NLN NEX SCIENCE PREP
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The transportation system of the cell. It moves materials around the cell
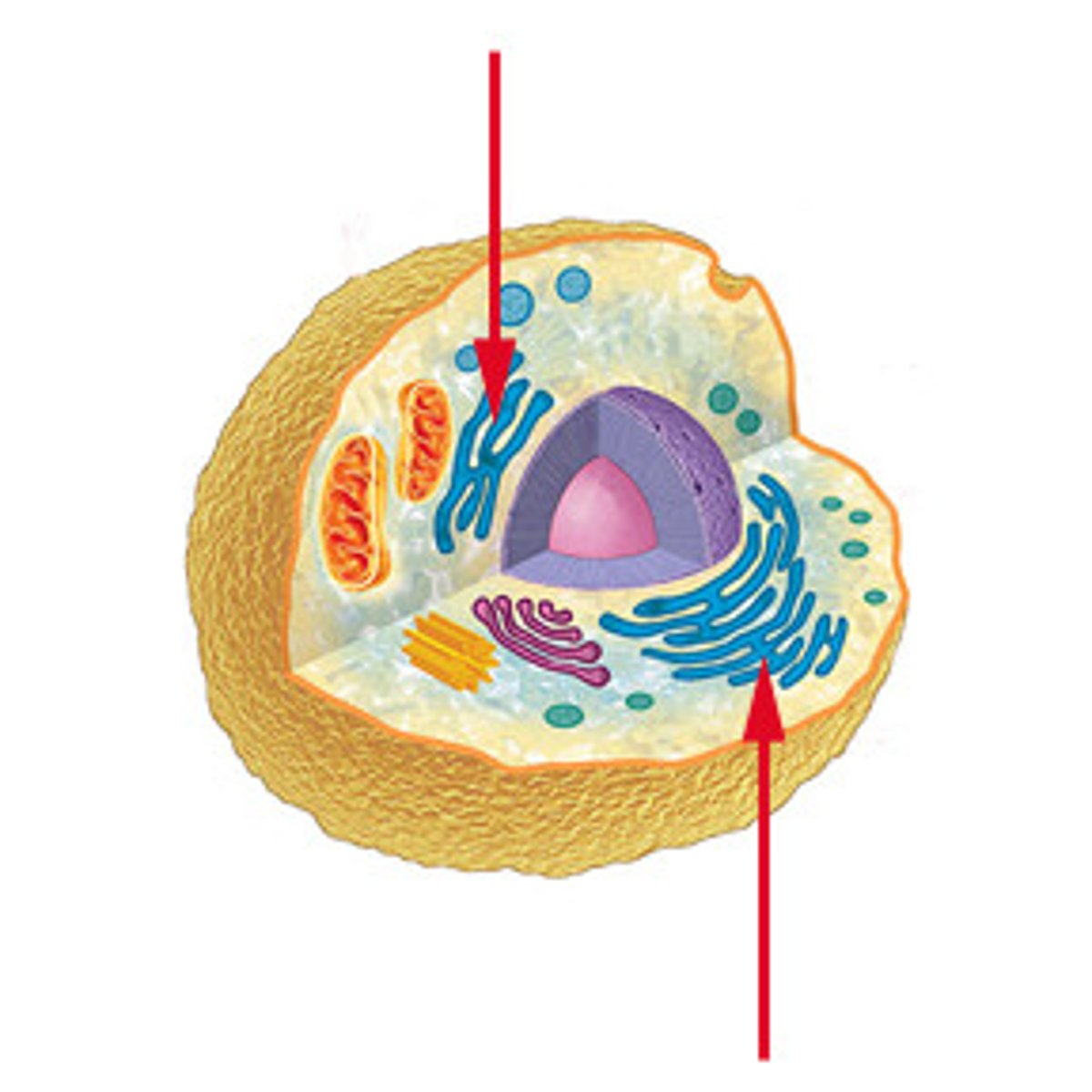
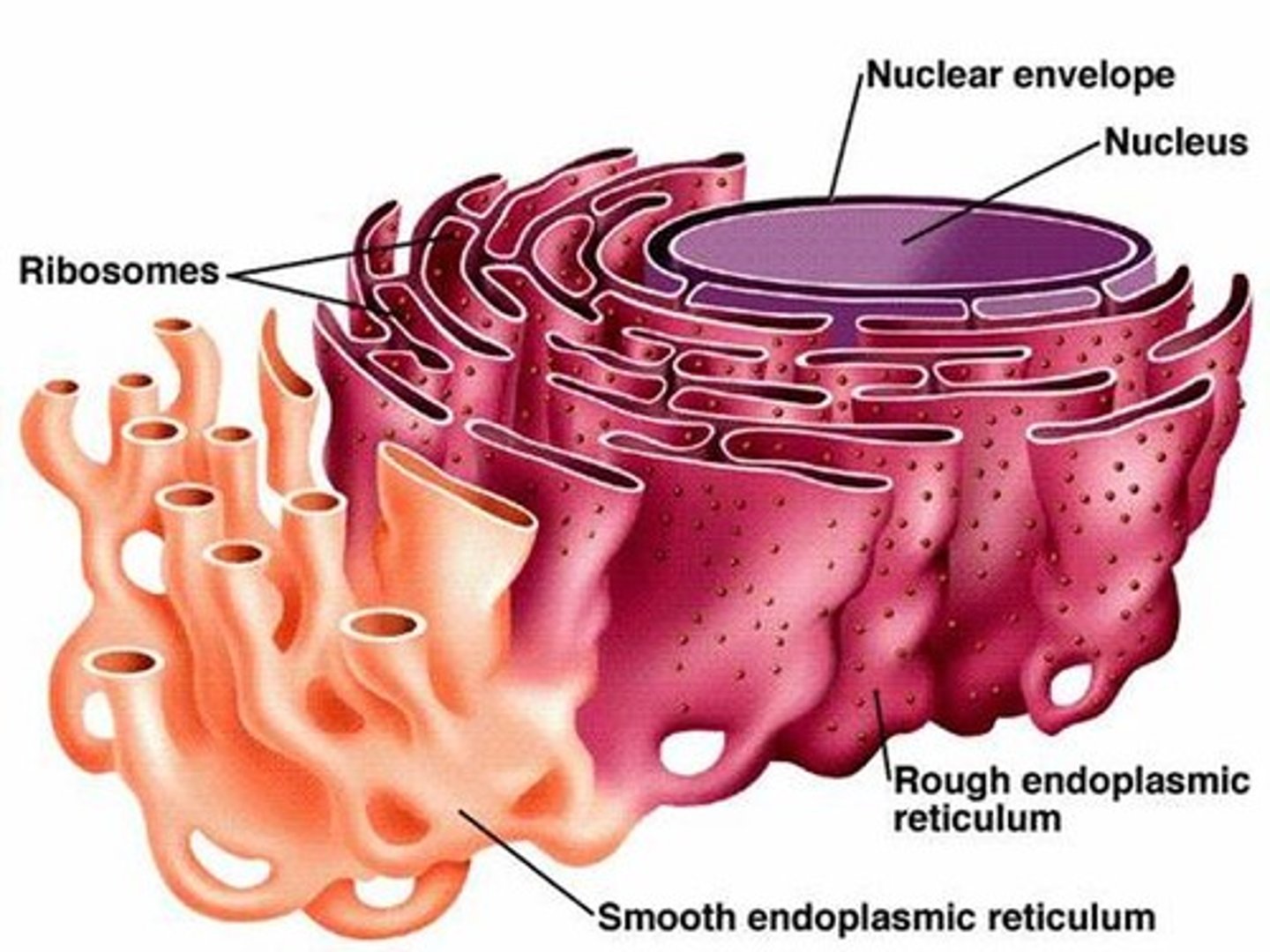
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Function -The production, folding quality control and despatch of some proteins, synthesizes phospholipids
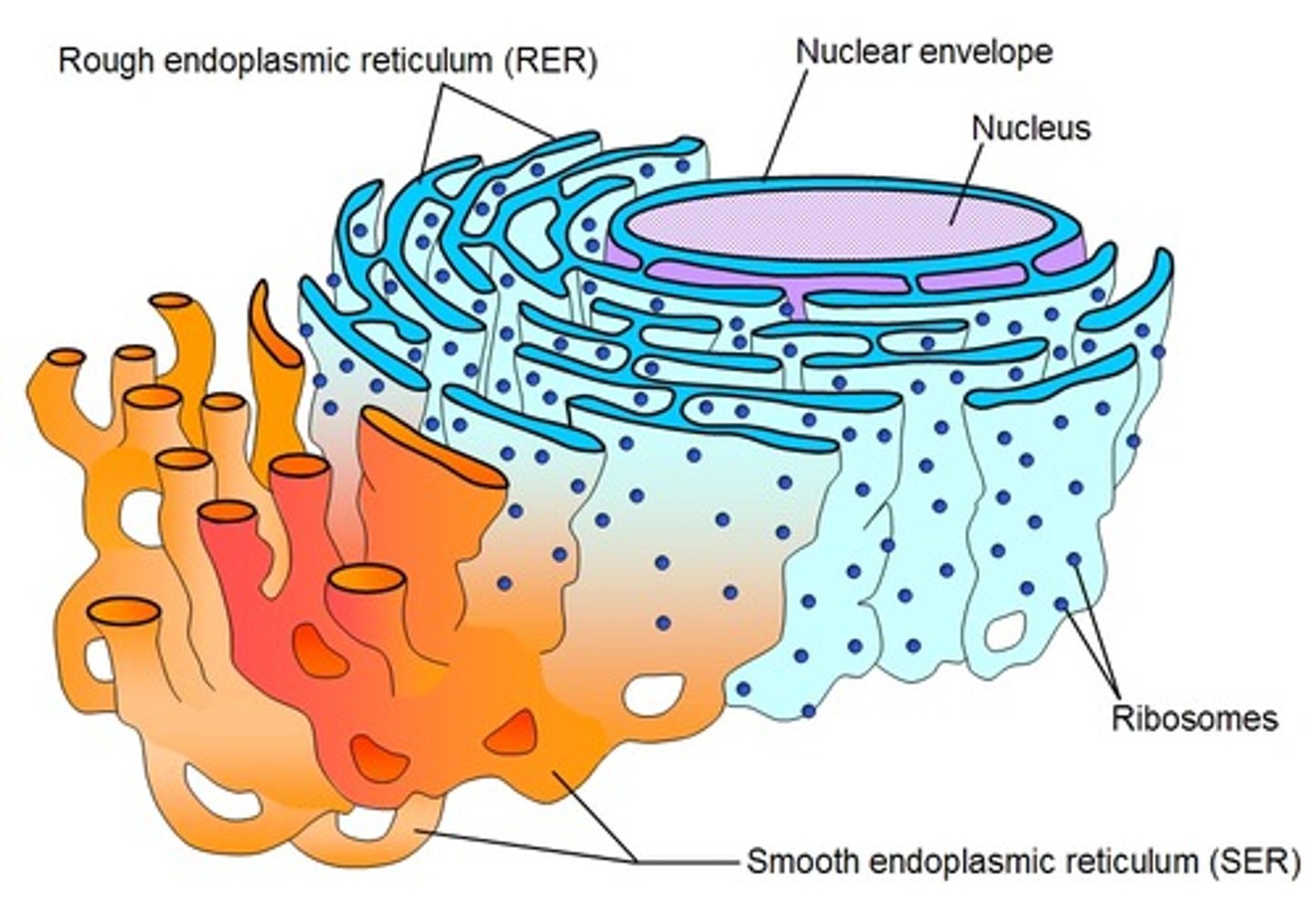
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
the region of the endoplasmic reticulum that has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface and it stores enzymes and minerals and the folding of proteins. Synthesizes carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones. Detoxifies chemicals like pesticides, preservatives, medications, and environmental pollutants, and stores calcium ions
Metabolism of fats
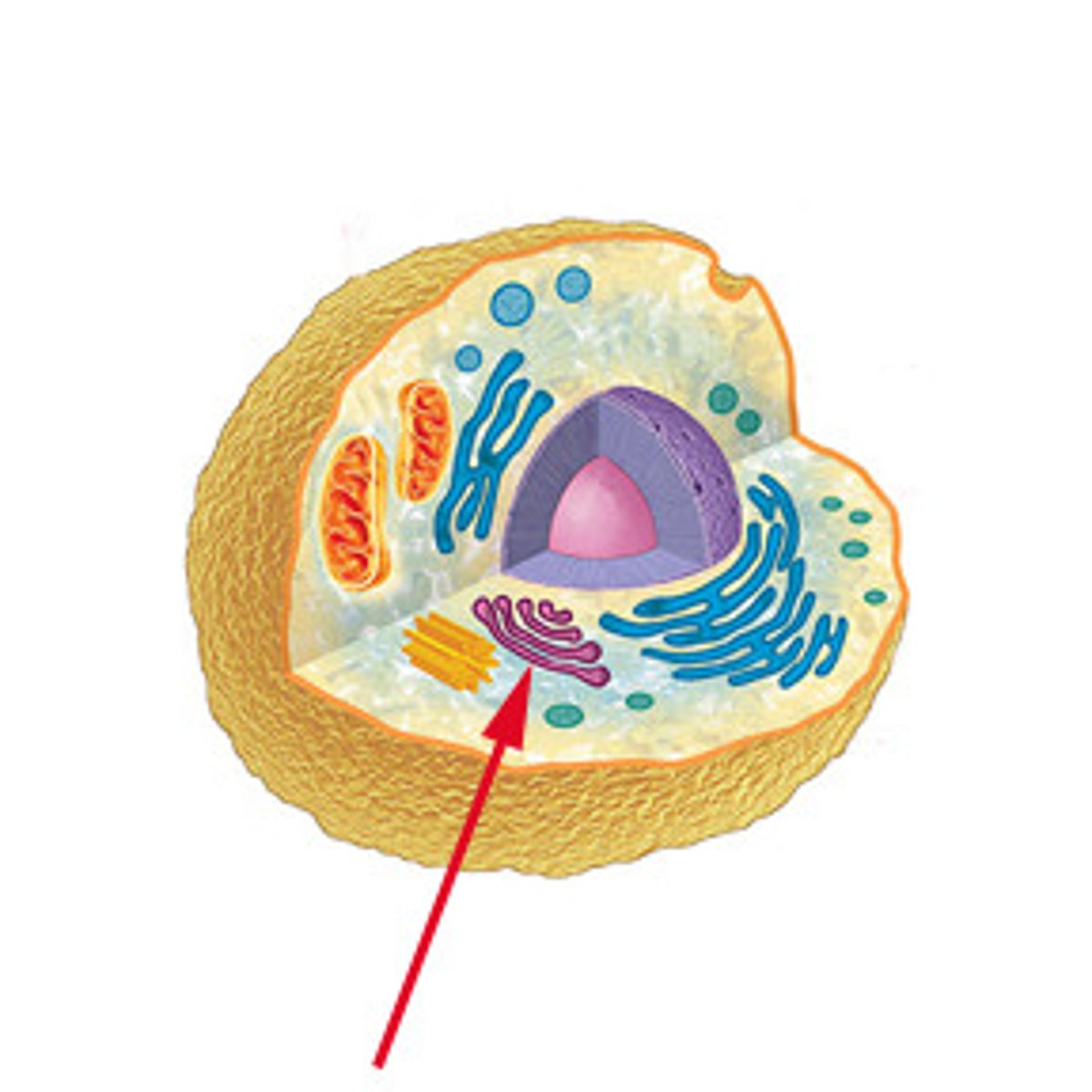
Golgi Apparatus
serves as a molecular warehouse and finishing factory for products manufactured by the ER. One side functions as a receiving dock and the other as a shipping dock
Lysosomes
is a membranous sac containing digestive enzymes.Also help digest food particle engulfed by a cell and remove or recycle damaged parts of a cell
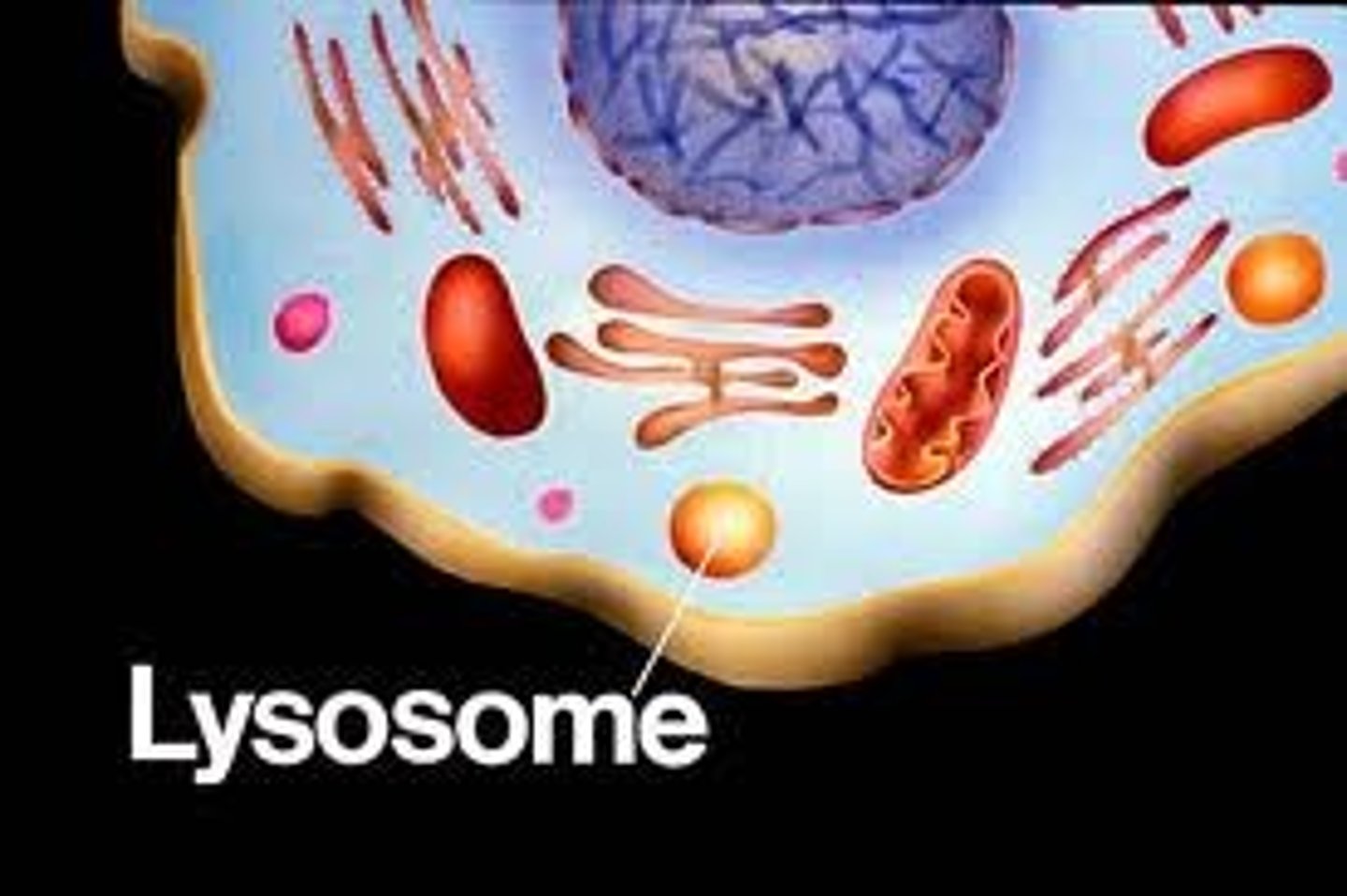
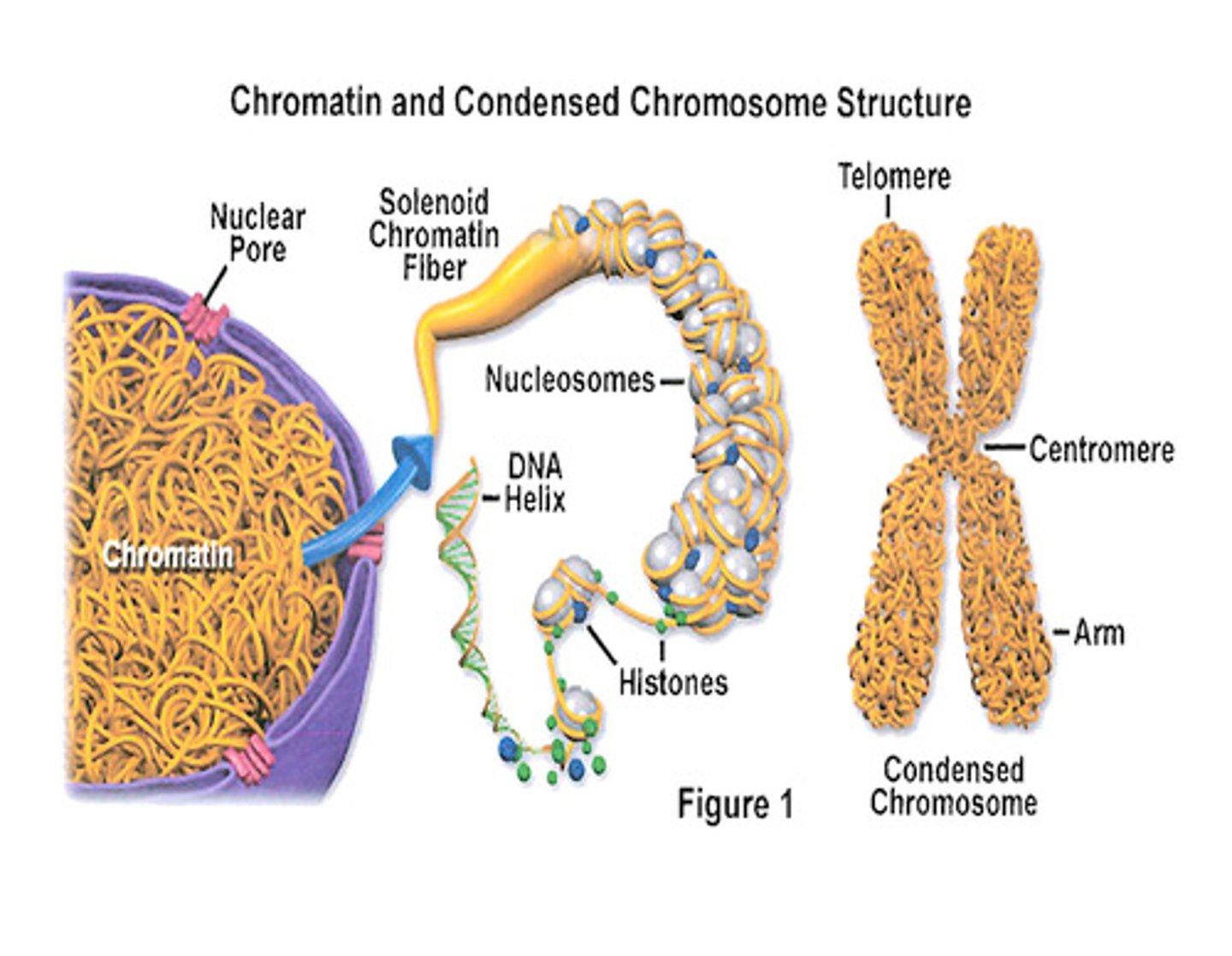
