econ u2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
circular flow model
private/public sector
factor/transfer payments/income
subsidies
private (businesses) VS public (government)
factor (received via indiv labor) VS transfer (gov programs)
subsidies (gov payments to businesses)
three macroeconomic goals for all countries
high economic growth
low unemployment
stable prices (limit inflation)
gross domestic product (GDP)
dollar value of all final goods/services produced IN a country (annually)
depends on productivity
GDP per capita (person)
GDP/population → each person produces an avg amt of?
best measure of a nation’s standard of living
not included in GDP (3)
intermediate goods
tires of a car don’t count
nonproduction transaction
financial transactions: stocks, real estate
used goods
nonmarket/illegal activites
homemade, drugs, unpaid work
rule of law
fair regulations → political stability → economic growth
calculating nominal GDP - expenditures approach (GICE)
GDP = consumer spending + business investment + government spending + net exports
Consumer: purchase of final goods/services (sandwiches)
durable: fridges, cars
non durable: food
services: repairs
Investment: businesses buying tools
Government: infrastructure, etc. (NOT transfer payments)
Net exports: exports - imports
calculating nominal GDP - income approach (RIPL)
labor (wages from work) + rental (property income) + interest (payment after loans) + profit (money after paying costs)
all FACTOR PAYMENTS (bc each contributed to production)
inventories
goods produced & held for later sale
counted in GDP the year they’re PRODUCED
unemployment def & calculation
workers actively looking for a job (but not working)
unemployment rate = 100 * # unemployed / # in labor force
3 types of unemployment
frictional
structural
cyclical
frictional: temporary/between jobs (HAS transferable skills)
