Coverings
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
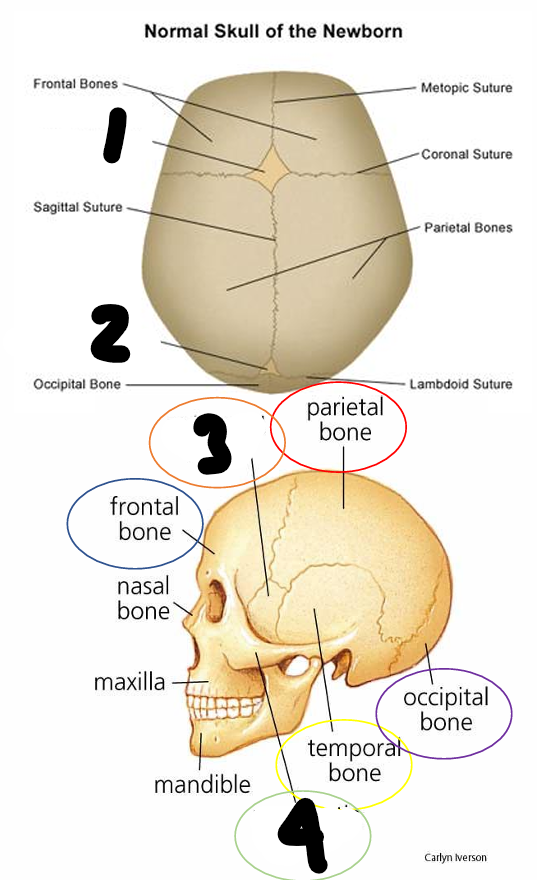
name all
1 anterior fontanelle 2 posterior fontanelle 3 sphenoid bone 4 zygomatic bone
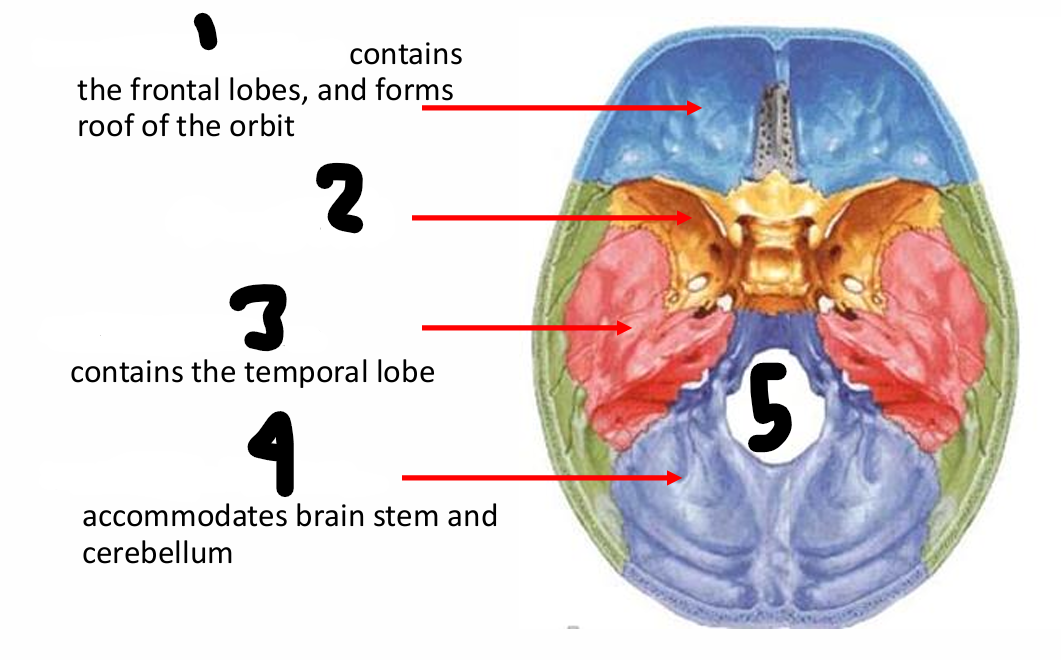
name all
1 anterior cranial fossa 2 sphenoid bone 3 middle cranial fossa 4 posterior cranial fossa 5 foramen magnum
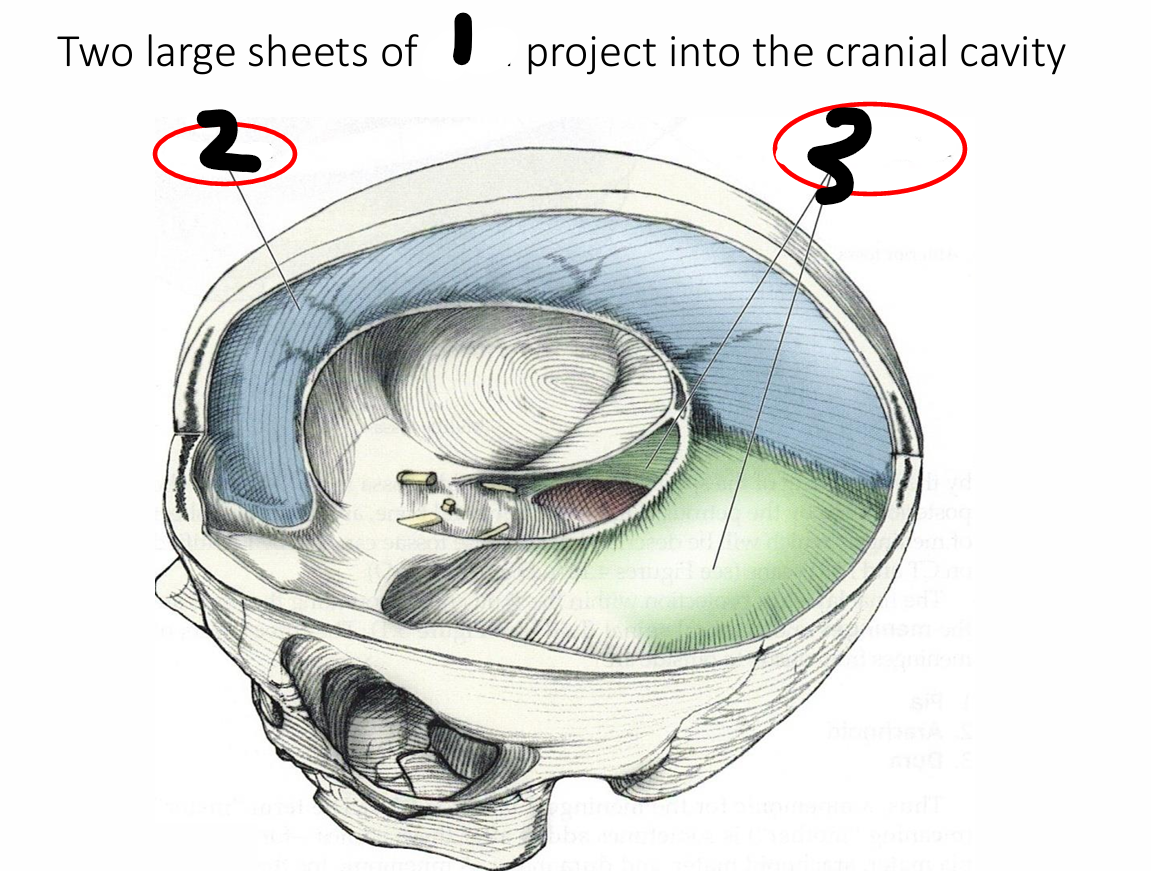
name all
1 dura 2 falx cerebri 3 tentorium cerebelli
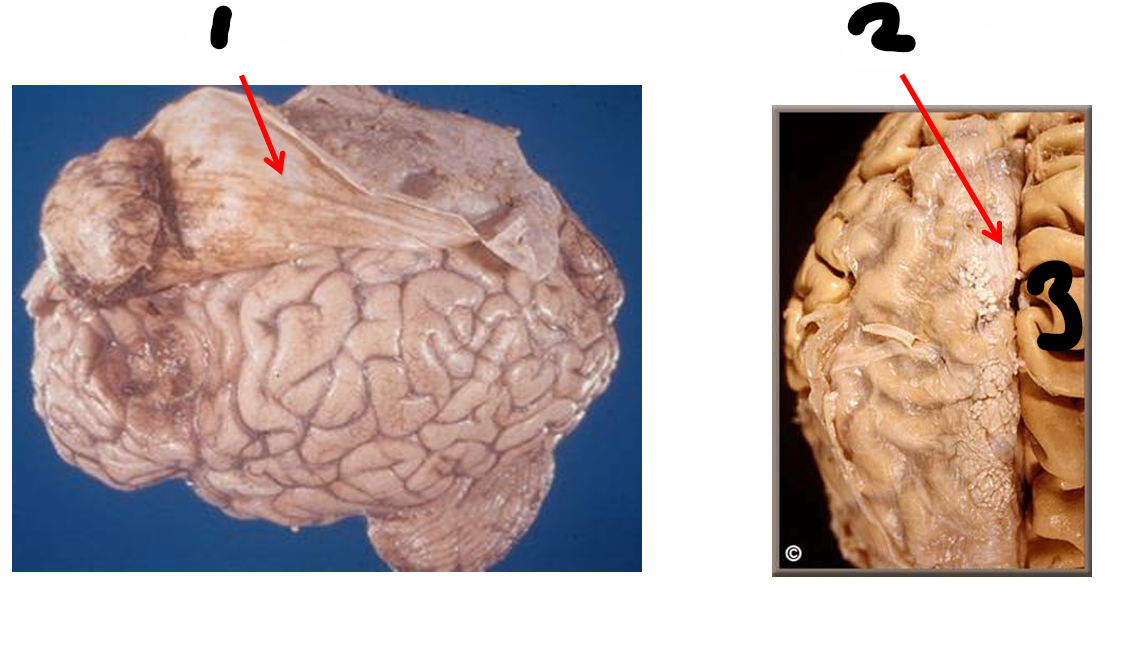
name all
1 dura 2 arachnoid 3 pia mater
The ______ _______ are projections of the arachnoid membrane into the dura (dural venous sinus), this is where CSF drains into the venous sinus system
arachnoid granulation