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins in the cell nucleus
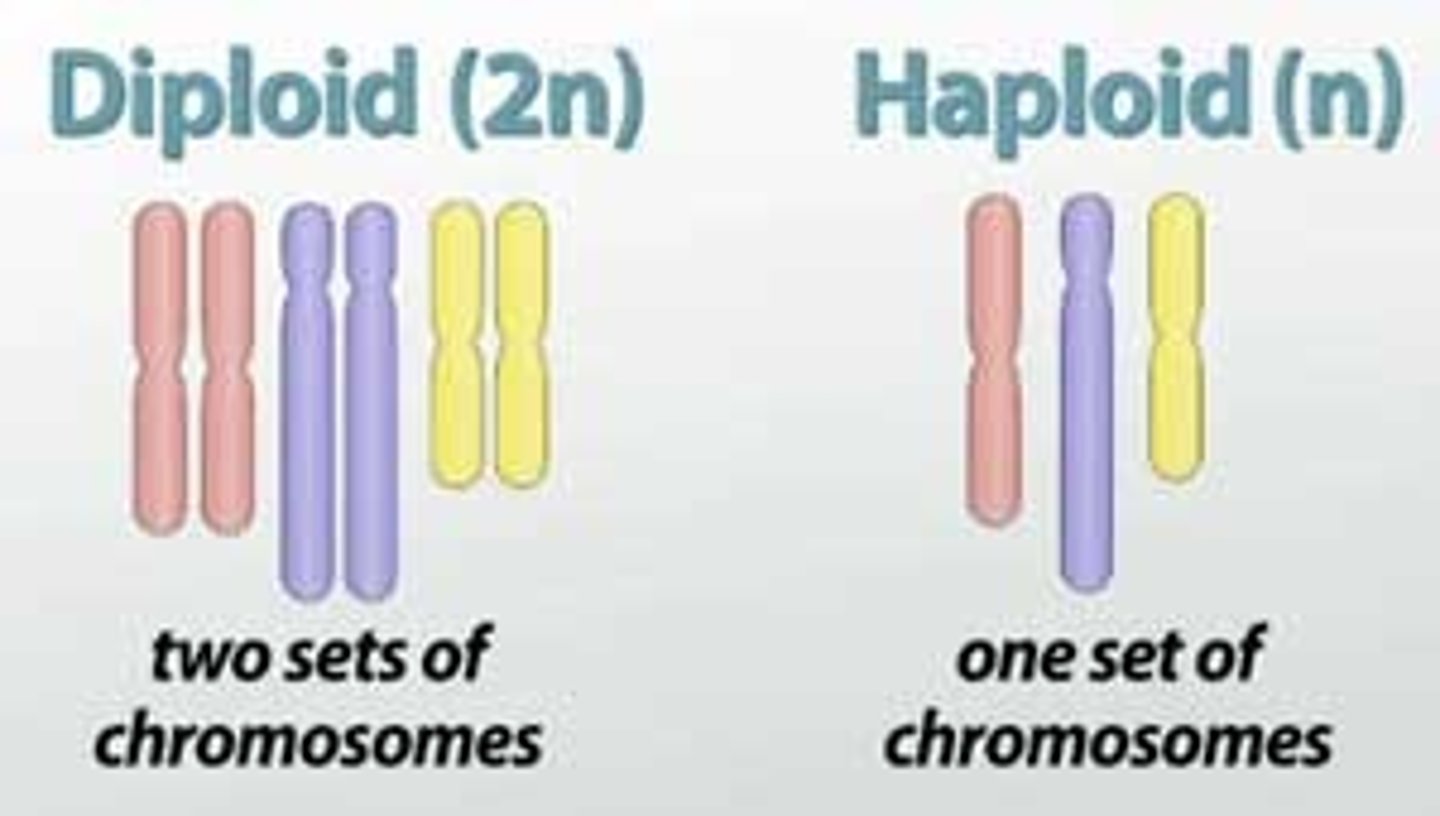
Gametes
Reproductive cells with half the normal number of chromosomes such as a haploid egg or sperm
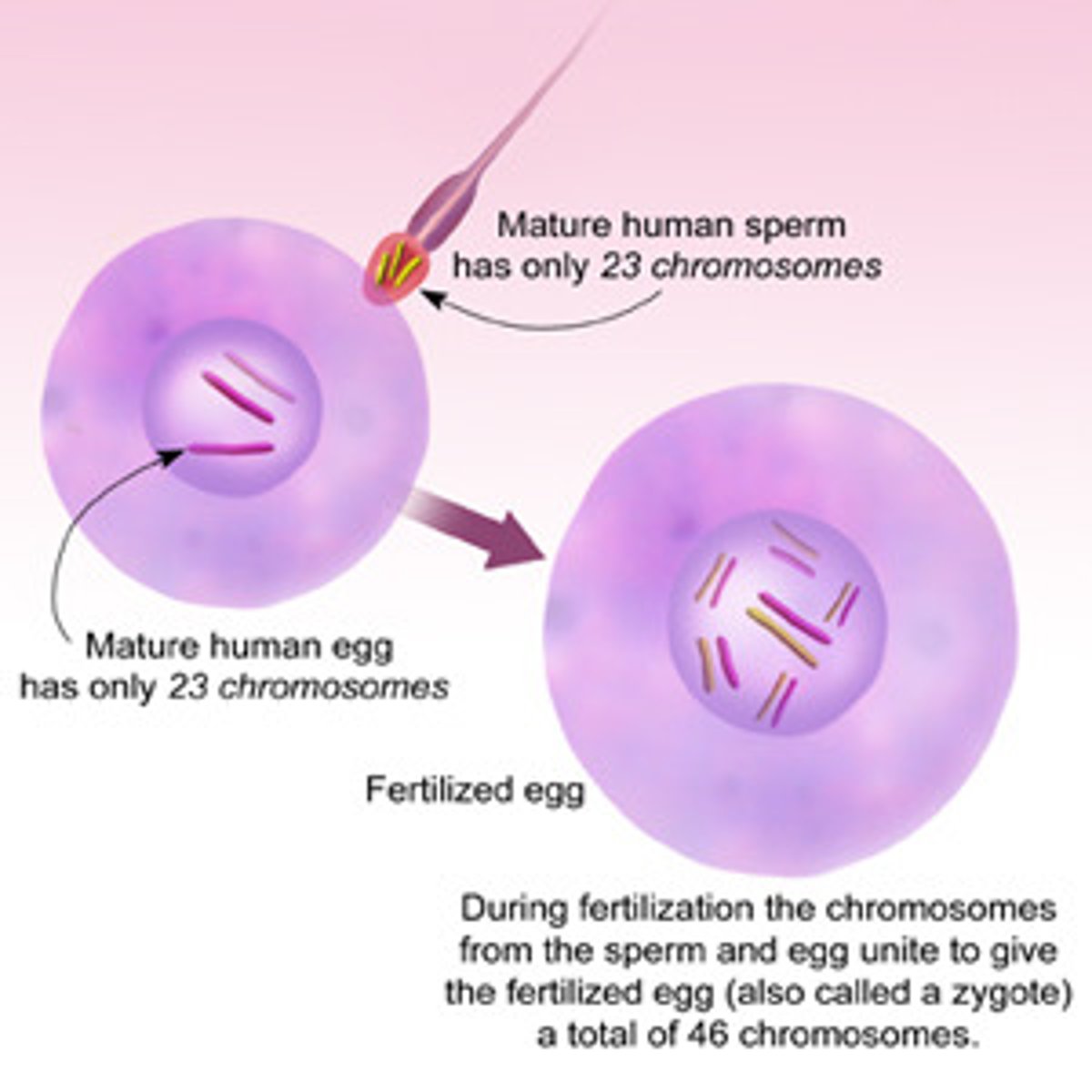
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell formed by the fusion of sperm and egg.
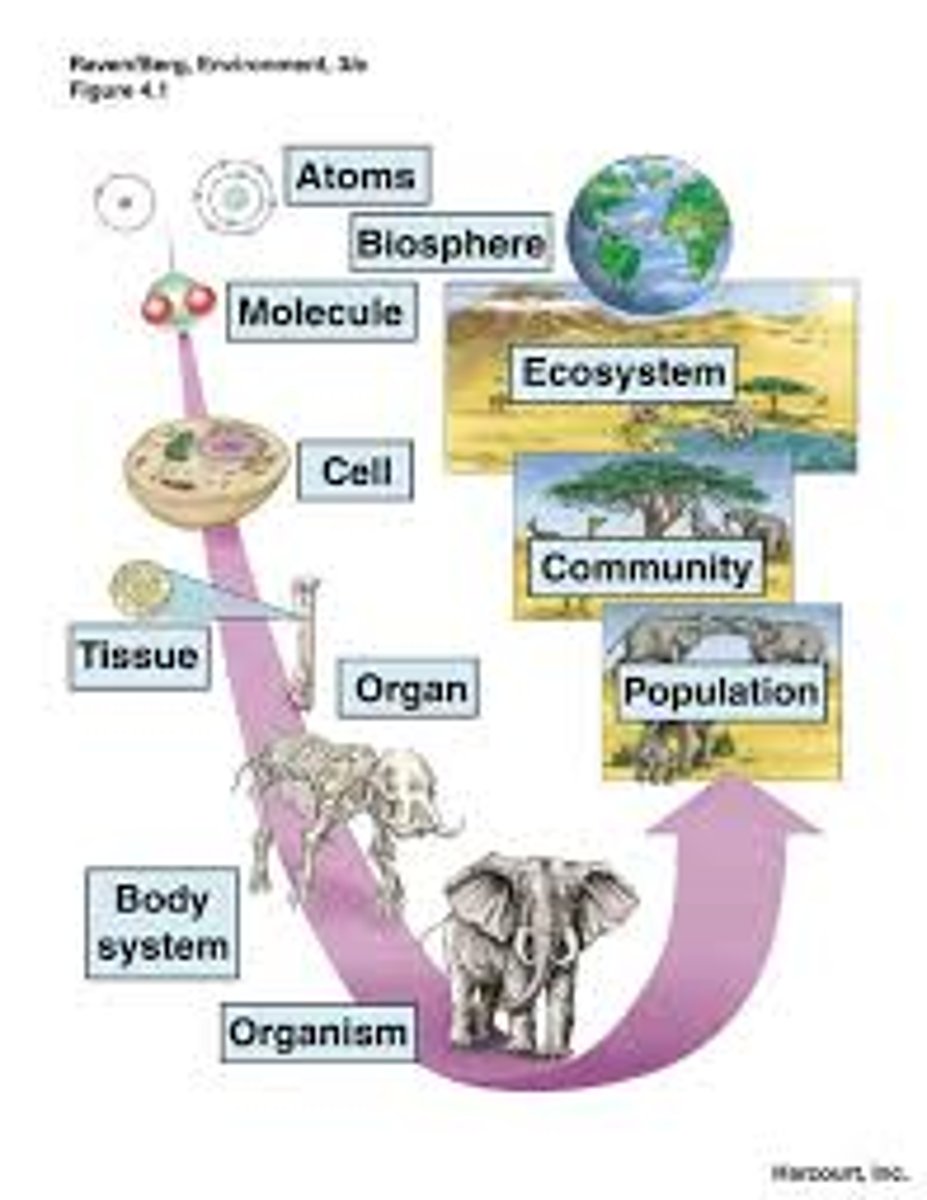
Levels of organization of Life
1. Molecule
2.Organelle
3. Cells
4. Tissue
5. Organ
6. Organ system
7. Organism
8. Population
9. Community
10. Ecosystem
11. Biosphere
Connective Tissue Types
1. Areolar
2. Adipose
3. Dense regular
4. Hyaline cartilage
5. Elastic cartilage
6. Fibrocartilage
7. Bone
8. Blood
Biology
the study of living things
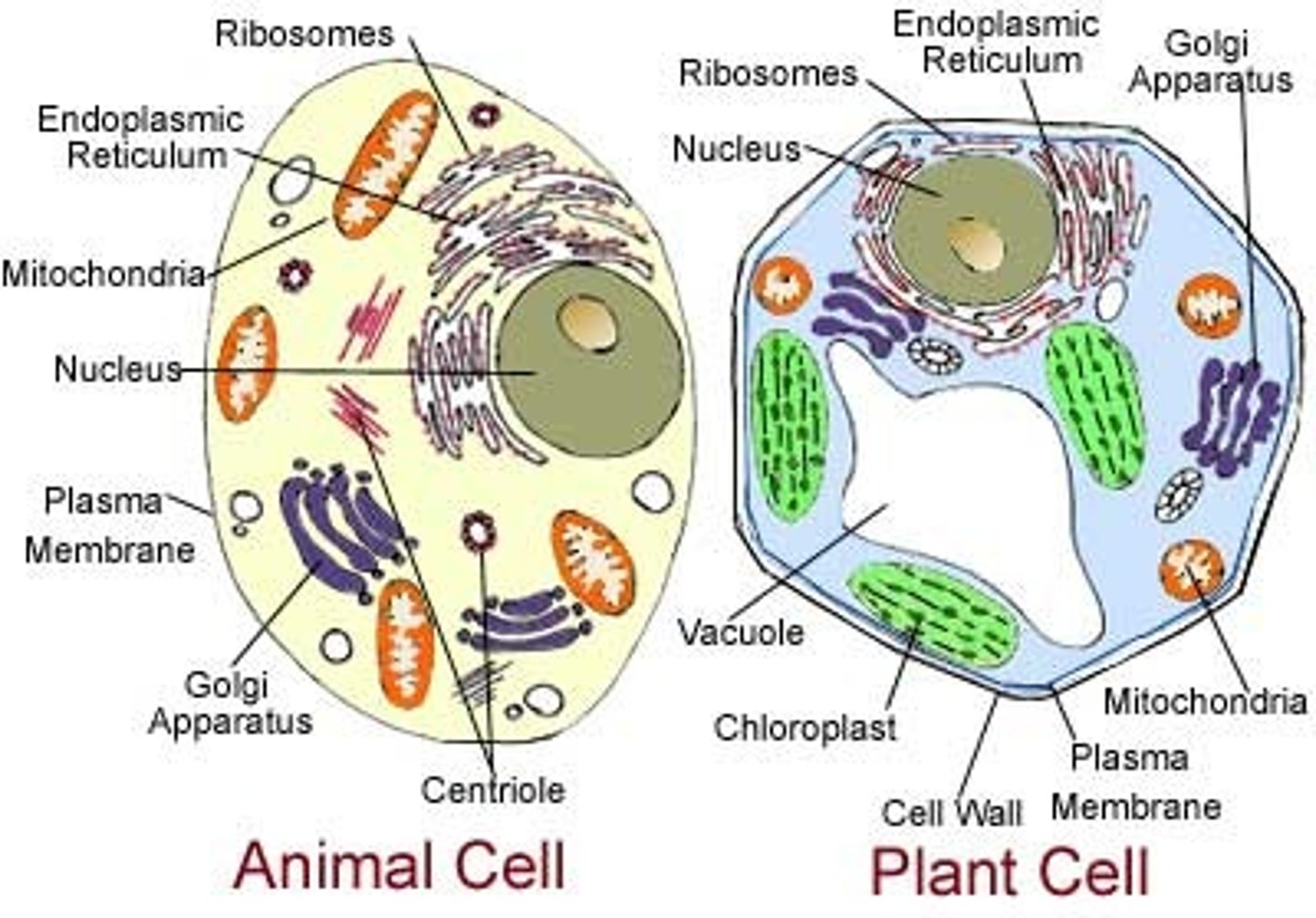
Cell
The smallest living unit with various functions and structures.
Cell Structure
membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes, lysosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria
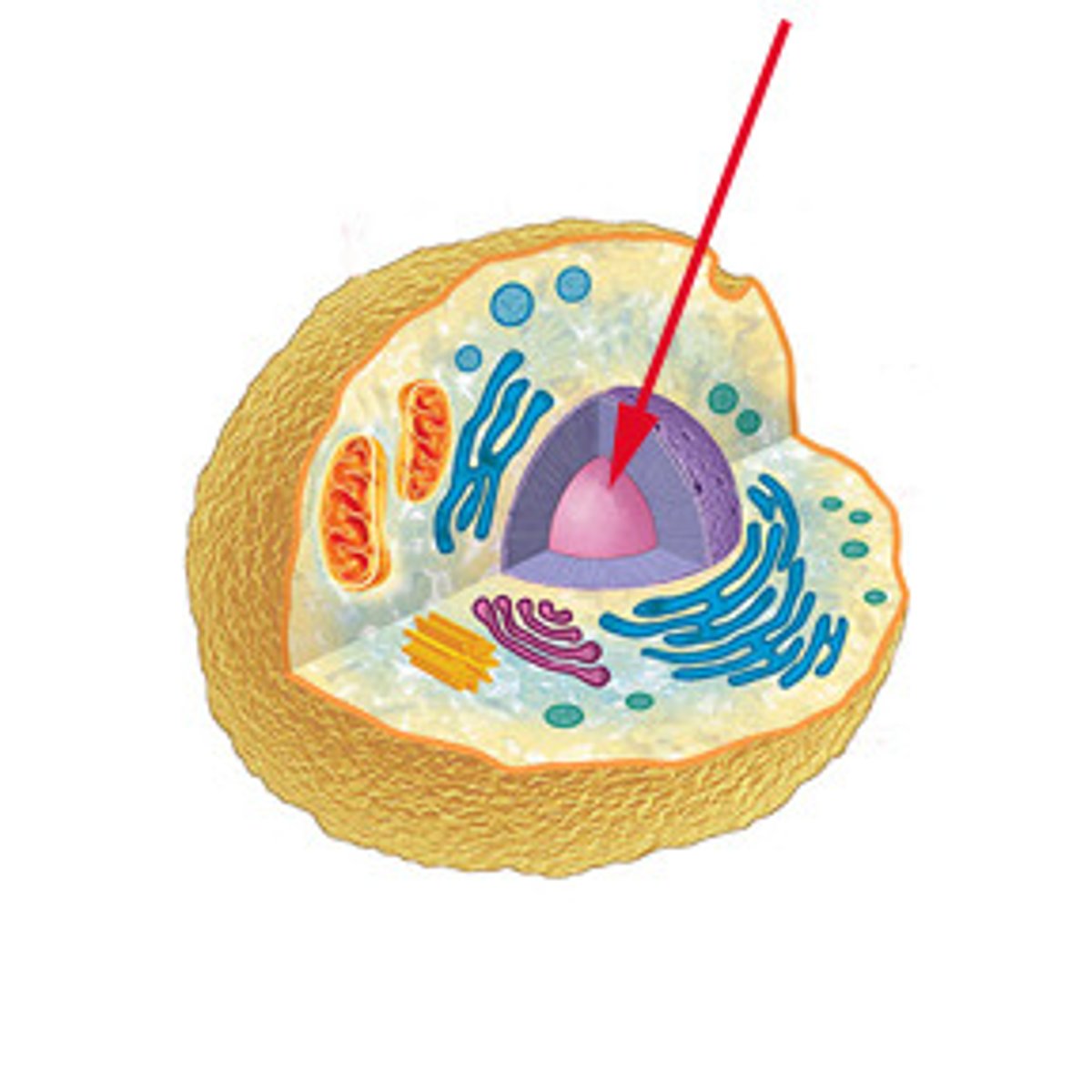
Nucleus
contains most of the cells DNA controls the cell's activities by directing protein synthesis by making messenger RNA (mRNA)
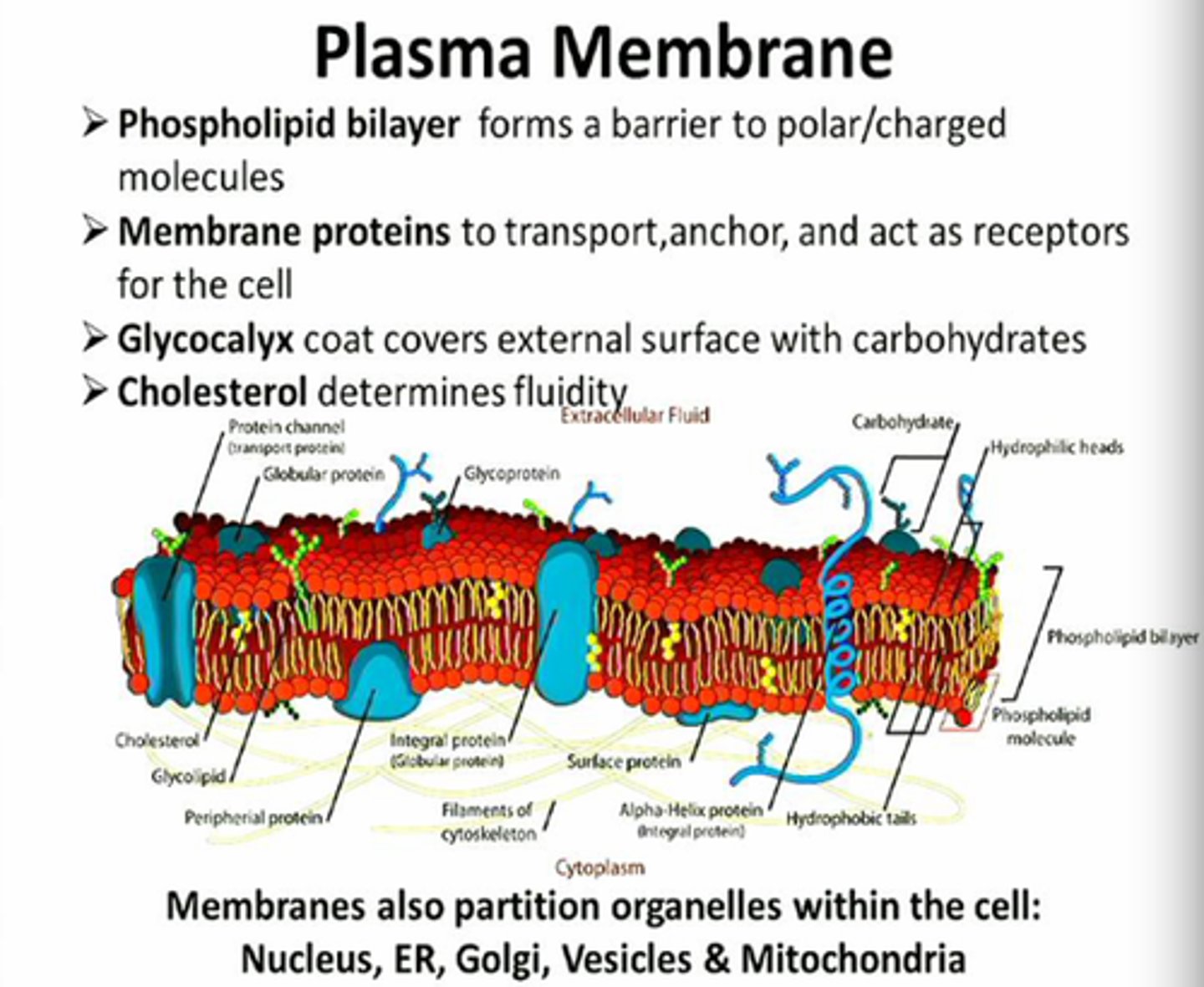
Plasma Membrane
protects the inside and outside of the cell, cell to cell identification, communication, lets things in and out of the cell.
