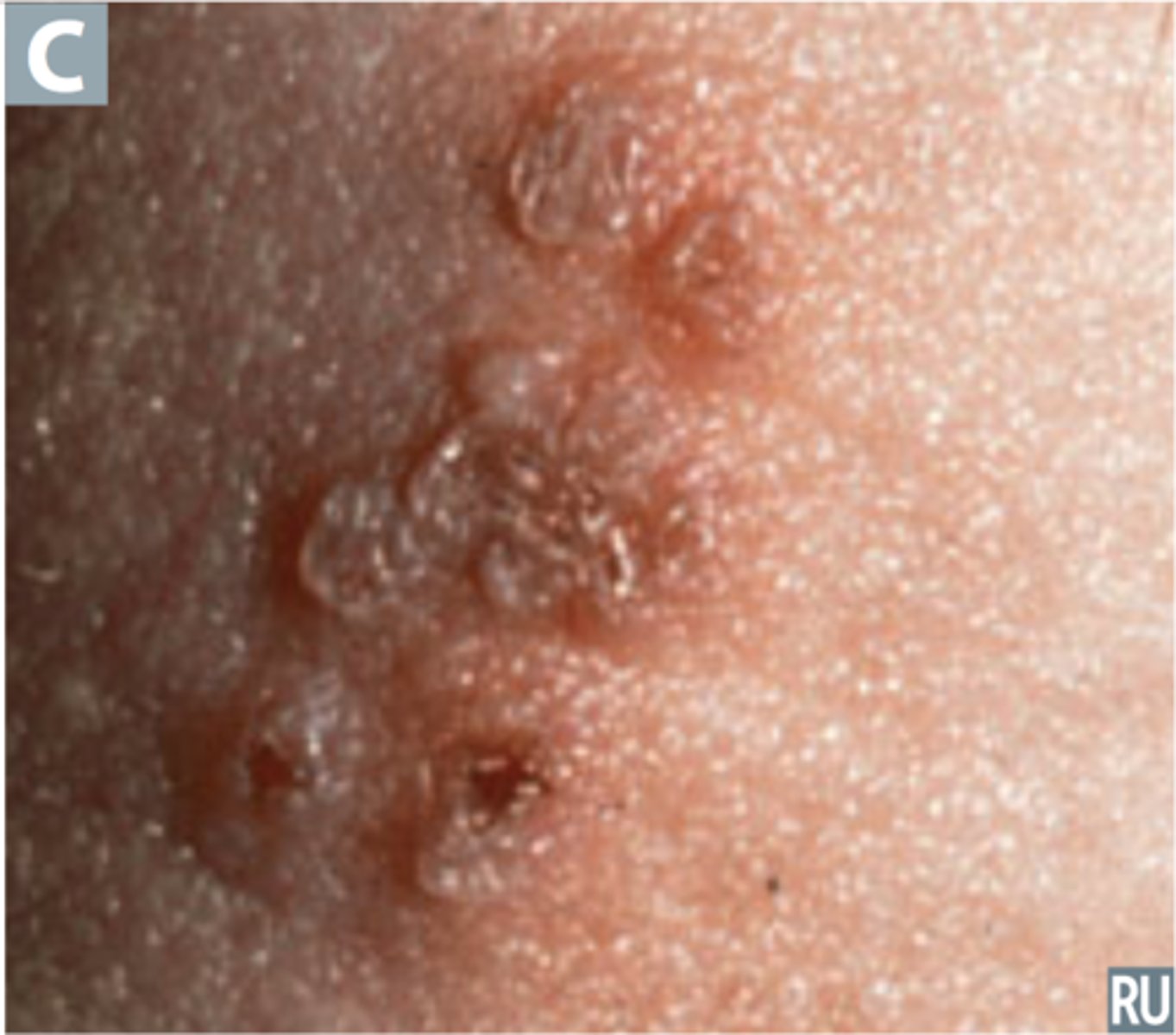
Herpes Genitalis transmission
Sexual contact (w/ infected secretions)
Herpes Genitalis prevention
Use condoms

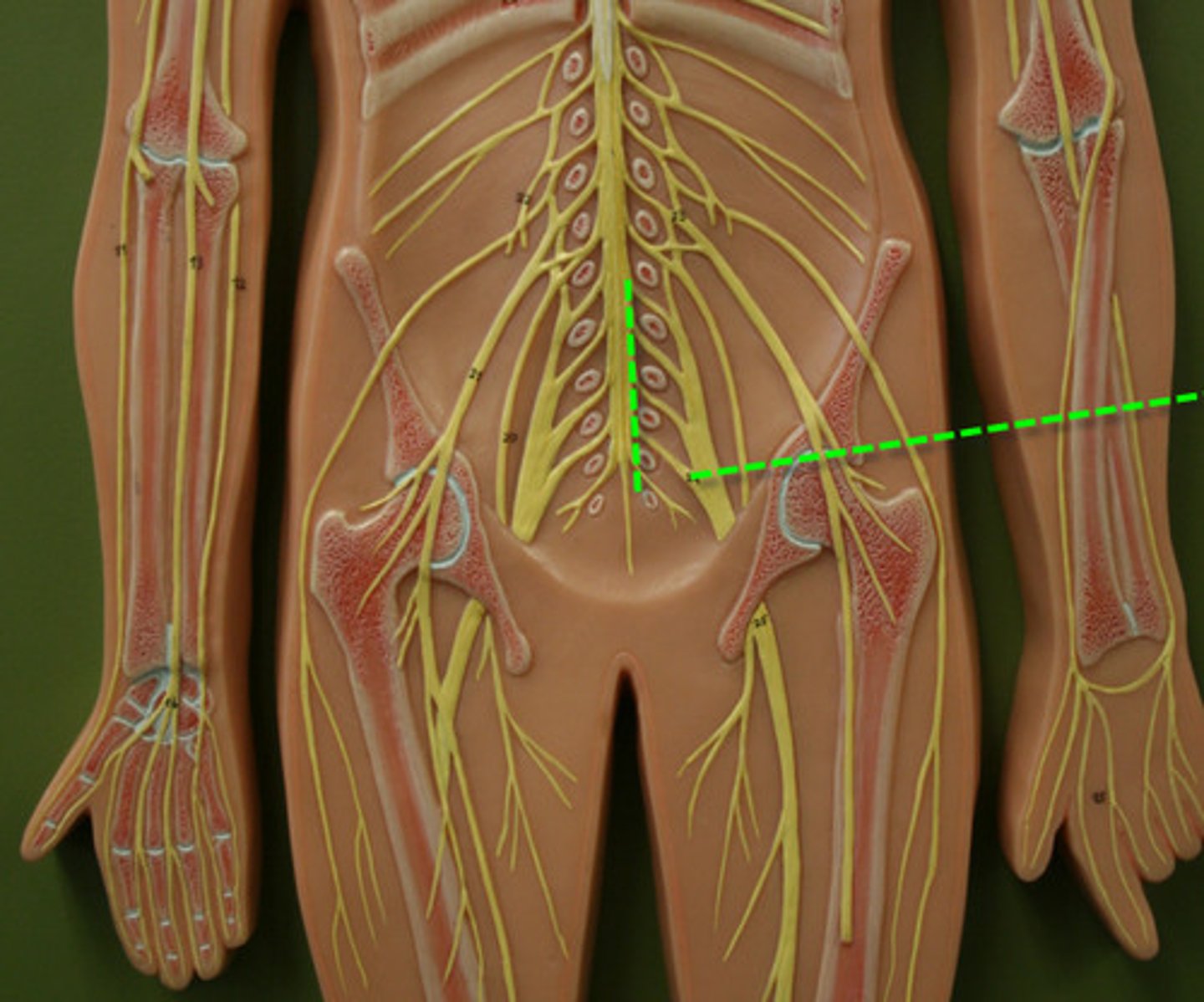
Herpes Genitalis recurrence
Virus lives in the dorsal root ganglion of the sacral spinal nerves
Condyloma Acuminatum pathogen
Human papillomavirus (>200 types)
Condyloma Acuminatum S+S
