Odontogenic Cysts
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Define a cyst
Pathological cavity lined by epithelium
Name some pseudocysts cysts
Stafne Bone Cyst
Traumatic Bone Cyst
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
What is another name for Stafne Bone Cyst?
Stafne defect
Lingual mandibular gland depression
What is a Stafne Bone Cyst?
Developmental defect of bone convacity containing portion of submandibular gland tissue
What is the treatment for Stafne Bone Cyst?
None
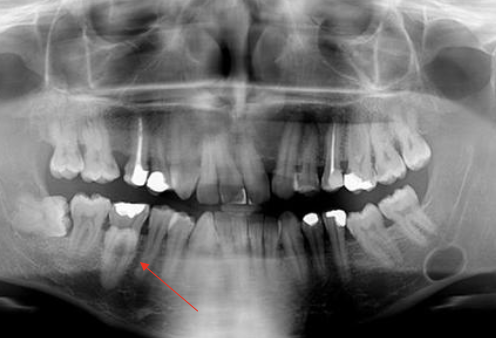
What are some radiographic and clinical features of Stafne Bone Cyst?
Asymptomatic radiolucent
Between molar teeth near angle of mandible
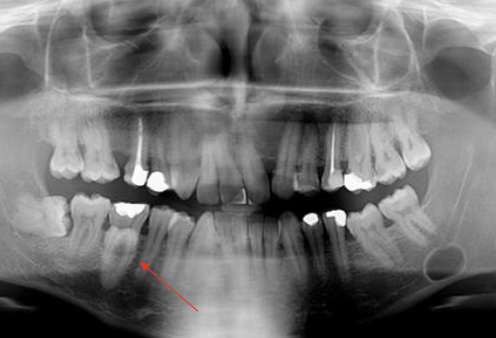
Where might you find Stafne Bone Cyst?
Below mandibular canal
What is another name for Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)?
Simple bone cyst
Idiopathic bone cyst
What is the cause of Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)?
Trauma-hemorrhage most widely accepted etiology (NOT a true cyst)
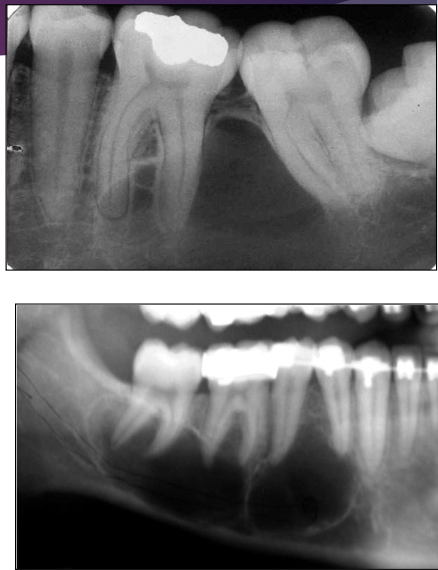
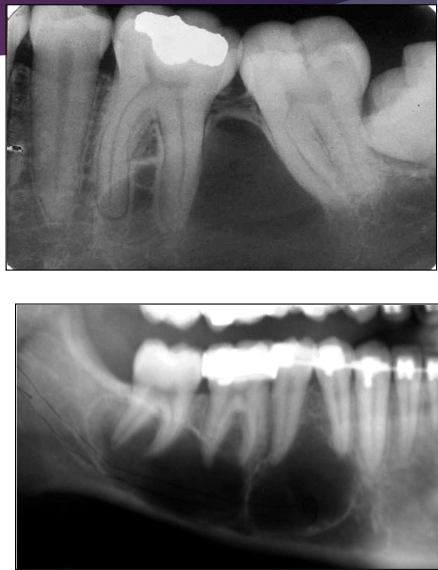
Which regions of the mandible are most commonly affected by Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)?
Molar, premolar, and symphysis regions
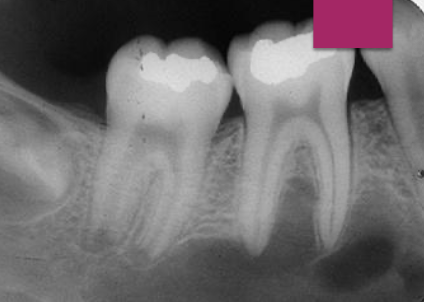
Are Traumatic Bone Cysts (TBC) symptomatic?