Interstitial Fluid (IF)
fluid between cells and it contains substances like amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, hormones, neurotransmitters and salts
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
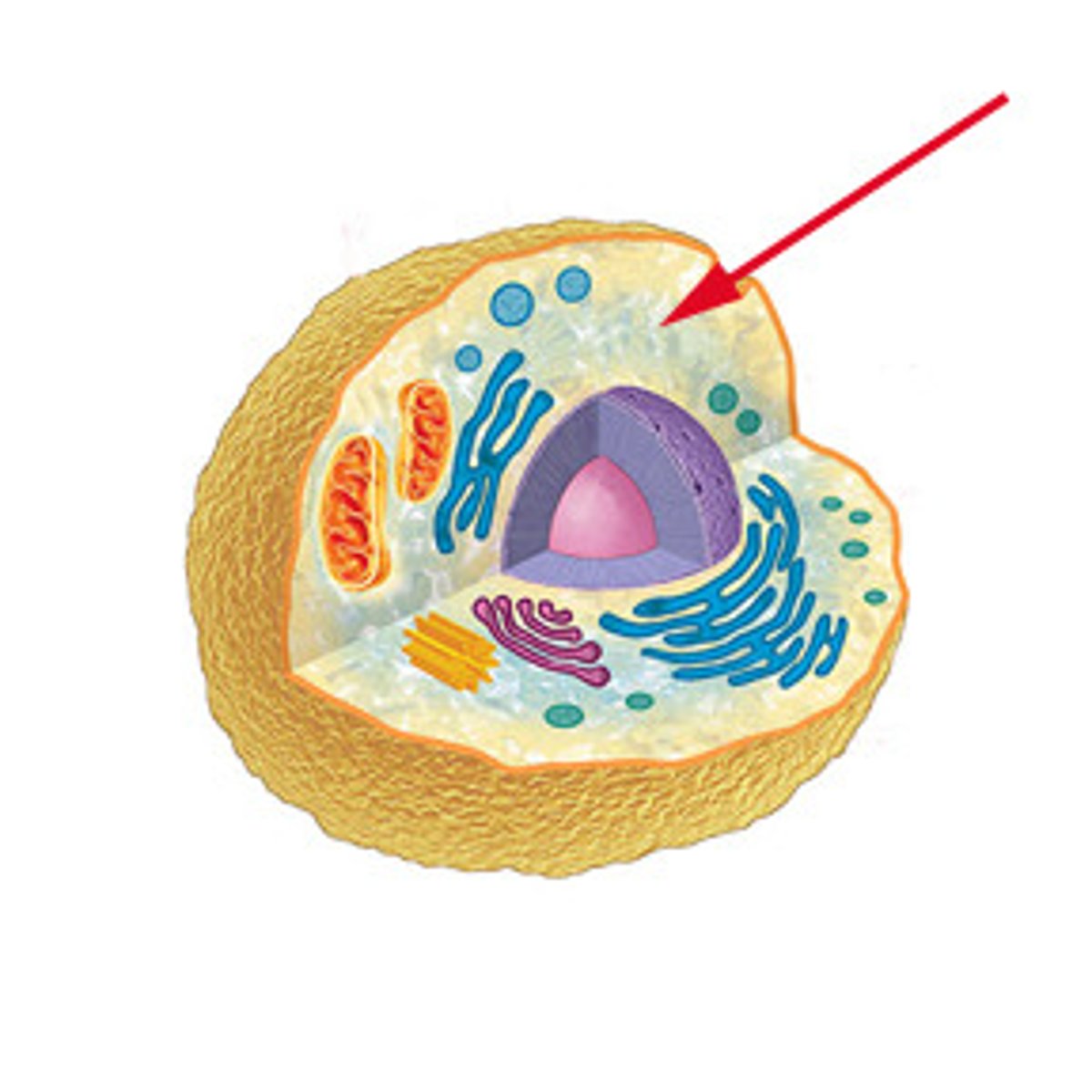
Organelles
Structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell.
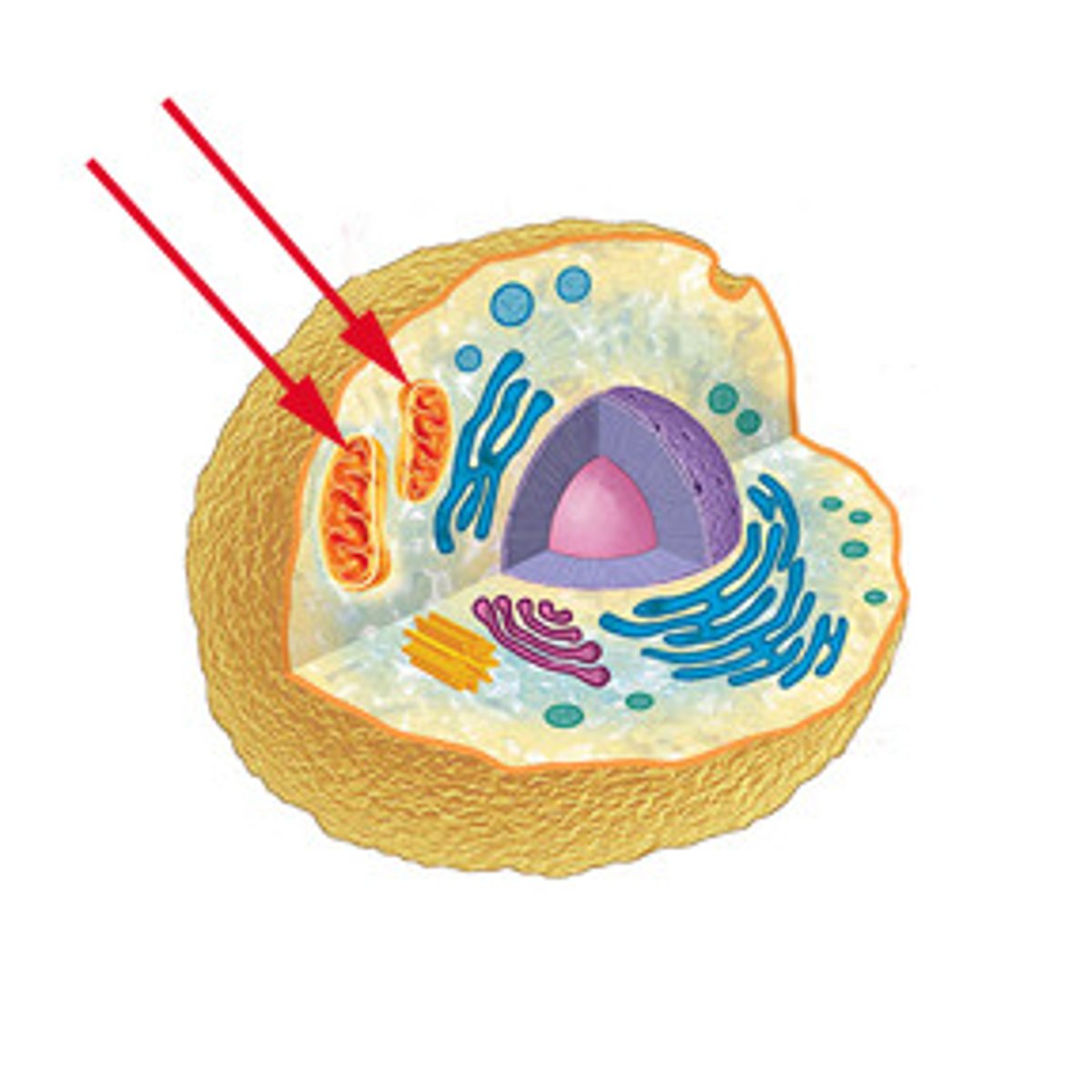
Mitochondria
organelles that carry cellular respiration which converts energy in food to chemical energy ATP
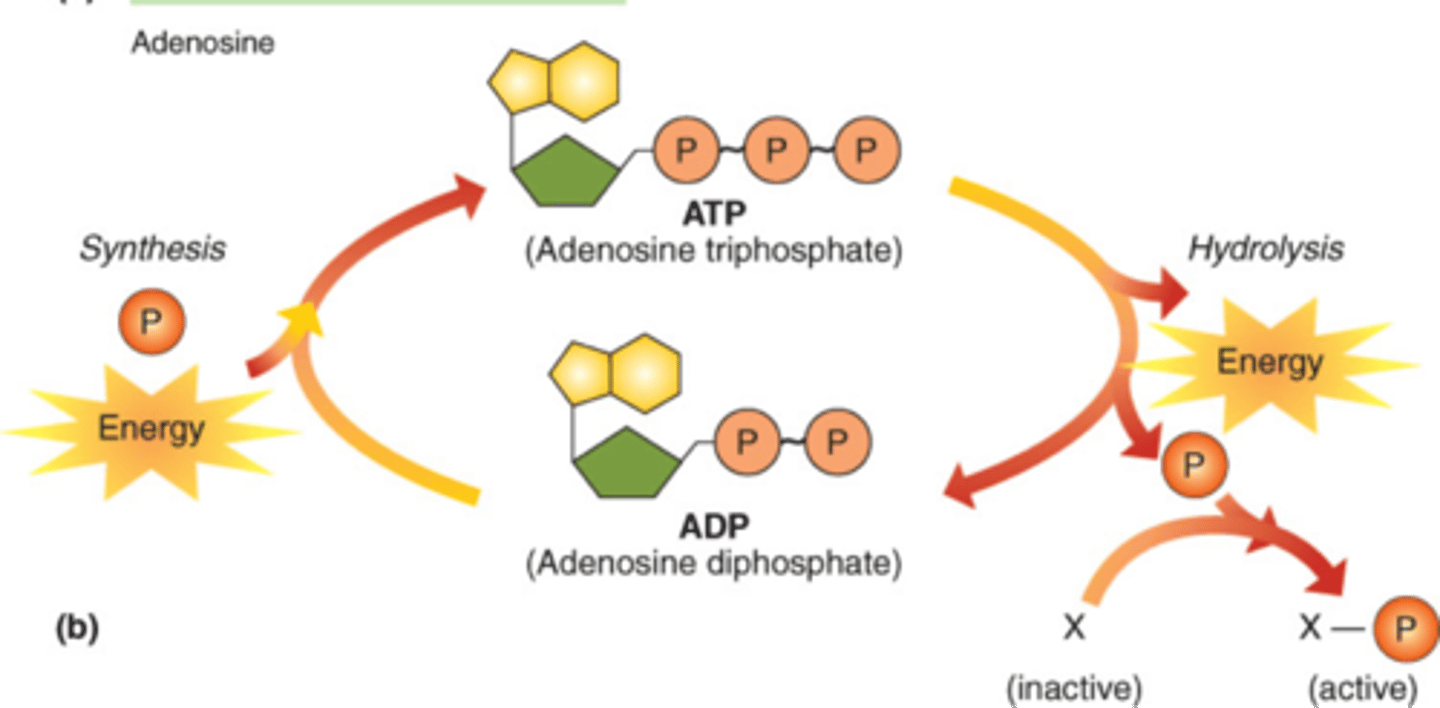
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) is a chemical the cell uses to store and transfer energy within itself
power nearly all forms of cellular work by coupling exergonic and endergonic reactionsit is a renewable energy source
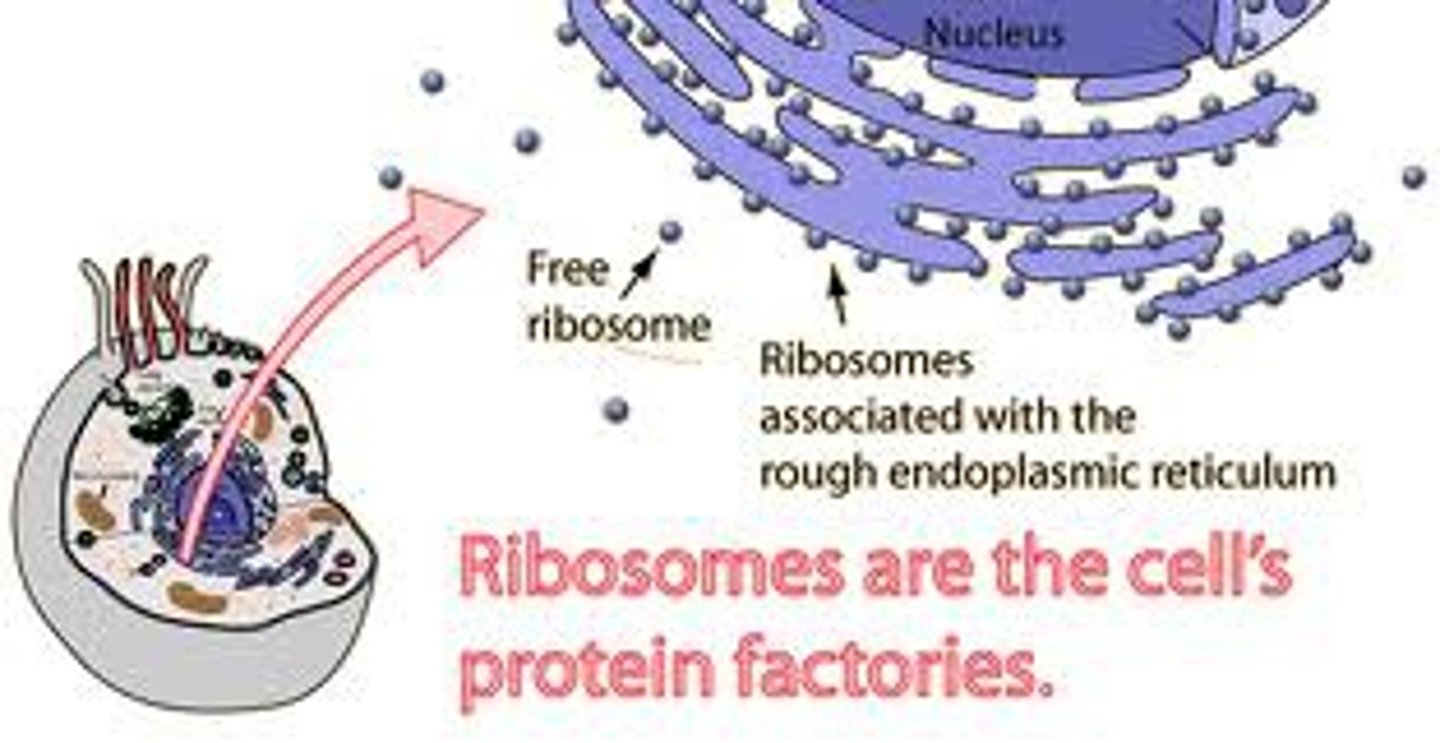
Ribosomes
are involved in the cells protein synthesis
Free ribosomes are suspended in the cytoplasm, typically involved in making proteins that function within the cytoplasm
Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, associated with proteins packed in certain organelles or exported from the cell.
