Toxicology Set 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
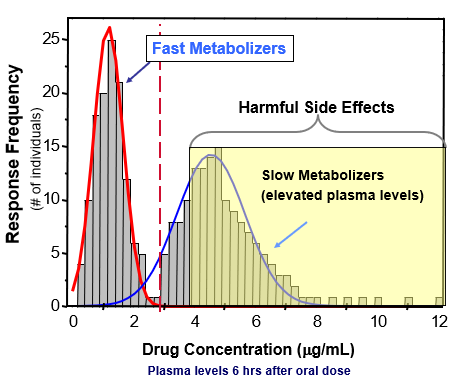
Severity of toxicity
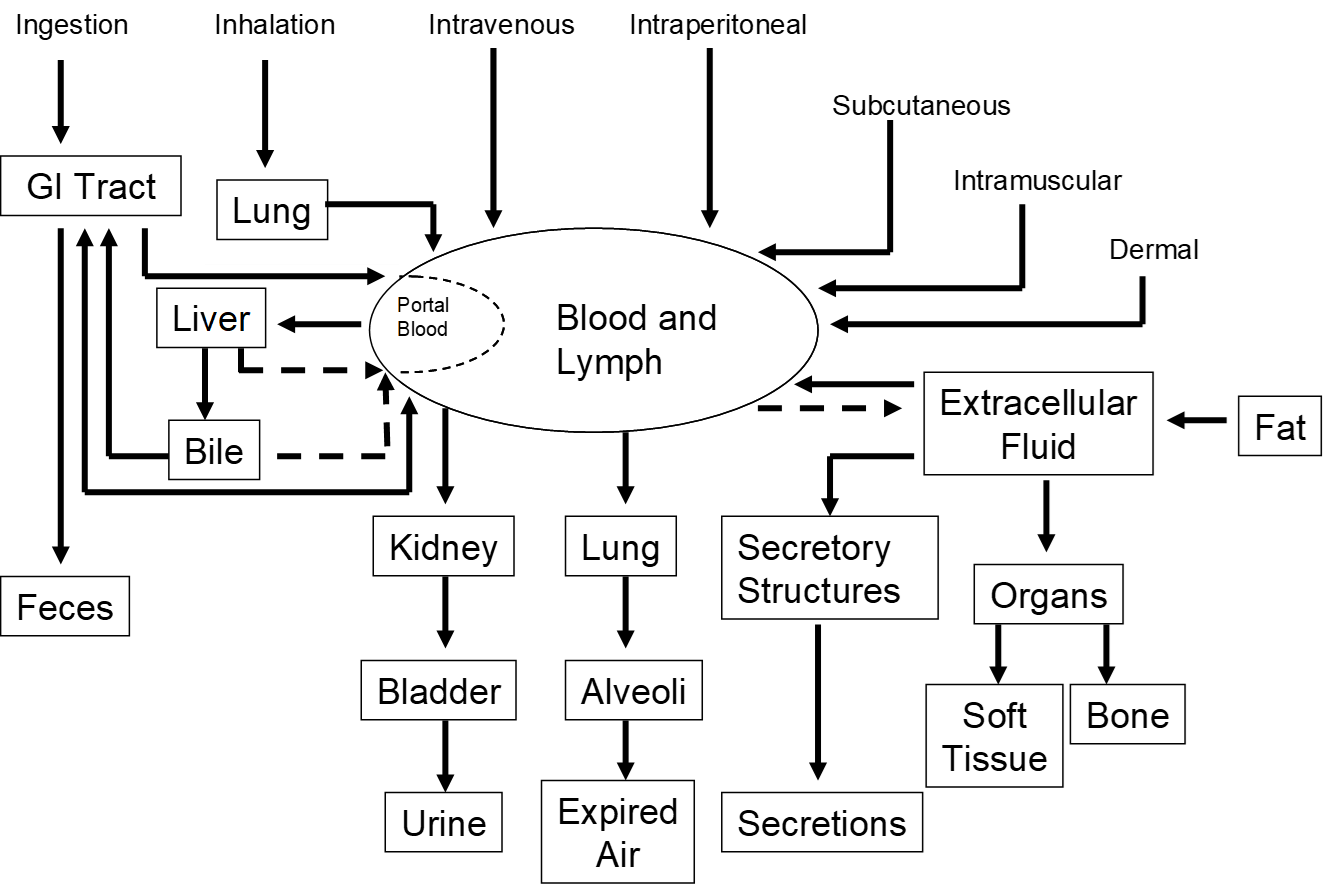
whenever a toxicant enters the body
oral (inject, swallowed) & dermal (on the skin)
The major routes for toxicant could be…
Route of exposure
an important factor that can affect the concentration of the toxicant (or its' metabolites) at any specific location within the blood or lymph
Gastrointestinal tract
a tube going through the body. Its contents are considered exterior to the body until absorbed
Respiratory Tract
Many environmental and occupational agents as well as some pharmaceuticals are inhaled and enter the respiratory tract. Absorption can occur at any place within the upper respiratory tract
Dermal
In contrast to the thin membranes of the respiratory alveoli and the gastrointestinal villi, the skin is a complex, multilayer tissue. For this reason, it is relatively impermeable to most ions as well as aqueous solutions.
