Lab 12: Brain & Cranial Nerves (Vocab)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
List the 4 major sections that the brain is composed of
cerebrum
dincephalon → thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
cerebellum
brain stem - midbrain, medulla oblongata, pons
What are the names of the 3 cranial meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
What are the venous sinuses?
drain blood from the brain to the internal jugular veins
What is the falx cerebri?
extension of the dura mater that separates the 2 cerebral hemispheres & attaches to the crista galli of the ethmoid bone
What are arachnoid granulations (villi)?
the arachnoid mater penetrates through the dura mater into the venous sinuses w/ extensions of tissue called arachnoid granulations — these reabsorb CSF into the blood
List the 4 lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
frontal
parietal
occipital
temporal
The surface of the cerebrum has many convultions in the tissue; deep grooves called (1)___ & shallow grooves called (2)___ (singular: (3)___). On the either side of a (2) is a bulge of tissue called a (4)___ (plural: (5)___)
Fissures
Sulci
Sulcus
Gyrus
Gyri
A prominent sulcus called the (1)___ forms a key landmark on the brain as it separates the frontal & parietal lobes of the cerebrum. The gyrus anterior to the (1) is called the (2)___ and the gyrus located posterior to the (1) is called the (3)___. The right & left hemispheres are separated from each other by the (4)___
central cerebral sulcus
precentral gyrus
postcentral gyrus
longitudinal cerebral fissure
Name the sulci that separate the cerebral lobes
parieto-occipital sulcus
lateral cerebral sulcus (separates frontal from temporal lobe)
What separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum?
transverse cerebral fissure
What is the arbor vitae?
cerebellar white matter; structure resembles a tree
What is the interthalamic adhesion (intermediate mass)?
a bridge of gray matter that joins the right & left halves of the thalamus in ~70% of brains; center dot inside thalamus
What is the corpus callosum?
white structure inferior to cerebrum; contains axons that connect right & left cerebral hemisphere
Constrast the pineal gland and pituitary gland
pineal gland (middle of the brain) → regulates sleep-wake cycles by secreting melatonin
pituitary gland (base of the brain) → “master gland” that controls growth, metabolism, & other hormones
What is the infundibular stalk?
a ventral down growth of tissue that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
List the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland
Growth hormone (GH)
Thyroid-stimualting hormone (TSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
What are the functions of melatonin
regulates cicadian rhythms; induces sleep, serves as an antioxidant, ihibits reproductive functions in certain animals
List the function of the frontal lobe
voluntary muscle movements (motor cortex)
higher intellectual processes (problem solving, language, concentration, planning, etc.)
List the functions of the temporal lobes
hearing & smelling (olfaction)
memory of complex sensory forms (music, visual patterns, etc.)
List the functions of the parietal lobes
perception of touch, pain, pressure, & heat in skin
understanding & formulation of speech
List the functions of the occipital lobes
vision
blend of visual & nonvisual sensory experiences
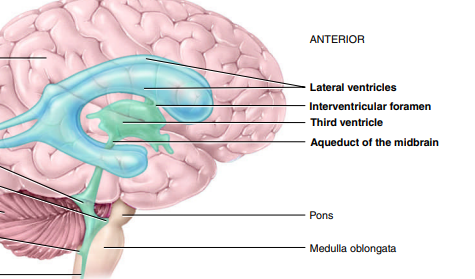
Within the brain are cavities called ___ that are filled with ___
ventricles; CSF
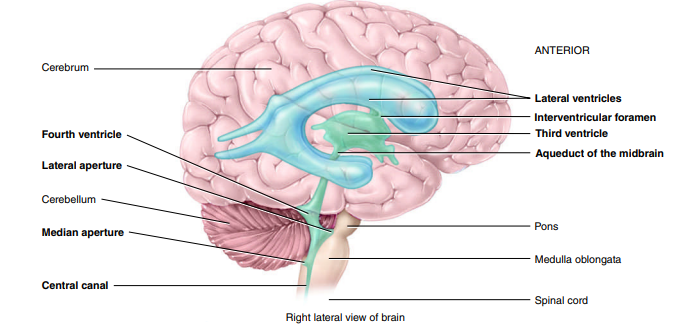
What are the 2 lateral ventricles separated by anteriorly?
