WPH11 Physics 2019-2025 past paper questions
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What other unit is equivalent to Watt (W)? (Oct 2024)
Js-1
Because P = Work done (J) / time (s)
So J/s which is Js-1
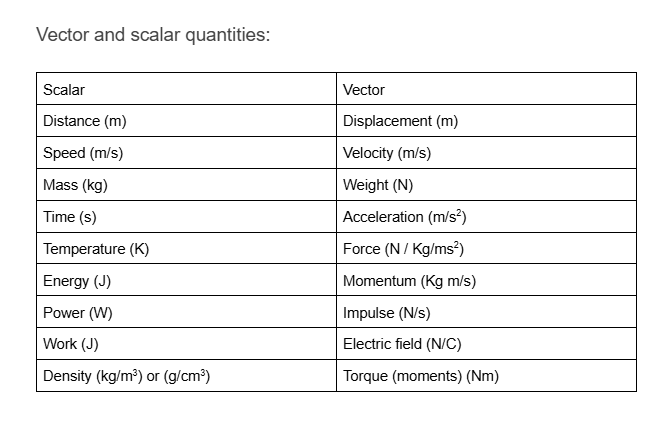
Name all scalar and vector quantities
from
Energy (J)
Distance (m)
Power (W)
Speed (m/s)
Mass (kg)
Time (s)
Velocity (m/s)
Weight (N)
Acceleration (m/s2)
Force (N / Kg/ms2)
Momentum (Kg m/s)
Impulse (N/s)
Electric field (N/C)
Torque (moments) (Nm)
Temperature (K)
Work (J)
Density (kg/m3) or (g/cm3)
Displacement (m)
A person stands on a moving staircase.
The moving staircase increases the G.P.E by 5000J in a time of 42s
The efficiency of the moving staircase is 0.63
Write an expression that gives the power input of the moving staircase in watts. (Oct 2024)

The wire at the elastic limit is called…. (Oct 2024)
Elastically deformed

(Oct 2024)

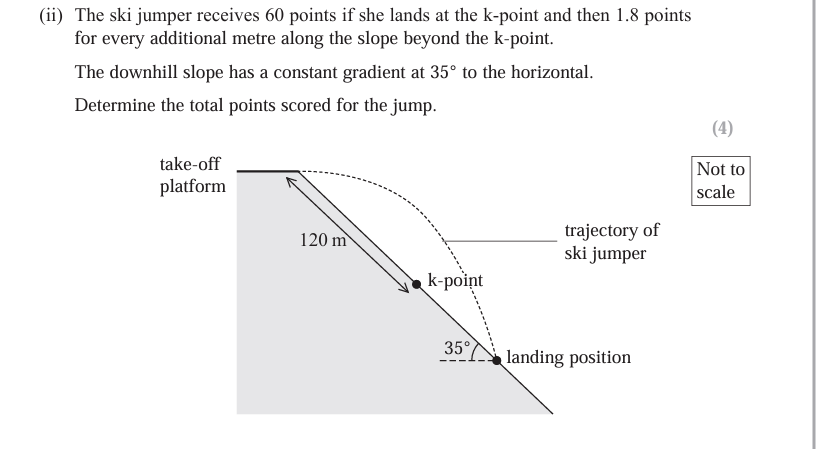
(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)

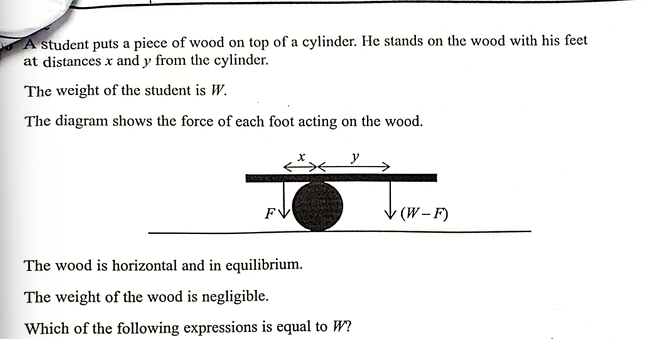
(Oct 2024)
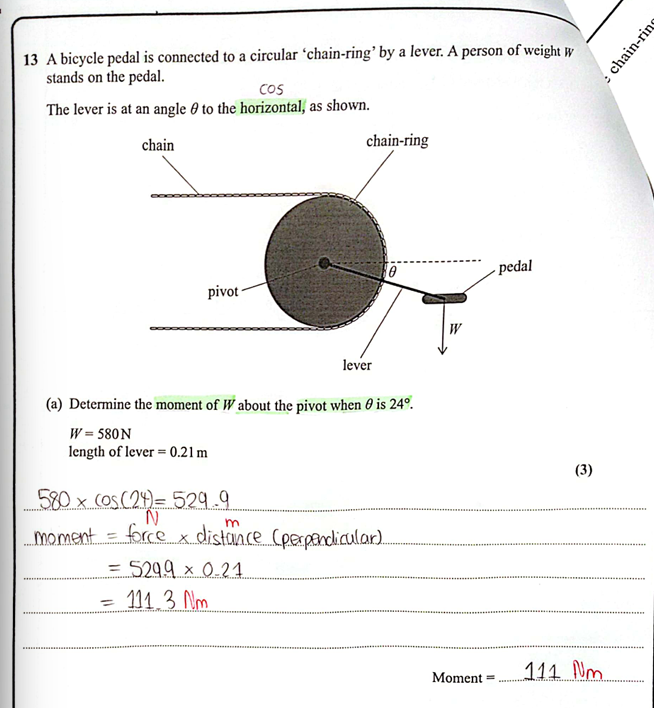
(Oct 2024)

