Systems Path II Exam 2 - Pregnancy related
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
those with ascending placental infections (MC) are at risk for what?
chorioamnionitis
with chorioamnionitis (ascending placental infection), membranes become inflamed and may trigger preterm contractions which could cause water to break early. what is this called?
preterm premature rupture of the membranes (PPROM)
signs/symptoms of ascending placental infection
neutrophils, edema, change in discharge, pain
MC cause of ascending placental infection
bacterial (STI or normal flora)
what type of placental infection is associated with placental villitis?
transplacental
what is placental villitis?
chorionic villi (structures covering the surface of placenta to ensure baby receives enough nutrients/gases from mom)
causes of transplacental infections
toxoplasmosis, other, rubella, CMV, HSV (TORCH)
non-uterine implantation resulting in a not viable pregnancy
ectopic pregnancy
90% of ectopic pregnancies are
tubal
Causes of ectopic pregnancy (risk factors)
previous ectopic pregnancy, inflammation/infection of fallopian tube, fertility treatment, tubal surgery, birth control
what is a big concern regarding ectopic pregnancies?
rupture during 1st trimester -> hemorrhage and shock, acute abdominal pain, future infertility
what is the leading cause of pregnancy-related maternal mortality in the 1st trimester and accounts for 4% of pregnancy-related deaths?
hemorrhage from ectopic pregnancy
signs/symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
missed cycle (hCG+), abdominal pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding
abnormal development of benign tumors due to abnormal fertilization
gestational trophoblastic disease
what creates the other layer of a blastocyst and normally develops into the placenta?
trophoblast
signs/symptoms of gestational trophoblastic disease
mimic early pregnancy (high hCG, no fetal heart sound)
Types of gestational trophoblastic disease
hydatidform mole, invasive mole & choriocarcinoma
benign tumor, cystic "grape-like" mass ; when an egg is fertilized, but the placenta develops into a mass of cysts instead of a fetus
hydatidiform mole/molar pregnancy
what type of hydatidiform mole develops from 1 or 2 sperm and 1 egg (no maternal DNA), and contains no fetal parts (risk for invasive mole)
complete
what type of hydatidiform mole develops from 1 egg + 1 or 2 sperm -> triploid and contains early fetal parts?
partial
when trophoblast cells form an abnormal mass that grows into the muscle layer of the uterus which is benign but locally invasive, forms complete moles and has a potential for life-threatening hemorrhage
invasive mole
cancerous tumor which forms inside a pregnant woman's uterus which usually occurs when growths from molar pregnancies turn cancerous
choriocarcinoma
remnants of choriocarcinoma
complete mole (50%), pregnancy (25%), abortion (25%)
signs/symptoms of a choriocarcinoma
severe uterine bleeding, extreme increased hCG
treatment for low risk choriocarcinoma
chemo (100% cure)
treatment for high risk choriocarcinoma
surgery, chemo, radiation
where does a choriocarcinoma MC metastasize?