Biotransformation
the process whereby a substance is changed from one chemical to another (transformed) by a chemical reaction within the body
Metabolism or metabolic transformations
are terms frequently used for the biotransformation process
eliminated from the body
The more water-soluble a substance, the more easily…
Liver
Out of the liver, kidney, lungs, GI tract mucosa, skin, & nasal mucosa, which one of the following is a major site of biotransformation?
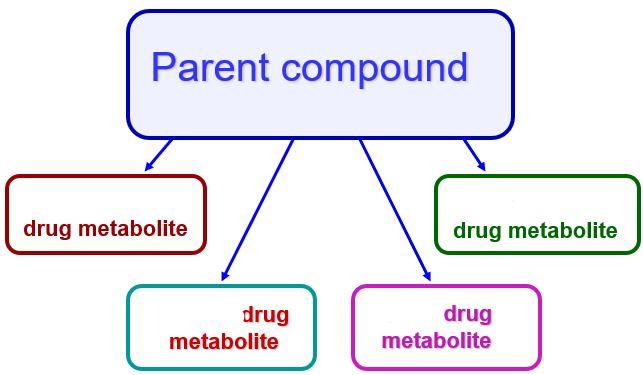
Less active, inactive, toxic, or more active
The parent compound can create what type of drug metabolite?
Phase I metabolism
results in addition or exposure of functional group on parent compound
Includes oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) v. important
hydroxylations, O-dealkylations, N-dealkylations, etc. etc.
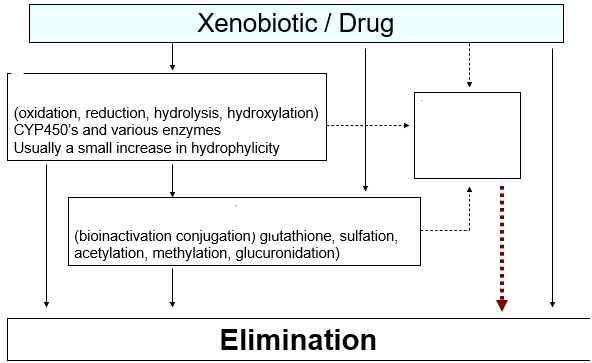
Phase II metabolism
addition of polar group to increase water solubility and hence excretion
Donor + Acceptor (drug) -------> Conjugate
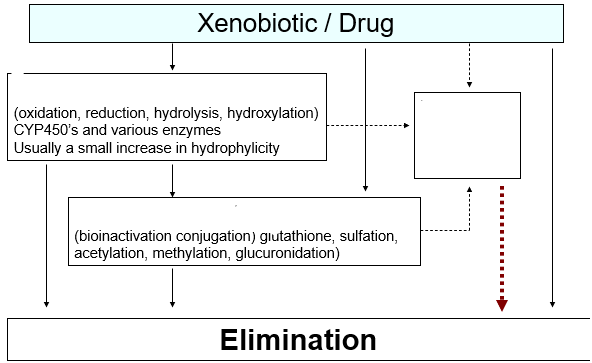
toxic/adverse reaction
Besides the metabolism, the xenobiotic or drug could cause what to happen regardless of the metabolism?
