Electromagnetism
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is a magnetic field?
A field surrounding a permanent magnet or a current carrying conductor in which magnetic objects feel a force
How are magnetic fields created?
When a wire carries a current, a magnetic field is created around the wire
What does the arrow on a magnetic field line tell you?
The direction in which a free North Pole would move
What does it mean if magnetic field lines are equally spaced and parallel?
There is a uniform field
What are the rules of repulsion and attraction of magnetic poles?
Like poles repel
Unlike poles attract
Sketch a magnetic field for a bar magnet?

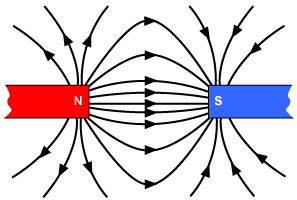
How would the magnetic field look like for 2 attracting poles?
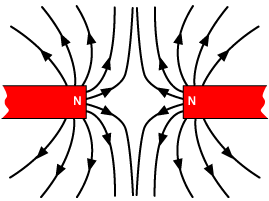
How would the magnetic field look like for 2 repelling poles?
What is the right hand grip rule?
The thumb points in the direction of the conventional current
The direction of the field is given by the direction in which the fingers curl around the wire

Draw a magnetic field pattern for a current carrying coil?
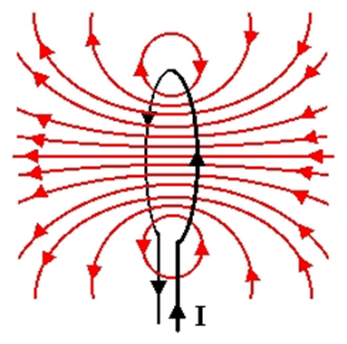
I = Current (In/out represented by direction of arrows)
Red lines is the magnetic field
North (Right)
South (Left)
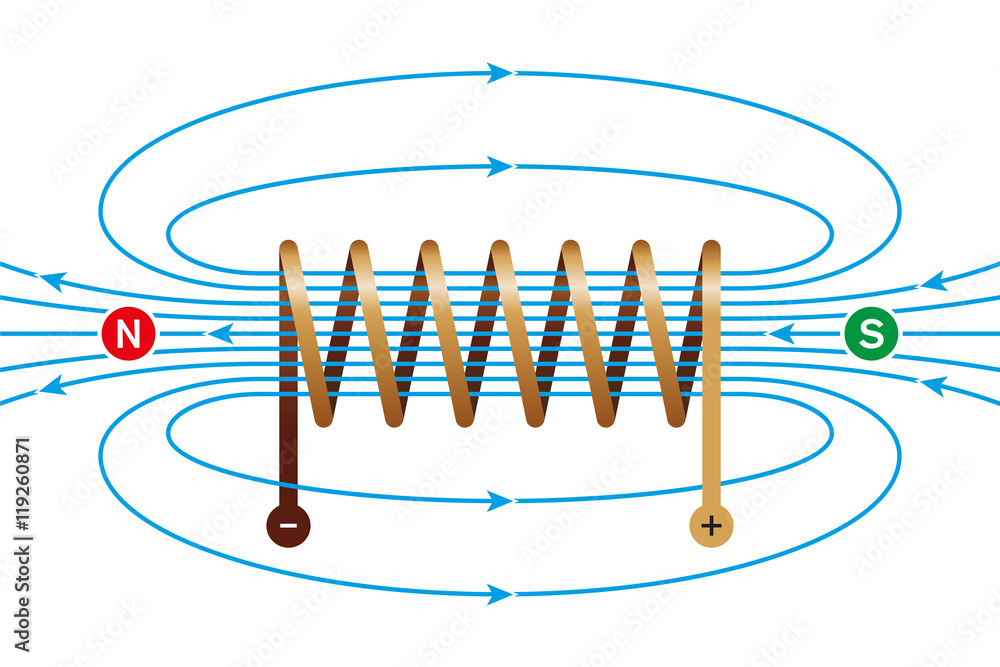
Draw the field pattern for a solenoid?
how does magnetic field pattern of a solenoid change is the direction of the current is reversed?
the direction of magnetic field also reverses
What happens when you place a current-carrying conductor in an external magnetic field?