Genital warts: rapid growing, tiny, moist, pink/red, may become cauliflower like
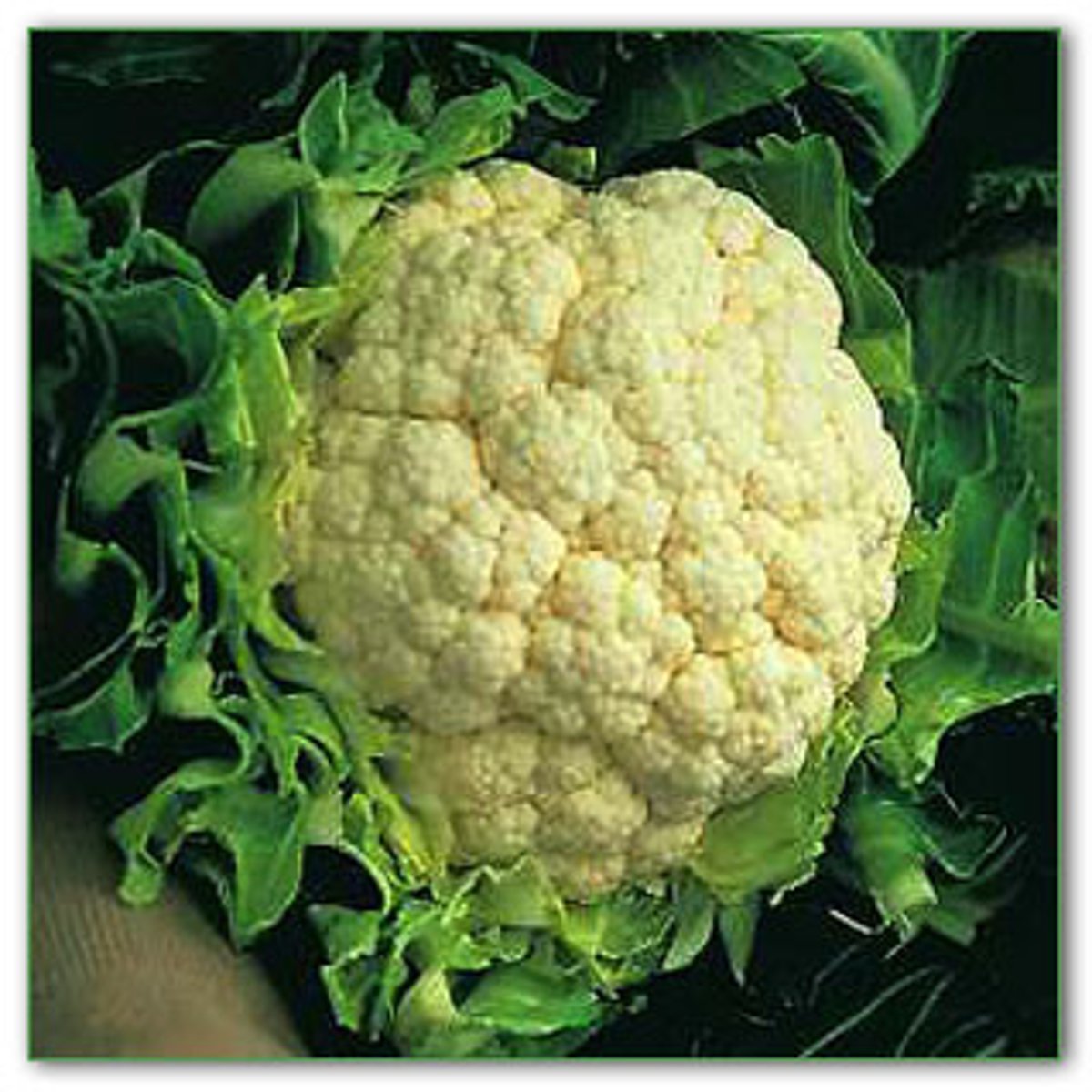

Condyloma Acuminatum transmission
Sexual contact
Condyloma Acuminatum prevention
HPV vaccine
2 doses usually given 11-12 years

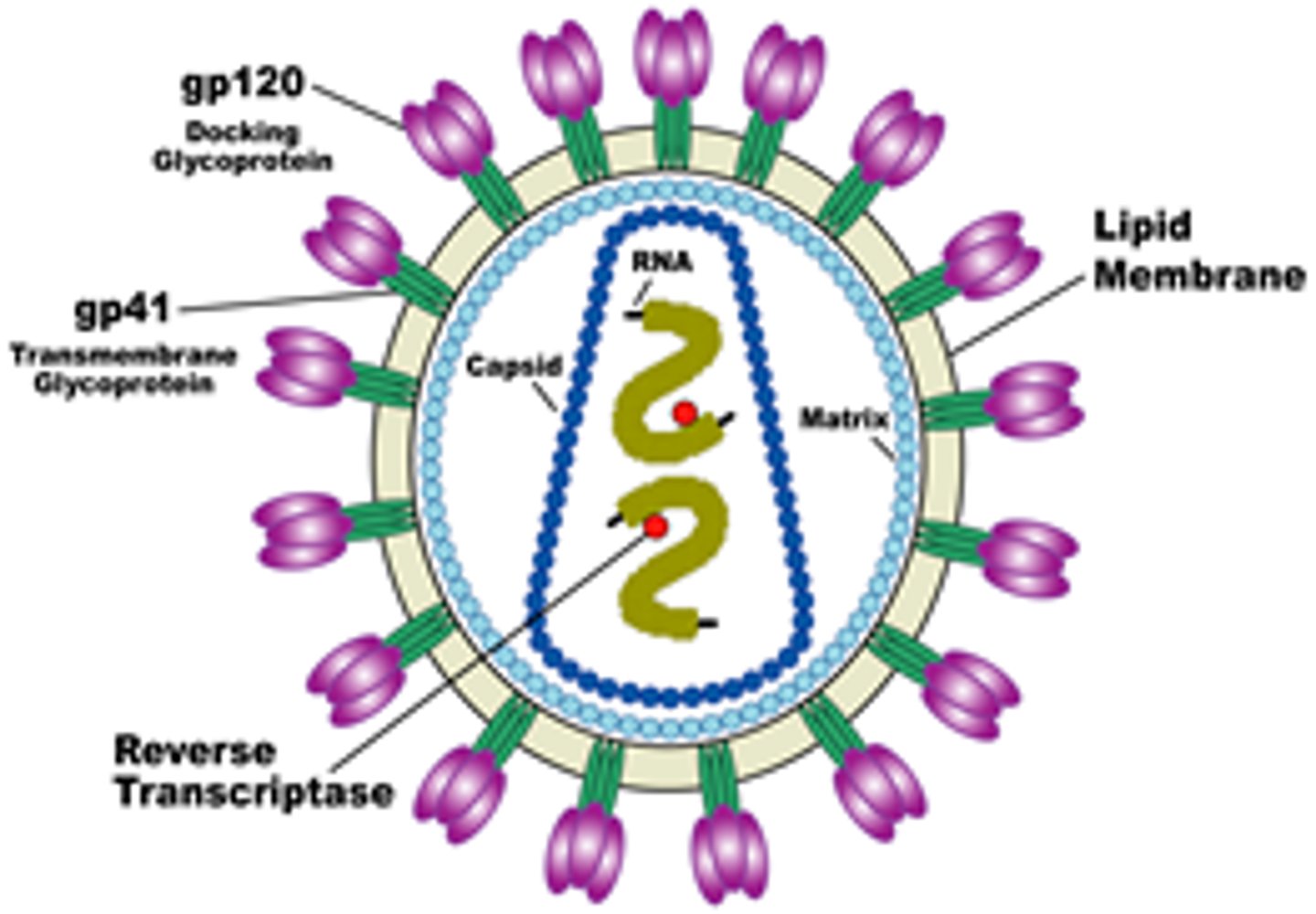
HIV Infection & AIDS pathogen
Human immunodeficiency viruses (types 1 and 2)
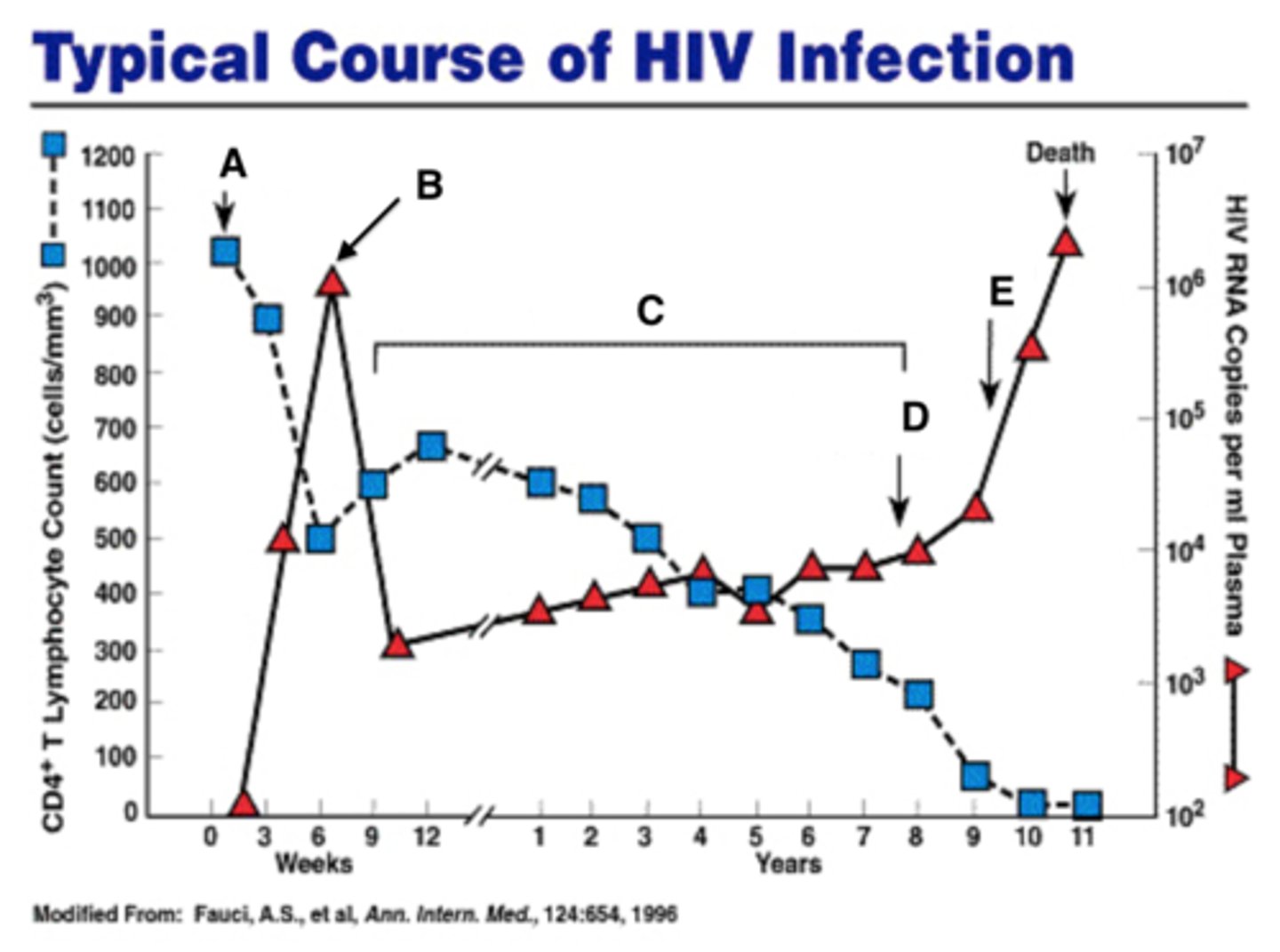
Acute HIV Infection