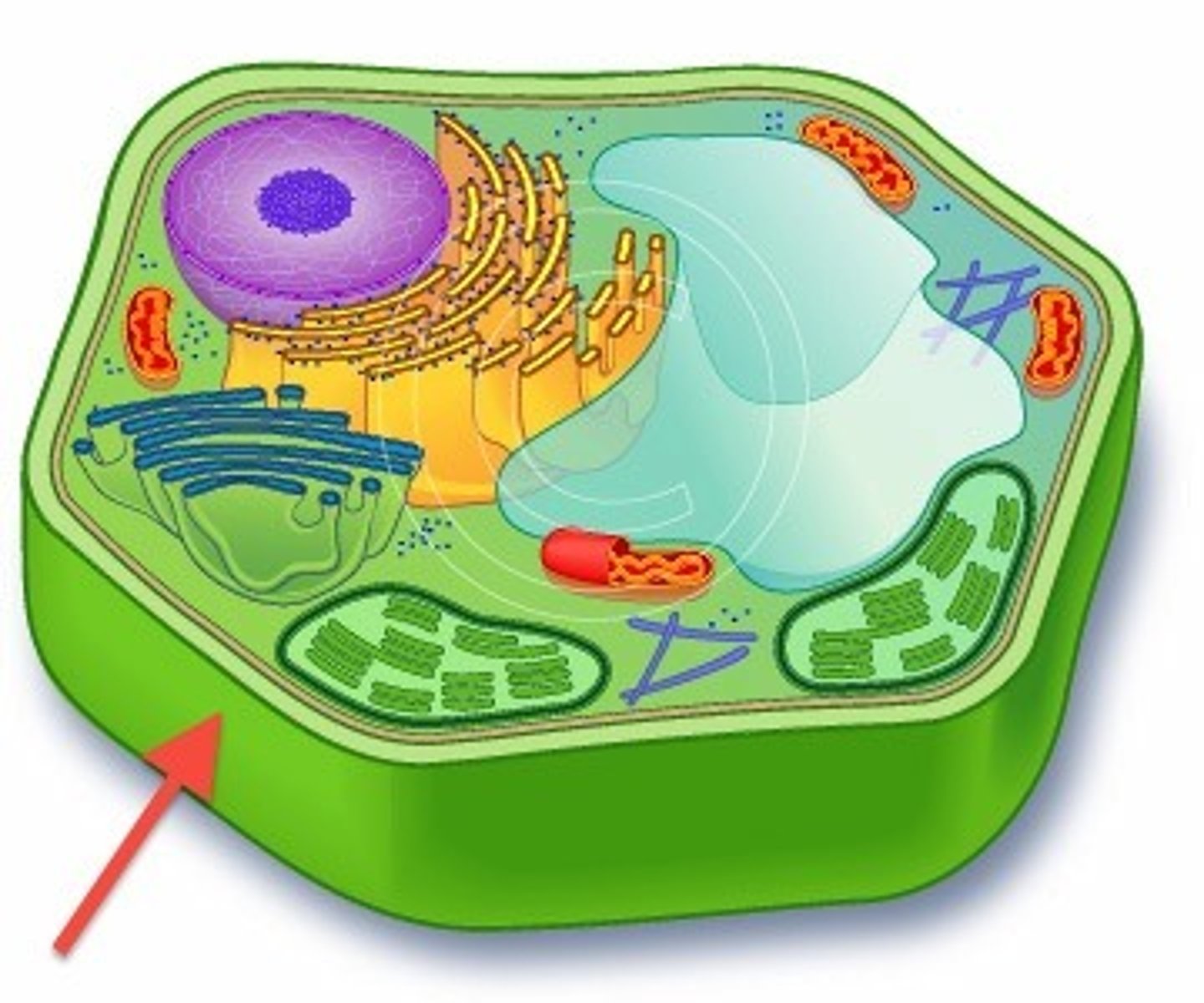
Cell Wall
protects and provides skeletal support that helps keep the plant upright composed of cellulosethe cell also has plasmodesmata that serve in communication between cells
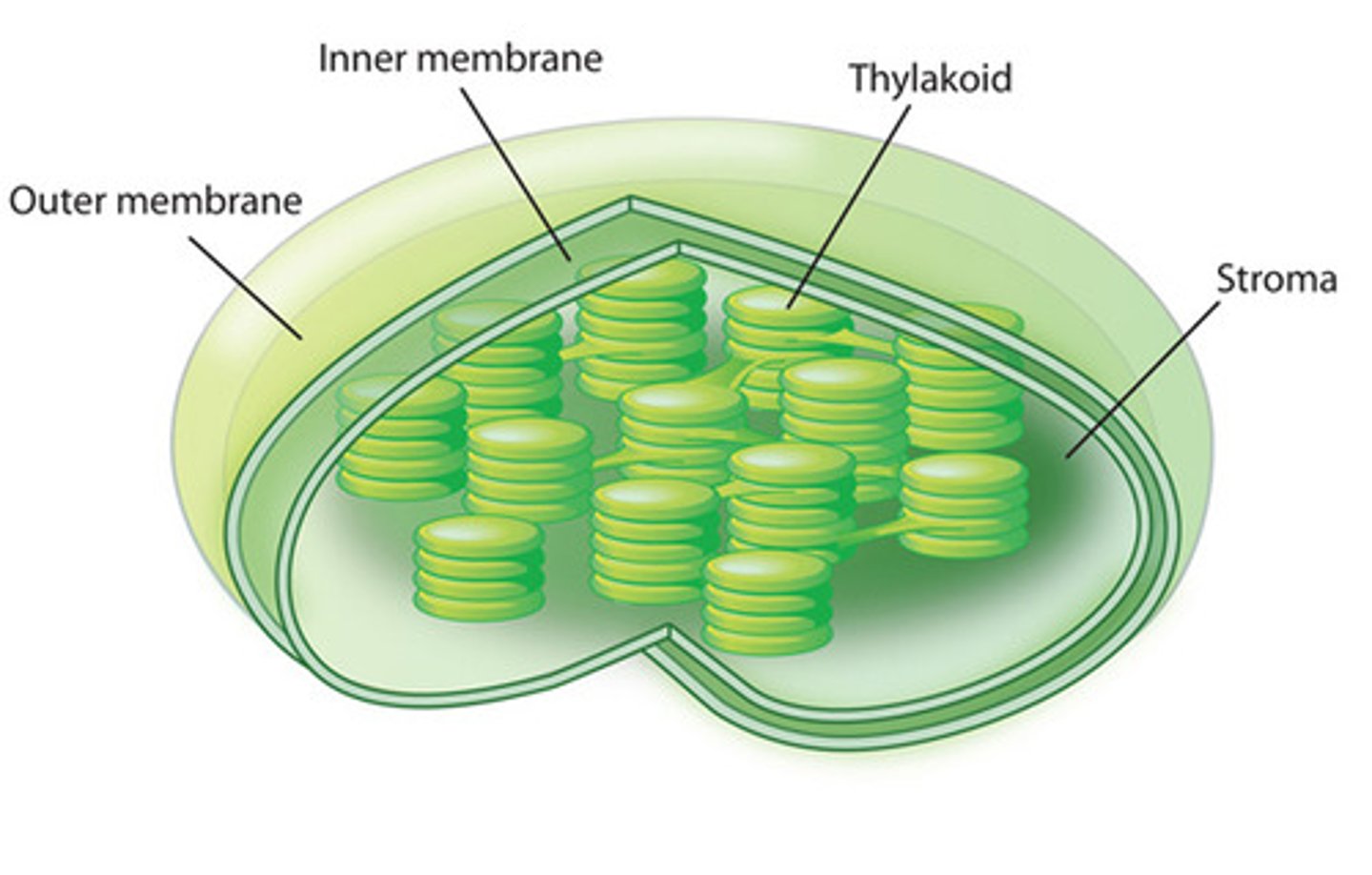
Chloroplast
are the photosynthesizing organelles which convert light energy from the sun to the chemical energy of sugar molecules
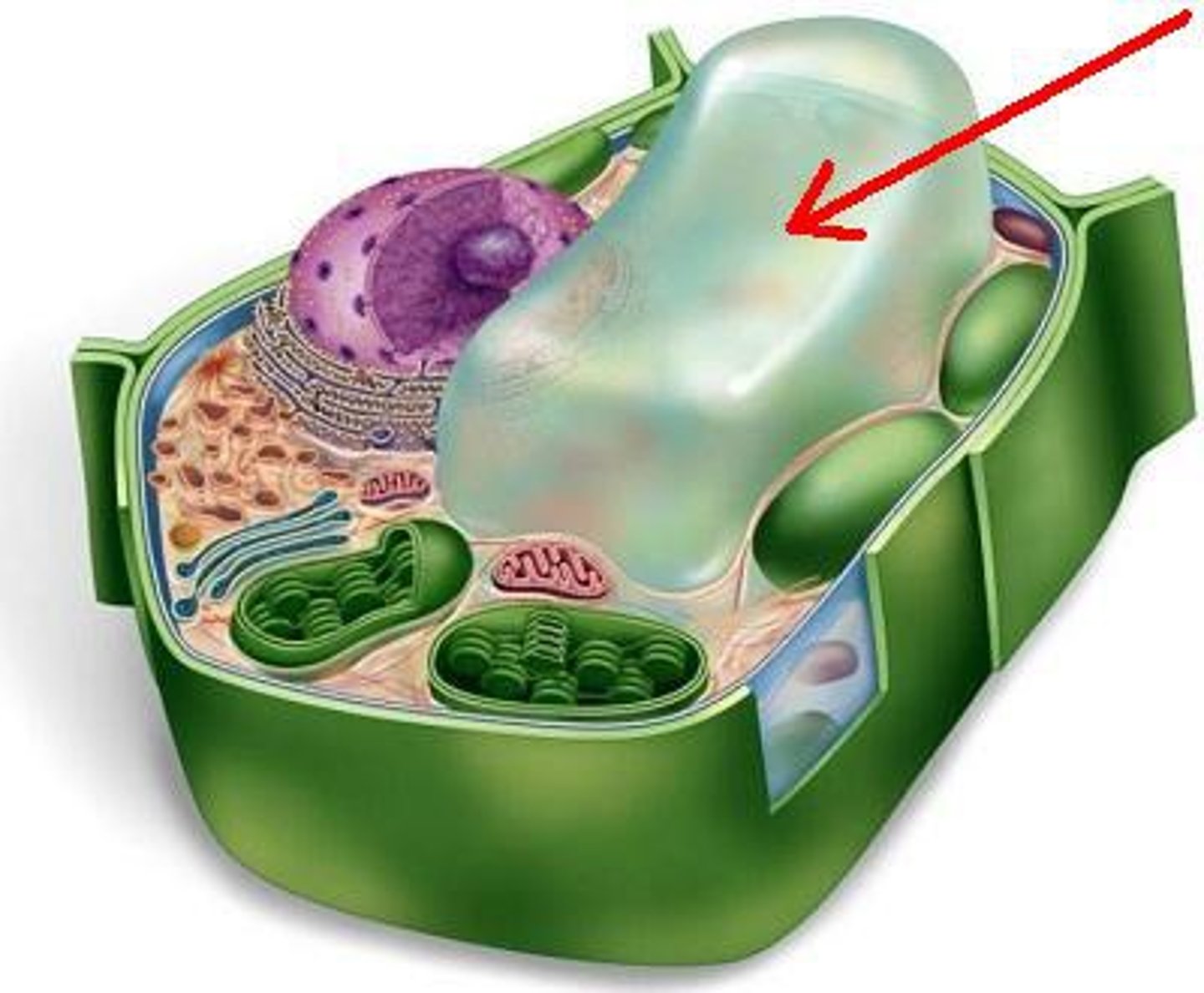
Central Vacoule (plant)
have digestive functions, contain pigment, contain poisons that protect the plant
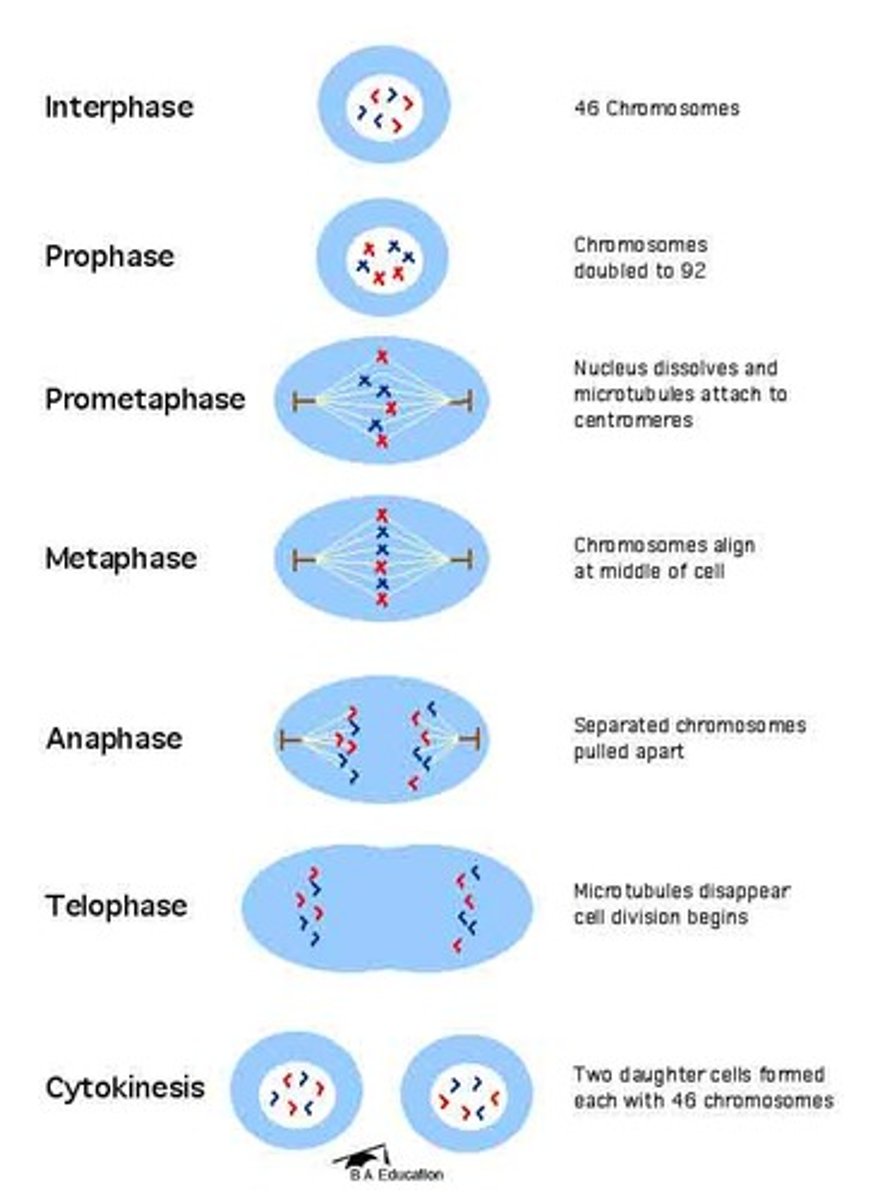
Mitosis
cell division of a single nucleus which divides into identical nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Meiosis
Cell division resulting in four daughter cells with half the genetic material.
Somatic Cells
Non-reproductive cells producing identical offspring through mitosis
Daughter Cells
Cells resulting from cell division with half the normal number of chromosomes
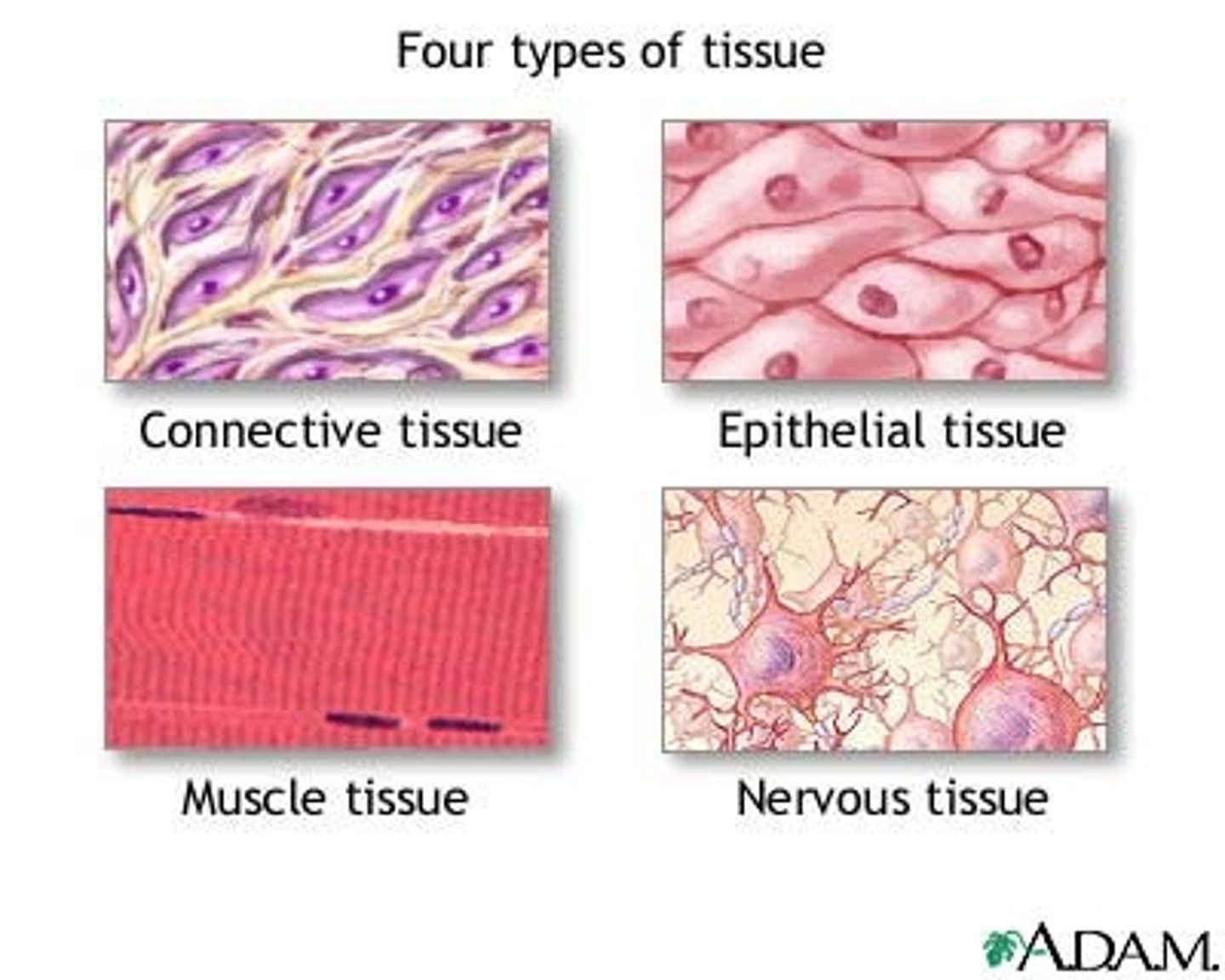
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
There are four types of tissues
1. connective
2. epithelial tissue
3. muscle tissue
4. nervous tissue
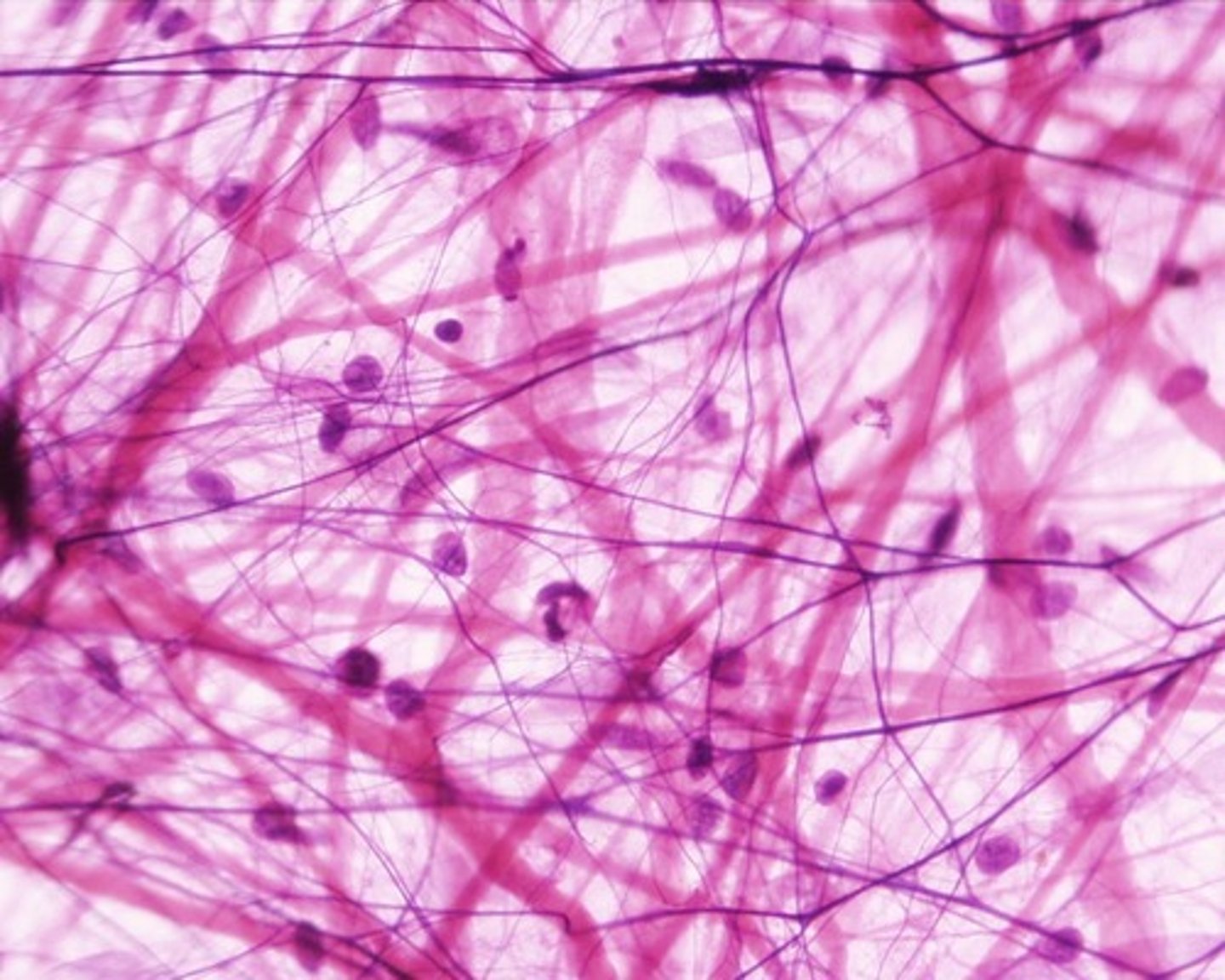
Connective Tissue Function
-Vary greatly depending on the structure of the tissue and its location
-Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues and organs.
-Connective tissue helps protect the body.
-Connective tissue helps insulate the body.
-Connective tissue is necessary for transporting materials throughout the body.