Usually asymptomatic, about 20% present with swelling
Are teeth associated with Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC) typically vital or non-vital
Teeth are vital
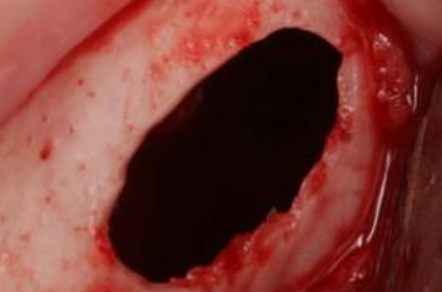
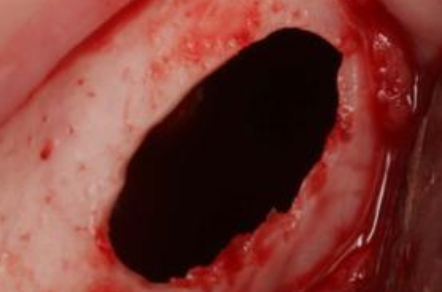
What does Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC) look like during surgery?
Benign, empty cavity within bone
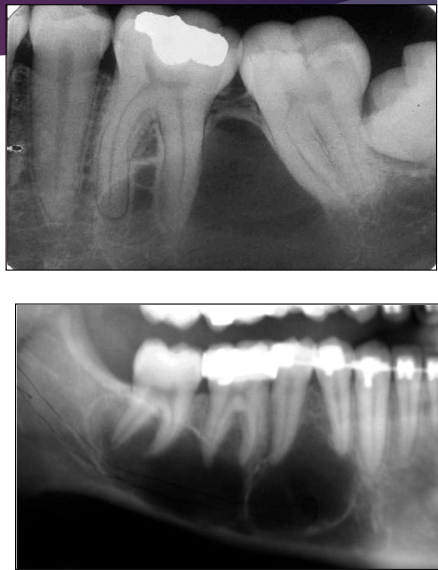
In what type of bone are Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC) more common?
Long bones
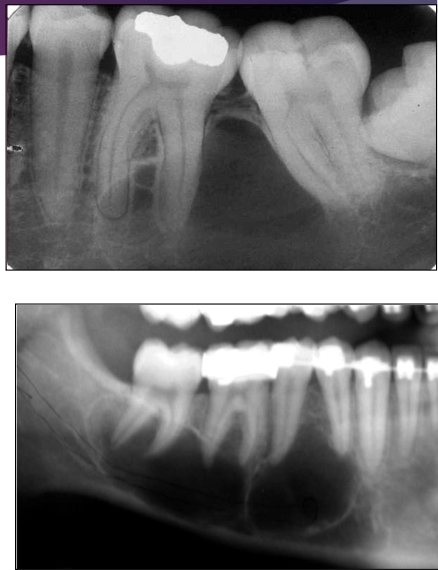
Radiographic characteristics of Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)
Well-delineated
Radiolucent
Margins can be ill- or well-defined
When several teeth are involved, the defect shows dome-like projections that scallop between the roots
Cone-shaped outline (pointed at one end) may be seen in large lesions
Scalloping in Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)
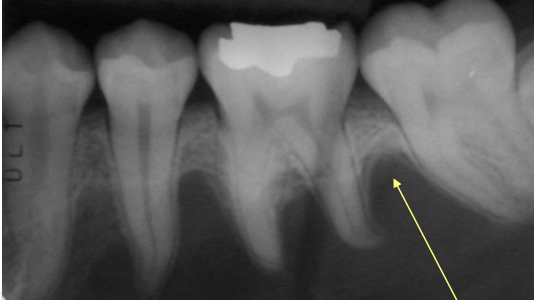
What is this?
Scalloping in Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC)
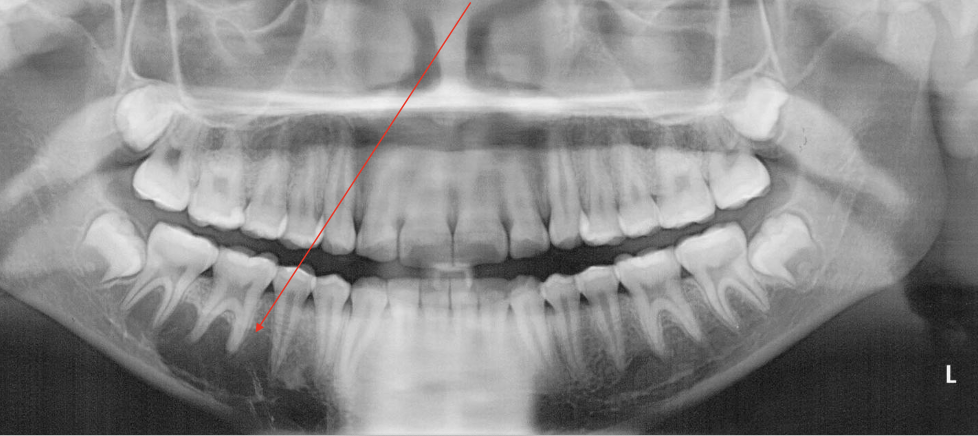
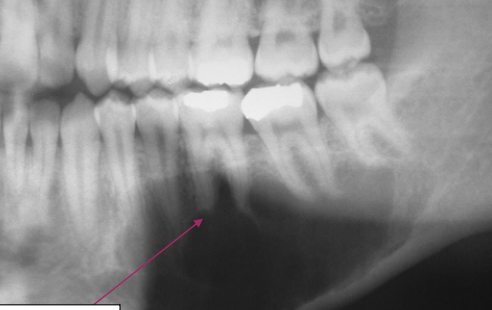
What is this pano showing?