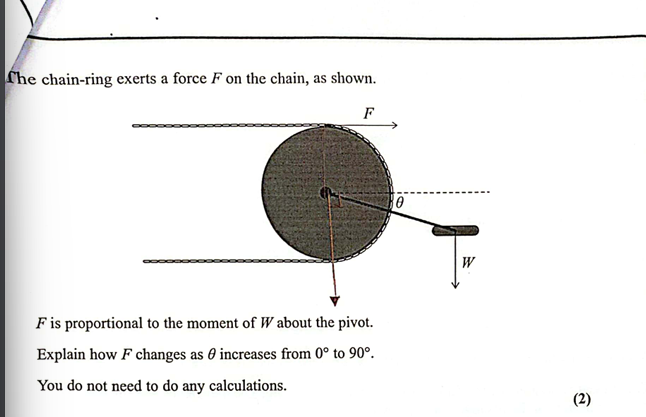
(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)
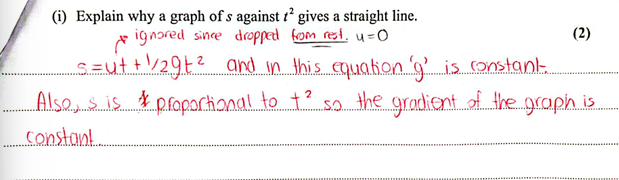
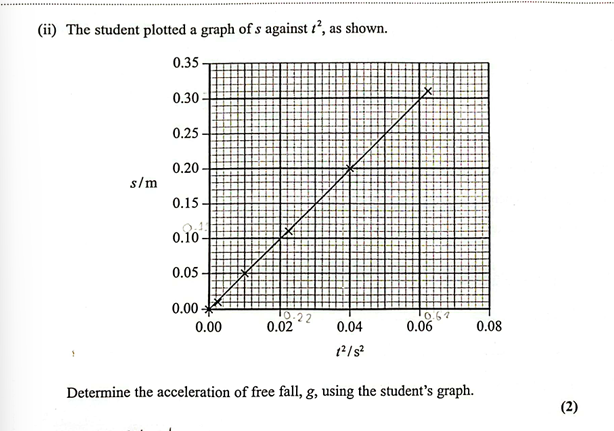
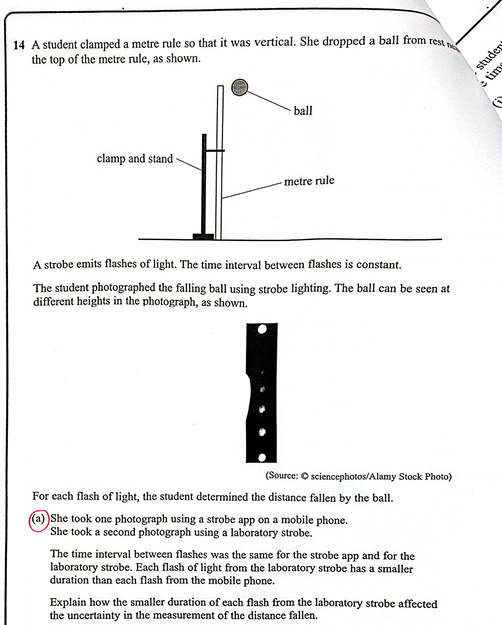
(Oct 2024)
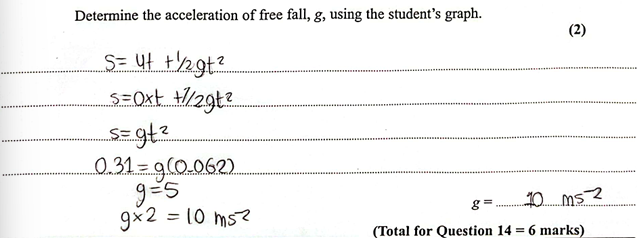

