General Ecology Exam 1
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Diploid individuals that possess two different alleles for a given gene are considered to be:
Heterozygous
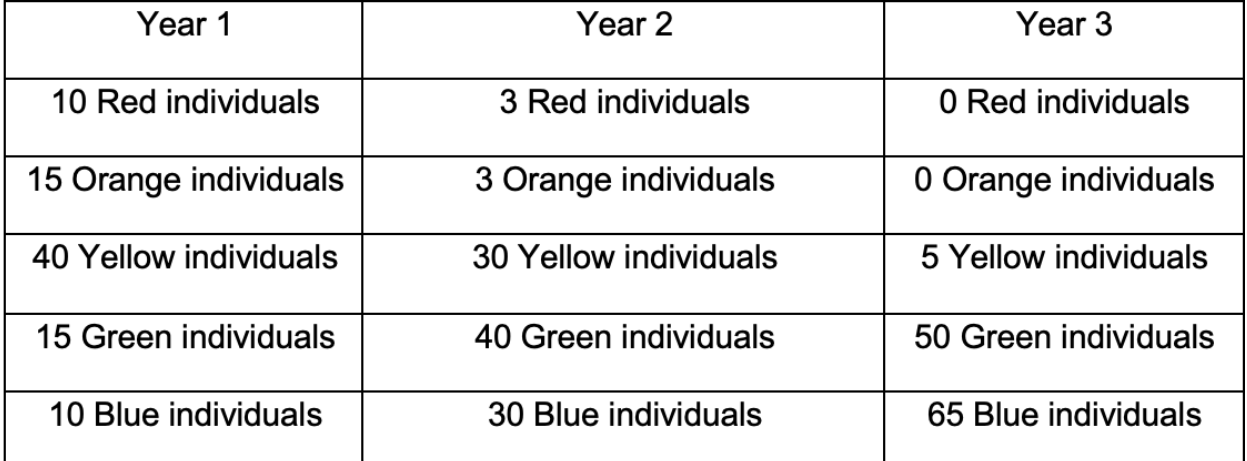
The table below illustrates the change in the number individuals of different color (which is genetically determined) of a hypothetical population of birdsover a three-year period, after the introduction of a population of feral cat that can distinguish colors and that feeds upon the birds.
Identify what type of selection is likely occurring within the population, based upon the changes in relative frequencies of the variants over the three years.
Directional
Neutral mutations:
Do not impact the relative fitness of individuals that possess them
Ernst Mayr’s biological species concept defines a species as:
Individuals that can interbreed and produce viable offspring
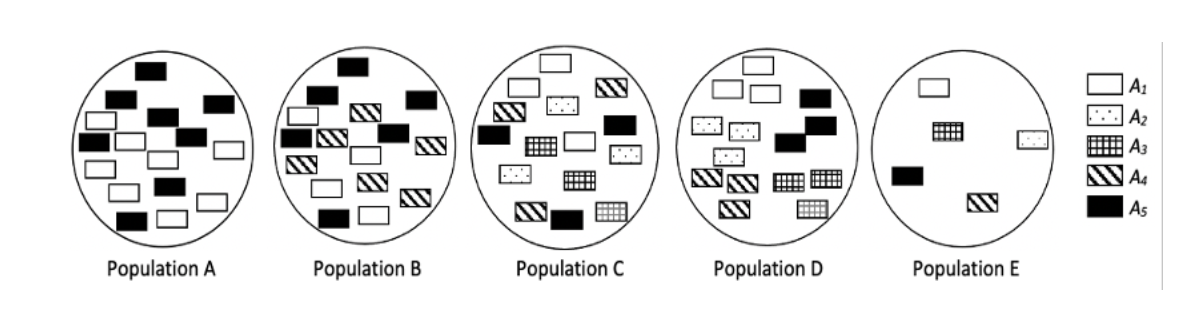
The following figures represent the alleles within five closed populations (A–E), whereby each allele (A1–A5) in each population is represented by a different patterned square:
Identify which of the five populations would most likely be susceptible to the loss of genetic variation through the process of genetic drift?