Flu-like symptoms that appear 2 weeks after contraction of virus

Chronic HIV infection
No specific S+S (can last 10 years or longer)
AIDS
Fatigue, recurrent fever, chronic diarrhea, weight loss, rashes
CD4+ helper T cell count < 200 cells per mm3 of blood
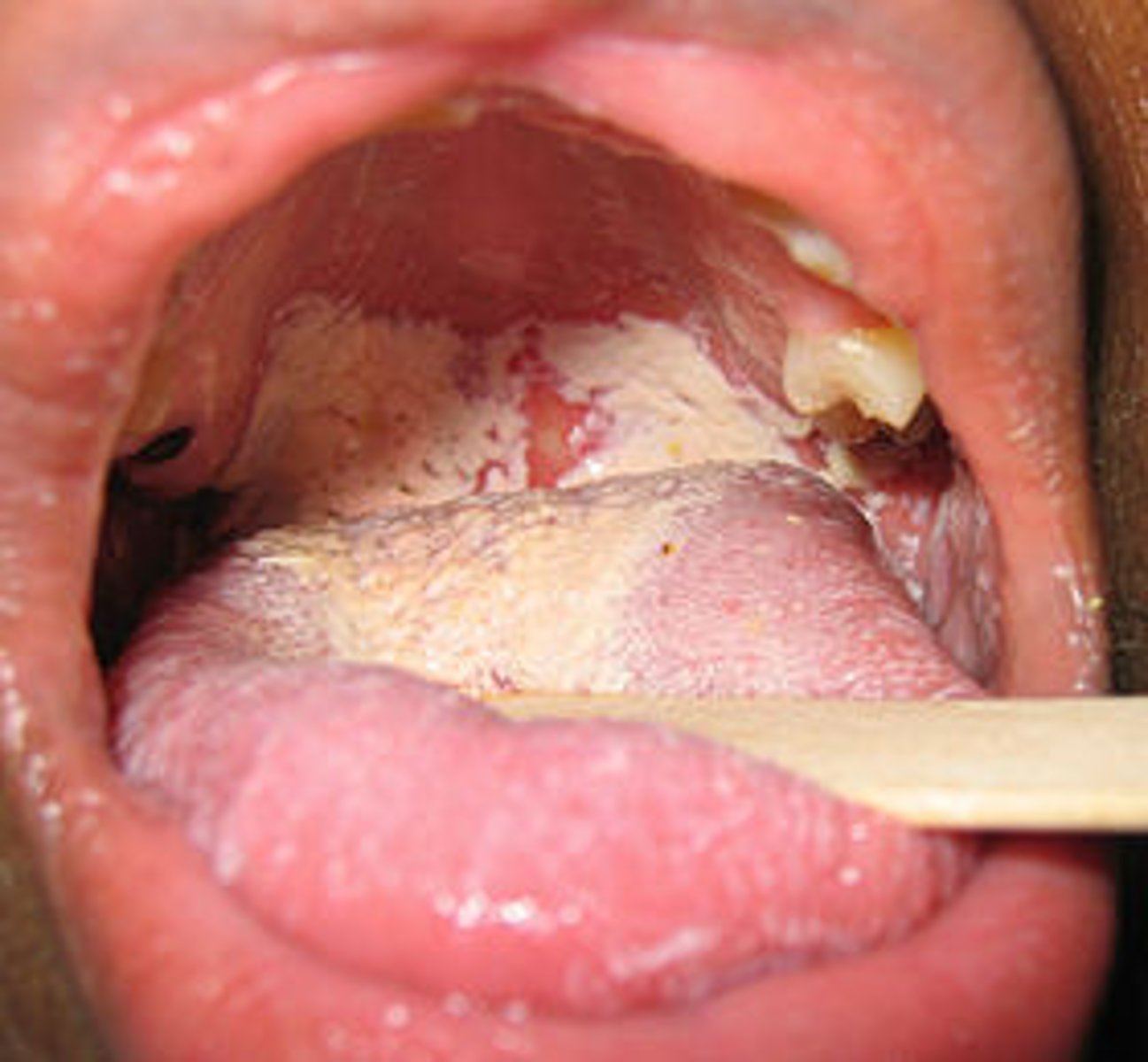
Candida albicans infection
HIV opportunistic infection --> causing yeast infection in the mouth, thrush
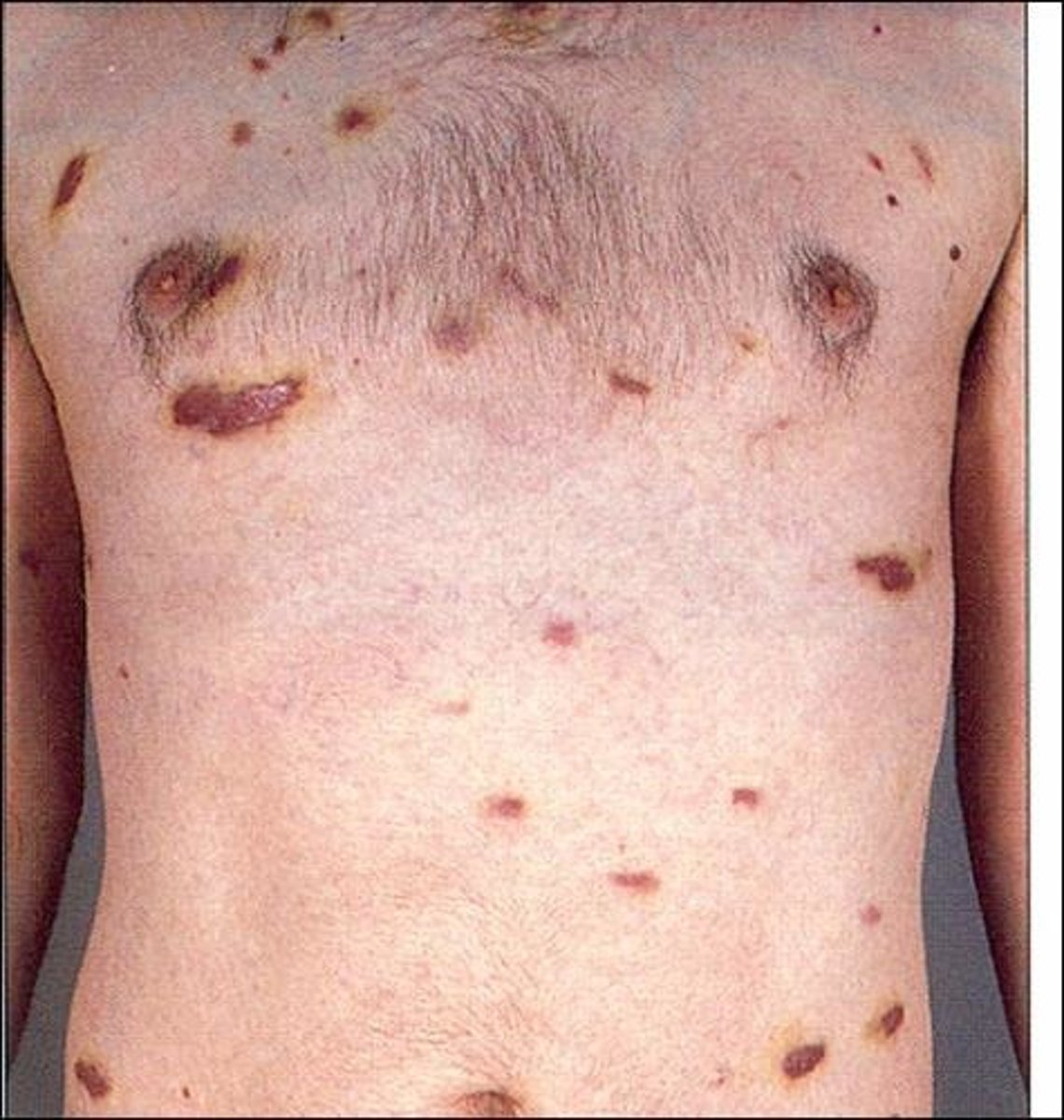