(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)
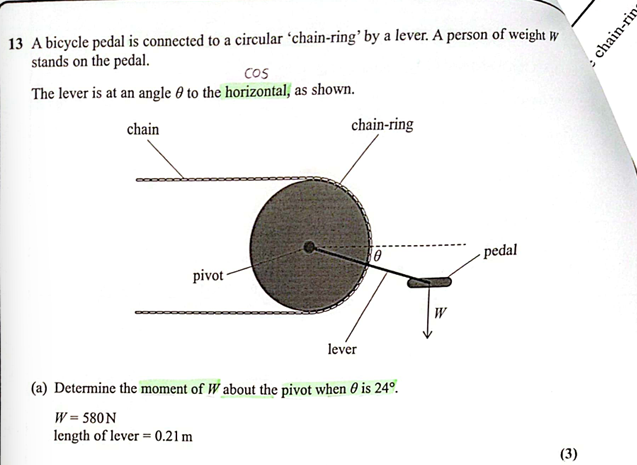
weight of athlete = 680 N


(Oct 2024)

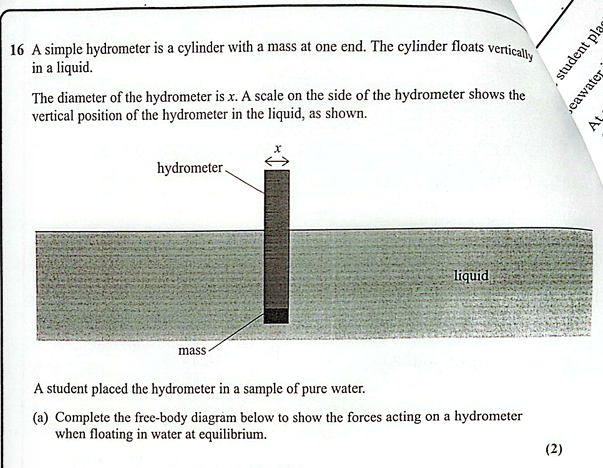
(Oct 2024)

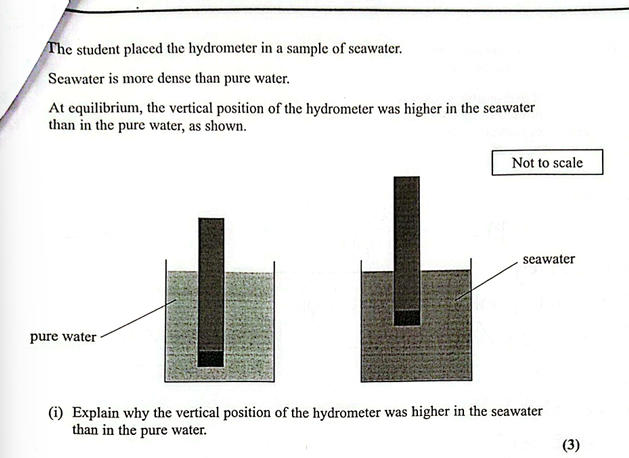
(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)

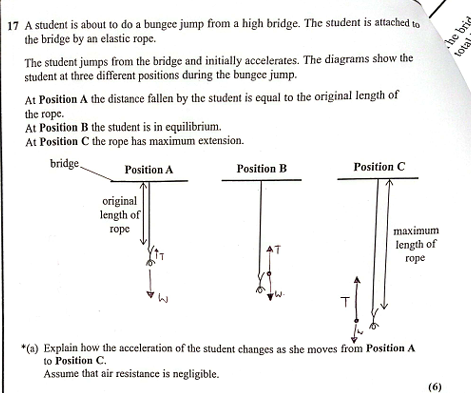
(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)


(Oct 2024)