______ _________ is the connective tissue strands within the subarachnoid space surrounded by CSF that connect the arachnoid mater to pia mater, this gives the arachnoid mater its spider web appearance AND ITS NAME
arachnoid trabeculae
___ and ________ are the two leptomeninges
pia arachnoid
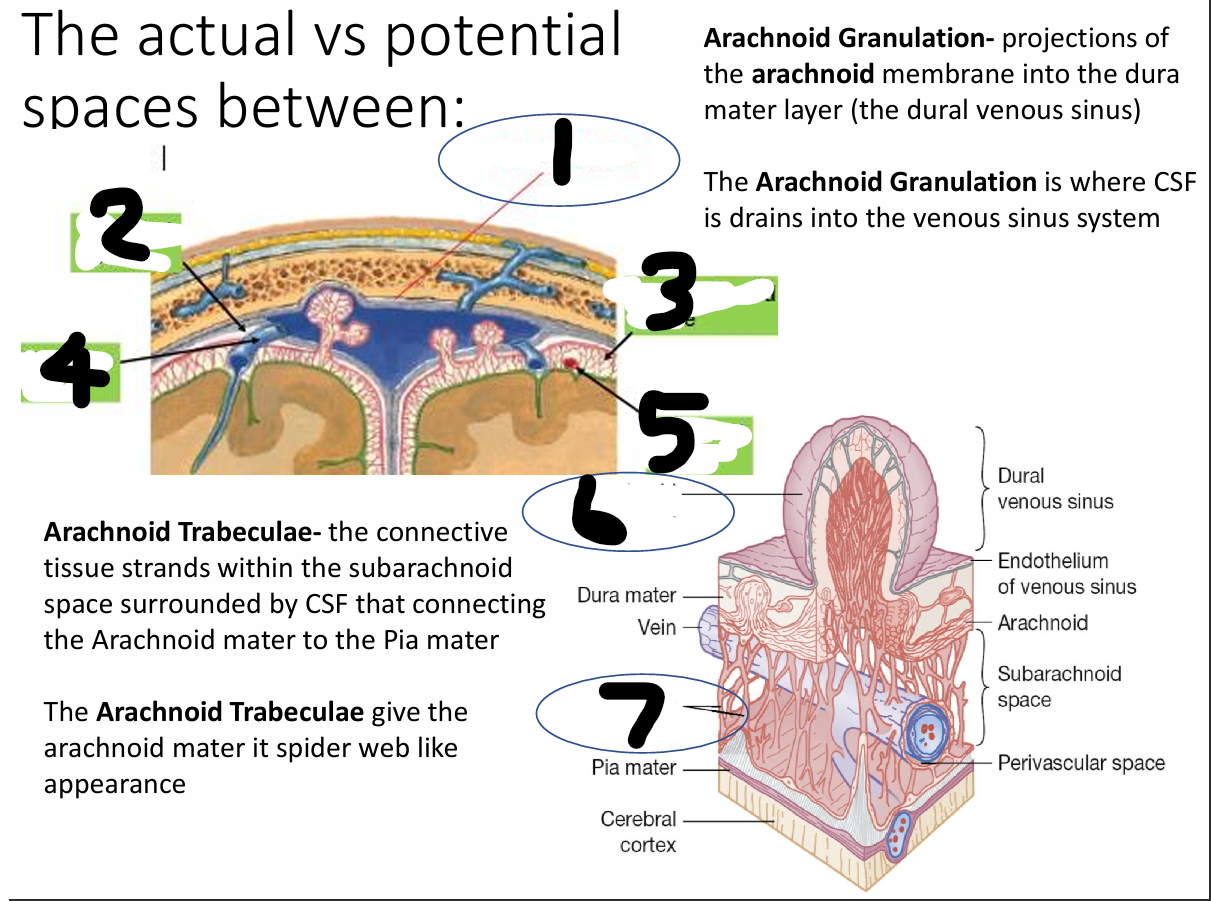
name all
1 epidural space 2 subdural space 3 subarachnoid space 4 bridging vein 5 cerebral artery 6 arachnoid granulation 7 arachnoid trabeculae
is there a true epidural space in brain: ____ (yes/no) is there a true epidural space in spinal cord _____ (yes/no)
no yes
when doing an epidural it will always be injected below ___ and ____, since that’s where the spinal cord ends, btu typically between ____ adn ____ to alleviate pain below waist