Areolar Connective Tissue
Cell: Fibrolast
Matrix: Collagen and Elastic fibers
Function: packaging material
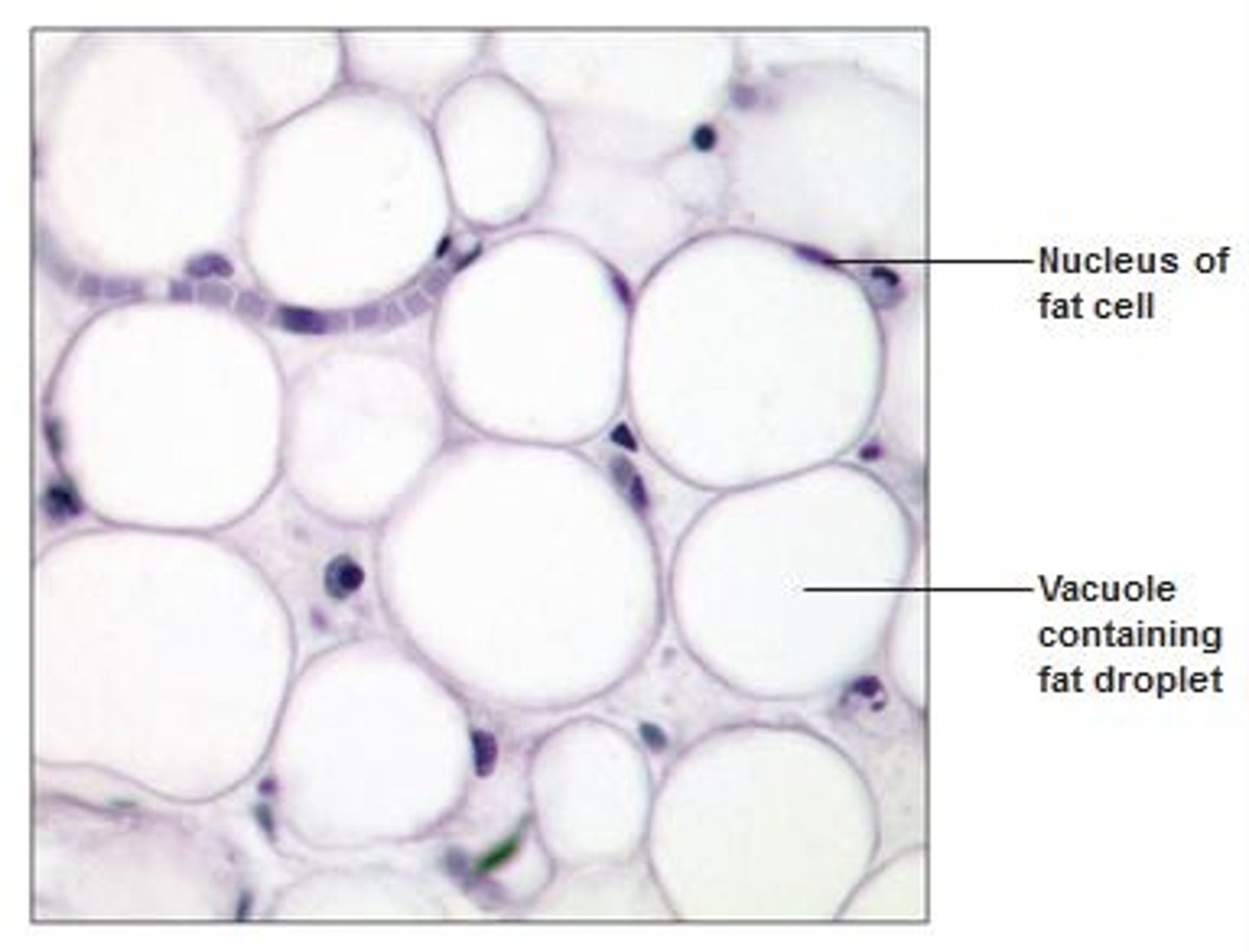
Adipose Connective Tissue
Cell: Adipocyte
Matrix: not important
Function: long term energy storage , insulation
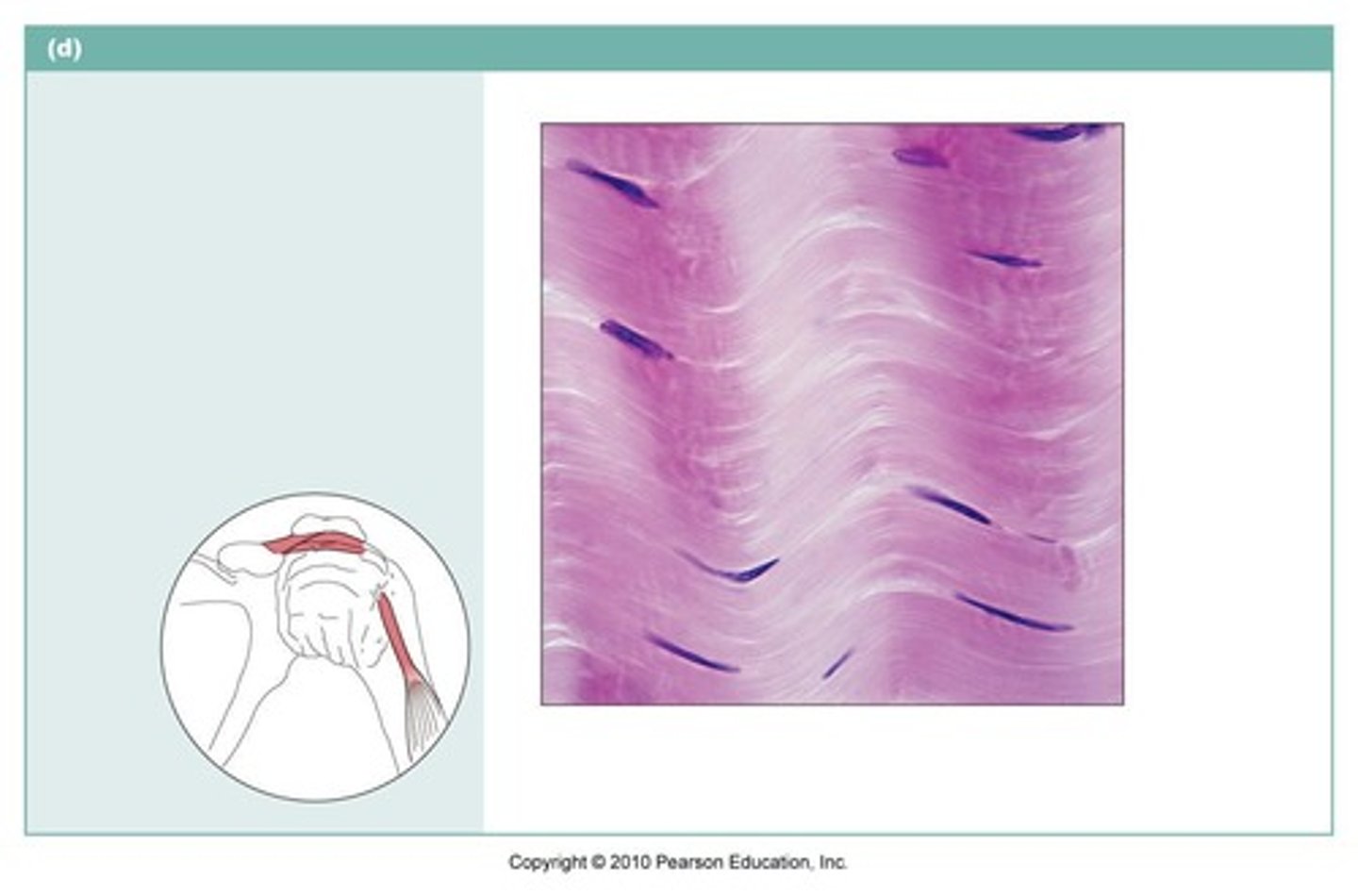
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Cell: Fibroblast
Matrix: Collagen fibers; arranged parallel
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; stretches a little when pulled
Location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
Cell Chondro-cyte
Matrix Collagen fibers not evident
Function: Supports and reinforces, provides a framework
Location: covers the ends of bones, costal cartilage in ribs, nose, rings in trachea, and larynx, forms most of the embryonic skeleton
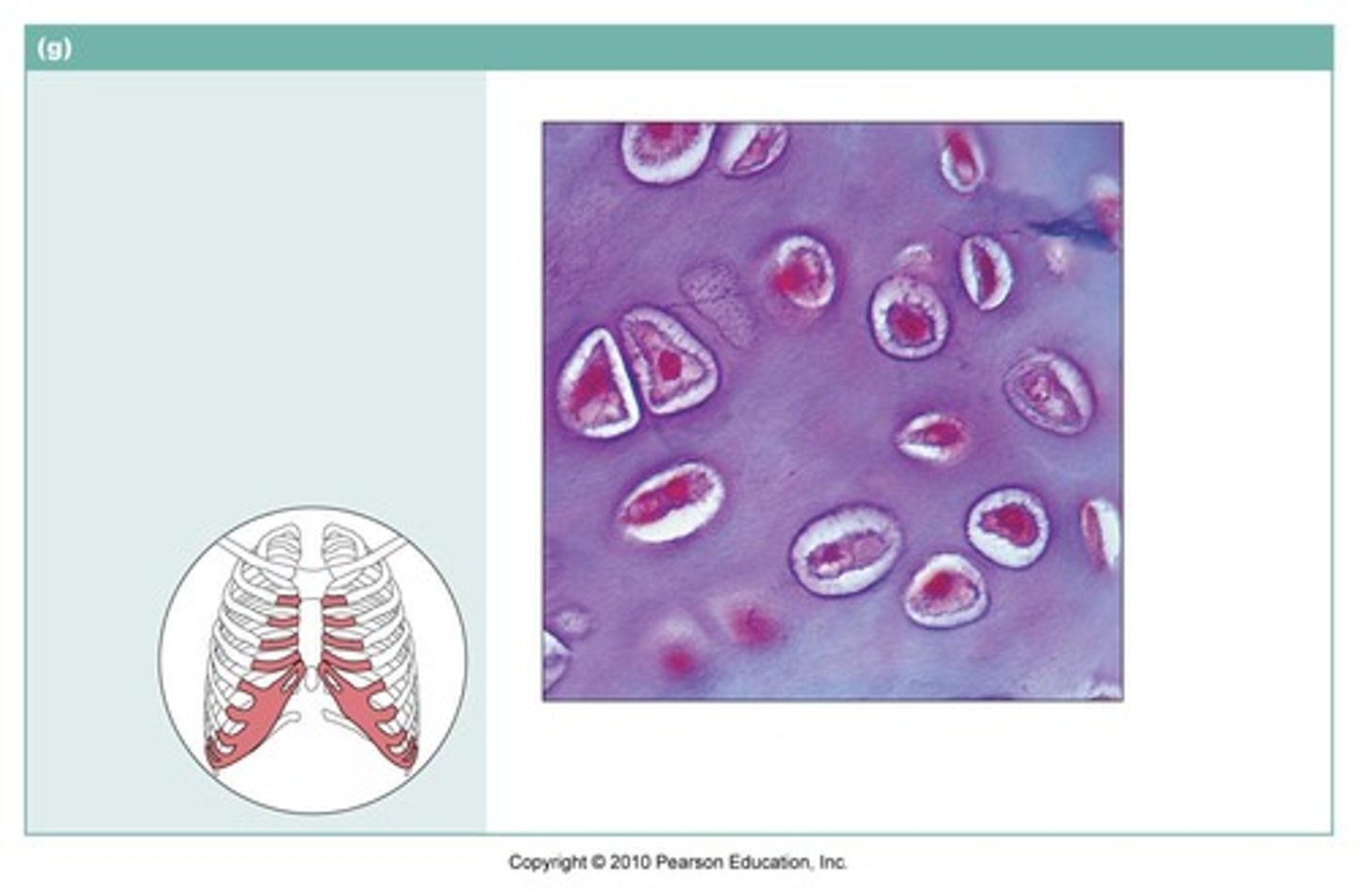
Elastic Cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
Matrix: Collagen and elastic fibers
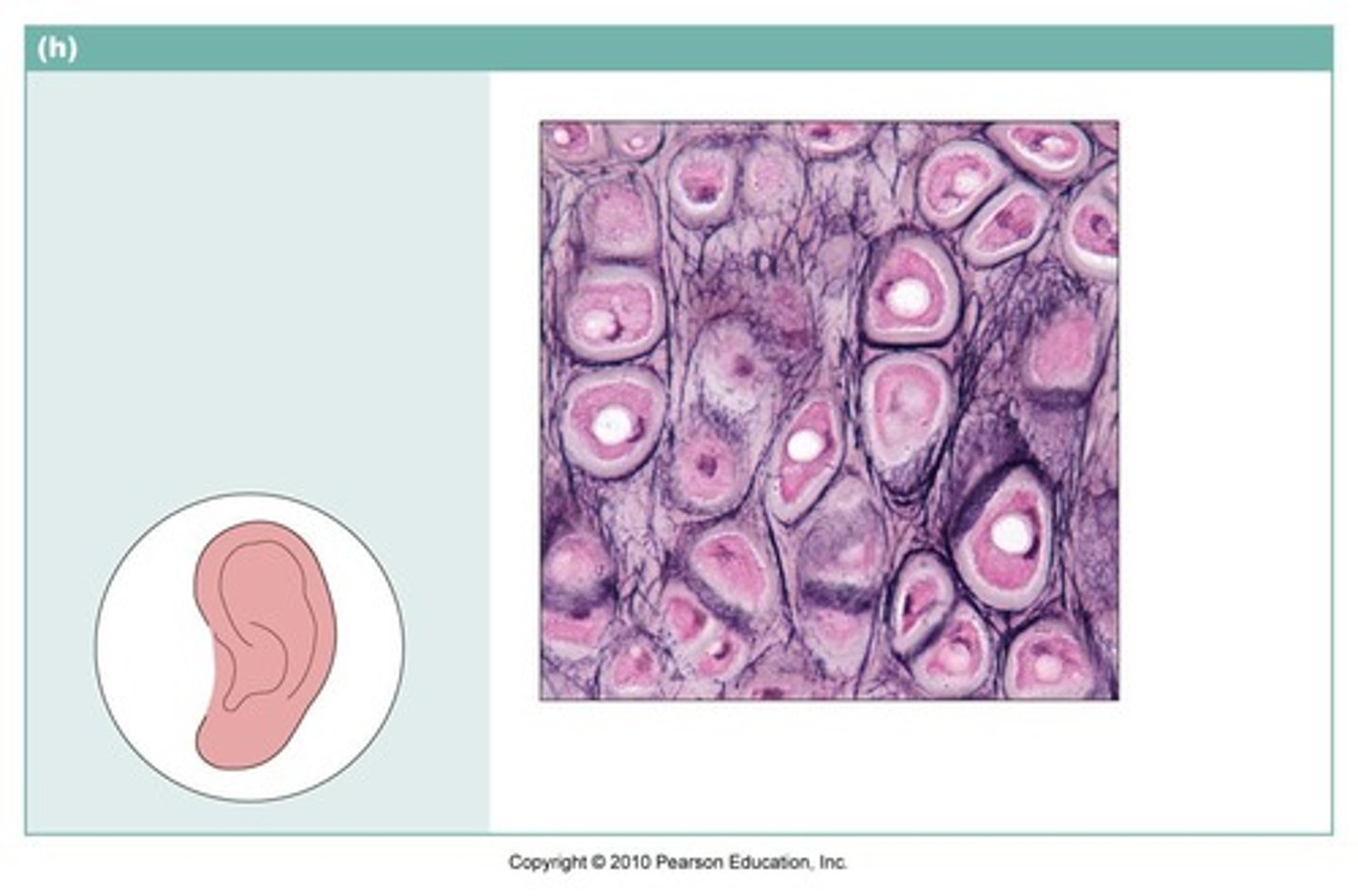
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
Highly compressible. Forms cusion-like discs between vertebrae.
Matrix: less firm than Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue that contains collagen (fibers are evident)
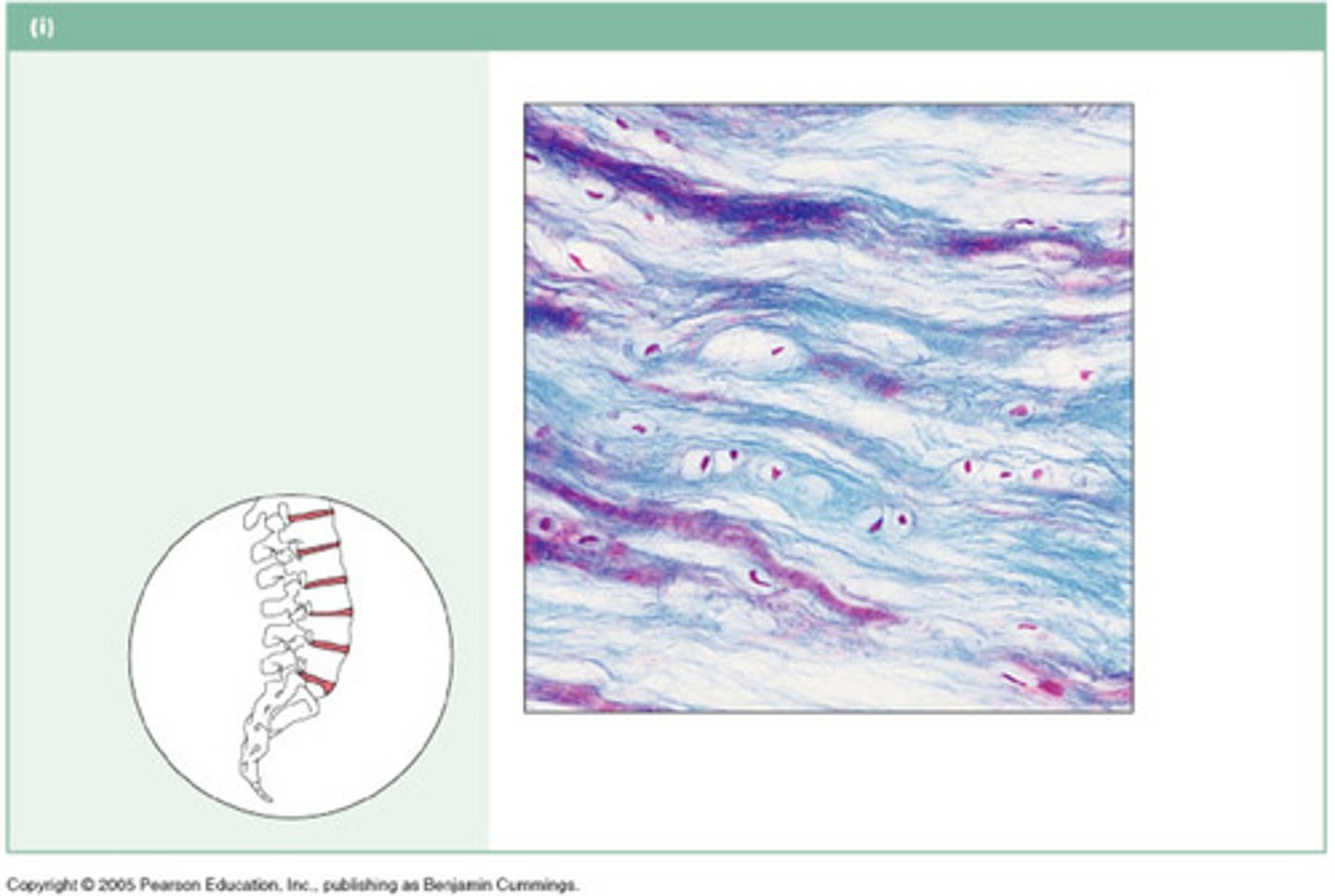
Bone Connective Tissue
Cell: Osteocyte
Matrix: organic collagen fibers
inorganic calcium salts
Functions: Support, Protection, Formed element prod, Movement, Fat storage, Mineral storage
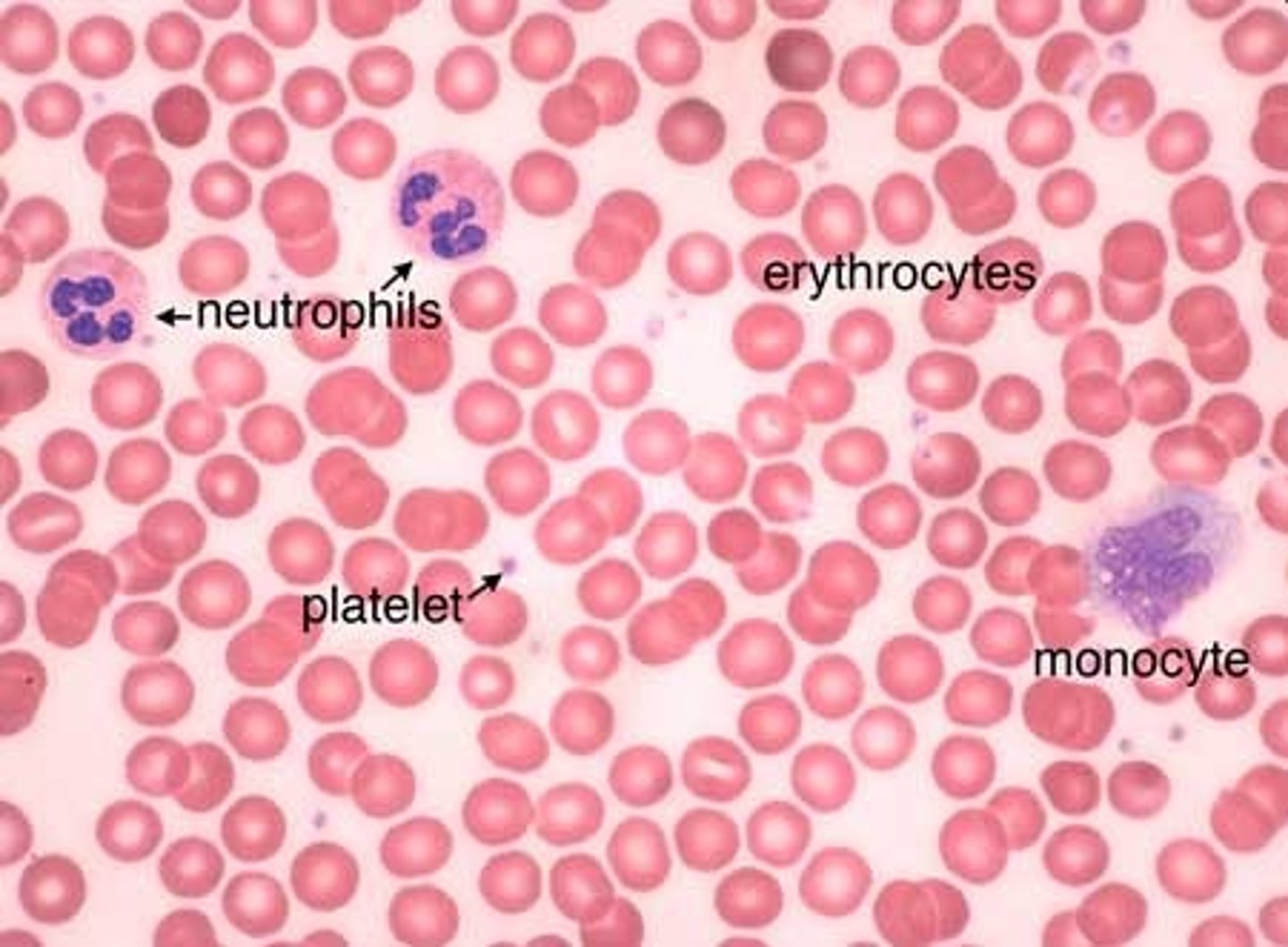
Blood Connective Tissue
Cells: Erythrocyte, Leukocyte
Platelet- not a cell
Matrix: liquid plasma
Function: fluid extracellular matrix used to transport substances throughout the body.