Population E
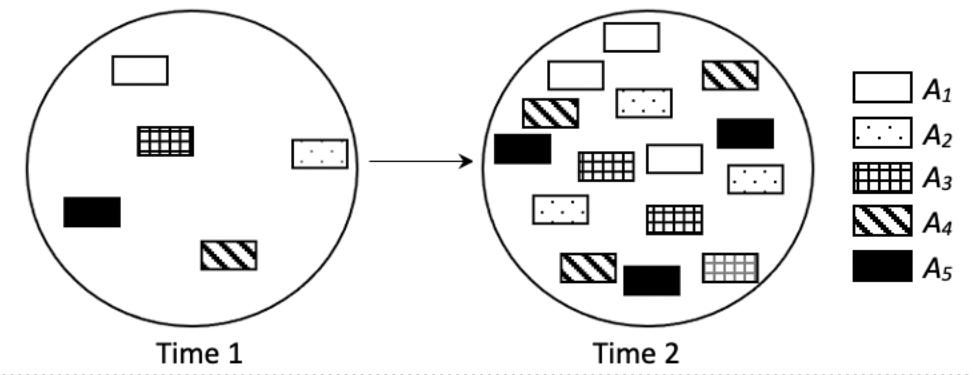
The following figures represent the change in the composition of alleles of a closed population over time, from Time 1 to Time 2, where the alleles in the population are represented by the different patterned squares and symbols (A1–A5):
Which of the following statements best describes the possible evolutionary change in the population from Time 1 to Time 2?
The population is not evolving, as the frequencies of alleles has not changed
Wildlife managers sometimes create habitat corridors to facilitate the movement of individuals from one isolated population to another as a result of habitat fragmentation. Such corridors are likely to help these once-isolated populations maintain or even enhance genetic diversity through what evolutionary process?
genetic flow
Alleles that have become fixed within a population:
represent 100% of the population’s alleles.
White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) are mammals in which adult males (and not females) possess antlers that they use to compete with other males during mating season. Winners of these fights, who are often the males with larger antlers (which are more costly to produce), consequently gain greater reproductive access to, and mate with, more females. The mechanism of evolution by which male deer, and not female deer, have developed antlers can be best explained by:
sexual selection
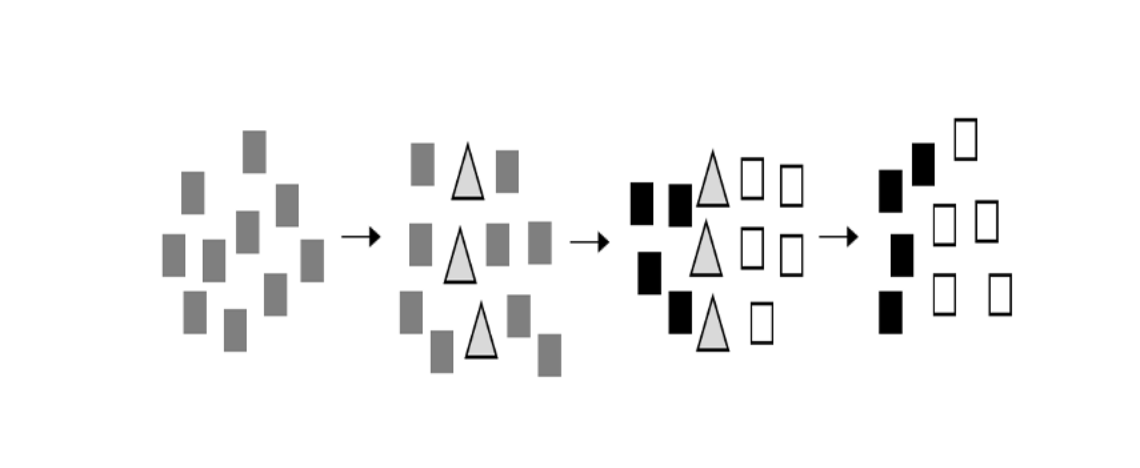
Over the course of geologic time, a population of gray butterflies was split into two separate populations by a mountain range. The two populations experienced trait divergence, in which a black trait dominated one population and a white trait dominated the other. With the erosion of the mountain range over time, the two populations were no longer separated, as illustrated by the figure below:
If the two populations indeed have become different species, which of the following best describes the type of speciation that has occurred?
Allopatric
Evolution is the process of heritable change within ______ over time.
populations
A scientist discovers three populations of grasshoppers. The number of each color of grasshopper (green, gray, and brown) has a strong correlation with the color of the soil in each population. To determine if the correlation is due to natural selection, the scientist places a few gray grasshoppers into the population of green grasshoppers, and a few gray grasshoppers into the population of brown grasshoppers. Then the scientist records which color of grasshopper is eaten most often by birds. Which of the four ecological science approaches is the scientist applying?
Experimental ecology and null hypothesis testing
When performing a manipulative experiment, researchers compare data collected from ____ to see how an ecological system responds to a manipulation, and from _____ to see how an ecological system responds to a lack of manipulation.
treatments; controls
What type of model is the figure below?