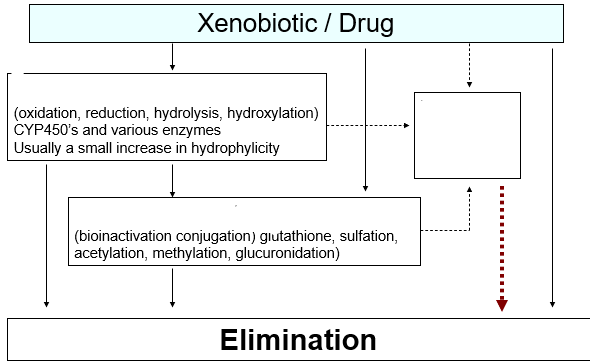
moving w/o any toxic/adverse effects
What is the ideal route in this photo when to move from the xenobiotic/drug → elimination
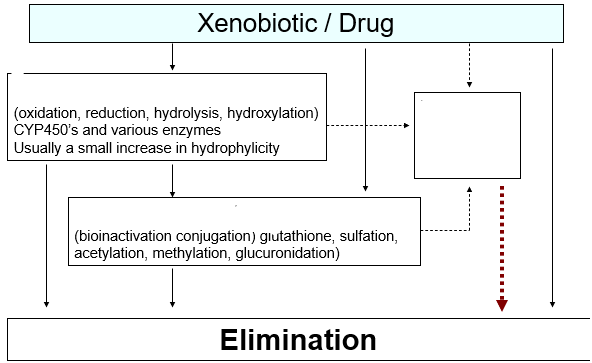
morphine, heroin, codeine (glucuronidation)
What drugs can go straight into phase II?
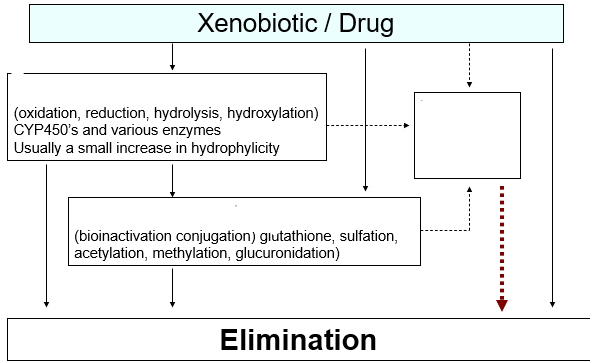
CY3A4
The one that contributes the most of the major P450 to human drug metabolism is…
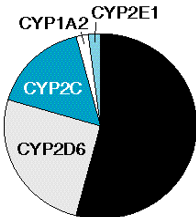
CYP3A4
the major isoform in humans with substantial extrahepatic expression especially in the gut wall
PHASE I biotransformation
Haem-containing proteins within the smooth ER responsible for most of what?
[ox]/[red] of its wavelength
What does the P450 system do?
enzyme induction
Certain chemicals or drugs will lead to an increase in synthesis of certain P450 isoforms
You will receive less of the enzyme itself
St John’s wort is an example because it is an inducing agent, meaning what?
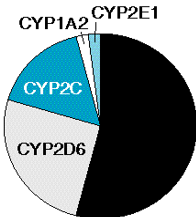
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
is the antidote for acetaminophen poisoning
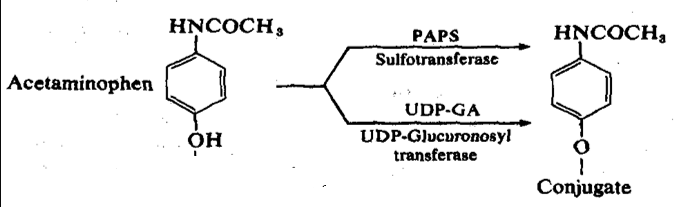
The toxic route
The following photo represents what route of acetaminophen?
Non-toxic route
The following photo represents what route of acetaminophen?