The 2 field interact like the fields of 2 permanent magnets (Experience equal and opposite forces)
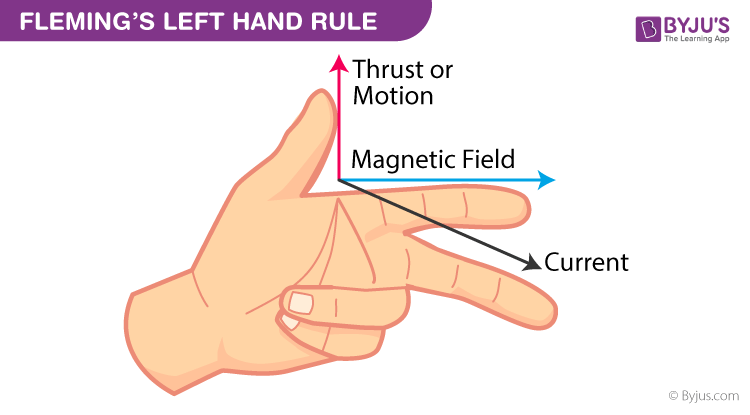
What is Fleming’s left hand rule?
Thumb - Thrust (Force)
First Finger- Field
SeCond Finger- Conventional current
What does the magnitude of the force experienced by a wire in an external magnetic field depend on? (Perpendicular/ Parallel)
The force must be a maximum when the wire is perpendicular to the field
Force must be 0, when it is parallel to the magnetic field
State the equation for the force on a current carrying wire in an external field?
F = B I L sinθ
Force = Magnetic Flux Density X Length of wire in field X Angle between field and current (sinθ)
What are the units of magnetic flux density and is it a vector or scalar quantity?
T (Tesla)
Vector
How is magnetic flux density defined?
The force per unit current per unit length on a current-carrying wire placed at 90º to the field lines.
Describe an experiment which can be used to determine magnetic flux density?

The balance is zeroed when there is no current in the wire
With the current, the wire experiences a vertical upwards force
According to N3L, the magnets experience an equal downward force
F=mg (g= acceleration of free fall)
Magnetic flux density between the magnets can be determined by B = F / I L
What happens when a charged particle moves in a magnetic field?
It will experience a force, provided it is not moving parallel to the magnetic field
How can you determine the direction of force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field?
Fleming’s left hand rule
Describe the path of a beam of electrons travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field?
Circular (in electric parabola)
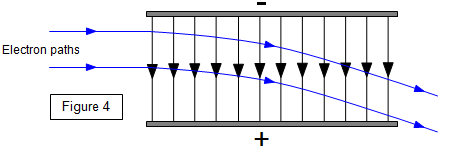
Explain why the speed of the electrons remains unchanged when travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field?
The force is 90 degrees to the velocity, so there is no component

State the equation for the force on a charged particle travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field?
F= B Q v
Force = Magnetic Flux Density X Charge X velocity
Derive an expression for the radius of the circular path described by a charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field?
B Q v = m v² / r
r = m v / B Q
radius= mass X velocity / magnetic flux density X charge
Do faster moving particles move in bigger or smaller circles?
Bigger circles
Do particles with greater charge move in smaller or bigger circles?
Smaller circles
Describe how a velocity selector works?
Electric Field (Fe) = V / d
Magnetic Field (Fb) = B Q v
v = E / B

What is electromagnetic induction?
Relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field
Describe what happens when a magnet is pushed towards a coil of wire?
How is energy conserved in this process?
An e.m.f is induced across the ends of the coil, and when the magnet is pulled away a reverse e.m.f is induced
Electrical energy is produced through the work done to move the magnet - energy is conserved
Explain (in terms of force experienced by the electrons in the wire), why a changing magnetic field induces a current in a wire?
