Electrochemistry
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a reducing agent?
Causes another atom to gain electrons
Gets oxidized
What is an oxidizing agent?
Causes another atom to lose electrons
Gets reduced
What does oxidation mean?
Loss of electrons
What does reduction mean?
Gain of electrons
How is electric current calculated?
I = q/s
I = current
q = charge in Coulombs
s = seconds
How is power calculated?
P = EI
E = voltage
I = current
How is delta G found?
Delta G = -nFE
n = mol electrons
F = Faraday’s constant
E = voltage
What is the reaction of a mercury cell?
Zn(s) + HgO(s) ←→ ZnO(s) + Hg(l) Eo = 1.35V
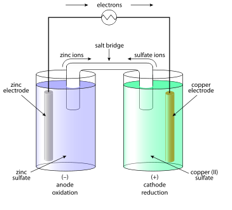
How do you draw a Galvanic cell?
Anode: where oxidation occurs; -
Cathode: where reduction occurs; +
Salt bridge connects them
Voltage measured
How is cell notation written?
Electrode | solid | electrolyte || electrolyte | solid | electrode
Oxidation half-cell || reduction half cell
What direction do electrons flow in a galvanic cell? Ions?
From anode to cathode
Ions flow opposite
How is oxidation number assigned?
Elements have 0
H is + 1
O has -2
For monoatomic ions, oxidation = net charge
Alkali metals +1
Alkaline earth metals +2
Halogens -1 unless combined with:
F is -1
Bount to eachother
Bound to more than one atom
Bound to oxygen
Sum of oxidation states = net charge of atom
How is direction of electron flow found?
From anode to cathode
Balance electrons in half reactions to determine
How are reactions balanced?
Assign oxidaiton states
Write half cell reactions
Balance each half reaction
Balance atoms except O and H
Add H2O to side lacking O and balance
Balance H by adding H+
Balance electrons
Add electrons to product side for oxidation
Add electrons to reactant side for reduction
Balance electrons between half cells
Add half reactions and cancel common
Check numbers of atoms are equal
In basic solution, neutralize H+ with OH-
What is standard electrode potential for Ag?
Reduced against SHE
Ag+ + e- ←→ AG
Eo = 0.7993 V
What is standard electrode potential of Cu against SHE?
Cu2+ + 2e- ←→ Cu
Eo = 0.34 V
What is standard electrode potential of Zn against SHE?
Zn 2+ + 2e- ←→ Zn
Eo = 0.76 V
What is reduction potential?
How likely something is to get reduced
Higher = more likely = electrons flow towards it = cathode
What is the cell potential equation?
Eocell = Eocathode - Eoanode
Cathode always has greater reduction potential
How is half cell potential determined?
E = Eo + 0.0592/n log Q
At 25 C
E = Eo - RT/nF ln Q
R = 8.314 (VC)/(K/mol)
T = temperature in K
n = number moles electrons
F = 96485 C/mol e-
Q is like equilibrium constant, but not at equilibrium
What are conditions of standard cell potential?
1 atm
25 C
1 M solution
What is standard hydrogen electrode?
2H+ + 2e ←→ H2
Eo = 0.000V
At standard conditions
What is the nernst equation?
E = E0 - RT/nF ln Q = Eo -0.0592/n log Q
How is K found from nernst equation?
K = 10nE^o / 0.0592
How does E relate to direction of electron flow?
Electrons flow from lower to higher E