septum pellucidum → thin membrane
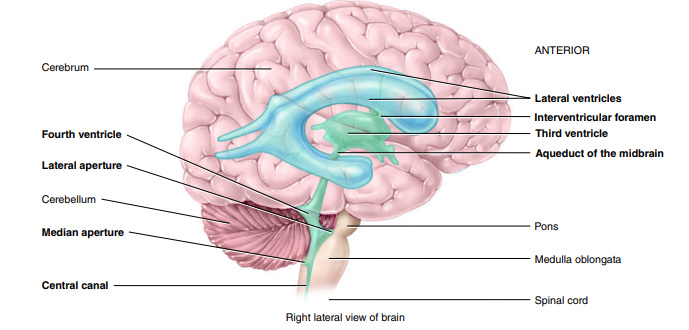
Where is the 3rd Ventricle found?
thalamus
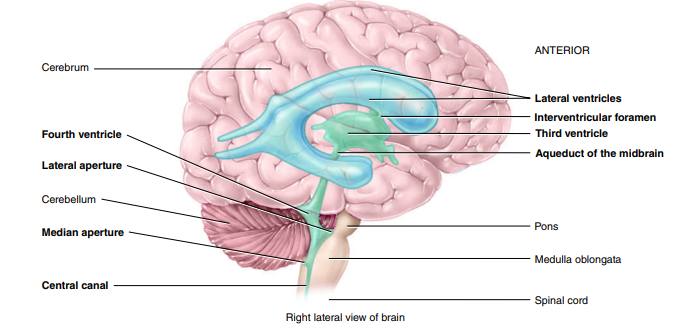
Where is the 4th Ventricle found?
between the brainstem & cerebellum
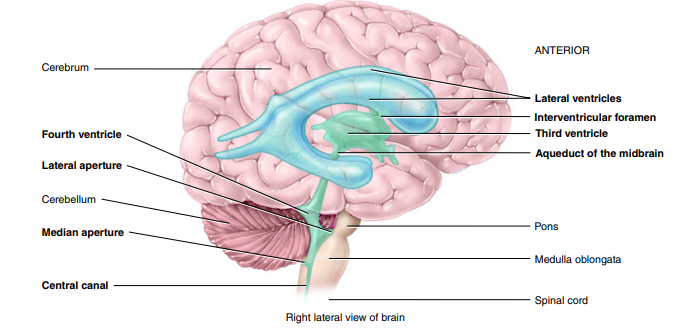
What type of neuroglial cell produces CSF?
Ependymal Cells
What are choroid plexuses?
networks of blood capillaries within each of the ventricles; lined by ependymal cells which produce CSF
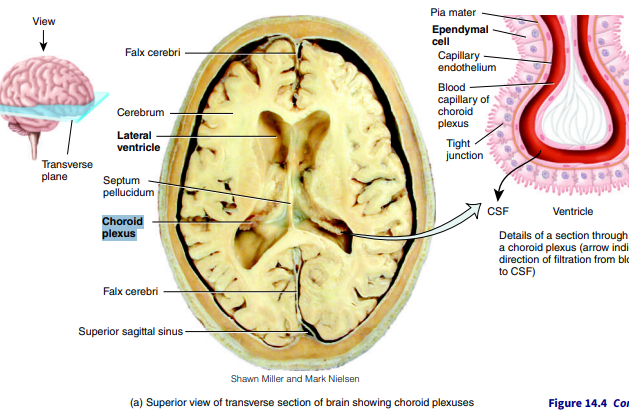
What are the 3 functions of CSF?
mechanical protection → shock-absorbing; protects the brain & spinal cord from physical injuries; allows bain to float
chemical protection → provides optimal chemical environment for accurate neuron signaling
circulation → minor exchange of nutrients & waste products between blood & adjacent tissue
What is the aqeuduct of the midbrain ?(cerebral aqueduct)
narrow channel in midbran connecting the 3rd ventricle to the 4th ventricle, facilitating flow of CSF
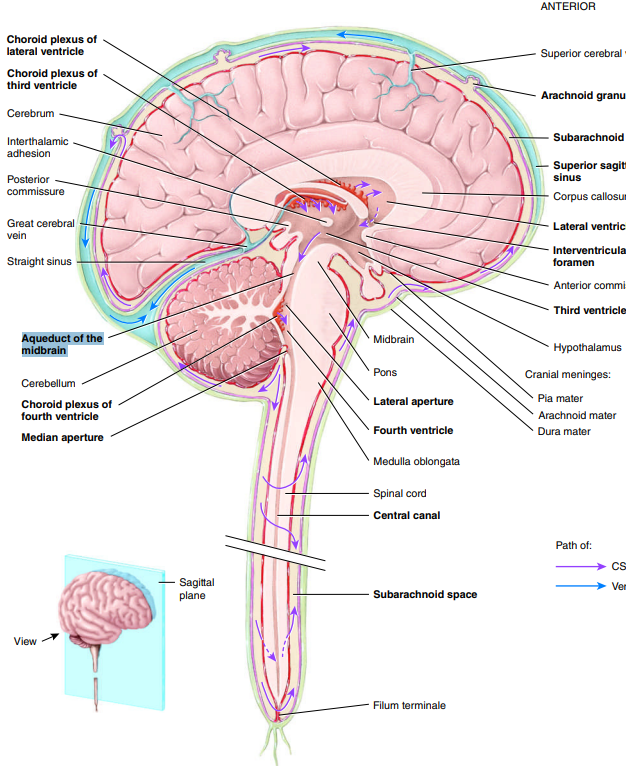
What is the central canal?