L1 L2 L3 L4
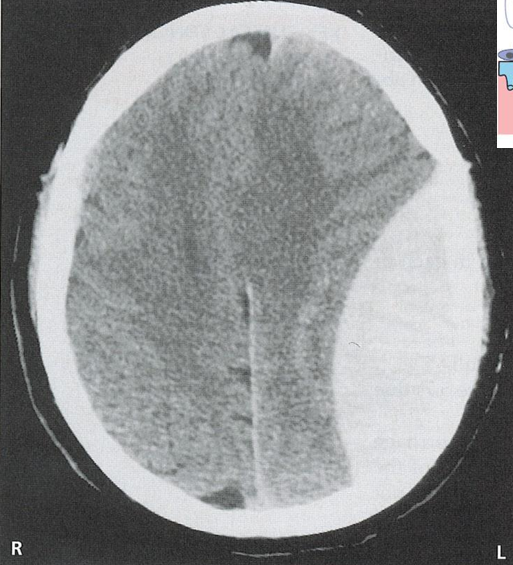
The tearing of the middle meningeal _____ which can occur due to head traumas leads to bleeding in extradural space or _____ ____________ , this happens very fast and causes a coma hours after incident , ____ shaped
artery epidural hematoma lemon
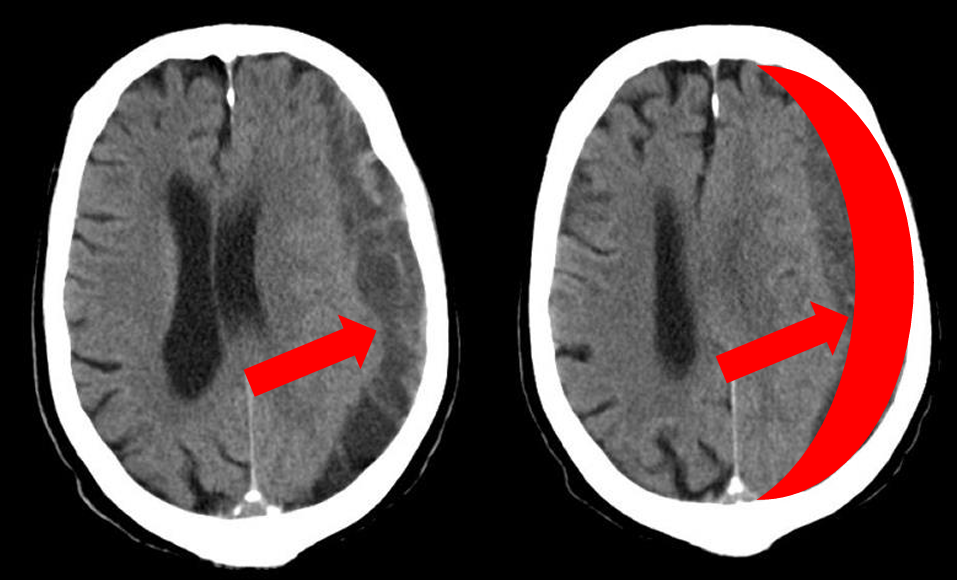
tearing of vein across subdural space (______ vein) causes gradual seepage of blood and results in a _____ ________, _____ shaped
bridging subdural hematoma banana
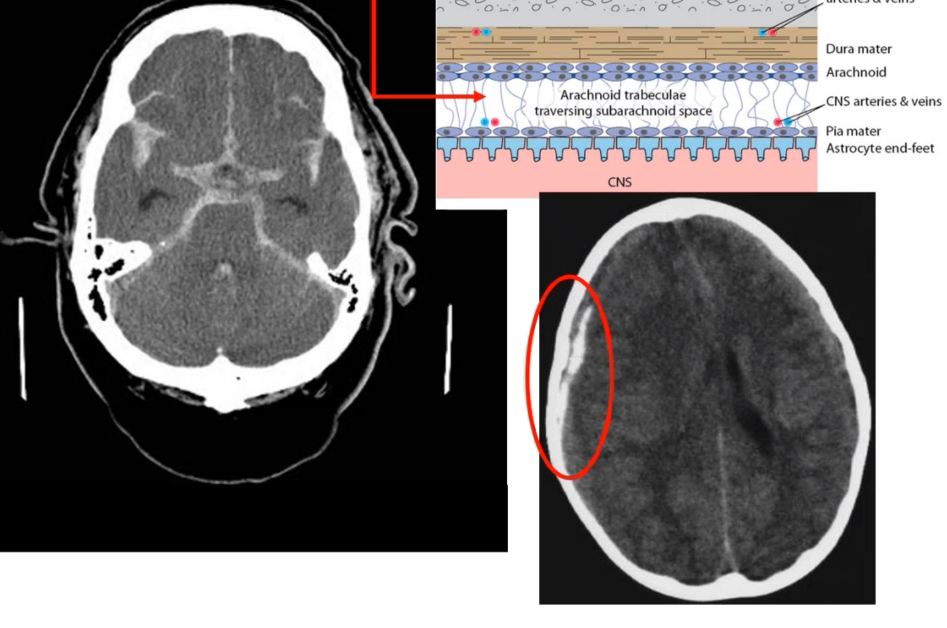
_____ ______ is indicated by blood filling up in the sulci
subarachnoid bleeding
_______ exhibits flu symptoms with a stiff neck
meningitis