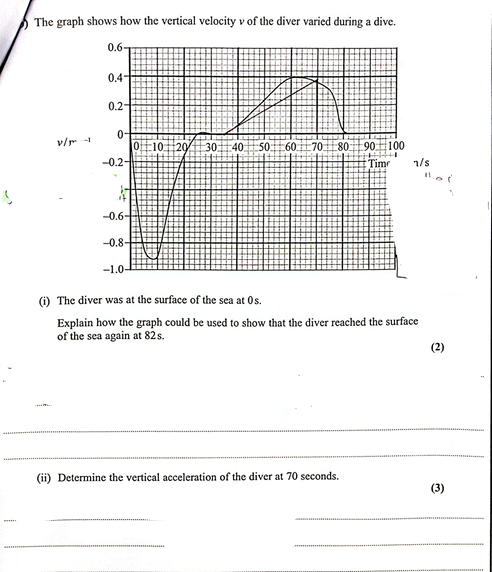
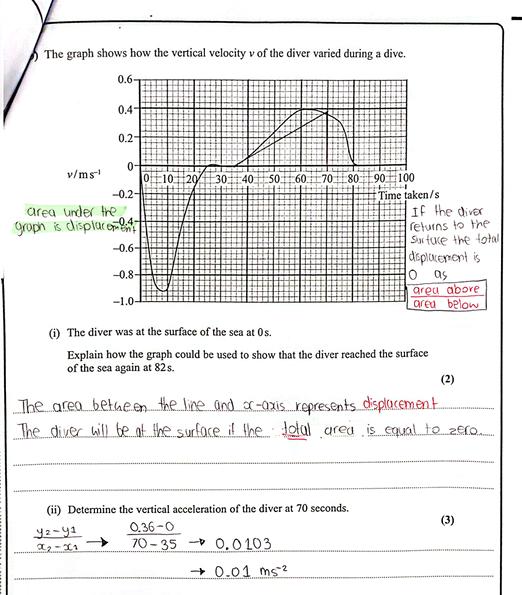
(Oct 2024)
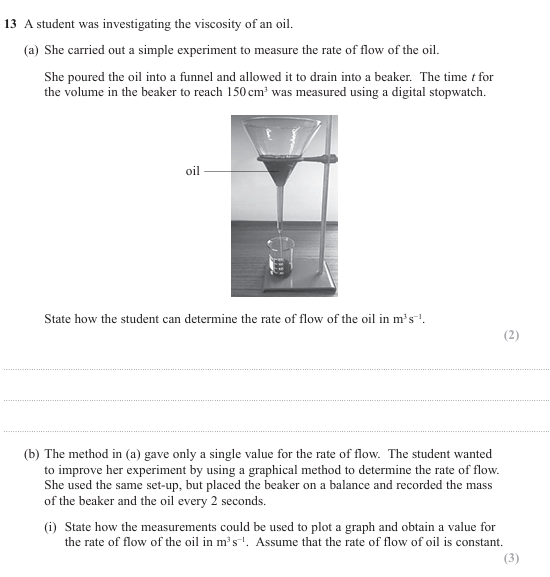
Why should the student use a longer, thinner wire? (6)
For a long wire, the extension will be larger, and for the same load the extension is proportional to the original length. For a thin wire, the extension will also be larger, since for the same load the extension is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area. This larger extension means the percentage uncertainty in measuring the extension will be lower, leading to a more accurate result. Furthermore, a smaller load cn be used with a long or thin wire to produce a measurable extension.
Define young modulus?
Stress per unit strain

(6)




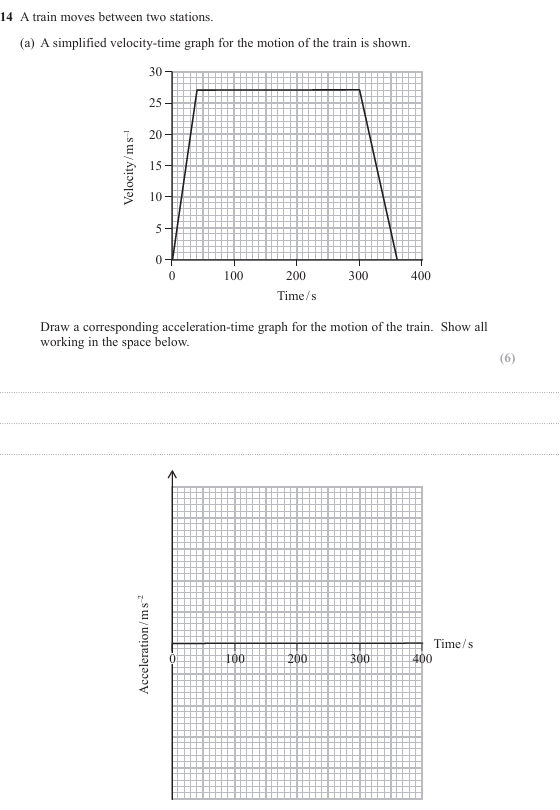
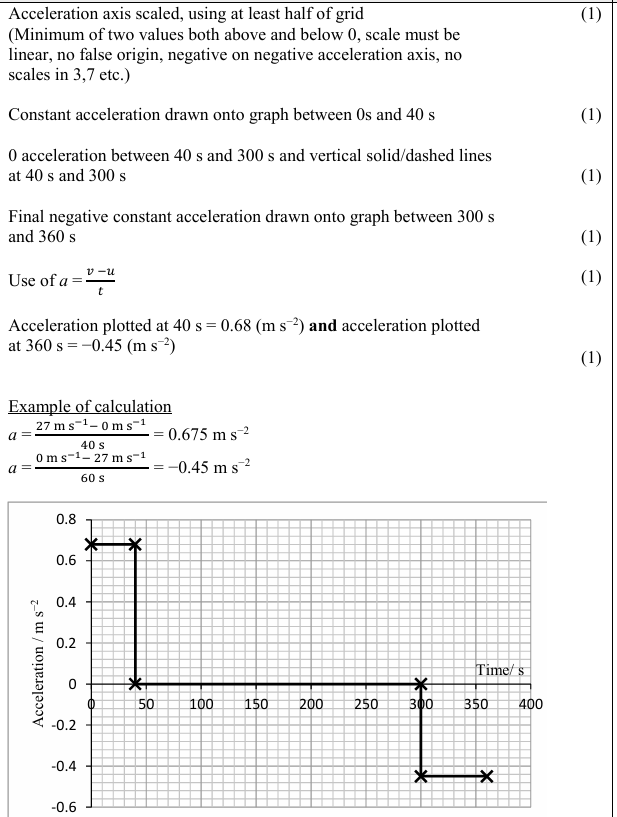
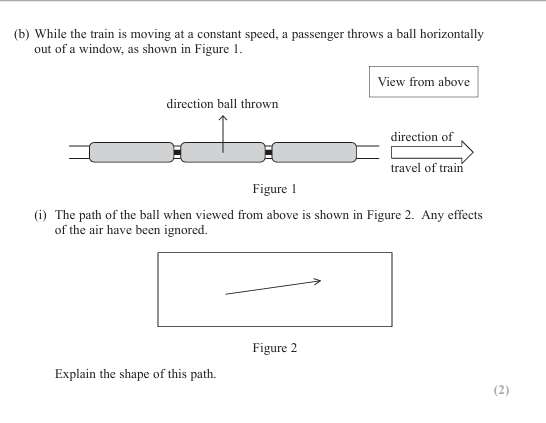