Traumatic Bone Cyst (TBC) scalloping
What is an Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC)?
Intraosseous accumulation of blood-filled spaces surrounded by connective tissue
Is ABC a true cyst? Why or why not?
No, Aneurysmal Bone Cyst is not a true cyst because it lacks an epithelial lining
What is the etiology of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst?
Etiology is unclear
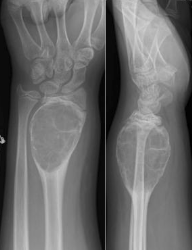
Where are ABCs typically found?
More common in long bones; jaw lesions are uncommon

At what age are jaw ABCs usually diagnosed?
Young age (typically 20s)

What is the most common location of ABC in the jaw?
Posterior mandible

What is the most common clinical sign of ABC?
Rapidly enlarging swelling

Is pain a common symptom of ABC?
Yes, pain is often reported
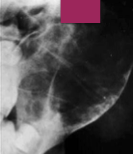
What does ABC look like on radiographs?
Radiolucent lesion with marked cortical expansion and thinning
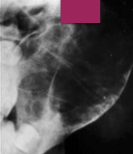
How is the expansion of an ABC described?
Ballooning or distension
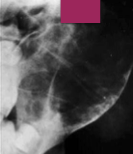
Is ABC usually unilocular or multilocular?
Usually unilocular, but can be multilocular
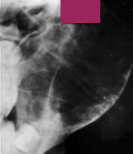
What are the radiographic borders of ABC like?
Can be well-defined or diffuse
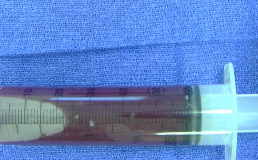
What is seen during surgery of an ABC?
A “blood-soaked sponge” appearance due to heavy bleeding
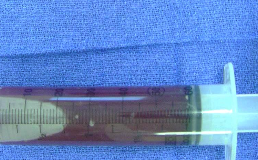
What are the treatment options for ABC?
Curettage or enucleation
What is another name for nasopalatine duct cyst?
Incisive canal cyst
What is a nasopalatine duct cyst?
The most common non-odontogenic cyst of the oral cavity
What are radiographic characteristics of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
Well circumscribed radiolucent in midline of anterior maxilla, between or apical to central incisors (teeth are vital)
What is a medial palatal cyst?
No association with incisive canal, and more posterior
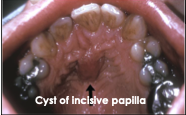
Where do cysts of the incisive papilla occur?
Only in soft tissue
What is the treatment for a nasopalatine duct cyst?
Surgical removal
What are some clinical features of a nasopalatine duct cyst?
Communication with incisive foramen
Swelling can occur
Heart or inverted pear shaped
6mm diameter is upper limit of normal size for incisive foramen
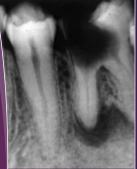
What is another name for a periapical cyst?
Radicular cyst or apical periodontal cyst
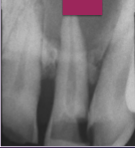
What is a periapical cyst?
Accumulation of inflammatory tissue at the periapex in response to pulp necrosis
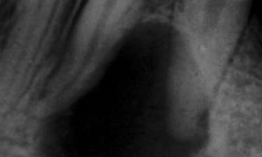
What symptoms occur with a periapical cyst?
It is asymptomatic
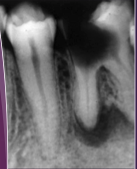
What would you see microscopically in a periapical cyst?
Epithelial lining (vs. a PA granuloma)
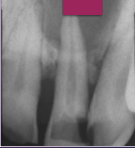
What are the radiographic features of a periapical cyst?
Well defined but may be somewhat diffuse
Loss of lamina dura at the root top in the area of the radiolucency
Root resorption can be seen
Not highly corticated
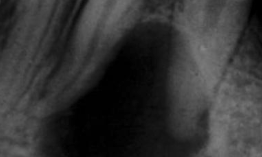
What is the treatment for a periapical cyst?