Liver necrosis
If tissue glutathione stores are depleted as a result of fasting, intake of excessive doses of acetaminophen or through induction of CYP2E1 as a result of chronic intake of ethanol (i.e. overwhelming GSH ability to deal with toxic metabolite), the quinone interacts with nucleophilic sites of cellular macromolecules, such as proteins. This causes what?
A chronic drinker, who stops drinking while taking acetaminophen
Who would potentially have a greater chance of liver toxicity with ingestion of a large dose of Acetaminophen:
A chronic drinker, who continues to drink while taking acetaminophen
A non-drinker, who takes acetaminophen with a triple shot of Jack Daniels (80 proof-40% alcohol)
A chronic drinker, who stops drinking while taking acetaminophen
A non-drinker, who is fasting and takes a triple shot of Jack Daniels
Inhibition
- Reduction in Active P450, to which other drugs might be metabolized
- decrease metabolism of parent drugs (increased half-life), increasing effect or potential adverse reaction (unless the metabolite is active form and thus reduced pharmaceutical effect)
Induction
- increased metabolism reduces availability of parent drugs
Competitive inhibition
Omeprazole decreases blood clearance of diazepam, increasing plasma half-life
Non-competitive
Terfenadine (antihistamine-no longer on market) metabolism inhibited by macrolide antibiotics. Macrolides (clarithromycin and erythromycin) metabolites bind so tightly to CYP3A4, that it prevents the enzymes for also metabolizing Terfenidine
The text above is an example of what?
It gets absorbed and reach myocytes.
Terfenadine is a prodrug, generally completely metabolized to the active form fexofenadine by intestinal CYP3A4.
What happens to this drug in case of inhibition of an enzyme that metabolizes it to the active form?
it increases the CYP3A4 amount
What will happen to Phenobarital when it interacts with the induction of enzymes?
Genetic variability
accounts for most of large variations in humans in bio transforming capability
Polymorphism
in biology occurs when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species. Associated with a difference in DNA sequence and hereditary mutations among individuals of a species.
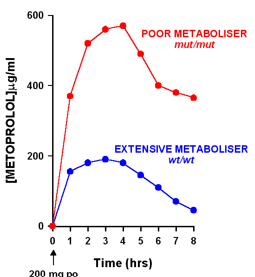
Genetic polymorphisms
- Subjects show extensive or poor metabolism of drugs transformed through specific P450s. Best characterized for CYP2D6 where Poor Metabolizer’s make up 10% of Caucasian subjects.
The mutant variant interferes with the formation of fully functional ALDH2 tetramer
What is the difference between ALDH2 vs ALDH2×2?
slow acetylators
acetylation is so slow that blood or tissue levels of certain drugs (or Phase I metabolites) exceeds their toxic threshold.
N-acetylation
a major route of biotransformation for xenobiotics containing an aromatic amine (R-NH2) (e.g. dapsone: an antibacterial, dapsone inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid) or a hydrazine group (R-NH-NH2) (e.g. isonizid)
mutation in NAT2 (decreases enzyme activity/stability)
What causes genetic polymorphism in N-Acetyltransferases?