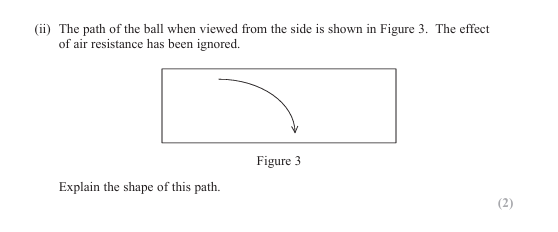
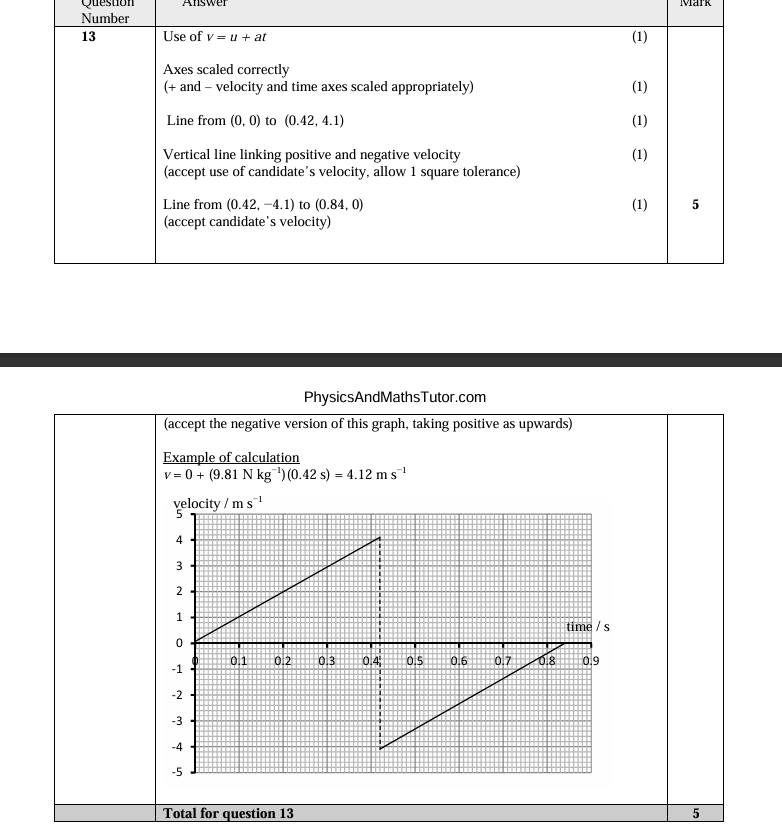
The vertical velocity is increasing Or there is a vertical acceleration/force
The horizontal velocity is constant Or there is no horizontal acceleration/force
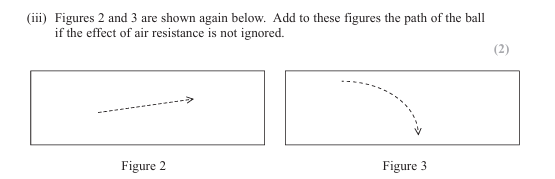
What is the advantage of using the graphical method to determine gravity/rate of flow/ etc
Greater accuracy/precision/reliability
Or the graphical method would show if/how the rate varies
Or anomalies could be identified (and removed)
The student repeated the experiment in (b) using samples of the oil with different temperatures. Explain how the rate of flow of the oil will vary with temperature. (2)
The greater the temperature of the oil the lower its viscosity (accept the viscosity is inversely proportional to the temperature)
The greater the temperature, the greater the rate of flow.
Accept converse
In order to land safely on the surface of the Moon, Verne suggested that gases could be ejected from the capsule to reduce its speed. Explain how ejecting gases from the capsule could reduce its speed. Your answer should include reference to newtons laws of motion.