epithelial tissue functions
1. protection
2. absorption
3. filtration
4. excretion
5. secretion- individual epithelial cell can secrete; epithelial cells arranged into exocrine glands
6. sensory reception- skin, special sense
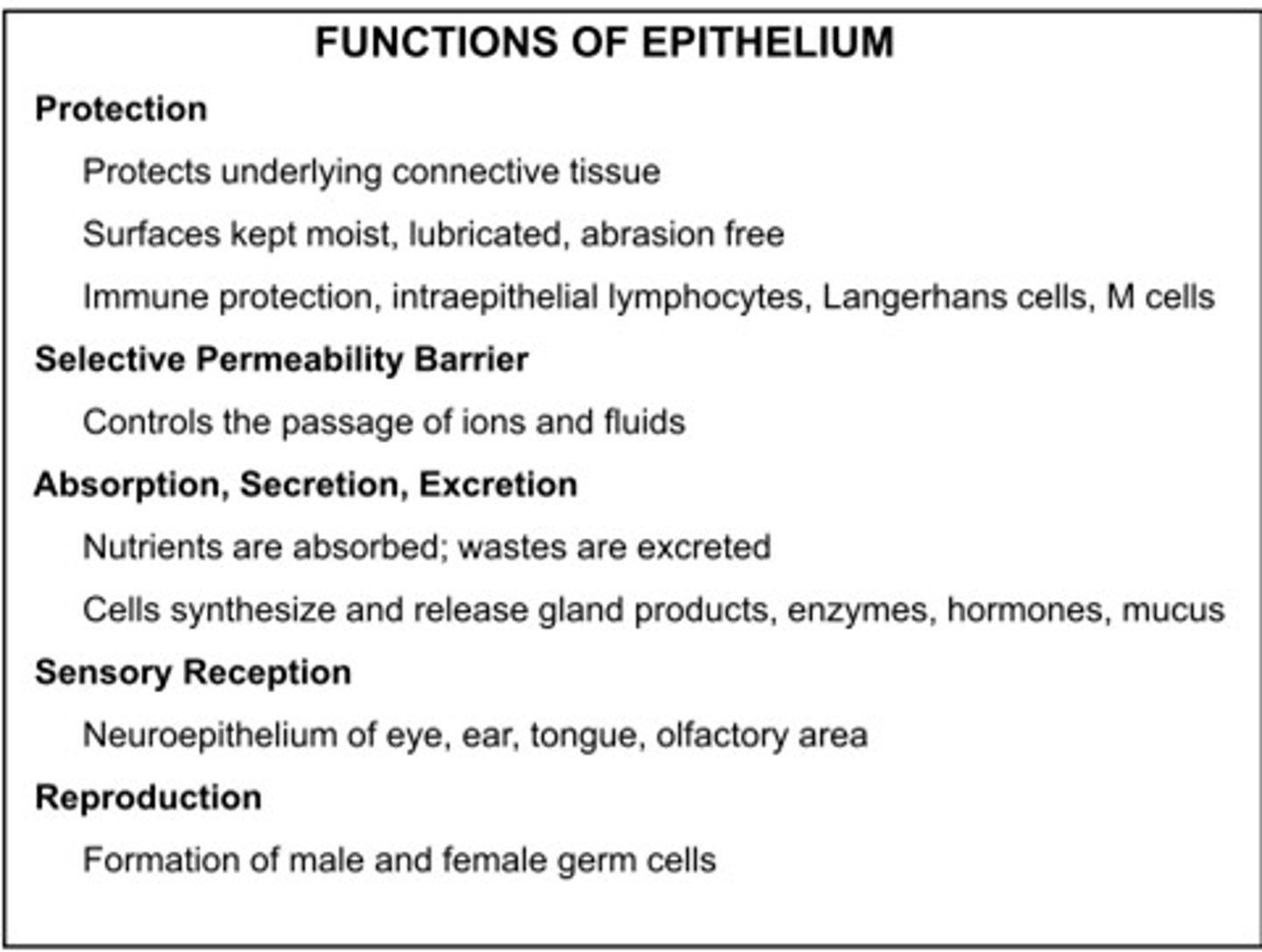
Epithelial Tissue Classification
number of cell layers and cell shape
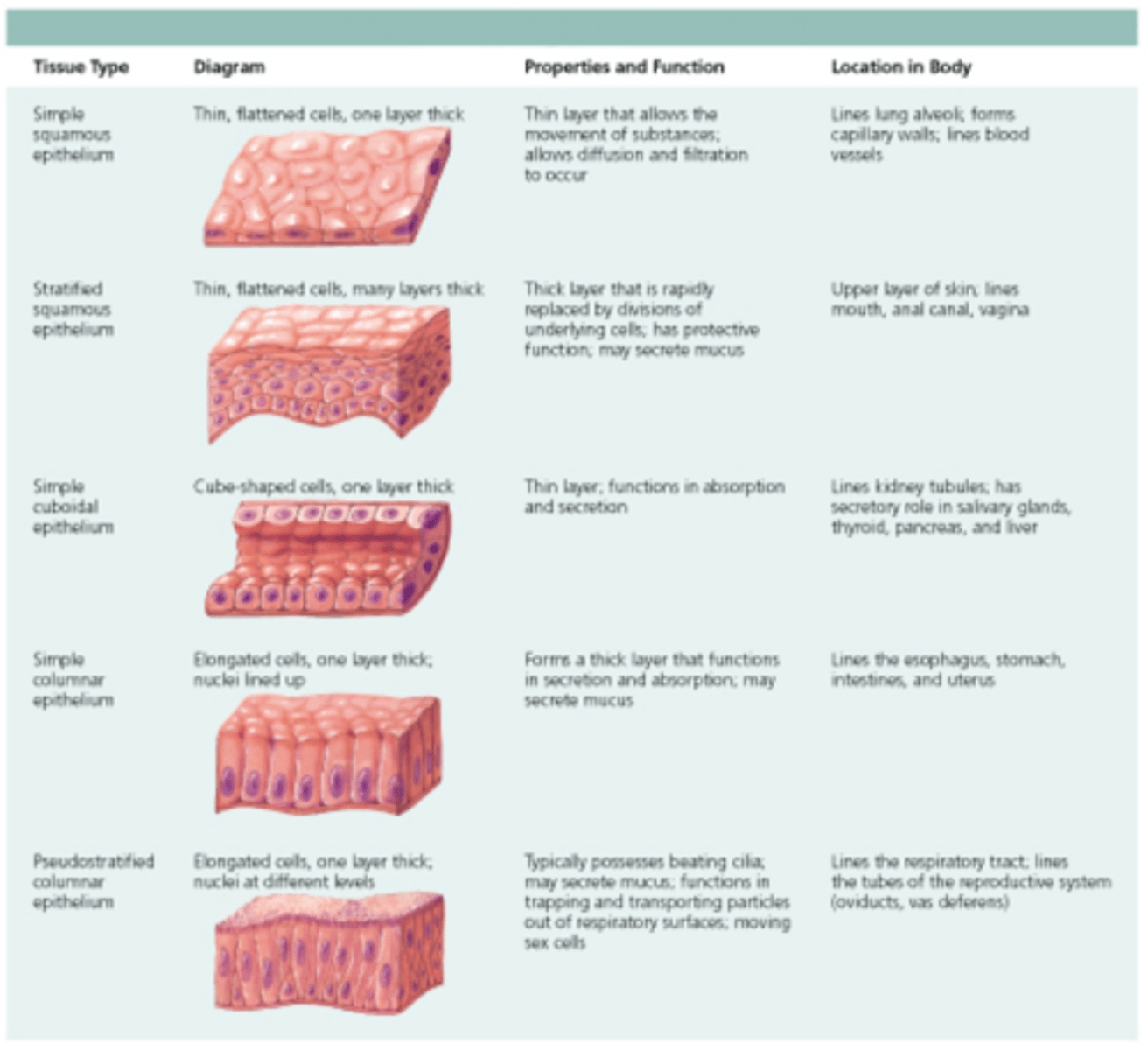
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that senses stimuli and transmits signals.
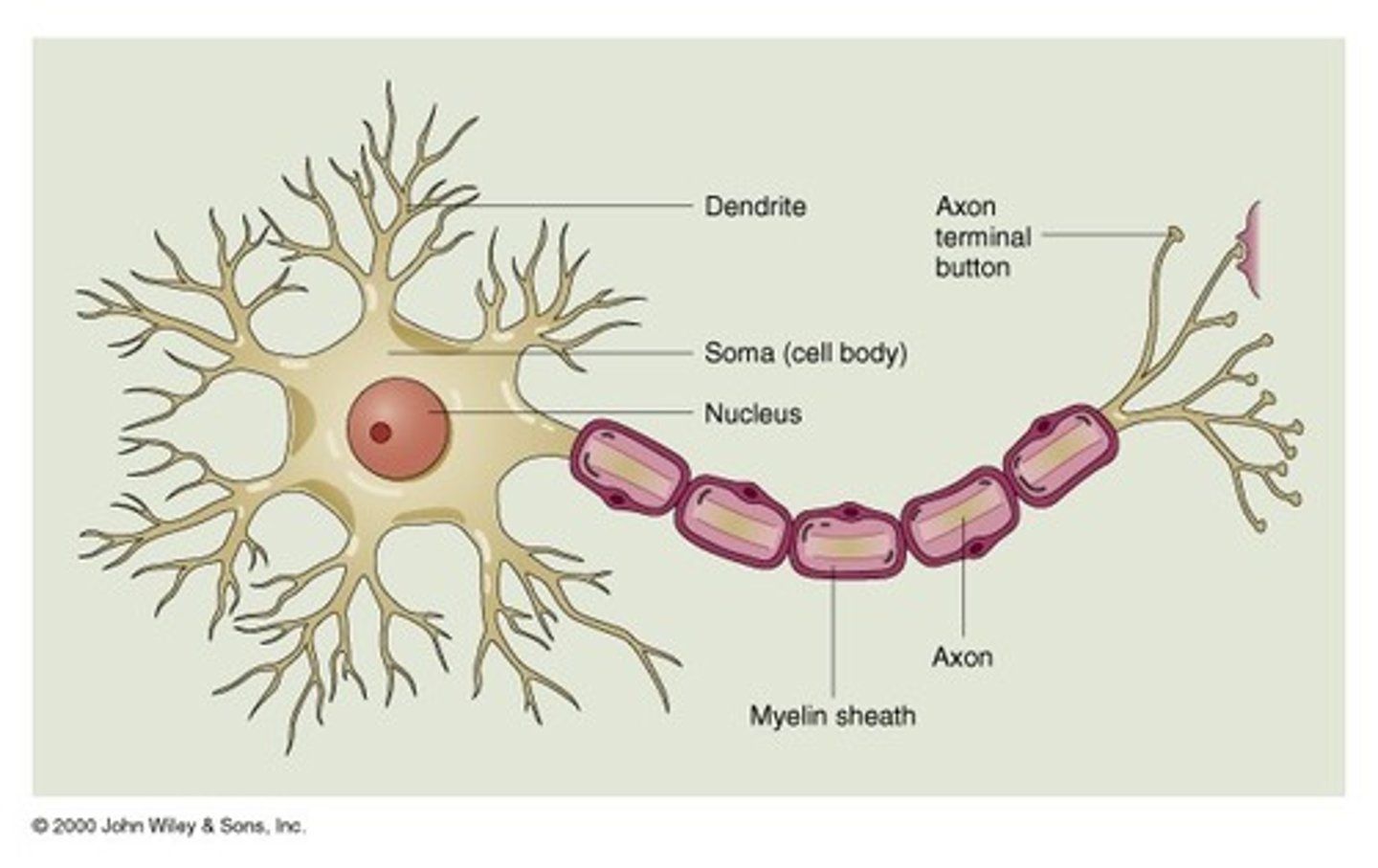
Muscle Tissue
There are three types of muscle tissue skeletal, cardiac and smooth
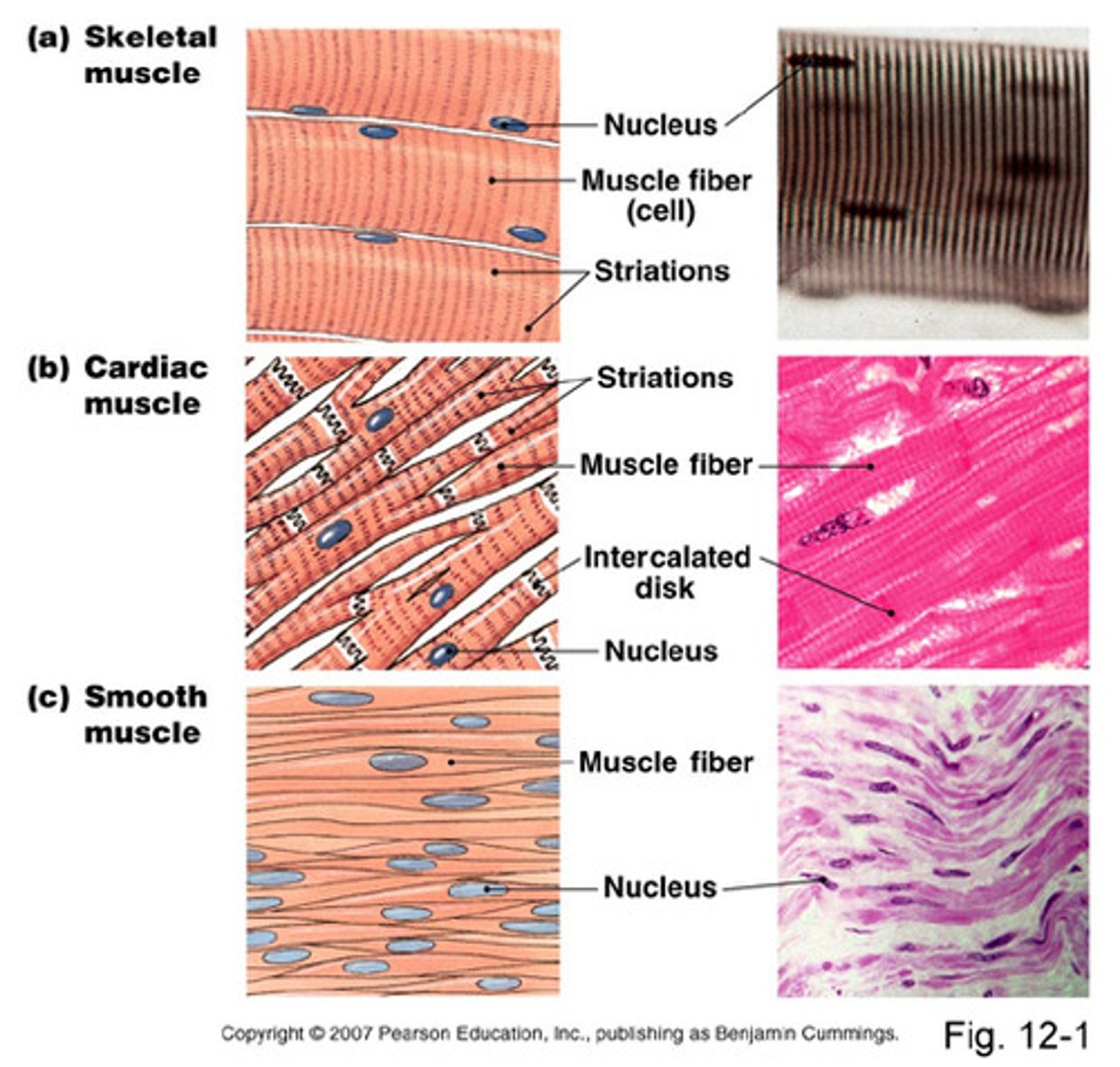
cardiac muscle tissue
the striated and involuntary tissue that forms most of the wall of the heart
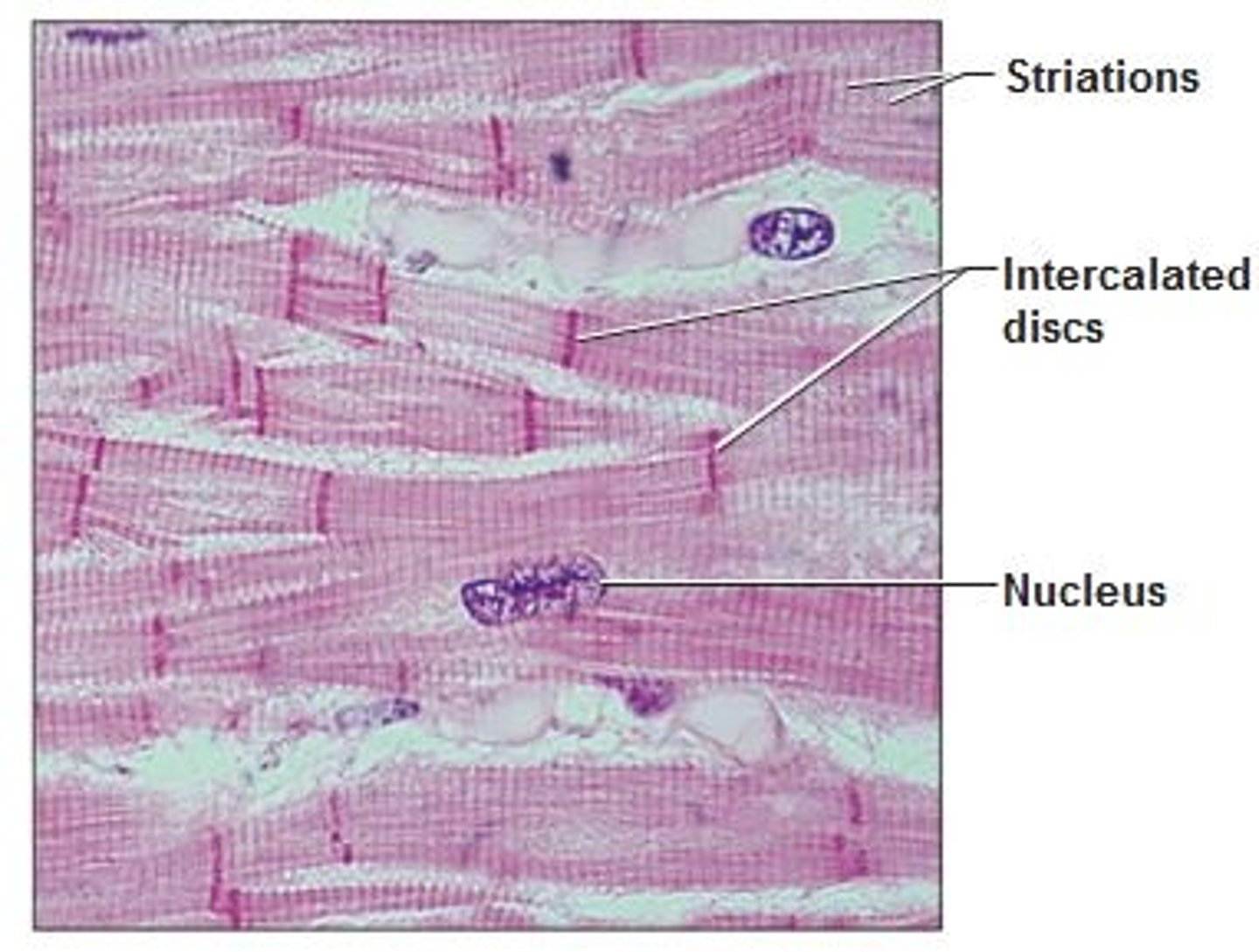
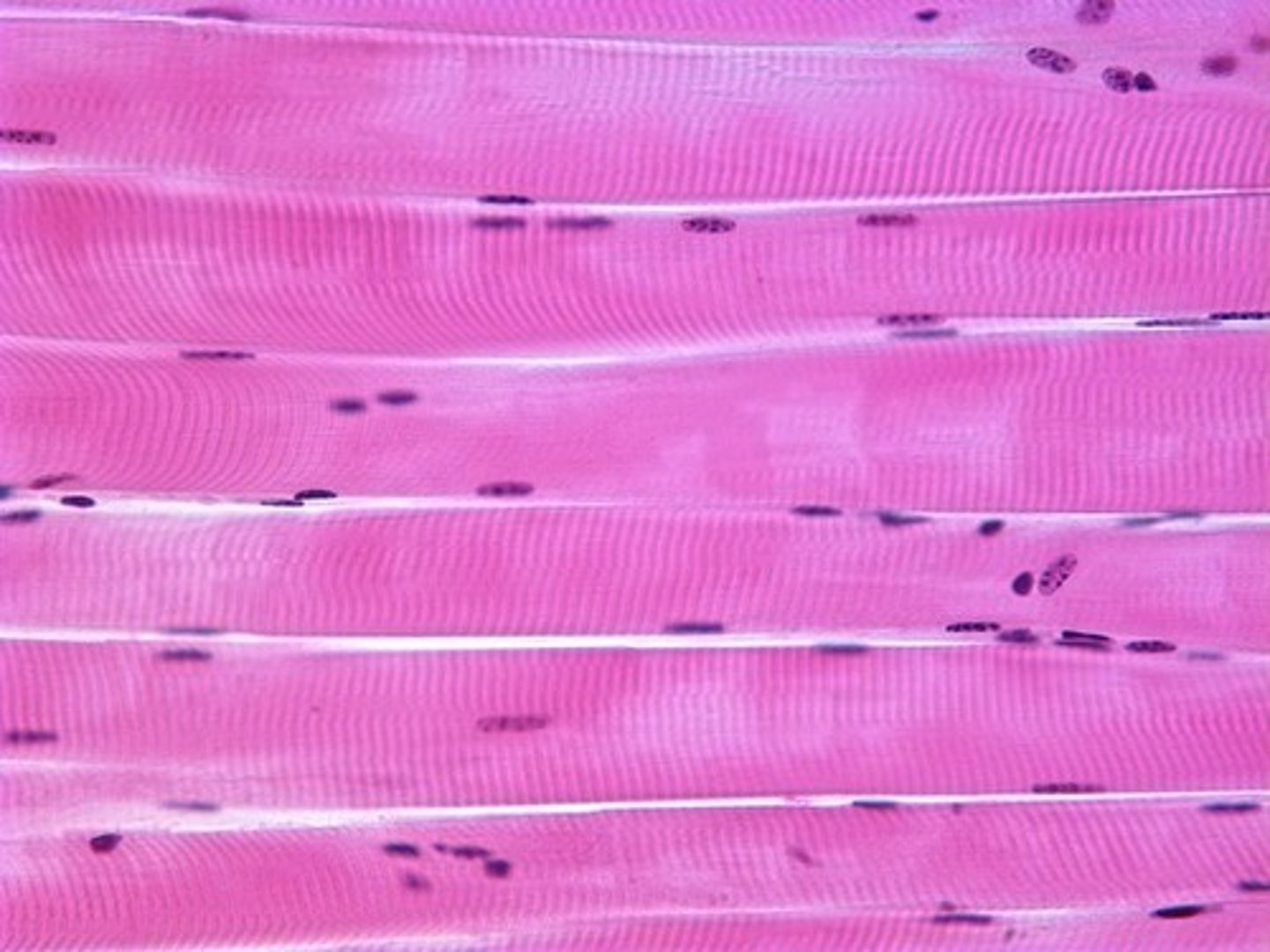
skeletal muscle tissue
striated and voluntary
Voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements.