The motion of the coil relative to the magnetic field makes the electrons move because they experience a magnetic force given by B e V
The moving electrons create an electrical current within the coil, producing electrical energy
Define magnetic flux and its units?
The product of the component of the magnetic flux density perpendicular to the area and cross-sectional area
Weber (Wm)
1 Wb = 1 Tm²
How is magnetic flux density calculated?
Φ= B A cos θ
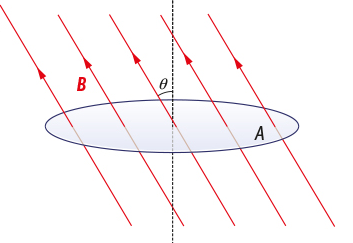

B = magnetic flux density
A = cross sectional area
θ= angle
What is the value of the magnetic flux when the magnetic field is normal to the area?
Maximum magnetic flux
What is the value of the magnetic flux when the magnetic field is parallel to the area?
0 Magnetic flux
Define magnetic flux linkage and its units?
The product of the number of turns in the coil, N, and the magnetic flux,Φ
N Φ
Wb
State the condition for an e.m.f to be induced in terms of magnetic flux linkage?
A change in B, A, N or θ
(Or spin it faster)
What is the difference between magnetic flux density and magnetic flux?
Flux is the magnetic flux density perpendicular to an area (Φ =B A cos θ)
Flux density is magnetic flux over area (B = Φ / A)
State Faraday’s law? (in words)
The magnitude of the internal e.m.f (ε) is directly proportional to the rate of the change of magnetic flux linkage
What is Faraday’s law? (equation)
ε is directly proportional to ΔNΦ / Δt
induced e.m.f directly proportional to change in magnetic flux linkage/ time taken