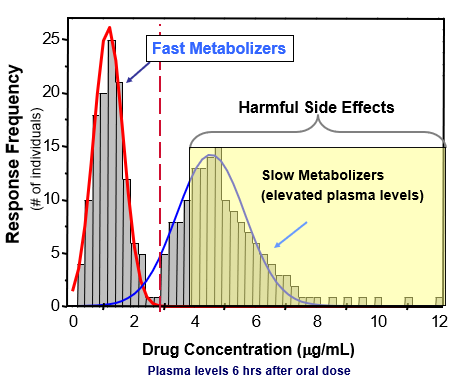
slow acetylators
cause nerve damage and hepatotoxicity from Isoniazid
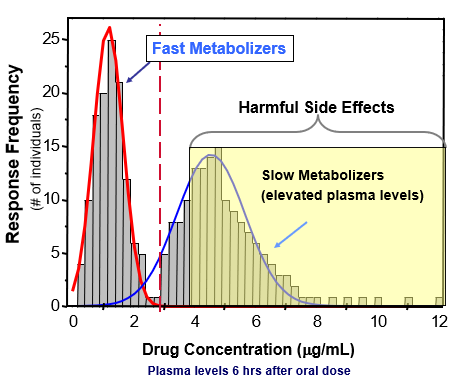
fast acetylators
N-acetylation retards clearance of antineoplastic drug amonafide (topoisomerase inhibitor)
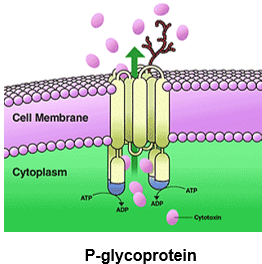
MRP1
Rare (<1% in Caucasians) Gln to Ser causes increased resistance of HeLa cells to doxorubicin
P-glycoprotein
a well characterized human ABC-transporter of the MDR/TAP subfamily. It is extensively distributed and expressed in normal cells such as those lining the intestine, liver cells, renal proximal tubular cells, and capillary endothelial cells comprising the blood brain barrier
P-gp (MDR1)
Numerous polymorphisms
Potential relevance to bioavailability of anticancer drugs that are P-gp substrate
Cellular Efflux Mechanisms
ATP transporter pump
Present in GI, renal, hepatic cells, blood-brain barrier, testes, and some immune cells
Present to reduce/eliminate toxicant uptake
Associated with efflux of Cancer chemotherapeutics from the brain
Can be modulated by diet, drugs, stress, and disease
MRP (multidrug resistance protein) , BCRP (breast cancer resistant protein)
This refers to what?
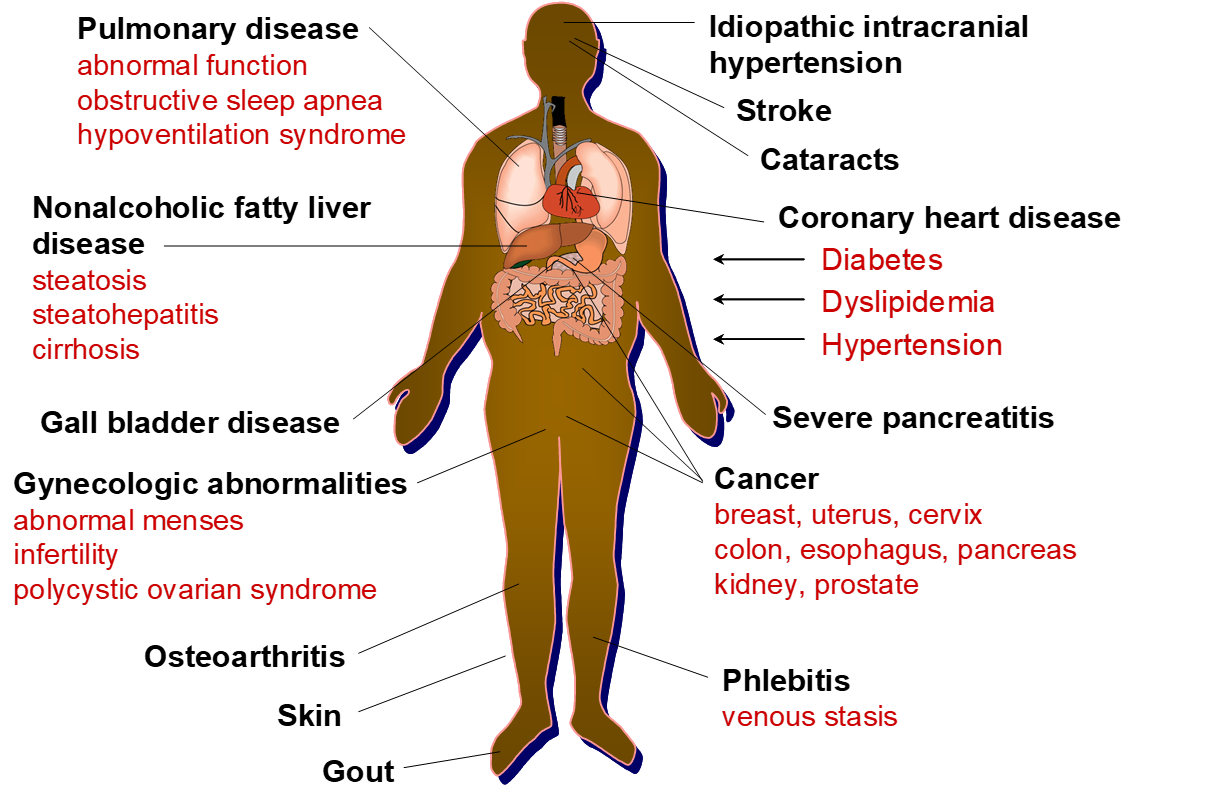
comorbidities
What causes polypharmacy (taking multiple medications)?