_____ meningitis causes an increase in opening pressure and is much more dangerous than ______ meningitis, this pressure reading is taken when doing a spinal tap on the ______ ______ in the subarachnoid space in spinal cord, normal opening pressure is around 7 to 28 cm H2O
bacterial viral lumbar cistern
the brain has one true space: _____ ______ while the spinal cord aslo has ________ ______
subarachnoid space epidural space
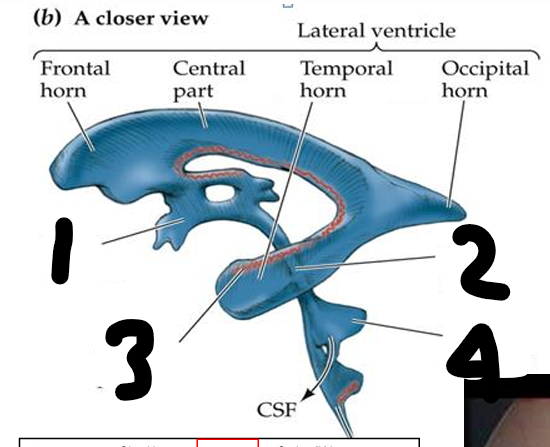
name all
1 third ventricle 2 cerebral aqueduct 3 choroid plexus 4 fourth ventricle
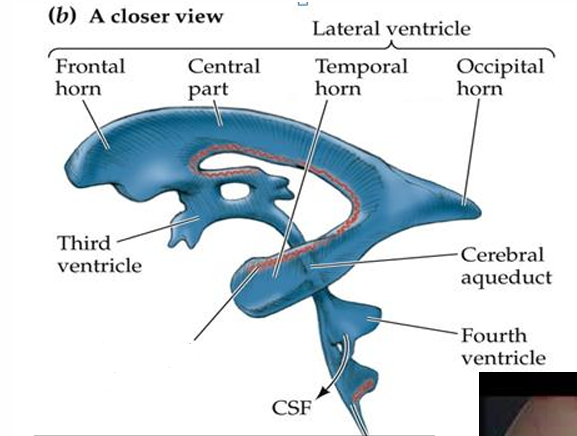
CSF is produced in ependymal cells in _____ _____ which are located in 4th ventricle, and stretch from temporal horn to 3rd ventricle
choroid plexus