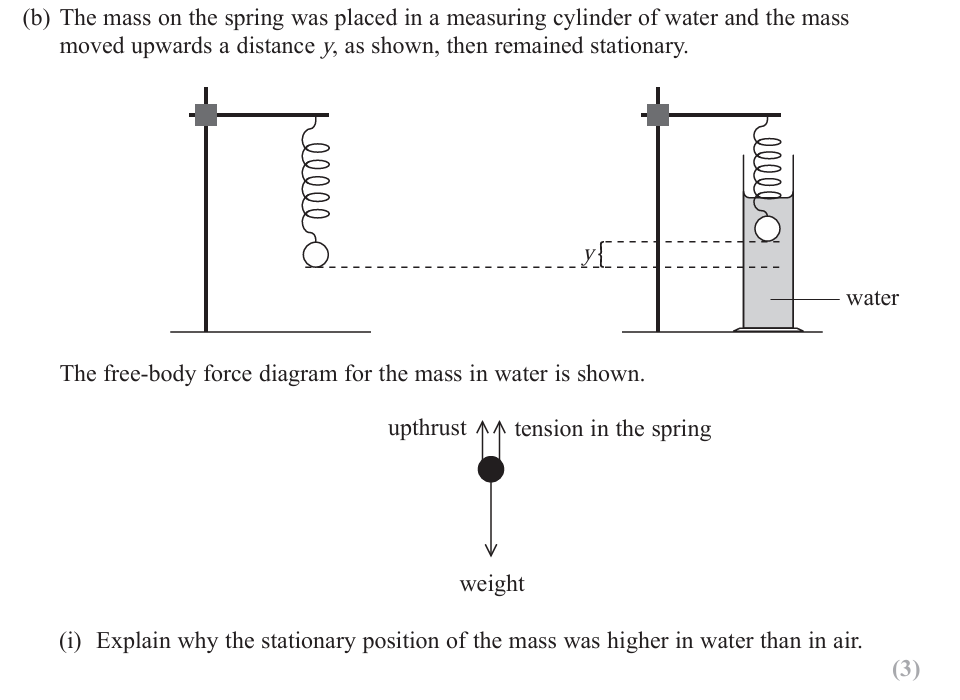
(ii) Determine y. You may assume that the extension of the spring when the mass was in air was 0.050m.
density of water=1.0×103kgm-3
spring constant of spring= 18Nm-1
volume of mass = 3.4 x 10-5m3
weight of mass on spring = 0.88N
Upthrust increases Or upthrust is no longer negligible Or there is upthrust in water
Weight = tension + upthrust
The tension (in the spring) decreases so the extension/Δx decreases (allow converse explanation for lower in air and all symbols other than Δx must be defined)
ii)

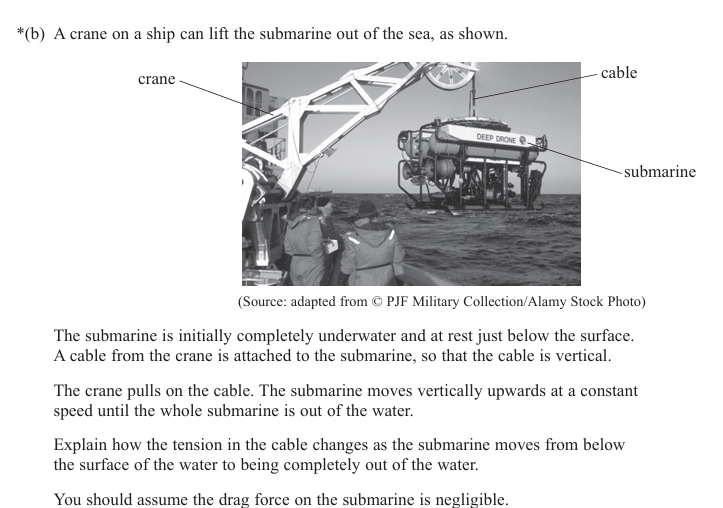





Explain the meaning of the following words:
- Stiffness
-Strength
-Hardness
stifness: Resistance to elastic deformation (bending, stretching, compressing) when a force is applied Returns to original shape when force removed.
_______________________________________________
Strength: Maximum stress a material can withstand before permanent deformation or fracture.
- yield strength = stress at which it starts to deform plastically.
-Ultimate tensile strength = max stress before breaking.
__________________________________________________
Hardness: Resistance to localized surface deformation (scratching, indentation, wear).
_________________________________________________
Toughness:
Ability to absorb energy and deform plastically without fracturing.
Measures: Area under stress–strain curve.