Analytical model
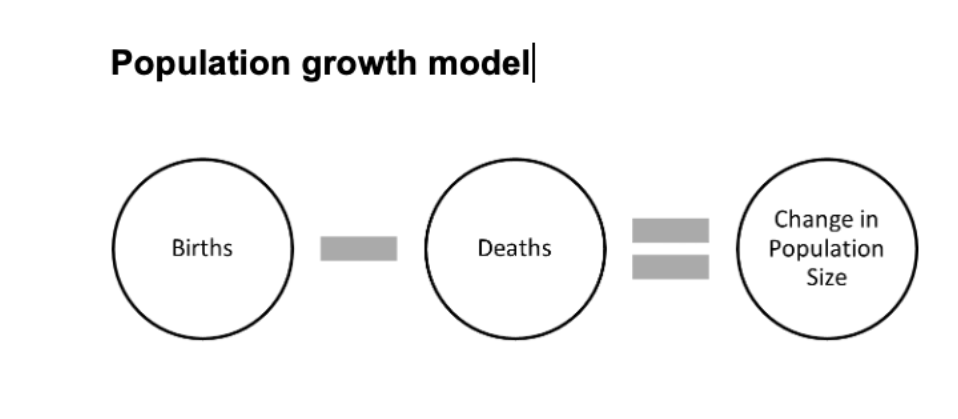
What type of model is the figure below?
Conceptual model
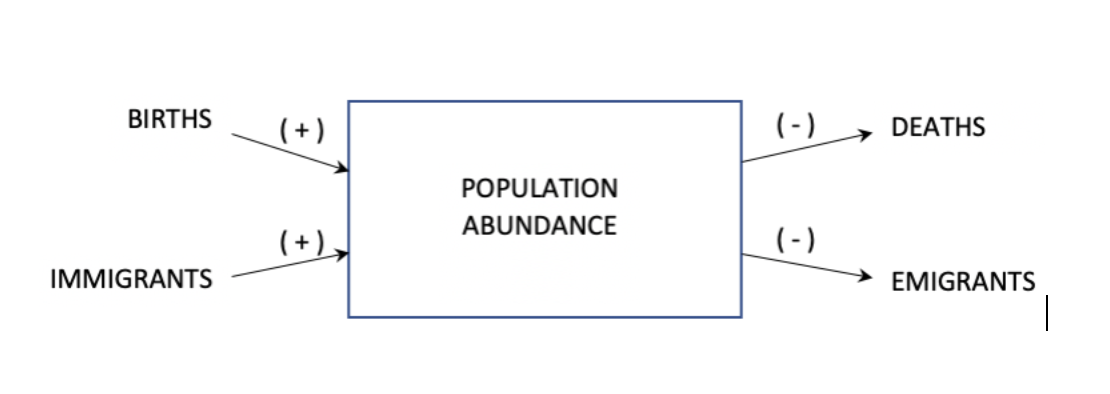
The following model represents how the abundance of individuals in a population may be influenced by four variables.
Which of the following appropriately depicts a mathematical model from this conceptual model?
Abundance change = # births − # deaths + # immigrants − # emigrants
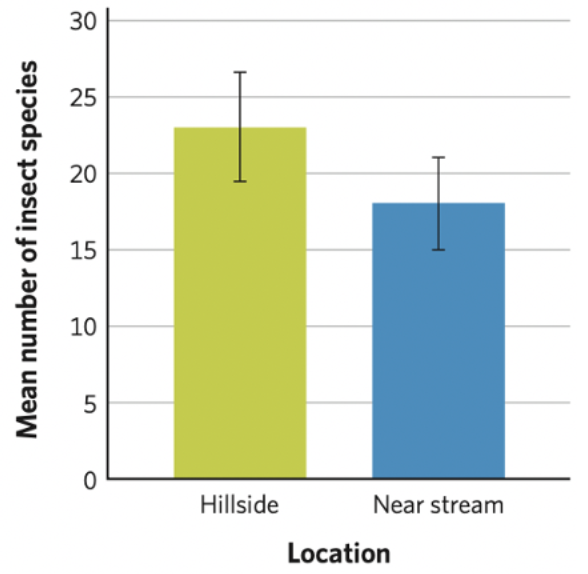
The following figure depicts the mean number of insect species found within two habitats (with error bars representing one standard error).
In this scenario, the number of insect species is best described as a:
discrete numerical variable
Generally, as the p-values resulting from statistical tests become lower,
the probability of finding a statistically significant difference increases.