RCT, apicoectomy, or EXT
Name some variants of periapical cysts
Radicular cyst
Lateral radicular cyst
Residual cyst
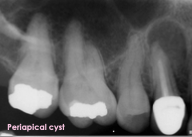
Radicular cyst/periapical cyst
Lesion surrounds the root tip
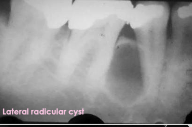
Lateral radicular cyst
Found on the side of the root
Probably arises in association with a lateral root canal
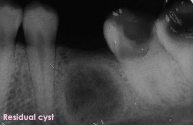
Residual cyst
Cyst remains following extraction of the tooth
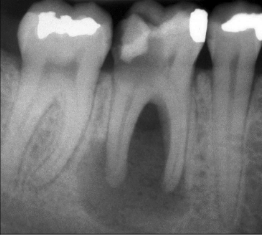
What is this?
Periapical cyst
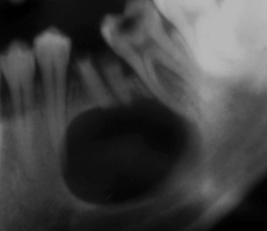
What is this?
Periapical granuloma
Growth of lateral radicular cyst over time
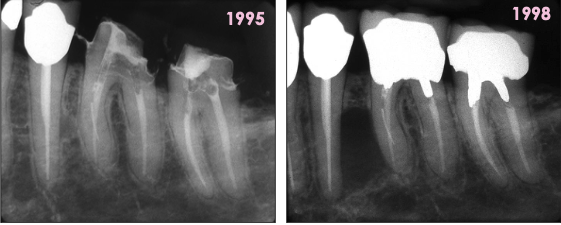
Growth of residual cyst over time
Following EXT of #12
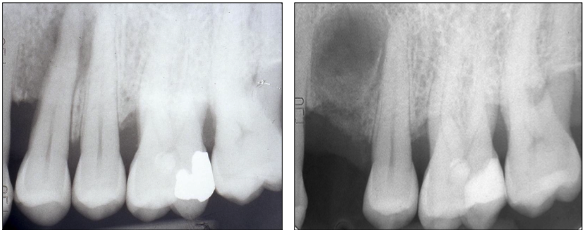
What type of cyst is the buccal bifurcation cyst?
An inflammatory cyst with uncertain pathogenesis
Where does the buccal bifurcation cyst typically develop?
On the mandibular first permanent molar
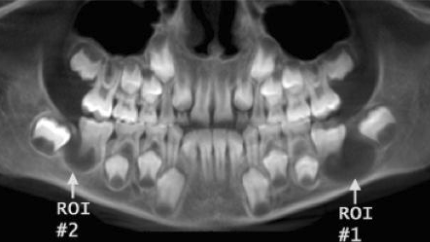
What age group does buccal bifurcation cyst affect?
Children, average age of 10
What are some clinical features of buccal bifurcation cyst?
Patient may experience tenderness, swelling, or foul-tasting discharge
Perio probing reveals pocket formation on buccal aspect
1/3 have bilateral involvement
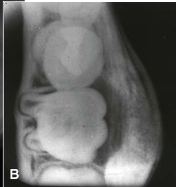
What is a common radiographic feature of buccal bifurcation cyst?