Human herpesvirus 8 infection
HIV opportunistic infection --> affects the endothelial lining of small blood vessels (resulting in Kaposi sarcoma)
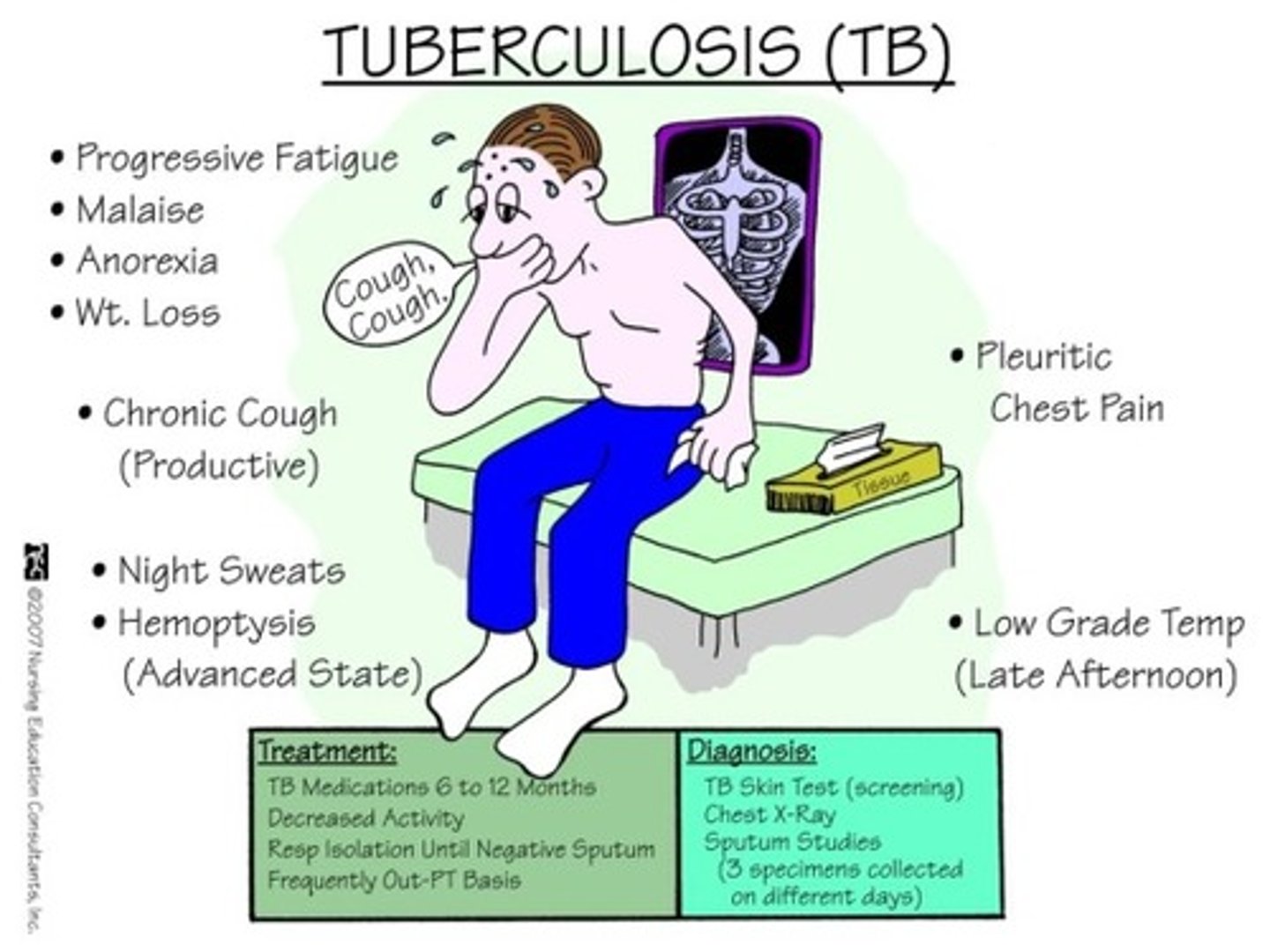
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
HIV opportunistic infection --> Bacterium that can affect the lungs (resulting in pulmonary tuberculosis)
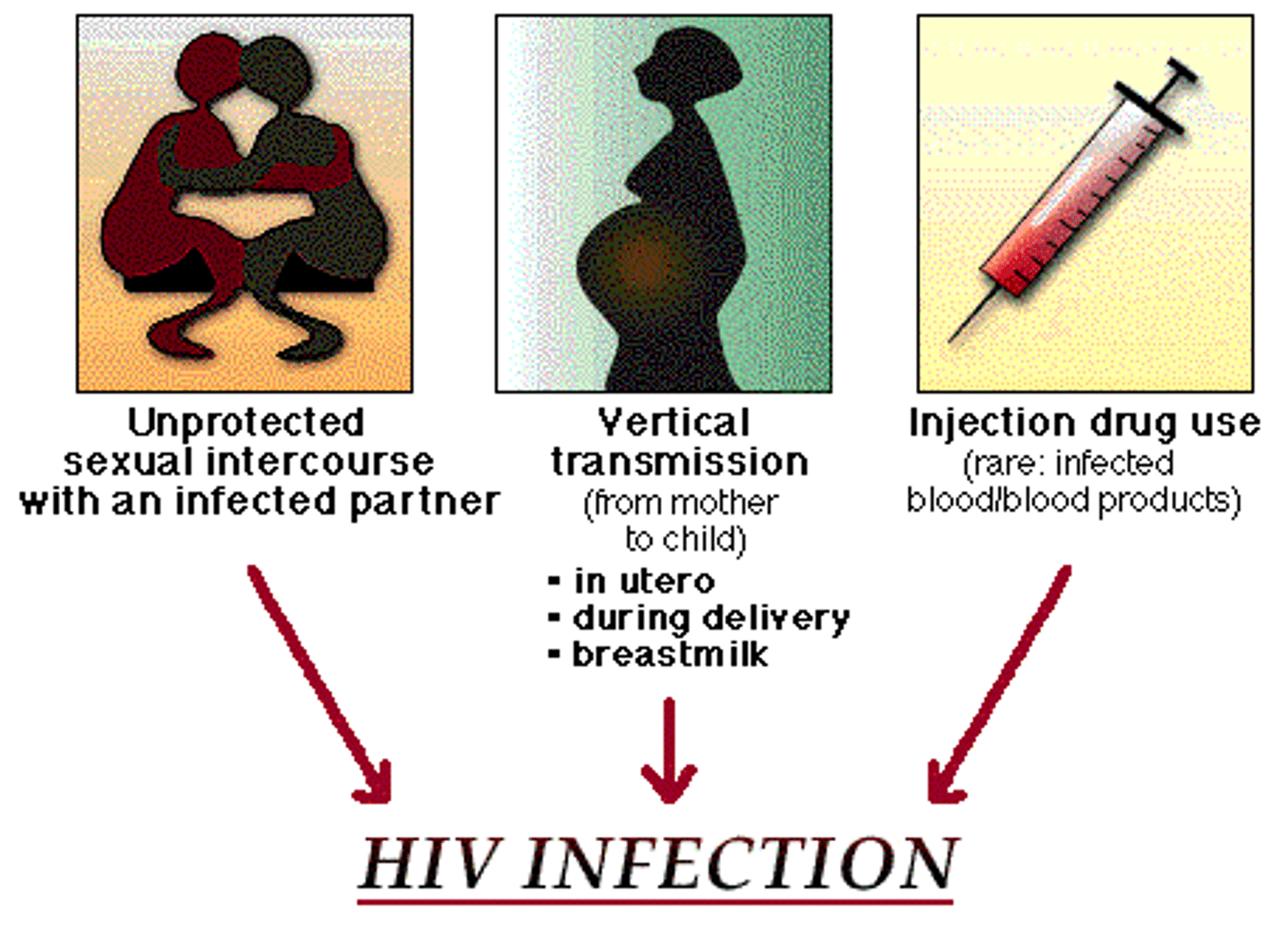
HIV Infection & AIDS transmission