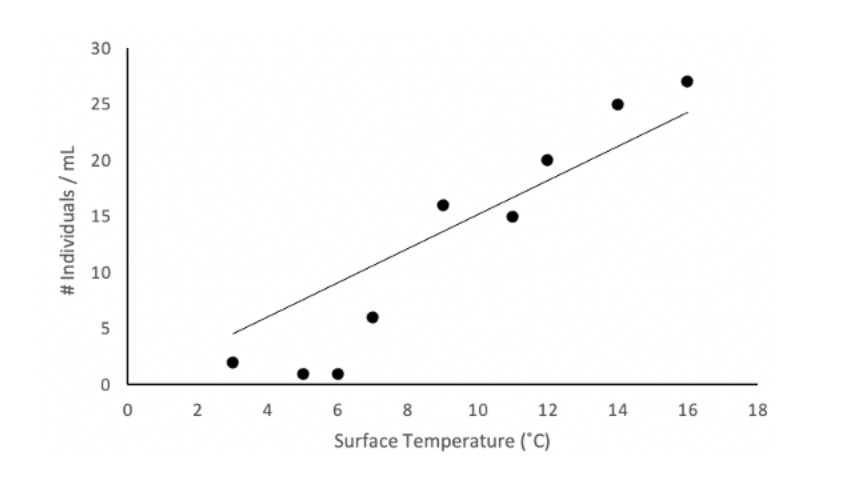
The following figure depicts data points from field sampling, as well as line modeling the relationship between the surface temperature of a freshwater pond and the density of a population of branchiopod cladoceran (a microscopic crustacean). The mathematical equation depicting the model and the associated p-value examining the significance of the trend are given below the figure.
Model:
Cladoceran Density (individuals/mL) = 1.516 x Surface Temperature (°C)
P = 0.008
From the model, identify which model element would be considered a constant.
1.516
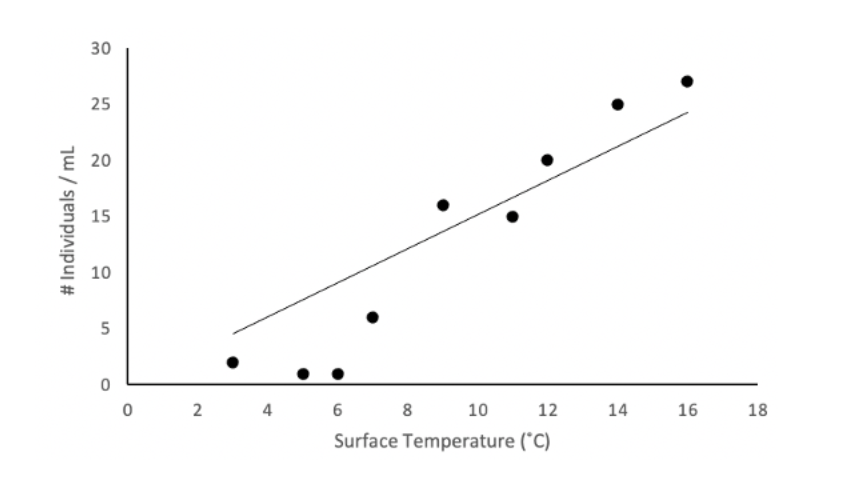
The following figure depicts data points from field sampling, as well as line modeling the relationship between the surface temperature of a freshwater pond and the density of a population of branchiopod cladoceran (a microscopic crustacean). The mathematical equation depicting the model and the associated p-value examining the significance of the trend are given below the figure.
Model:
Cladoceran Density (individuals/mL) = 1.516 x Surface Temperature (0C)
P = 0.008
From the model, identify the null hypothesis explaining the relationship between the two variables.
There is no relationship between the surface temperature of a pond and cladoceran density.
A scientist is interested in determining the efficacy of a pesticide sprayed on a population of 100 insects. The scientist counts the number of dead individuals within ten minutes of application. In doing so, the response variable measured by the study would be considered to be a:
discrete numerical variable.
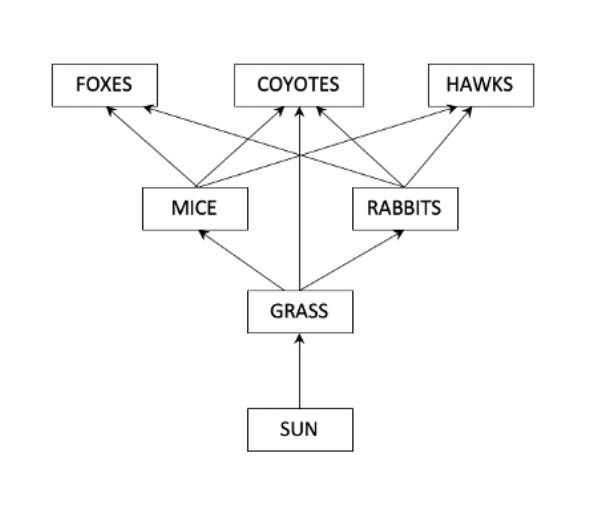
The following figure models the movement of energy through an ecosystem, with arrows reflecting the movement of energy from one source to another.