Well-circumscribed unilocular radiolucency superimposed on the roots of the mandibular first permanent molar
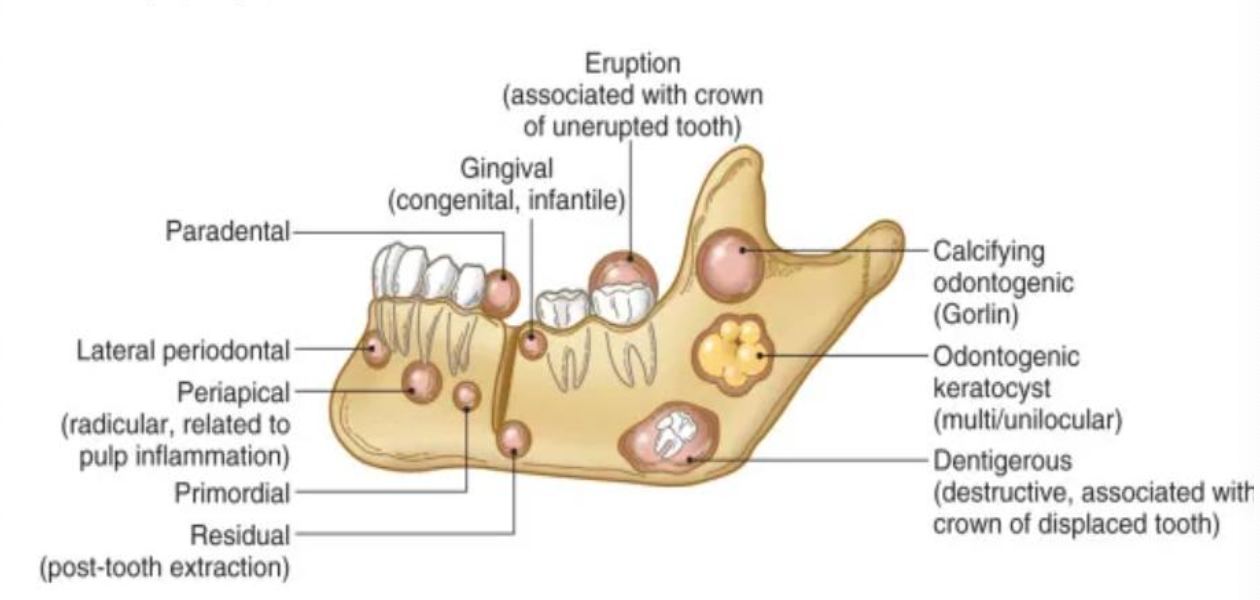
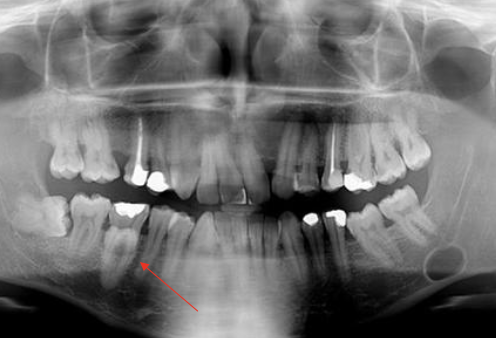
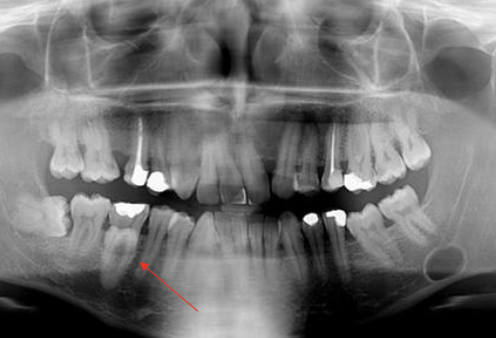
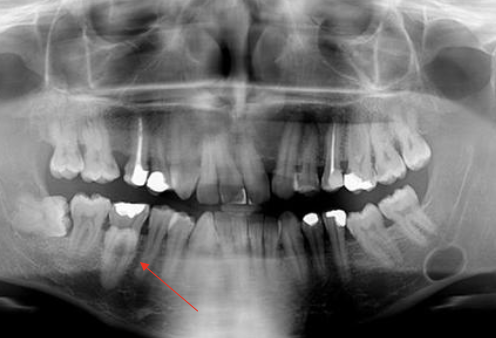
Name some intraosseous odontogenic cysts
Dentigerous cyst
Odontogenic keratocyst
Lateral periodontal cyst
Buccal bifurcation cyst
Glandular odontogenic cyst
Calcifying odontogenic cyst
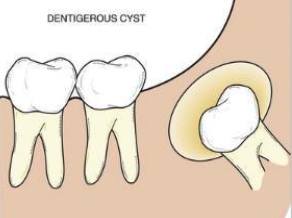
What is a dentigerous cyst?
A cyst that originates by the separation of the dental follicle from around the crown of an unerupted tooth; it develops by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the tooth crown
Which demographic does dentigerous cyst affect?
Gender: M=F
Age: Most common 10-30 years old
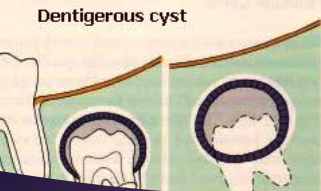
Where might you find dentigerous cyst?
65% mandibular molar area
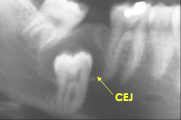
What is the prevalence of dentigerous cyst?
Most common developmental odontogenic cyst
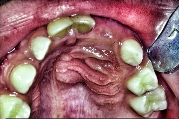
What are some clinical features of a dentigerous cyst?
Usually do not, but can grow to considerable size and expand bone, causing facial asymmetry, and is usually painless
Expansion is buccal-lingual vs OKC
Completely asymptomatic and discovered on routine x-ray
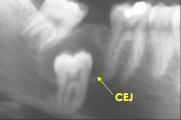
What are the radiographic features of a dentigerous cyst?