seasonal, fired → looking for new job
structural: loss of jobs (NO transferable skills)
technological unemployment, VCR repair
cyclical: lowered demand for goods/services (recession)
being laid off during great depression
natural rate of unemployment & full employment output (Y)
NRU = frictional + structural
healthy economy
full output (Y) = GDP where cyclical = 0
why’s 0% unemployment bad?
without choices btwn workers, companies have to pay higher wages AND charge consumers higher prices (who are now buying MORE)
rising wages → higher prices → demand even higher wages
unemployment rate can misdiagnose actual
discouraged workers (they’ve given up)
lowers # in LF
underemployed workers (wants more hours)
race/age inequalities (doesn’t show disparity for minorities)
inflation, deflation, disinflation
inflation: each $ buys fewer goods → reduces purchasing power
banks don’t lend and people don’t save
deflation: negative inflation (decrease in prices)
ppl will hoard money and not spend
disinflation: price inc at slower rates
real GDP
100 * nominal GDP / GDP deflator
GDP deflator measures prices of ALL produced goods
includes increases in products bought by gov/businesses
CPI measures prices of BOUGHT goods
consumer price index (CPI)
CPI = 100 * current MB / base MB
base index = 100
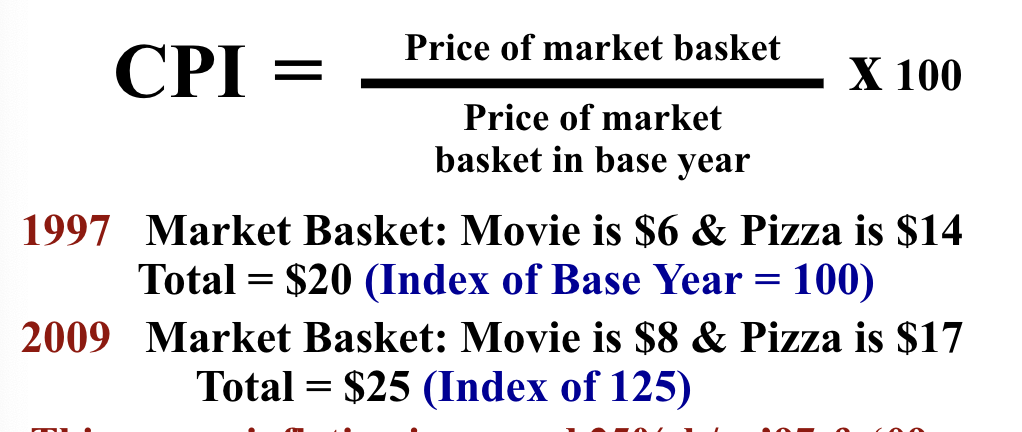
inflation rate
(new - old ) / old
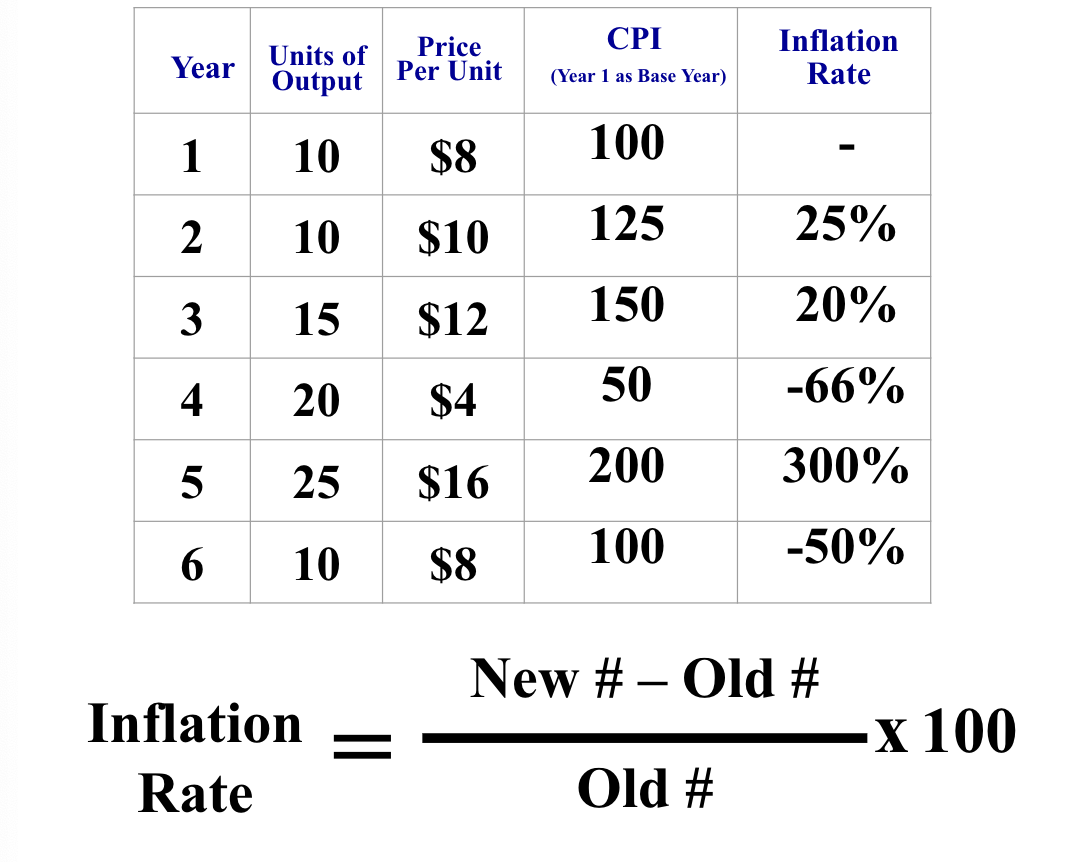
problems with CPI
substitution bias: ppl buy more substitutes (not in MB)
new products: MB isn’t updated to include these
product quality: ignores changes in product quality
costs of inflation
menu costs (updating listed prices)
shoe leather costs (increased cost of transactions)
unit of account costs (currency is unreliable, uncertainty around spending)
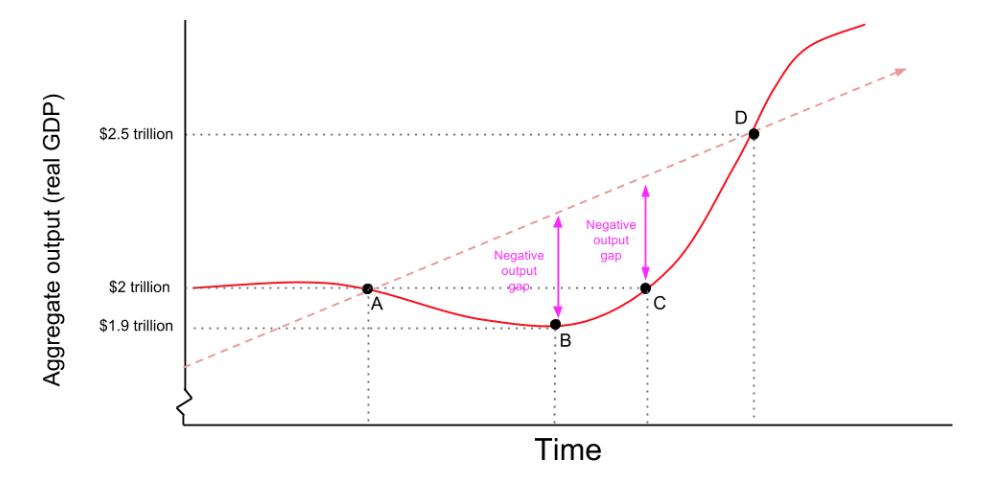
the business cycle
shifts in aggregate supply/demand → short-run fluctuations in real GDP and employment