Which of the following modifications to the model would begin the transition of this conceptual model into a mathematical model?
The addition of values of the amount of energy associated with each arrow
It is almost impossible to count every individual grass plant within a 100-acre plot of land. Instead, you count the number of plants in ten 0.01-acre plots, and you use the average density of plants in these 10 plots to estimate the abundance of individuals in the 100-acre plot. The data gathered from each of the 10 plots that were used to estimate the abundance in the larger plot is technically referred to as a:
sample
A scientist is interested in examining whether ambient incubation temperature determines sex in a species of reptile by manipulating the incubation temperature for a number of sample eggs and recording the sex of the hatchling. For this experiment, the response variable would be considered to be a:
nominal categorical variable
Which of the following statements provides an example of anthropogenic climate change?
Burning of fossil fuels increases global greenhouse gases.
Which of the following statements provides an example of anthropogenic extinction?
The dodo goes extinct due to hunting by sailors.
Which of the four ecological science approaches was used by Charles Darwin in developing his theory of evolution by natural selection?
Observation and natural history
A null hypothesis is a:
proposed explanation where the focal factors do not have an effect that accounts for the observed pattern or process.
______ follows long-term patterns in precipitation, whereas _____ follows short-term patterns in precipitation.
Climate; weather
Which of the following statements about solar radiation is part of our conceptual climate model?
During different parts of the year, the Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer will receive higher amounts of solar radiation as compared with the Equator.
Which of the atmospheric circulation cells is the result of warm dry air drawing water away from deserts and dumping it on higher latitude areas?
Ferrel
Why does the meeting of the Hadley cells produce large amounts of rain for the equator?
They circulate warm wet air so that when these cells meet, the warm air collides and rises in the atmosphere, and this causes the water to rain down on the equator.
What is the Coriolis effect?
It is a phenomenon where changes to wind patterns and oceanic currents result in changes to both temperature and precipitation patterns.
A rain shadow will result in the leeward side of a mountain having low _____ and high _____ as air moves down the mountain.
amounts of precipitation; amounts of evaporation
_____ seen at 90˚ latitude and at the tops of high-elevation mountains results in low levels of precipitation and snowfall that does not melt.
Cold, dry air
Besides temperature and precipitation, what other climatic feature will be important to a biome as it can help dictate plant growth?
solar radiation
Why do we find deserts at 30˚ north and south latitudes?
The meeting of the Ferrel and Hadley cells forms a high-pressure system that dries the air in those latitudes.
When defining a terrestrial biome, we can rely in major part on the _____.
dominant plant community composition
The main difference between a temperate forest and a boreal forest is that:
a boreal forest has more extreme temperature variation than a temperate forest.
The main difference between a temperate grassland and a tropical savanna is that:
a temperate grassland has more extreme temperature variation than a tropical savanna.
The main difference between a tropical rainforest and a tropical dry forest is that:
a tropical rainforest has lower variation in precipitation than a tropical dry forest.
Which two factors of the aquatic environment are the photic and aphotic zones dependent on?
Light availability and depth
Which of the following nearshore aquatic biological zones is the interface between rivers and oceans?
Estuaries
Which of the following nearshore aquatic biological zones has plants that have specialized structures called pneumatophores?
Mangrove forests
Coral reefs are not found near estuaries. This is because estuaries have certain characteristics that would prevent their establishment. Which of the following would prevent a coral reef from establishing near an estuary?
Estuaries can have very high turbidity, and corals need high water clarity to thrive.
Which term describes the process by which solar radiation is able to enter into Earth’s atmosphere and some of the reflected solar radiation is prevented from leaving Earth’s atmosphere?
Greenhouse effect
How do increasing global temperatures result in rising sea levels throughout coastal regions?
Increasing global temperatures are melting ice sheets and glaciers, creating an influx of new liquid water and increasing sea levels in coastal areas.
The main difference between a desert and a tundra is that:
the average temperature is lower in a tundra compared with a desert.
Which of the two following traits will likely lead to the highest primary productivity in a terrestrial biome?
High solar radiation and high precipitation
Which of the following nearshore aquatic biological zones lacks a dominant plant/algal community?
Sandy bottom zones