Unilocular radiolucent associated with crown of unerupted tooth at CEJ
Well defined and sclerotic borders
What is the treatment of dentigerous cyst?
Enucleation with the tooth
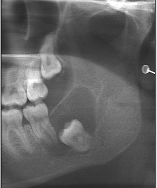
Central dentigerous cyst
Most common
Cyst surrounds the crown of the tooth
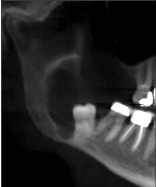
Lateral dentigerous cyst
Mesioangular impacted mandibular 3rd molars that are partially erupted
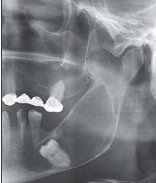
Circumferential dentigerous cyst
Cyst surrounds the crown and extends further along the root
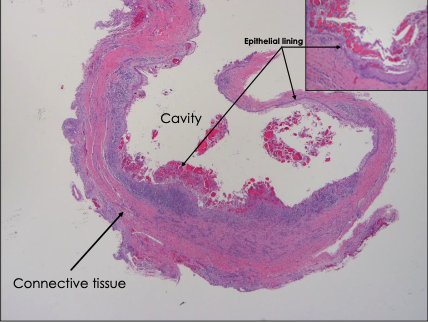
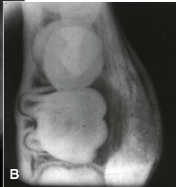
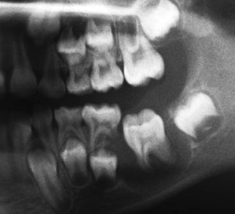
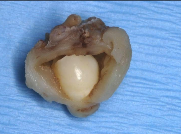
What is this a histological image of?
Dentigerous cyst
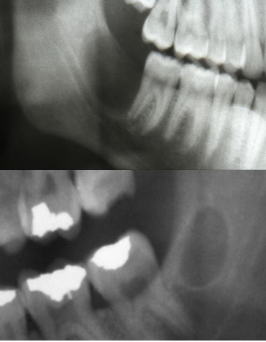
What is a primordial cyst?
A unilocular radiolucency in area of missing tooth with no history of extraction or surgery
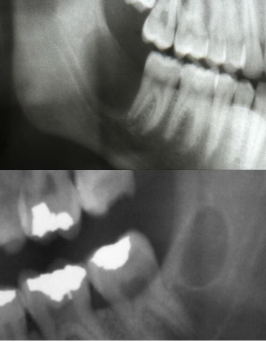
Europeans argue that the primordial cyst is the same as what?
Odontogenic keratocyst
What other lesion shares microscopic features with primordial cyst?
Odontogenic keratocyst
Where might you find a primordial cyst?
Develops in place of a tooth, before any mineralized material is deposited
Is a primordial cyst common?
Not only is it rare, but it is also controversial
What is the treatment for a primordial cyst?
Enucleation
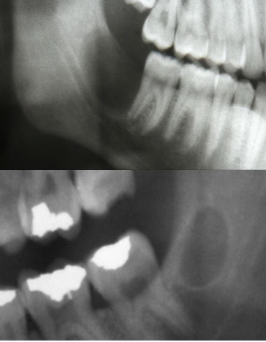
Is there any evidence of calcified material in a primordial cyst?
No
What is another name for odontogenic keratocyst?
Keratocystic odontogenic tumor (KCOT)
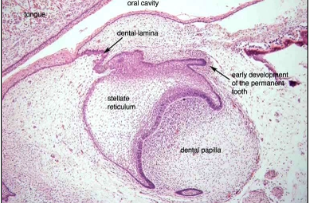
What tissue does an odontogenic keratocyst arise from?
Cell rests of dental lamina
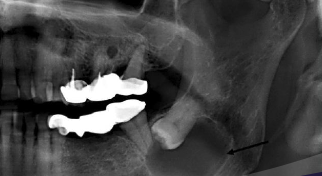
Where are odontogenic keratocyst commonly found?
Posterior body and ramus of mandible (50%)
What is odontogenic keratocyst associated with?
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome (Gorlin Syndrome)
What demographic does odontogenic keratocyst mostly affect?