hepatitis, liver cancer, cardiac insufficiency, uremia
Examples of factors that affect drug metabolism include …
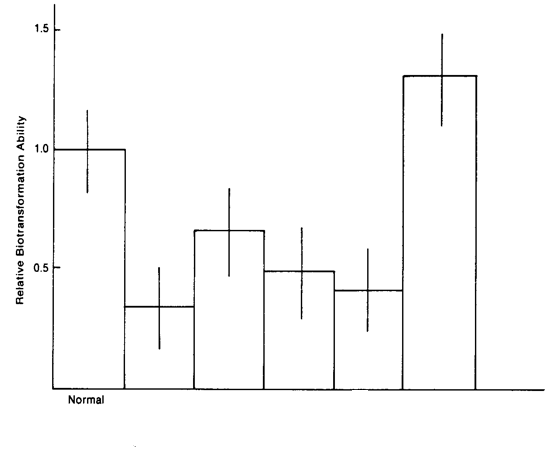
Aging
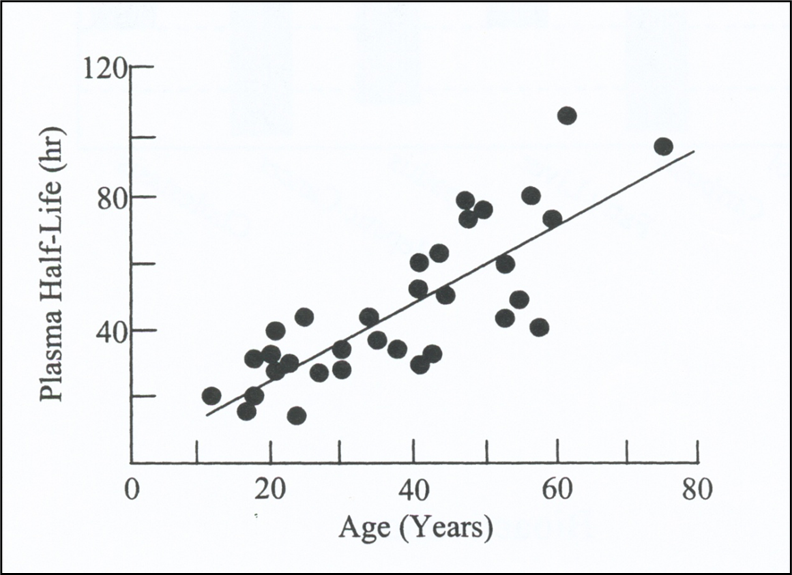
The following describes the effects of what?
increases the half-life
How does aging effect diazepam?
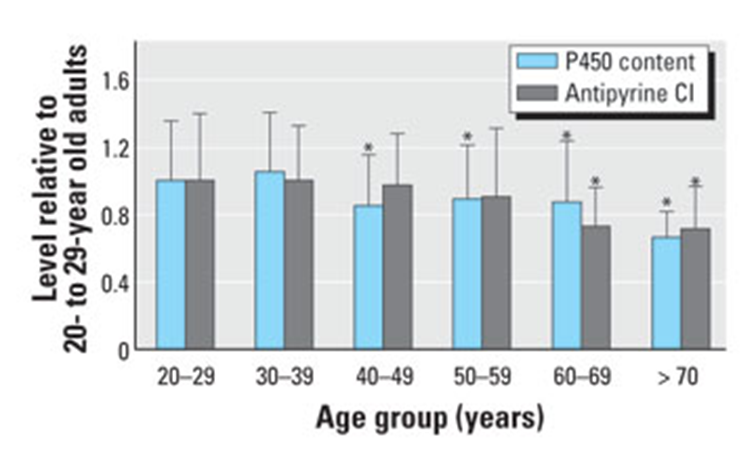
It declines the function
How does aging affect the hepatic CYP function?