Organ
group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions
Organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
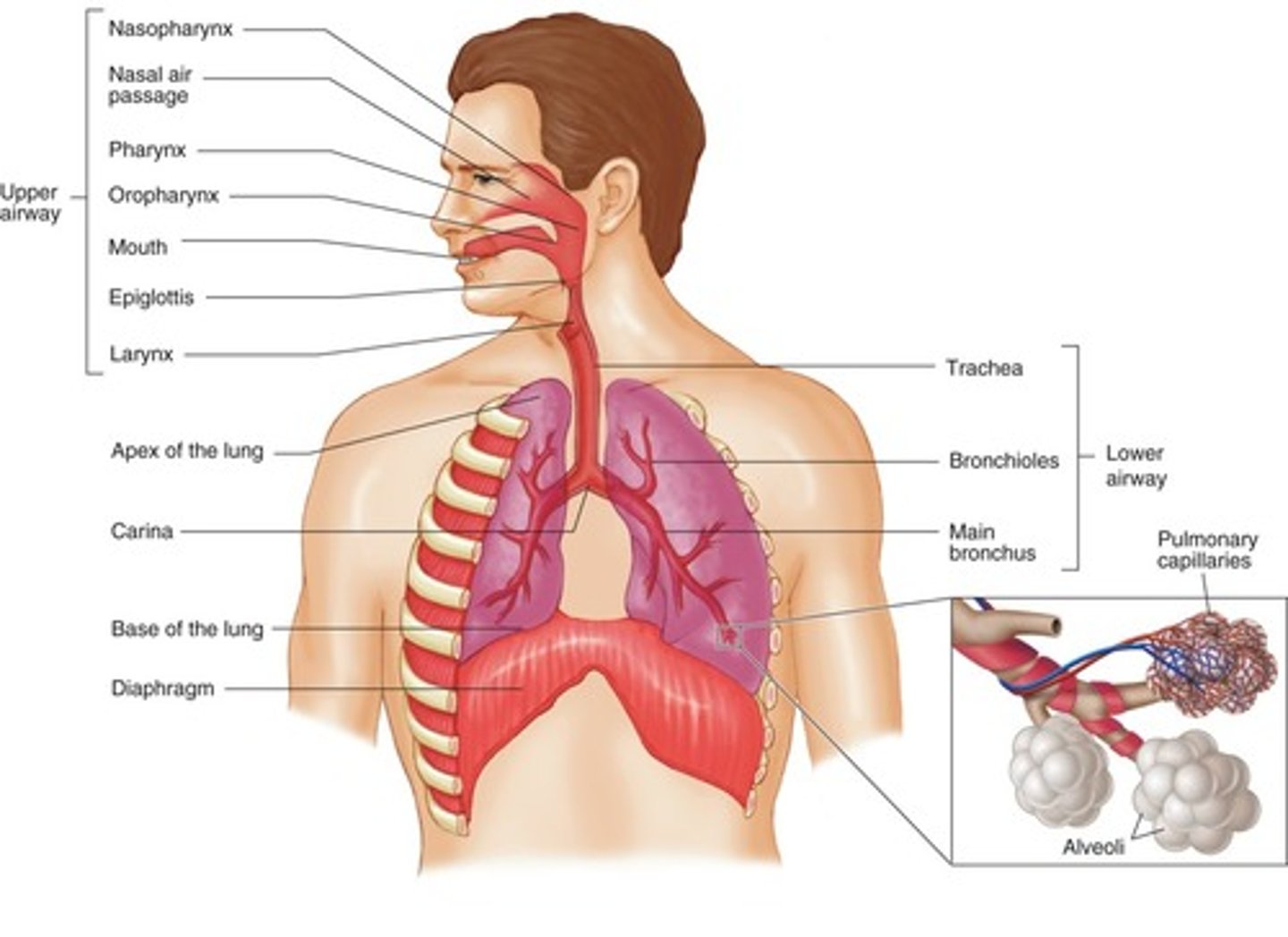
Respiratory System
Organs involved in breathing
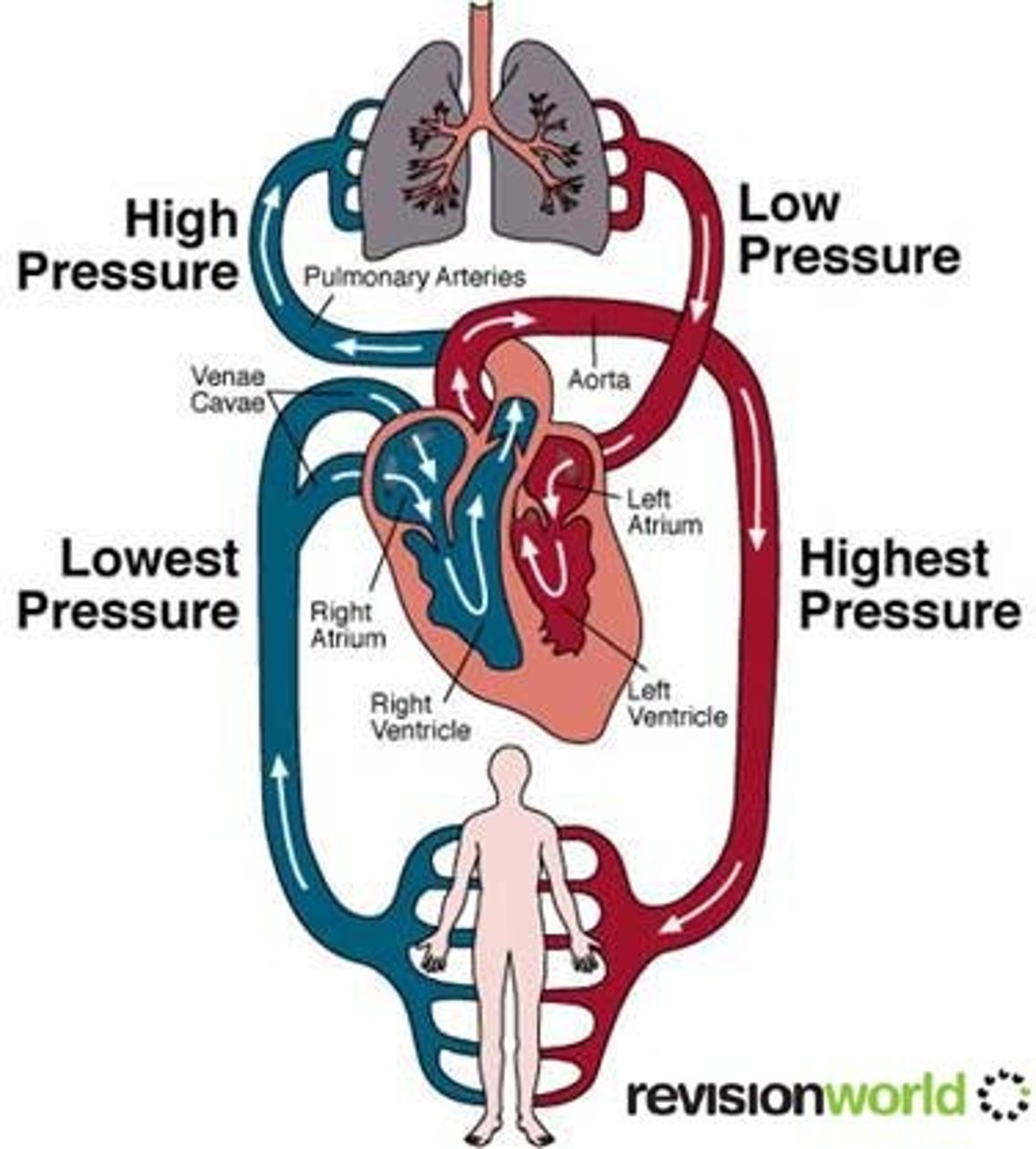
Circulatory System
System responsible for blood circulation
Nervous System
System responsible for transmitting signals
Musculoskeletal System
System of muscles and bones
Gastrointestinal System
Organs involved in digestion
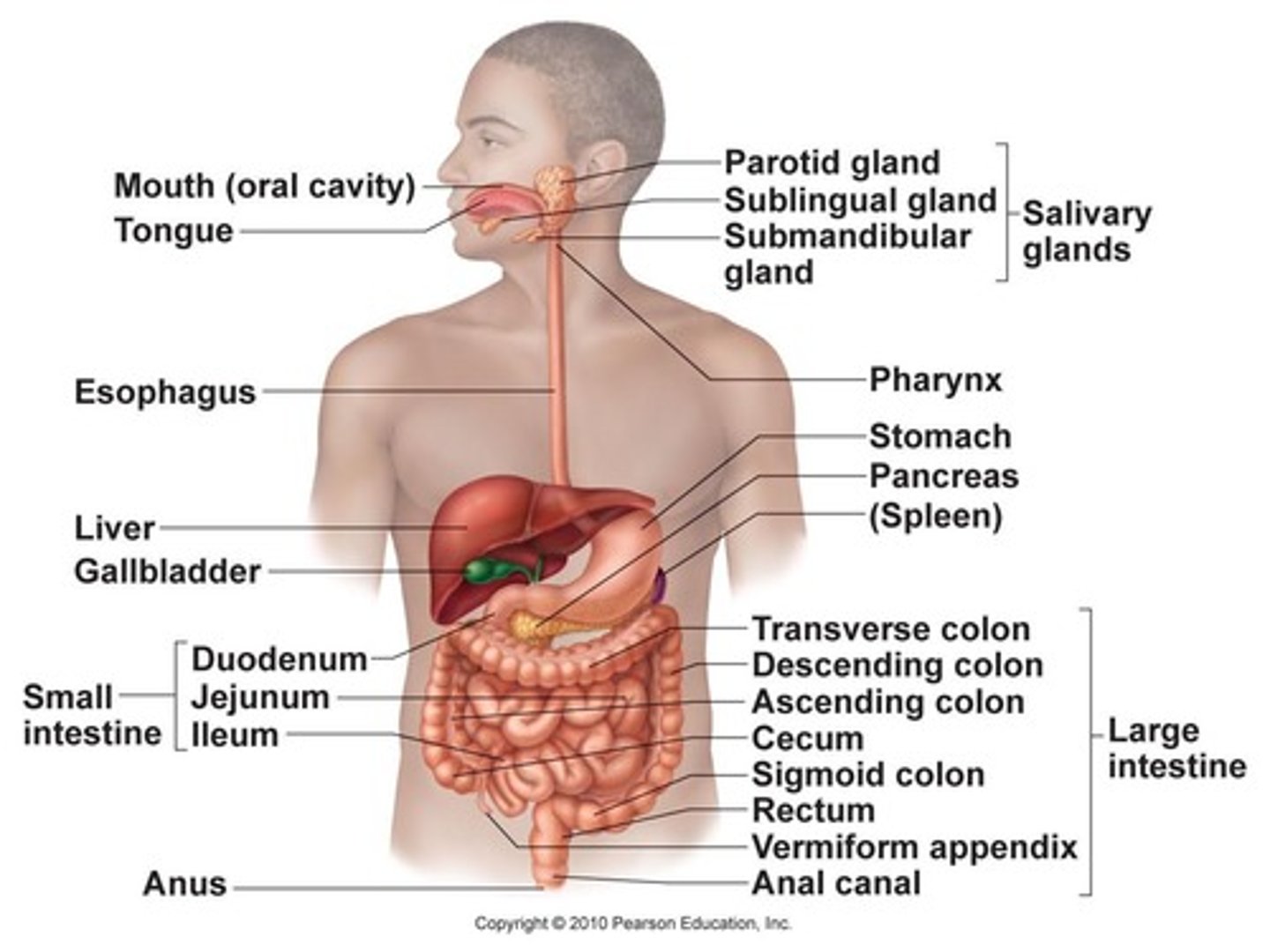
Endocrine System
System of glands producing hormones
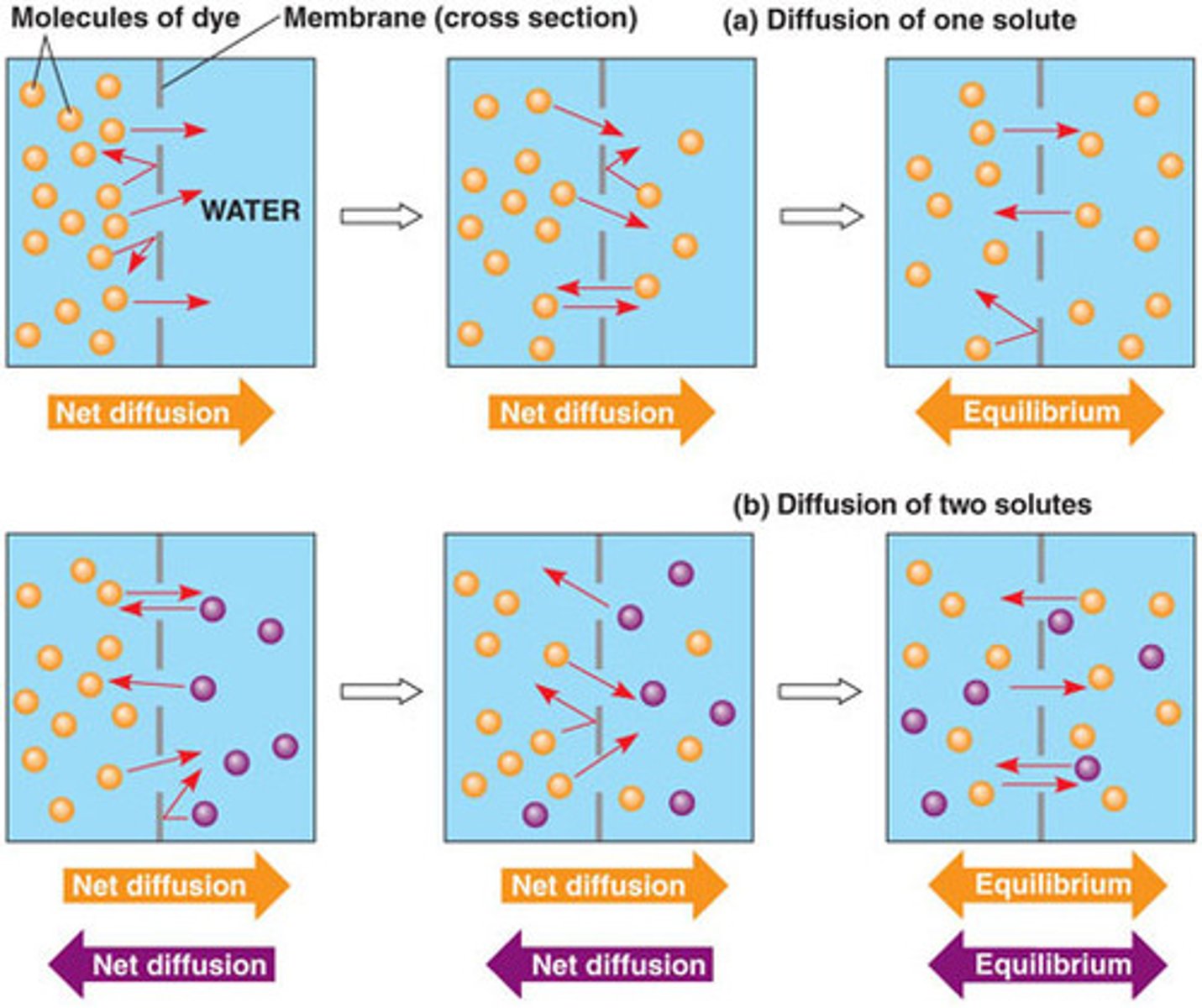
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area high concentration to an area of low concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
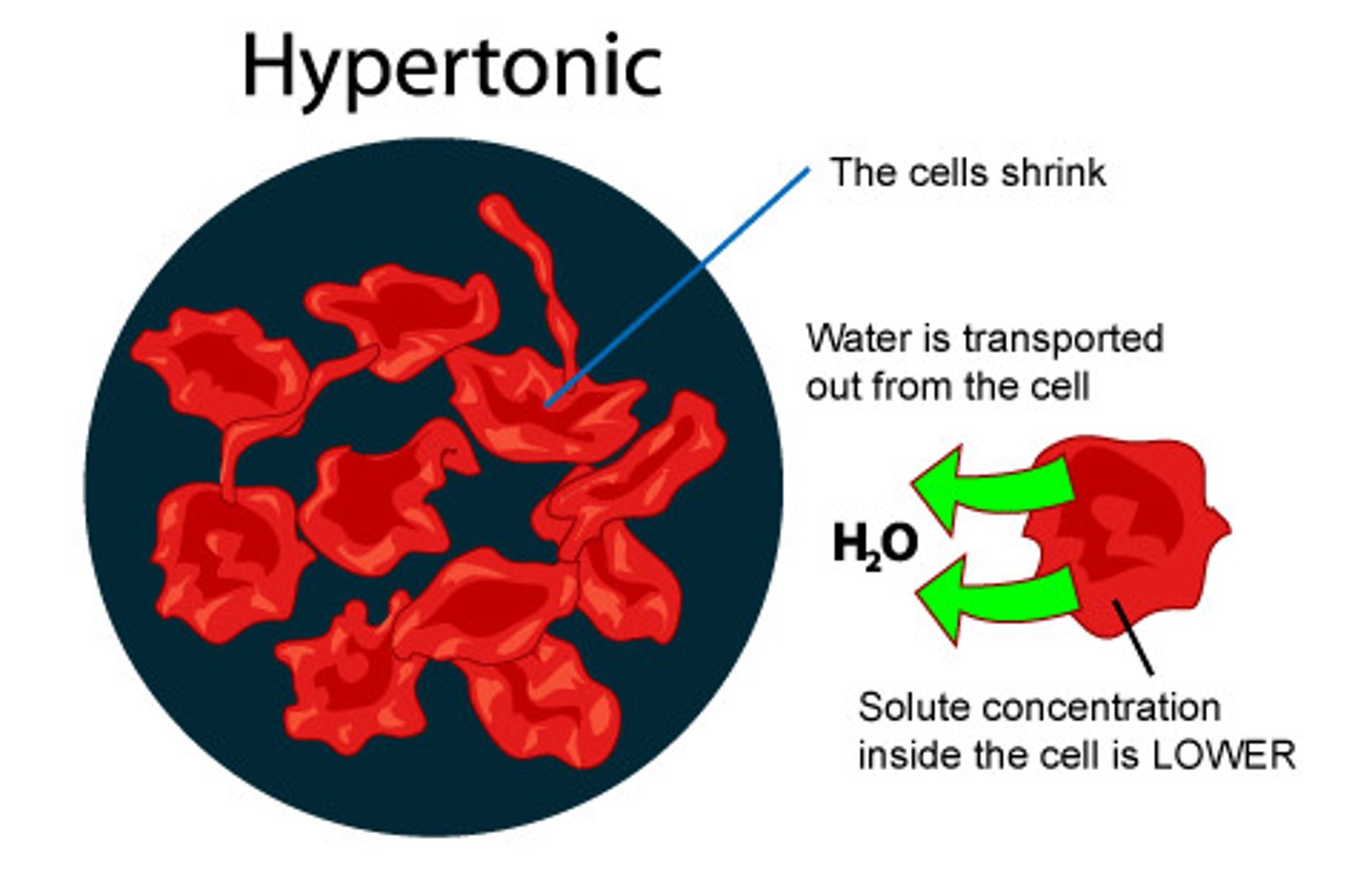
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution. Hypertonic solutions also have lower concentration of water
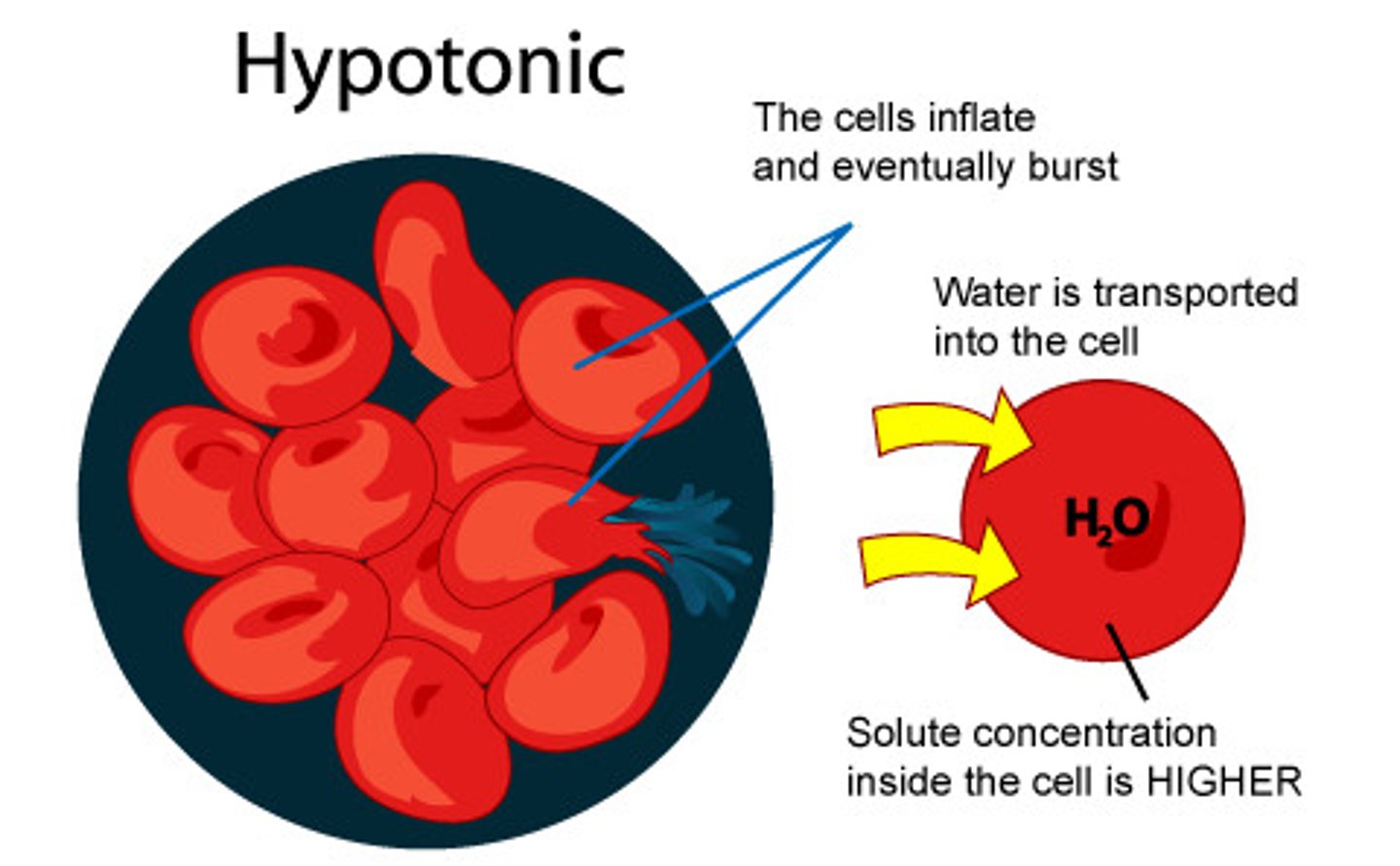
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solutionit will have a greater concentration of water
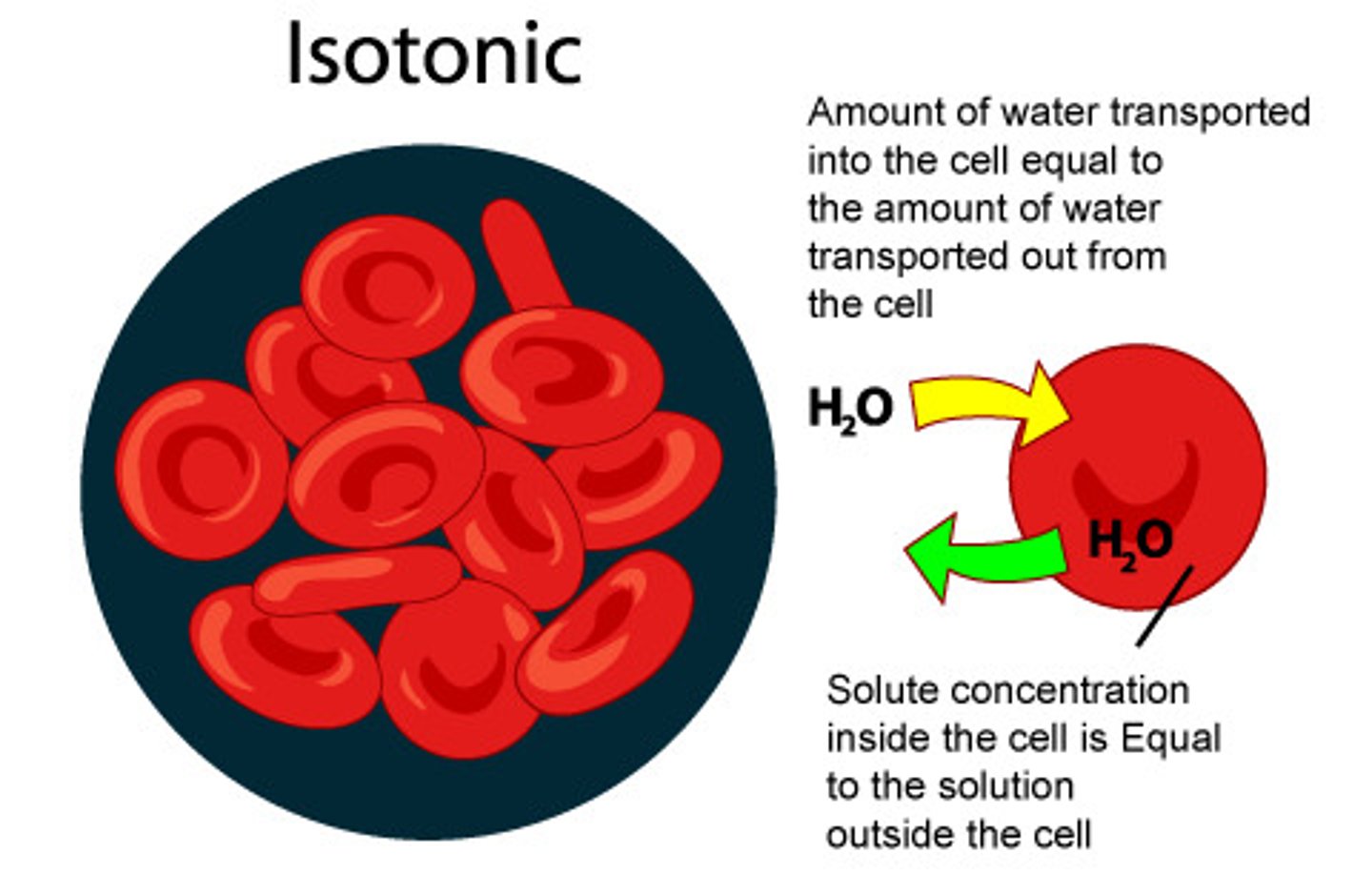
Isotonic
two solutions that have an equal solute concentration
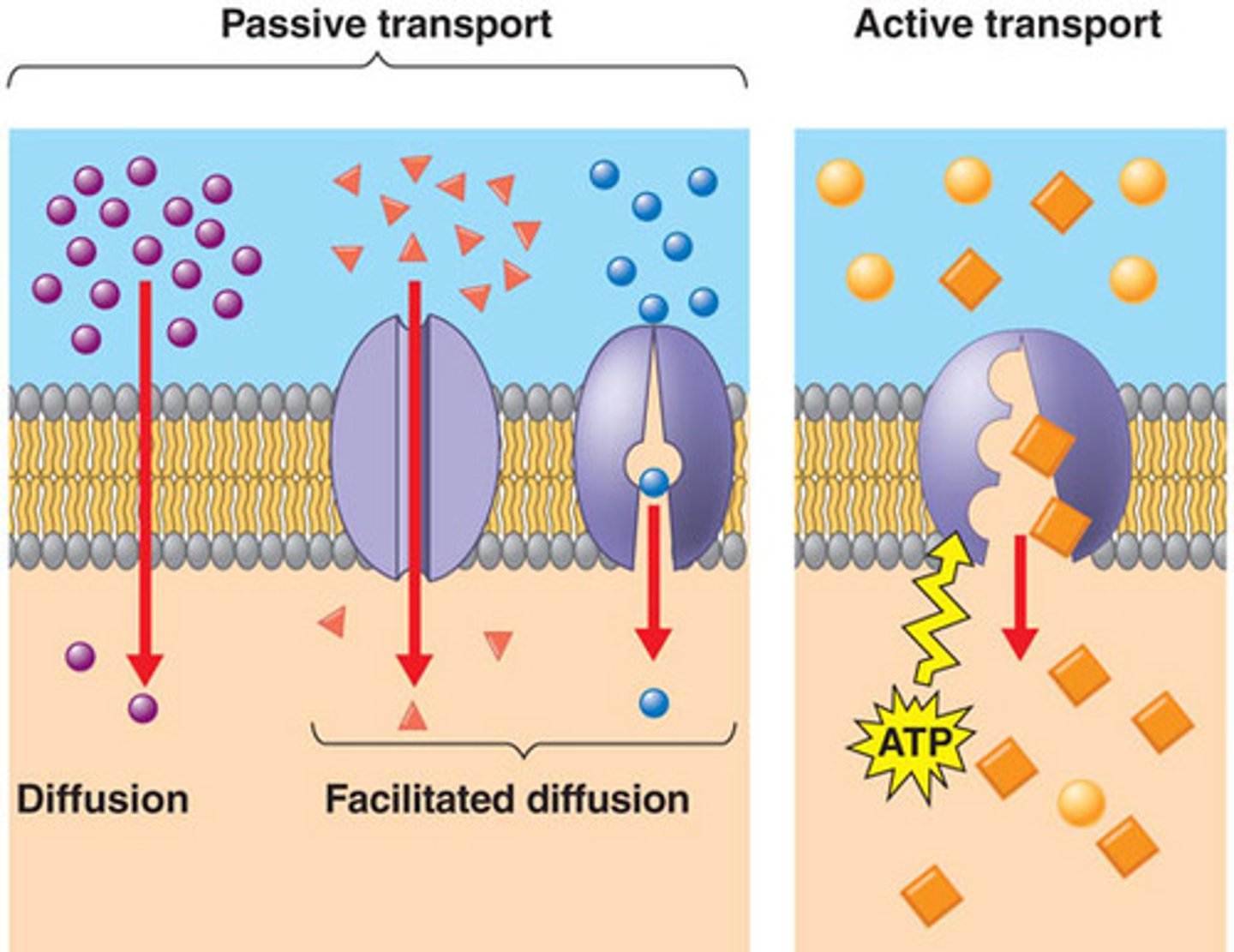
Passive Transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient
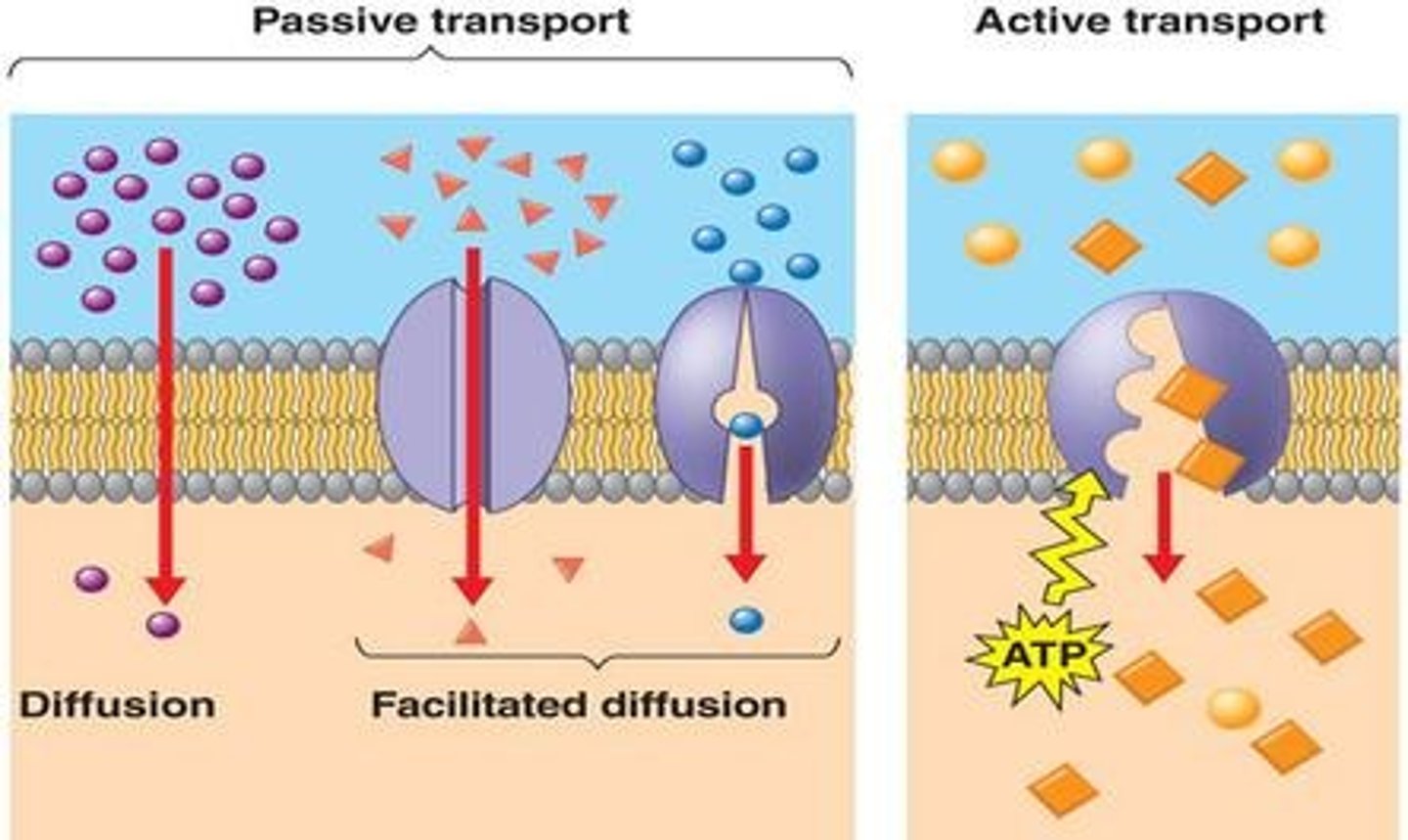
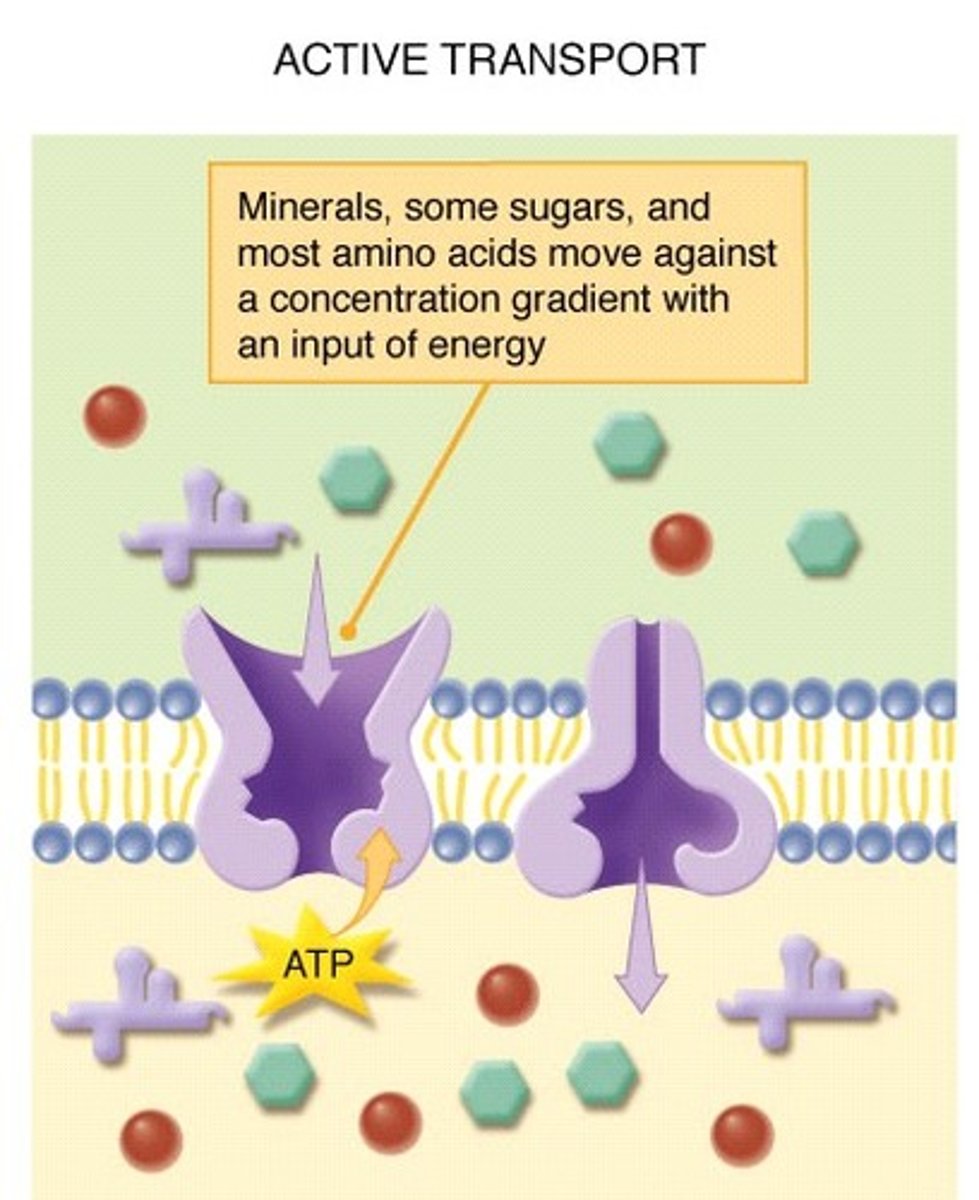
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Filtration
movement of water and solutes through the membrane by fluid, or hydrostatic pressure
Chemistry
Physiology
Health
Evolution
Process of gradual change in organisms over time
Microbiology
Study of microscopic organisms