M=F
Between ages 10-40 (60%)
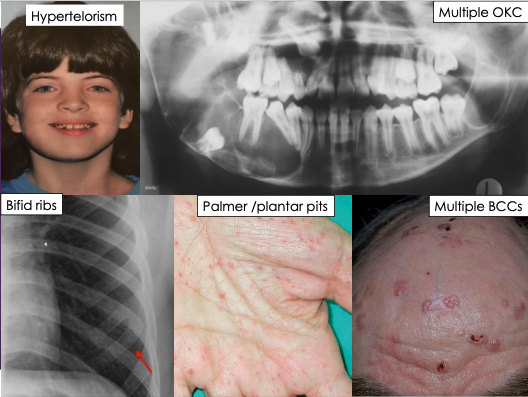
What are the clinical features of odontogenic keratocyst?
Usually asymptomatic but some larger odontogenic keratocyst may cause pain
Hypertelorism
Multiple OKC
Bifid ribs
Palmer/plantar pits
Multiple BCCs
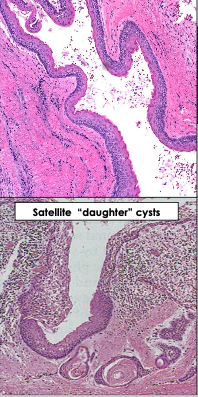
What are key histological features of odontogenic keratocyst?
Thin, friable wall
Epithelial lining is a uniform 6-8 layers thick
Basal cell layer shows palisading and is hyperchromatic
Epithelium is surfaced by waxy parakeratin
May have small satellite cysts away from primary lesion- “daughter cysts” that cause recurrence
Is the associated tooth vital in odontogenic keratocyst?
Yes, teeth are vital
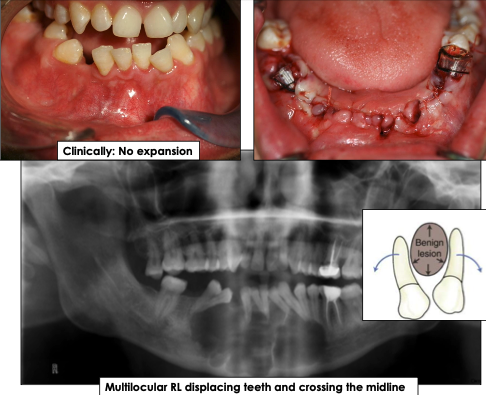
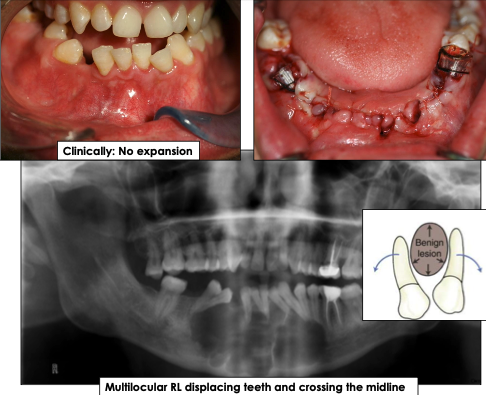
What is the growth pattern for odontogenic keratocyst?
Grows in anterior-posterior direction and does not cause bone expansion
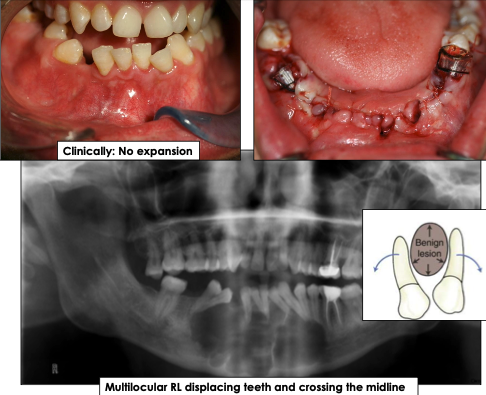
What are the radiographic features of odontogenic keratocyst?
Well-defined radiolucency with corticated borders
Can be unilocular (small) or multilocular (larger lesions)
May displace teeth, cross midline or mimic other cysts
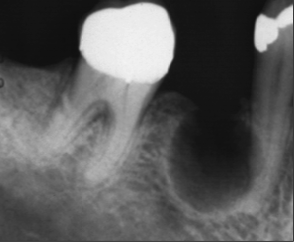
What are common differential diagnoses for odontogenic keratocyst?
Residual cyst
Lateral radicular cyst
odontogenic keratocyst
Lateral periodontal cyst
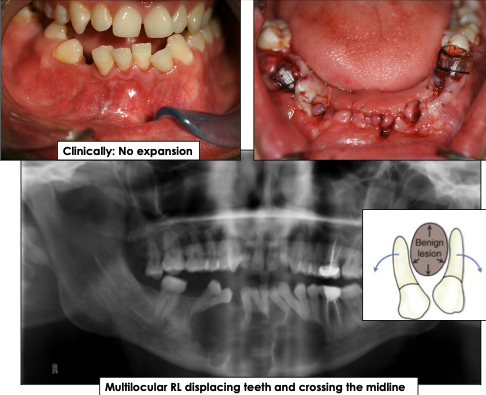
What is the recurrence rate of odontogenic keratocyst?