State Lenz’s law?
The direction of the induced e.m.f or current is always such as to oppose the change producing it
State the equation that combines Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law?
Which section is Lenz’s law?
ε = -ΔNΦ / Δt
The negative sign is Lenz’s law
Describe the purpose of a search coil and explain how it works?
Include diagram
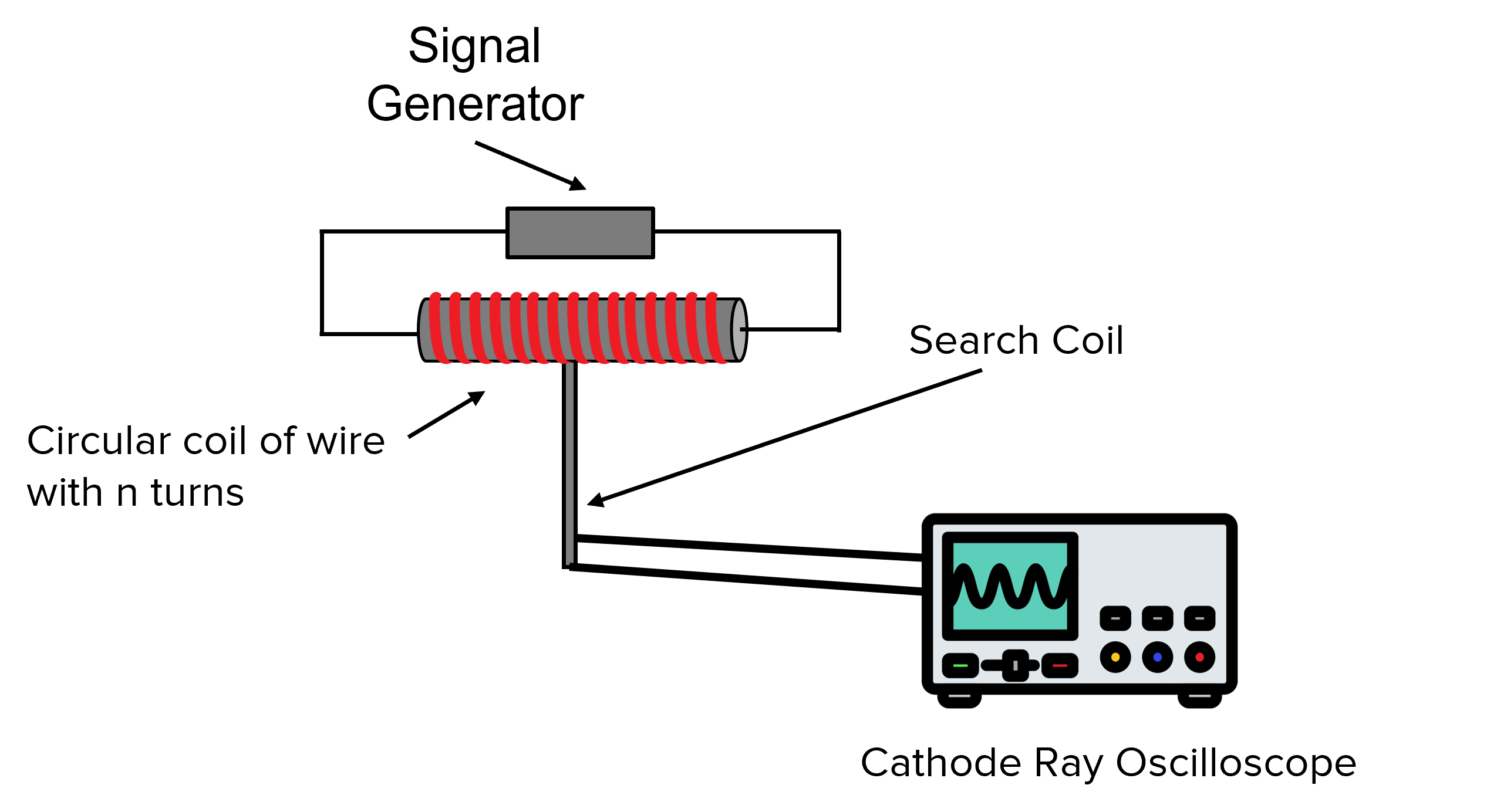
A search coil is used between the poles of a strong magnet at right angles to the magnetic field of flux density, and then is quickly removed
The average e.m.f can be calculated on the ends of the search coil, as the search coil measures magnetic fields/ rate of change of flux
Explain how an alternating current generator works?
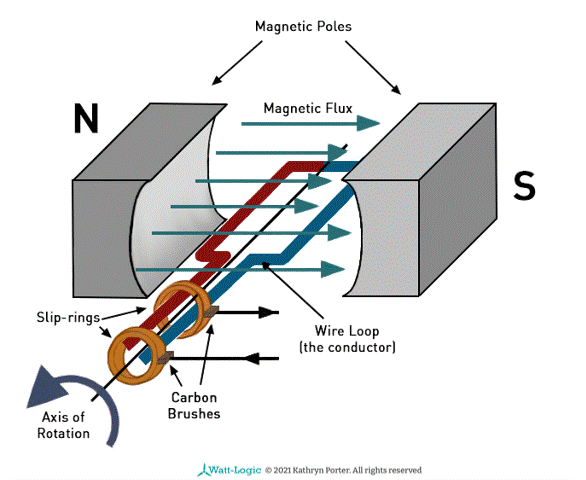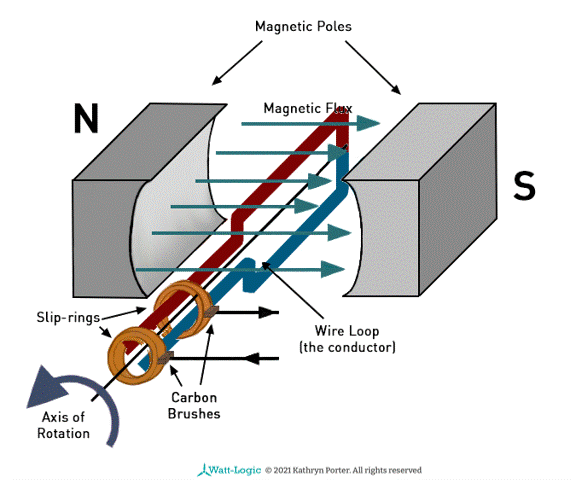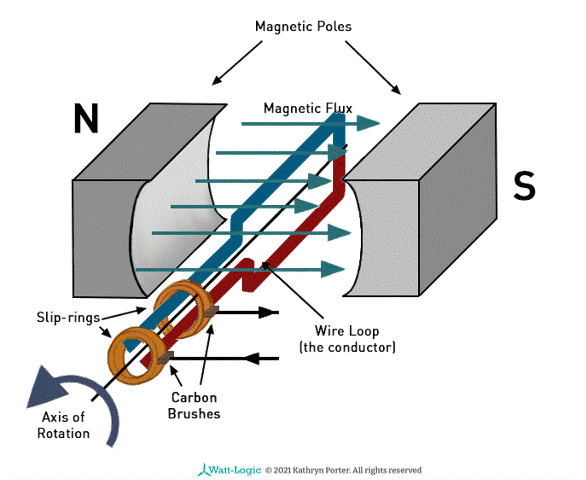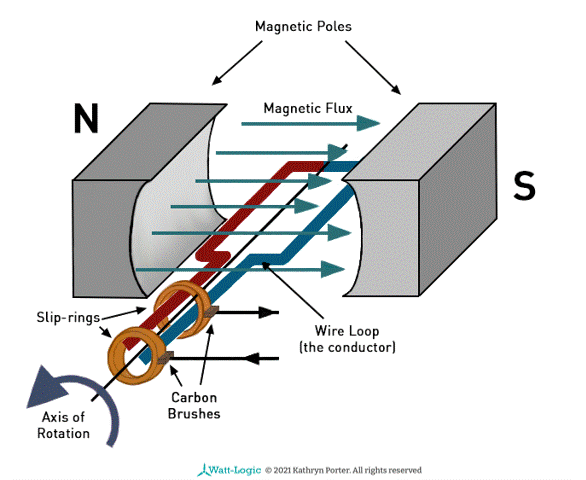
As the coil rotates, the flux linkage changes with time, This is caused by the changing cos θ factor
According to Faraday’s law, the induced e.m.f = - BAN cosθ / t
The magnitude of the gradient from the flux linkage against time is equal to the induced e.m.f

e.m.f is directly proportional to cosθ / t (B, A, N are constant)
What is the purpose of a transformer?
Changing alternating voltages to higher or lower values
Give an example where transformers are used?
Power stations use transformers to convert energy
Describe the construction of a transformer?
Include a diagram
A laminated iron core, a primary (input) coil and a secondary (output) coil