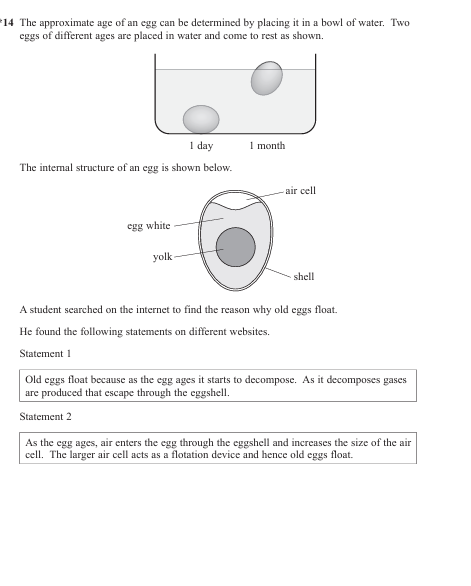
(6)

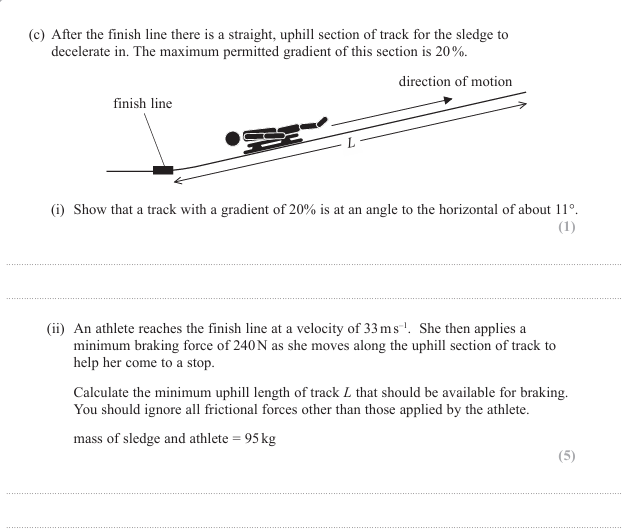

explain the shape of the graph (5)

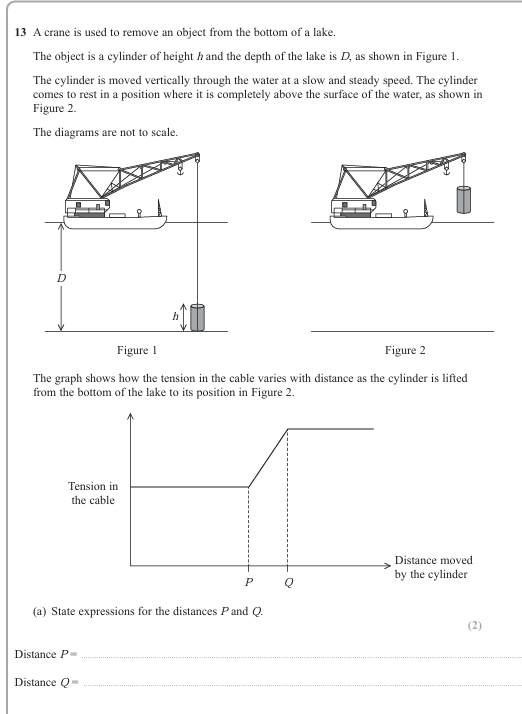
Rain consists of droplets of water of different sizes. Explain why larger droplets of rain reach the ground more quickly. You may assume that the upthrust acting on a rain droplet is negligible. (4)