Sexual contact, blood contact, mother-to-baby
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
Pill containing antiviral drugs that is taken before exposure to HIV to prevent infection

Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
Antiviral drugs used after possible HIV exposure

Treatment as prevention (TasP)
The use of antiretroviral therapy among infected individuals to decrease their risk of transmitting HIV to their partners
Infectious Parotitis pathogen
Mumps virus
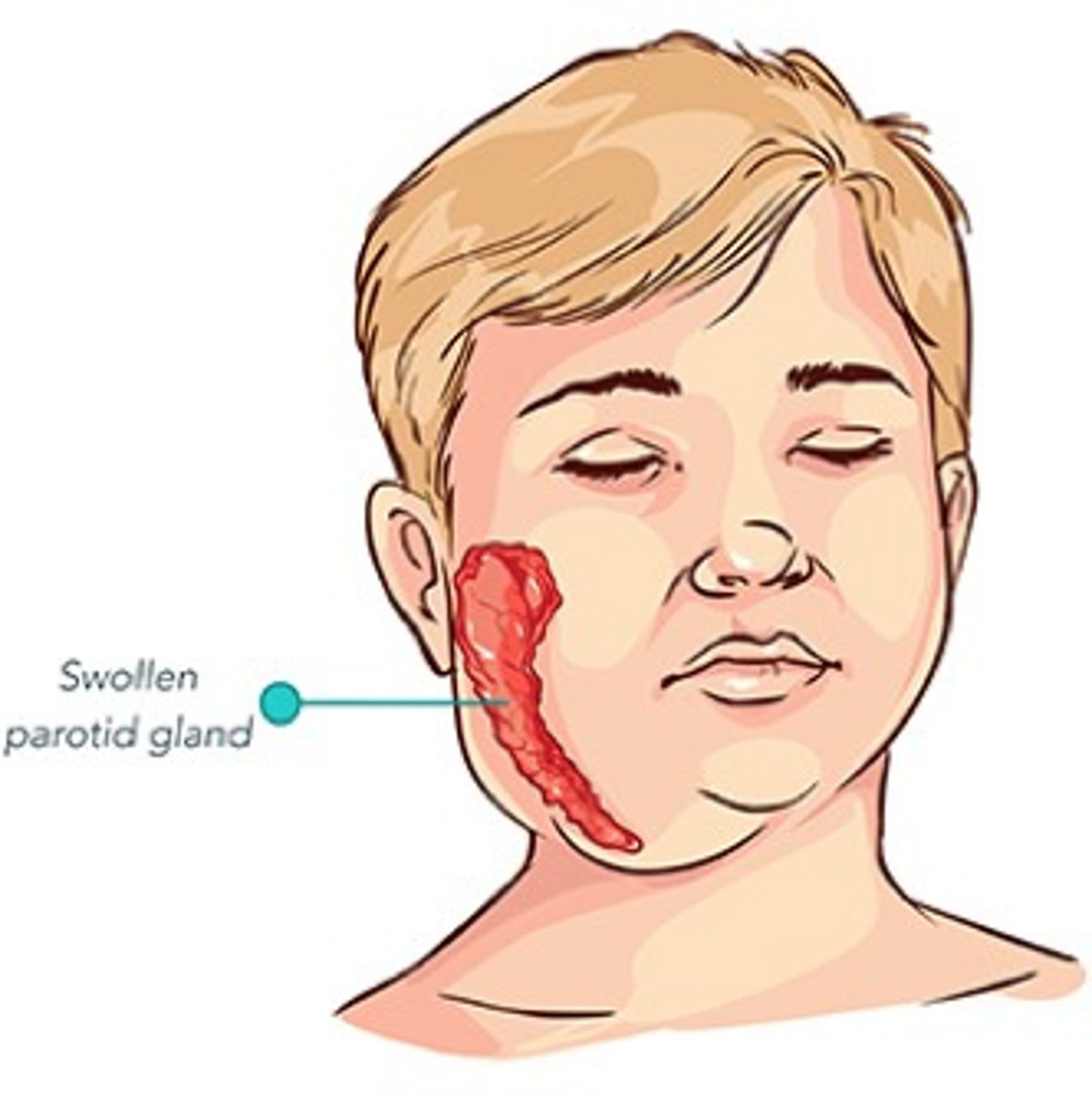
Infectious Parotitis (Mumps) S+S
Fever, poor appetite, fever, myalgia, malaise → painful swelling of parotid glands
Complications: oophoritis, orchitis

Infectious Parotitis (Mumps) transmission
Inhalation or contact with oropharyngeal secretions
Infectious Parotitis (Mumps) prevention
MMR Vaccine