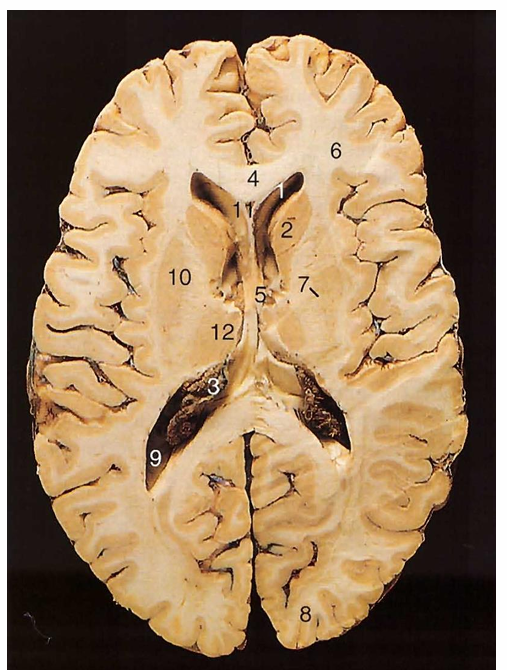
name 1 3 9 11
1 anterior horn 3 choroid plexus 9 posterior horn 11 septum pellucidum
from fourth ventricle, CSF exits into _____ _______ and around the spinal cord via the medial aperture (_____ of _____) and two lateral aperture (______ of ______) where it eventually passes through _____ _____ (granulations) to return to venous circulation via the _____ ______ _______
subarachnoid space foramen Magendie foramena of Luschka arachnoid villi dural venous sinuses
CSF in ventricles cannot reach subarachnoid space if there is obstruction of an _______ foramen, _______ ________ or outflow foramen of the ______ ventricle, in children less than 2 years of age the head _______, this is called _________ hydrocephalus (WILL SEE ENLARGEMNET OF VENTRICLES)
intraventricular cerebral aqueduct fourth enlarges non communicating
________ hydrocephalus occurs when CSF is obstructed in the subarachnoid space, like from bleeding or meningitis, scars the arachnoid with a block of return flow channels (arachnoid villi)
communicating
We have 7 cervical vertebra but ____ cervical nerves
8
___ - ____ exit above their vertebra. __ exits between __ - ___ , and all others exit below, after __ the nerves form the _____ _____ or the nerves that continue after teh spinal cord ends
C1 C7 C8 CVII T1 L2 cauda equina
there are __ cranial nerves, __ cervical neves, __ thoracic nerves, ___ 5 lumbar nerves, __ sacral nerves, __ coccygeal nerve
12 8 12 5 5 1