(continuous w/ the 4th ventricle) small space in center of gray commissure; extends entire length of spinal cord and is filled with CSF
What is the interventricular foramen?
2 narrow, oval openings that CSF from the lateral ventricles flows out through
The brain does not have the ability to store ___
glucose
Oxygen & glucose must be brought to the brain via the ___ & ___
internal carotids; vertebral arteries
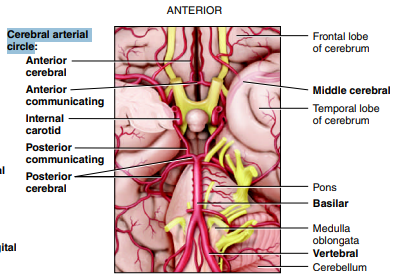
What is the Circle of Willis? List its 2 functions
cerebral arterial circle
group of blood vessels that creates redundancies (duplicates/backup) in cerebral blood to ensure that if one side of the circle is damaged, the other side can compensate & maintain adequate blood supply to brain tissue
equalizes blood pressure to the brain
Venous blood circulates through the ___ ___ that are found between the 2 layers of the ____ ___ & leaves the brain via the ____ ____
venous sinuses; dura mater; jugular veins
List the blood vessels of the cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis)
Anterior Cerebral
Anterior Communicating
Posterior Communicating
Posterior Cerebral
Middle Cerebral
Internal Carotid
Basilar
Vertebral
Explain the diff. between a gyrus and a sulcus
gyrus → elevated ridge of the cerebral cortex
precentral gyrus → frontal lobe; primary motor cortex
postcentral gyrus → parietal lobe; primary somatosensory cortex
sulcus:
cerebral sulcus → grooves that separate cerebral gyrus
interlobar sulcus → grooves that separate the lobes of the cerebrum
e.g. parieto-occipital sulcus, central cerebral sulcus, lateral cerebral sulcus
Explain the difference between a sulcus and a fissure
sulcus:
cerebral sulcus → grooves that separate cerebral gyrus
interlobar sulcus → grooves that separate the lobes of the cerebrum
e.g. parieto-occipital sulcus, central cerebral sulcus, lateral cerebral sulcus
fissure → grooves that separate the parts of the brain
e.g. longitudinal cerebral fissure
List two tasks that demonstrate the function of the cerebellum. Exactly how do these demonstrate the function?
w/o looking at feet, walk in a straight line placing the heel of one food directly in from of the toe of the other foot
close eyes and stand erect w/ feet together for 1 min
cerebellum → coordinates voluntary movements, balance, coordination, posture, muscle tone
List 2 cerebral function tests
Category Clustering → read through a list of words then write down as many words as you can remember
Visual VS Verbal Coding → Look at words VS images sequentially and write down as many as you can remember
List the 12 cranial nerves and indicate if sensory, motor, or both
Olfactory I S
Optic II S
Oculomotor III M
Trochlear IV M
Trigeminal V B
Abducens VI M
Facial VII B
Vestibulocochlear VIII S
Glossopharyngeal IX B
Vagus X B
Accessory XI M
Hypoglossal XII M
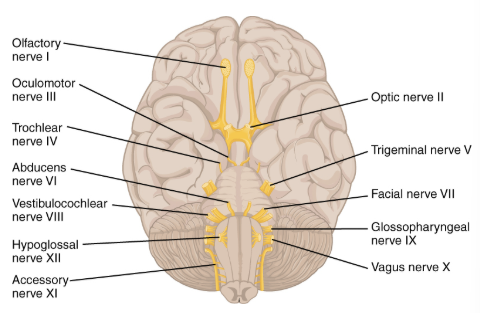
What are the body part(s) and effect of the olfactory bulbs/tracts?