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers pathogens
1. Ebola virus
2. Marburg virus
3. Dengue virus
4. Zika virus
5. Yellow fever virus

Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers S+S
High fever, fatigue, dizziness, myalgia, arthralgia, bleeding under the skin, in internal organs, or from facial cavities
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers transmission
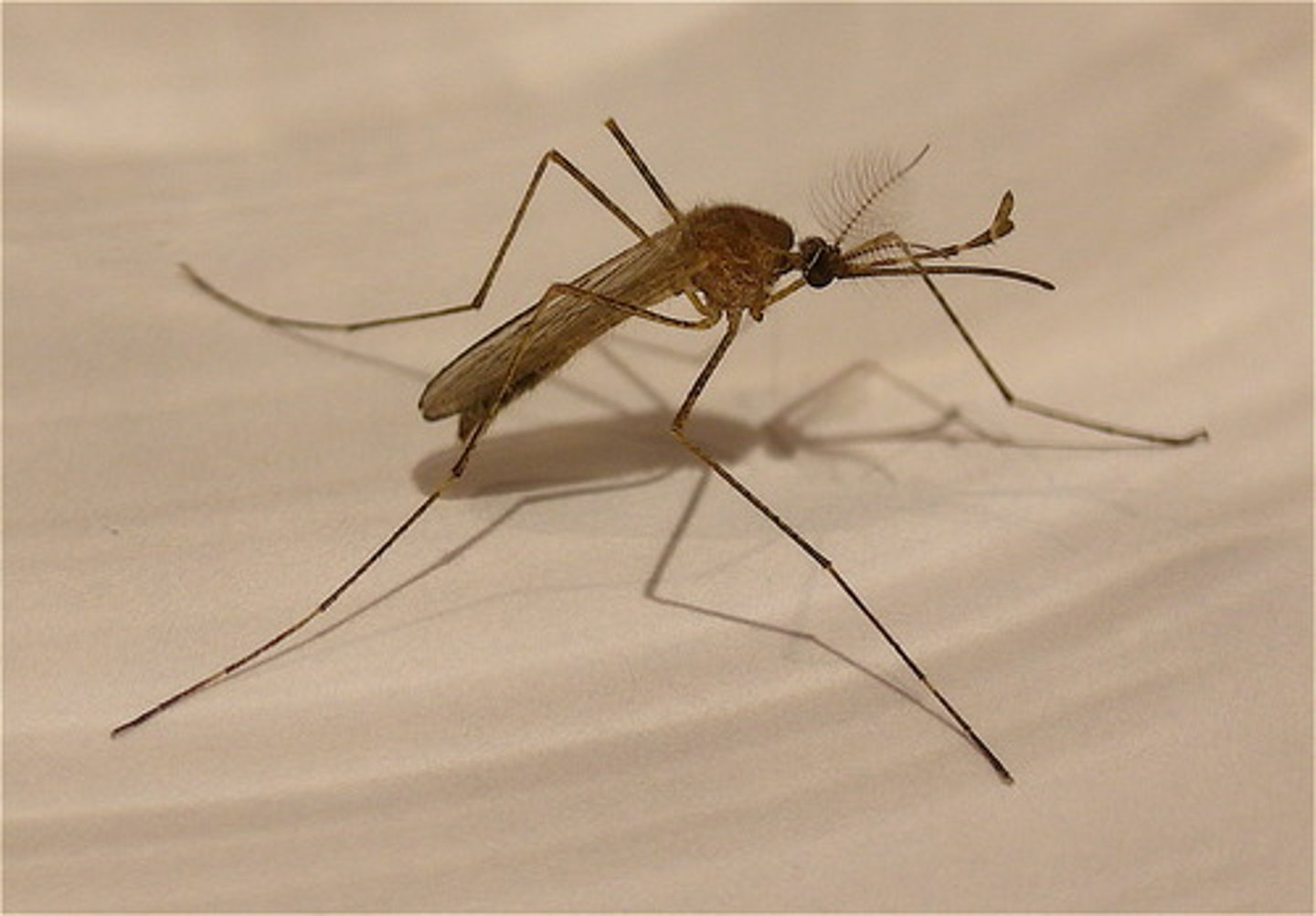
Ebola/Marburg: body fluid contact
Zika/Dengue/Yellow fever: Aedes mosquito bite

Viral Meningitis pathogen
Several types of viruses
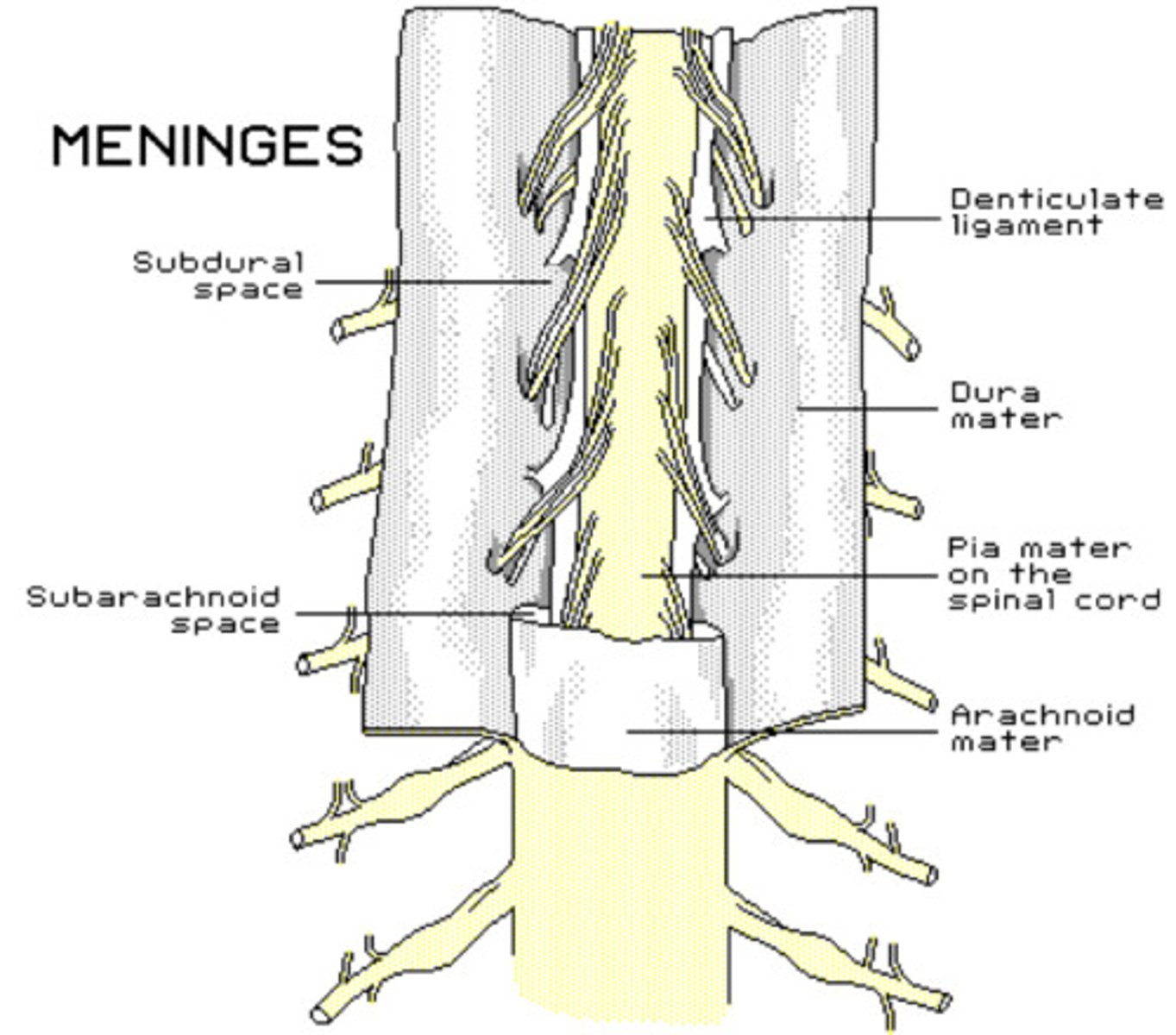
Viral Meningitis S+S
Fever, headache, nuchal rigidity, altered mental status (aseptic meningitis)
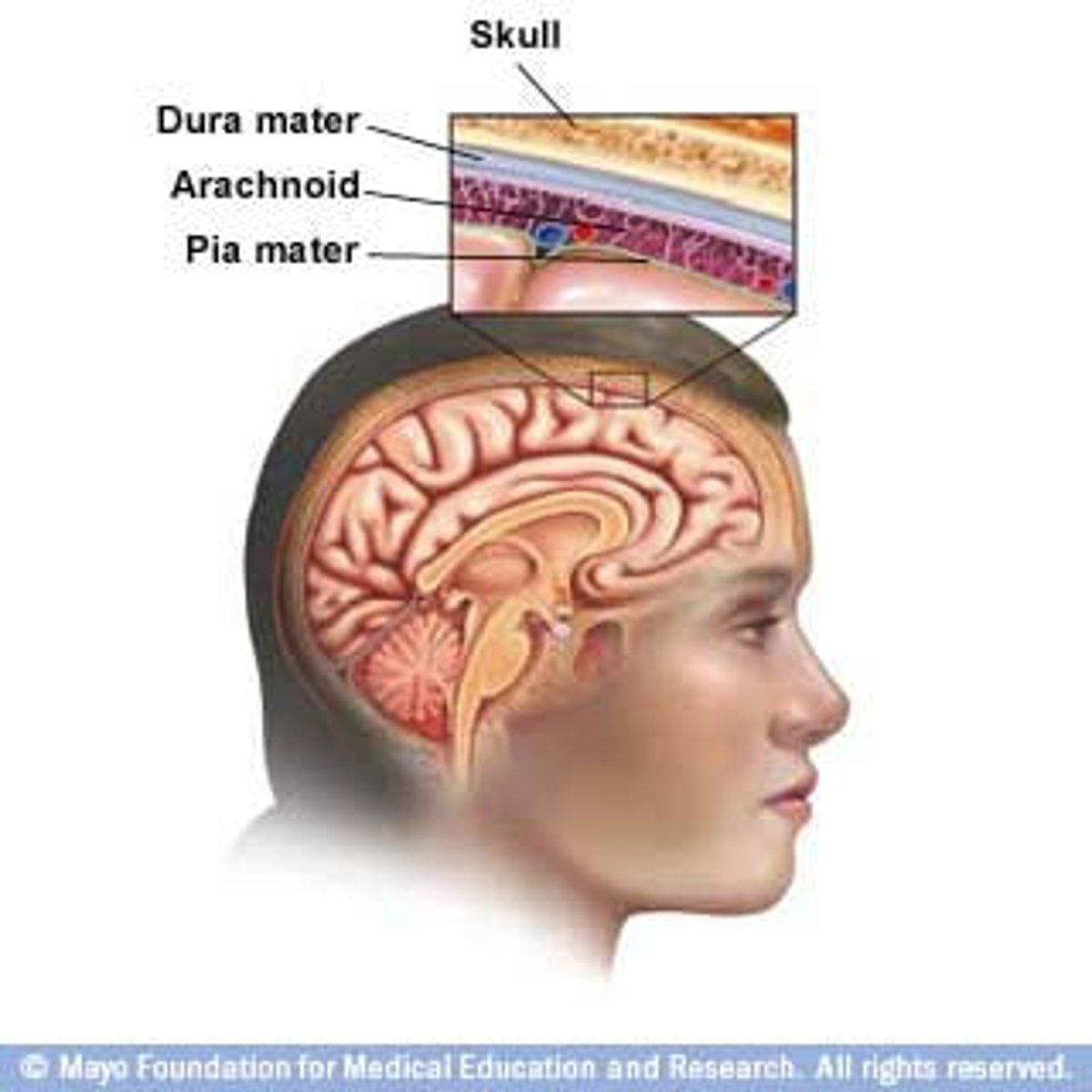
Viral Meningitis transmission
Varies depending upon the type of virus