lungs : cannonball metastasis
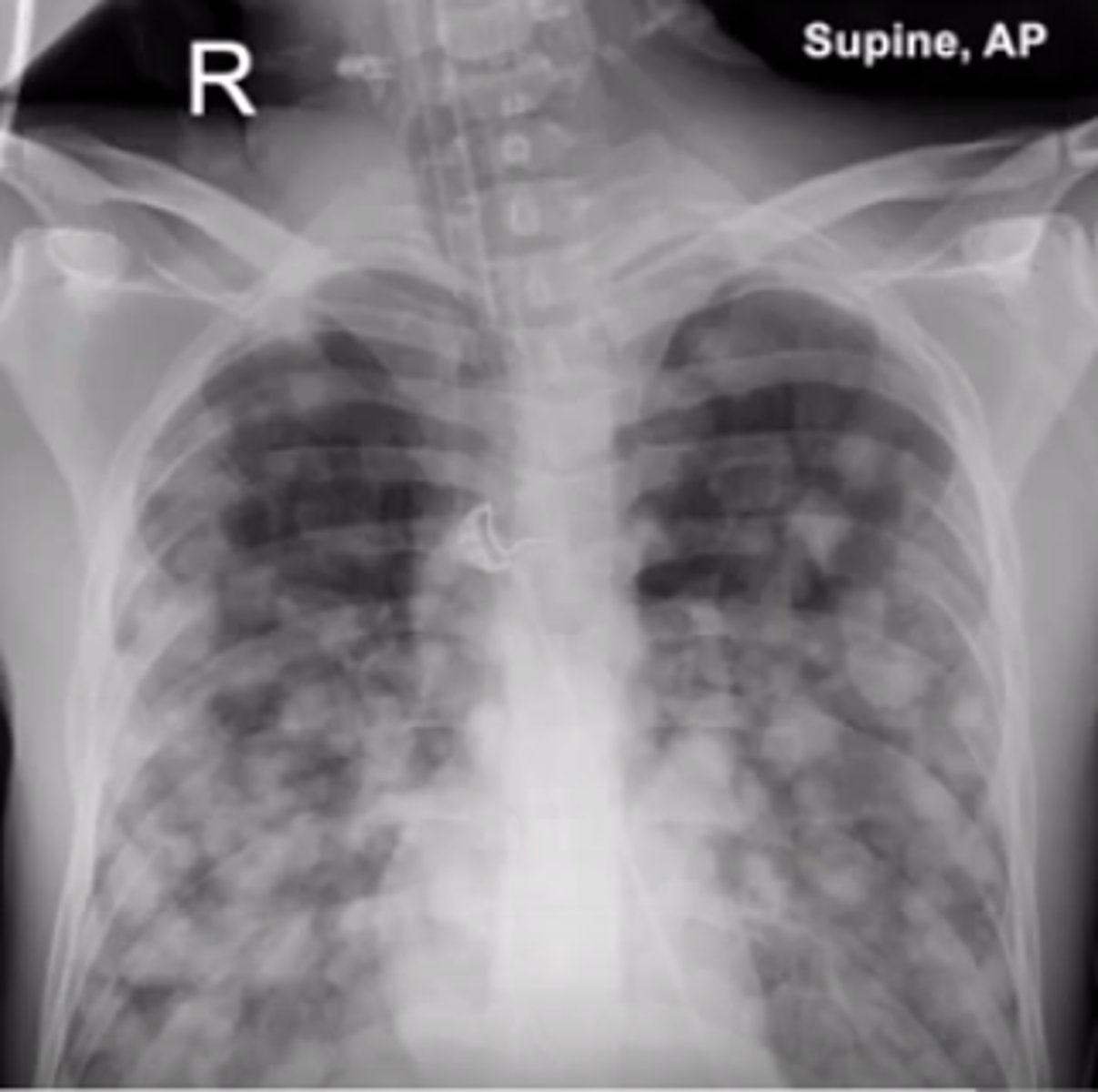
what other cancers may produce a cannonball metastasis appearance?
testicular choriocarcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, prostatic adenocarcinoma
extremely rare, slow-growing tumor which develops where the placenta attaches to the uterine wall
placenta-site trophoblastic tumor
toxemia of pregnancy
preeclampsia
MAIN signs of preeclampsia
HTN, proteinuria, edema in face or periphery
Causes of preeclampsia
idiopathic (effective spiral artery remodeling), endothelial dysfunction
When does preeclampsia usually occur?
>20-weeks gestation, 3rd trimester
risk for preeclampsia
1st pregnancy (primigravida), >35 years-old
other signs/symptoms of preeclampsia
placental hypoxia (fetus), end-organ damage (liver and kidney, maternal), pitting edema, proteinuria, pulmonary edema, RBC damage, thrombosis, low platelets
total number of times a woman has been pregnant
Gravidity
number of pregnancies that reached >20 weeks or fetus >500g
parity
advanced preeclampsia
eclampsia
signs/symptoms of eclampsia
seizures, worsening HTN, headache, diplopia, epigastric pain, worsening organ damage (kidneys, liver, CNS)
10% of eclampsia cases develop what?
HELLP syndrome
What is HELLP syndrome?
hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets
treatment for eclampsia
delivery/induction (>37 weeks), Mg sulfate, anti-hypertensive meds