Explain how a transformer works in terms of changing magnetic flux?
An alternating current is supplied to the primary coil → Producing a varying magnetic flux in the soft iron core
The secondary coil, is linked by this changing flux
The iron core ensures that all magnetic flux created by the primary coil links to the secondary coil
This induces an e.m.f and produces an alternating current out of the secondary coil
State the turn-ratio equation?
n(s) / n(p) = V(s) / V(p)
n (secondary) / n (primary) = V (secondary) / V (Primary)
n= number of turns
V= voltage
What is a step up transformer?
It has more turns on the secondary than on the primary coil
V(s) < V(p)
What is a step down transformer?
It has fewer turns on the secondary than on the primary coil
V(s) > V(p)
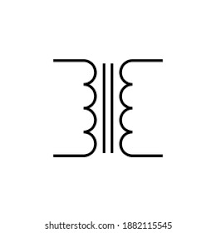
What is the circuit symbol of a Transformer?
What does it mean if a transformer is 100% efficient?
The output power from the secondary coil is equal to the input power into its primary coil
What is the relationship between current and voltage in a 100% efficient transformer?
I (p) / I (s) = V (s) / V (p)
Why are transformers not 100% efficient in reality?
Some power is lost due to the heating effect of the eddy current (loops of current) in the core
Which design feature of a transformer increases the efficiency and how?
A laminated iron core being separated by an insulator → helps minimise currents induced in the core, minimises loss of power due to heating