body part:
olfactory epithelium
effect:
convey impulses relate to smell
What is the body part(s) and effect of the optic nerve?
body part:
retina
effect:
vision
What is the body part(s) and effect of the oculomotor nerve?
body parts:
inferior rectus
medial rectus
superior rectus
inferior olbique
ciliary muscle
circular muscle of iris
upper eyelid muscle
effect:
moves eye superiorly & medially; rotates medially
moves eyes medially
moves eyes inferiorly and medially; rotates medially
moves eyes superiorlu & laterally, rotates eyes laterally
What is the body part(s) and effect of the trochlear nerve?
body part:
superior oblique muscle
effect:
moves eyes inferiorly & laterally; rotates medially
What is the body part(s) and effect of the trigeminal nerve?
body parts:
Masseter
Temporalis
Effect:
clench teeth (onto tounge depressor)
clench jaw (temporal region)
What is the body part(s) and effect of the abducens nerve?
body parts:
lateral rectus muscle
effect:
moves eyes laterally (abduction)
What is the body part(s) and effect of the facial nerve?
body parts:
taste buds (anterior 2/3 of tongue)
frontalis
orbicularis oris
effect:
wrinkle forehead; raise eyebrows
inflate cheeks, pucker mouth
saliva & tear production; taste
What is the body part(s) and effect of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
body parts:
cochlear branch → cochlea (& auricles)
vestibular branch → vestibule
effect:
hearing
balance; posture
What is the body part(s) and effect of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
body parts:
taste buds (posterior 1/3 of tongue)
throat muscles
effect:
swallowing; gag reflex
saliva production
What is the body part(s) and effect of the Vagus nerve?
body parts:
throat muscles
effect:
swallowing; “Ahhh” test
speech
What is the body part(s) and effect of the Accessory nerve?
body parts:
Trapezius muscles
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
effect:
shrugging shoulders
rotating head
What is the body part(s) and effect of the Hypoglossal nerve?
body part:
muscles of the tongue
effect:
movement of tongue during speech & swallowing
Identify the test for the olfactory I nerve
eyes closed, one nostril pugged
identify garlic powder or ground coffee smell one at a time
olfactory epithelium
Identify the test for the optic II nerve
Read paragraph for one minute
Count # of words read
Retina
Identify the tests for the oculomotor III neve
A:
cover one eye with hand
shine pen light in other eye and note change in pupil diameter
muscles of the iris
B:
open both eyes as wide as possible
note any eyelid drooping
upper eyelid muscles
Identify the test for the trochlear & abducens muscles
A: Trochlear & Abducens
Partner hold pencil in front of subject & slowly moves it up,down, medially, laterally, upper laterally, lower laterally
Subejct follows pencil w/o moving head
lateral rectus, superior oblique
B: Abducens
Cover left eye
Look laterally w/ right eye
Switch eyes & repeat
lateral rectus
Identify the test for the trigeminal nerve
A: Masseter
clench teeth on tongue depressore while partner tries to pull it out
B: Temporalis
partner holds on hand firmly under chin
subject tries to open mouth
Identify the test for the facial nerve
A: frontalis & orbicularis oris
smile & show teeth
inflate cheeks
wrinkly forehead
raise 1 or both eyebrows
B: salivary glands & taste buds of 2/3 anterior tongue
dip cotton swab in sweet liquid & swab front of tongue
Identify the test for the vestibulocochlear nerve
A: cochlear branch (cochlea & auricles)
sit w/ eyes closed
partner holds ticking clock 1m from right then left ear
is sound heard from both ears & can u determine the direction
B: vestibular branch:
stand w/ feet together and eyes closed; maintain balance
Identify the test for the glossopharyngeal & vagus nerves
open mouth and carefully touch uvula w/ swab
open mouth & have partner hold tonguedown w/ tongue depressor; say “Ahhh”
throat muscles
Identify the test for the accessory nerve
A: trapezius
sit & have partner push down o shoulders
try to raise shoulders
B: sternocleidomastoid
partner hold sides of head
try to rotate head
Identify the test for the hypoglossal nerve
stick tongue out then retract tongue
note any deviation from midline
tongue muscles