30%, even 10+ years post-treatment
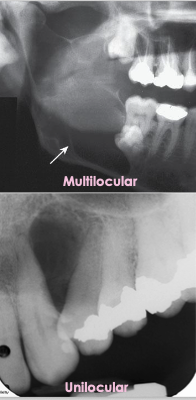
What is the treatment for odontogenic keratocyst?
Smaller lesions: Enucleate in one piece
Larger lesions: Marsupialization followed by enucleation
Requires a long term follow-up
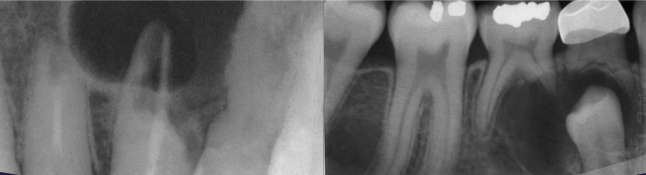
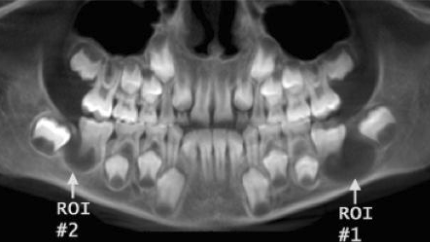
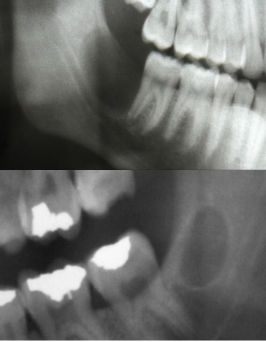
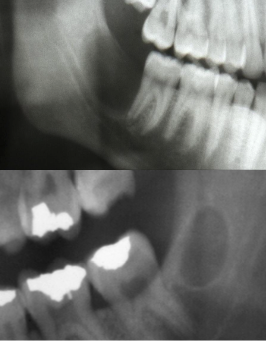
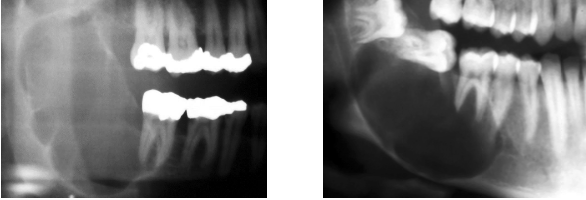
What is this image and what is it showing?
odontogenic keratocyst mimicking dentigerous cyst
What is this?
odontogenic keratocyst
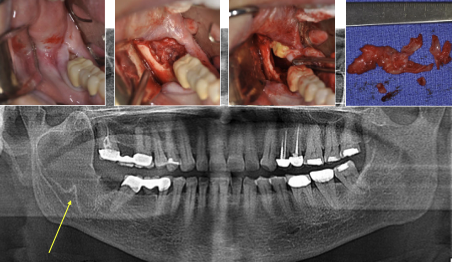
What is required for diagnosis of odontogenic keratocyst?
Biopsy —> most lesions are treated with enucleation and curettage
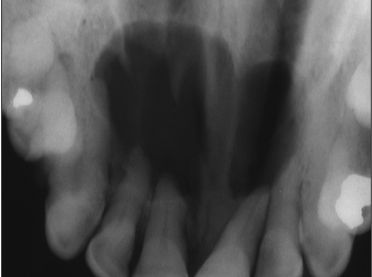
What is this image showing?
odontogenic keratocyst mimicking a nasopalatine duct cyst with divergent roots and resorption of roots
What is another name for Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma syndrome?
Gorlin syndrome; Gorlin-Goltz syndrome
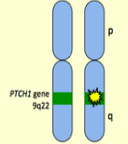
What is the mode of inheritance for Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma syndrome?
Autosomal dominant
Chromosome 9q22
PTCH gene (tumor suppressor gene)
Do patients with Gorlin Syndrome usually have life-threatening anomalies?
No
Why might patients with Gorlin Syndrome develop jaw deformities?
Due to repeated surgeries for multiple OKCs
A diagnosis for Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma syndrome can be made if a patient has
2 major criteria
1 major and 2 minor
1 major and a genetic confirmation
What are the major diagnostic criteria of Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma syndrome?
Five or more basal cell carcinomas or one before the age 30 yrs
Multiple OKC’s
Lamellar calcification of the falx cerebri
Two or more palmer or plantar pits
First degree relative with NBCC syndrome