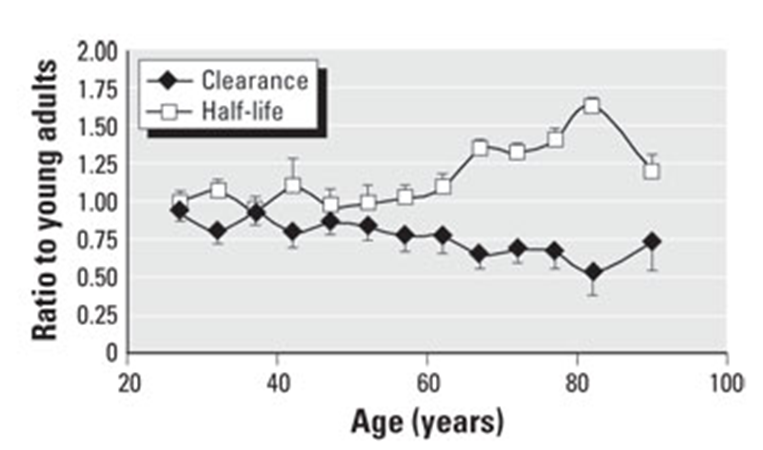
increases & decreases
How does aging effect drug CL & half-life?
DME
body weight/lean mass
plasma volume
gastric emptying time
plasma protein levels
cytochrome P450 activity
drug transporter function
the following refers to what?
Gender
Percent body fat & drug metabolism are factors that relate to what?
Female population
Based on the graph, who has a higher percent body fat?
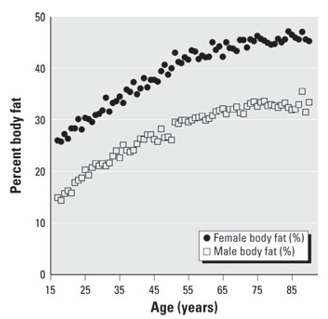
Women
Who has a greater incidence of adverse events Neuropathy, pancreatitis, more allergic reactions, and toxicity driven regiment changes on nucleocide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Poor nutrition
can have a detrimental effect on bio transforming ability. This is related to inadequate levels of protein, vitamins, and essential metals. These deficiencies can decrease the ability to synthesize bio transforming enzymes
Phenacetin
is used principally as an analgesic for cooking style.
P450 activity
The cooking style modulates…
Felodipine (brand: Plendil)
a calcium channel blocker (calcium antagonist), a drug used to control hypertension (high blood pressure).
CYP3A4
Grapefruit inhibits what?
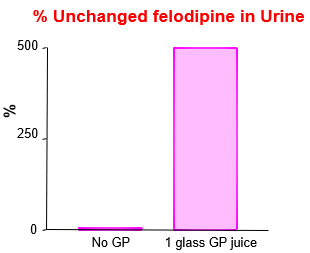
P450 activity (died from overdose)
A 63 year old man receiving medication for major depression showed he boarded a plane in Toronto to fly to London. On arrival he was unrousable. In his Carry-on bag he had Mefadazone (for depression), Ketoconazole (for fungal infection) and Triazolam (an antipsychotic also used for insomnia). All three of these drugs bind to CYP3A4. Ketoconazole inhibits CYP3A4 and caused the other two drugs to become overdosed during 6 hr flight (sitting still is a factor).
This example describes how drug interactions affect what?
‘cheese effect’
In people who are taking certain drugs known as MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors), the enzyme is inhibited and a buildup of tyramine can occur, leading to life-threatening high blood pressure as well as a range of symptoms including headaches, itchy skin rashes, heart palpitations and diarrhea
The inhibition of MAO-A
What cause the rise of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in the synaptic cleft, of MAO-B only of dopamine?