State and explain two properties that should be considered when selecting a material for the vault pole. (4)
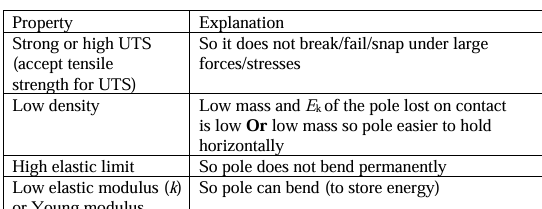
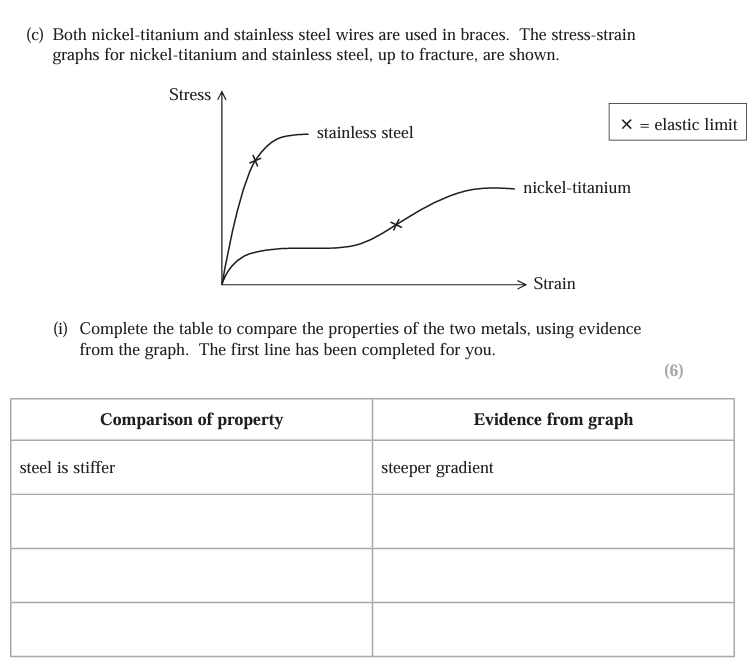
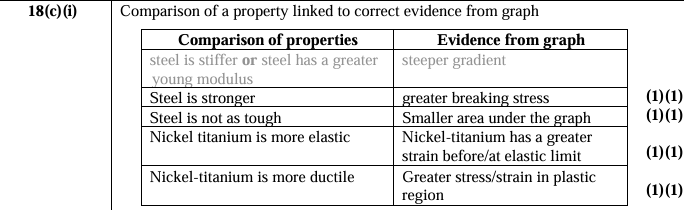


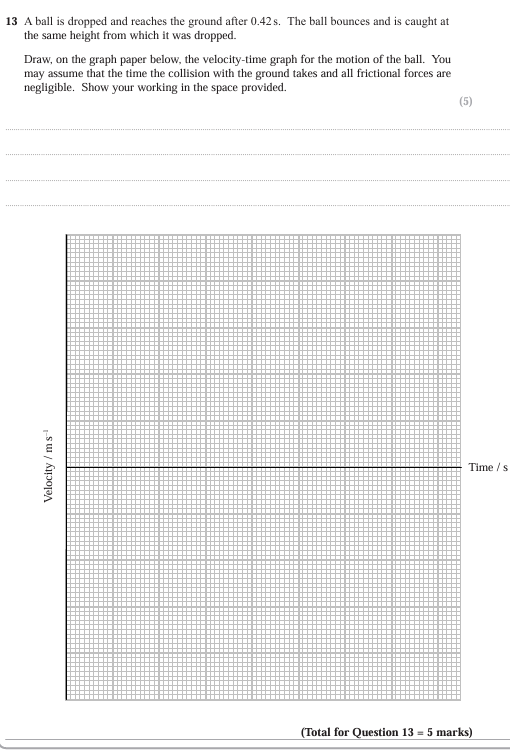
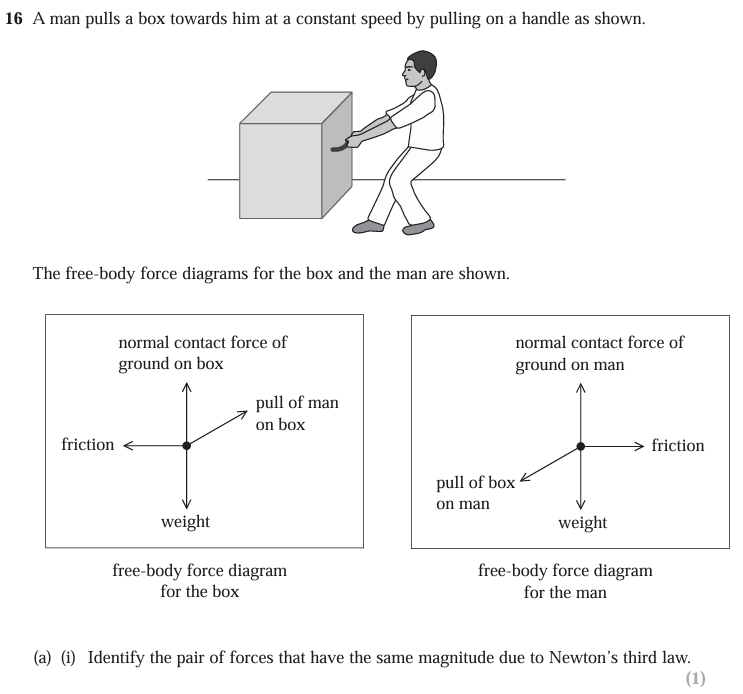
Pull of box on man and pull of man on box

(card 55 continued)


card 56 continued