Ecology
Study of interrelationships in nature
Genetics
Study of genes and heredity
DNA
Genetic material in cells
Atomic Structure
Composition of an atom
Bonding
Chemical attachment between atoms
Chemical Reactions
Process of forming new substances
Health
Overall well-being of an individual
Rest and Sleep
Essential for physical and mental health
Diet and Nutrition
Food intake affecting health
Exercise
Physical activity for health benefits
Hygiene
Practices for cleanliness and health
Substance Abuse Disorder
Addiction to harmful substances
Environment
External surroundings affecting health
Prevention and Safety
Measures to avoid harm and promote well-being
Vaccinations
Administration of vaccines for immunity
Gram Staining
Process classifying bacteria as gram positive or negative based on cell wall characteristics
Antibiotic Resistance
Ability of bacteria to withstand effects of an antibiotic over time
MRSA
Abbreviation for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, an example of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Bacteriology
Study of bacteria
Viruses
Microorganisms with DNA or RNA surrounded by protein, requiring host cells for replication
Antiviral Drugs
Medication to treat viral infections
Virology
Study of viruses
Fungi
Microorganisms with nucleus, organelles, and cell wall, producing spores for reproduction
Mycology
Study of fungi
Algae
Photosynthetic organisms varying in size, living in water or moist environments
Phycology
Study of algae
Protozoa
Single-celled microorganisms lacking cell walls, some obtaining energy through photosynthesis
Protozoology
Study of protozoa