PHYL 141 (FINAL) EXAM 3
1/451
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
452 Terms
What makes up the central nervous system?
brain and spinal cord
What makes up the peripheral nervous system?
-sensory and motor neurons
-muscle contractions, organ and glandular functions
-everything else, all nerves other than brain and spinal cord
division of PNS that sends sensory signals toward the CNS
afferent division
division of PNS where motor signals exit the CNS and carry toward effectors (muscles, glands, and adipose tissue)
efferent division
sensory structures that either detect changes in the environment or respond to specific stimuli; may be neurons or specialized cells of other tissues
receptors
controls skeletal muscle contractions
somatic nervous system
contractions under conscious control; ex: raising a glass of water to your lips
voluntary
contractions that may be simple, automatic responses or complex movements, but they are controlled at the subconscious level, outside your awareness
involuntary
automatically regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glandular secretions, and adipose tissue at the subconscious level; includes a parasympathetic and sympathetic division
autonomic nervous system (visceral motor system)
extensive network of neurons and nerve networks in the walls of the digestive tract
enteric nervous system
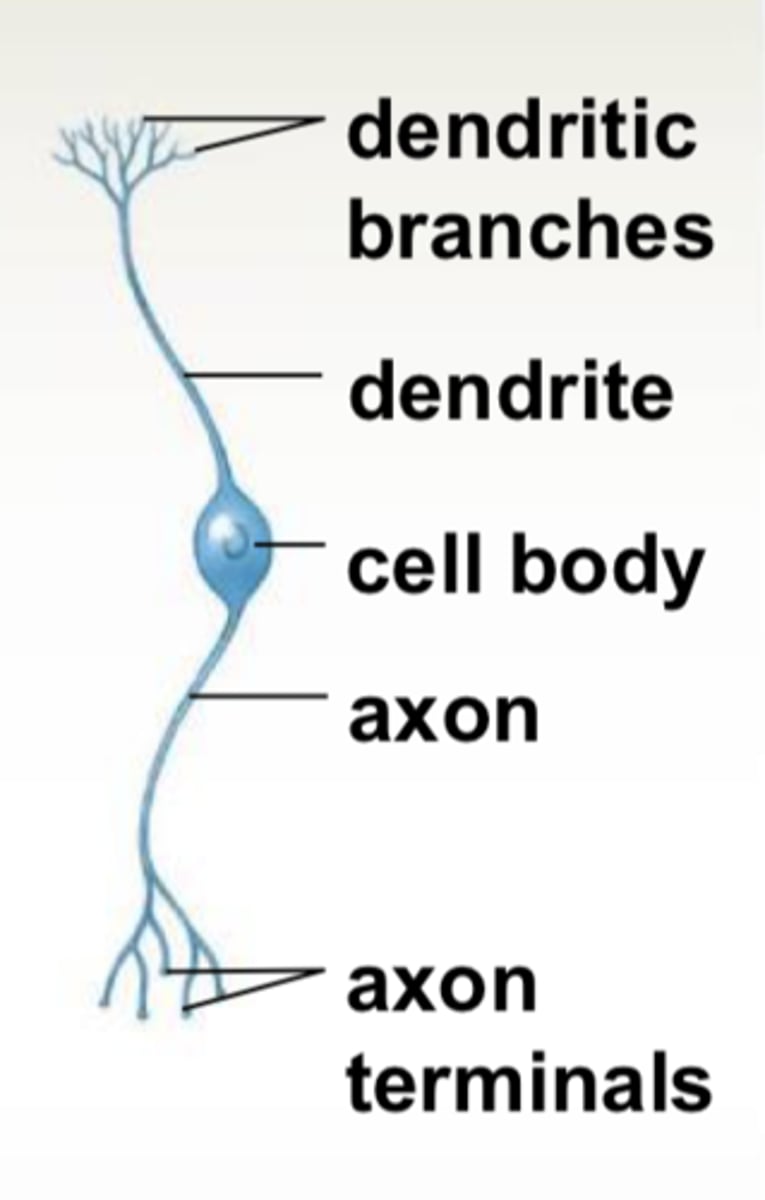
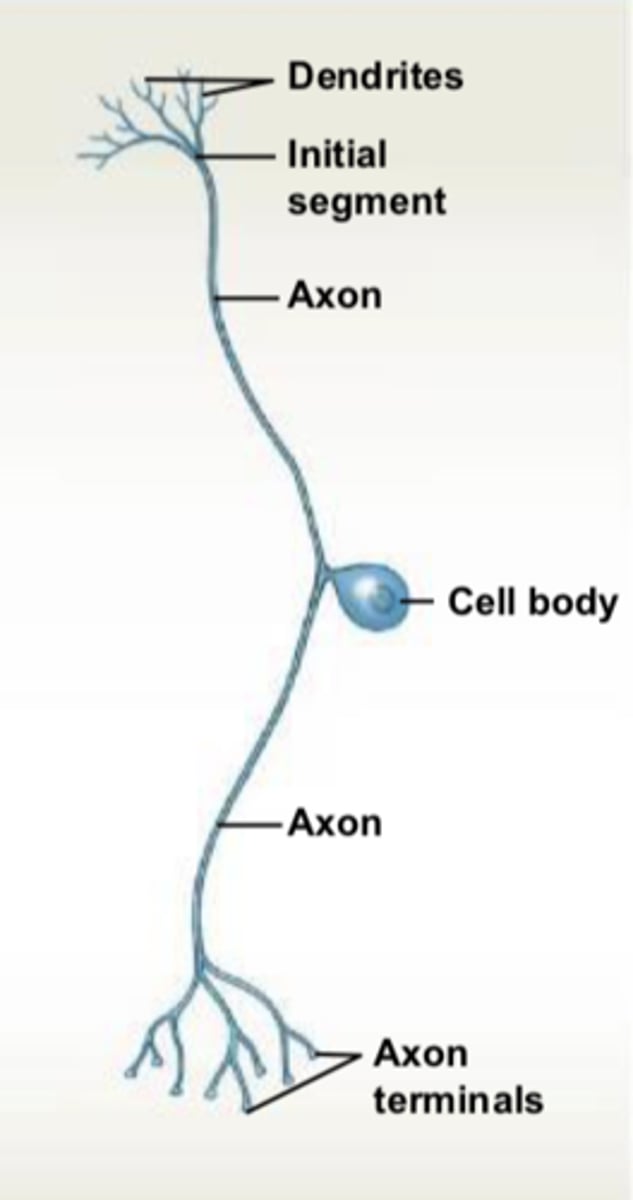
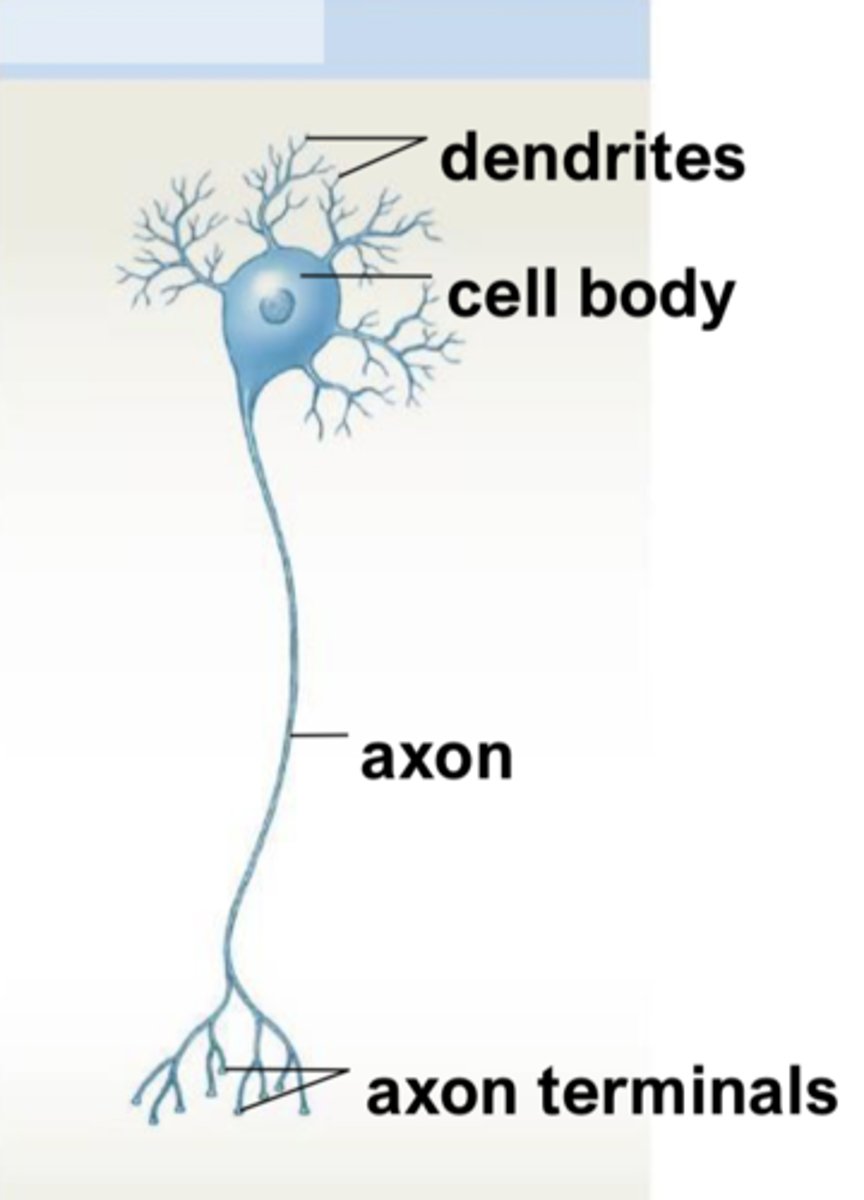
dendrites
detect signals; tend to be excitatory
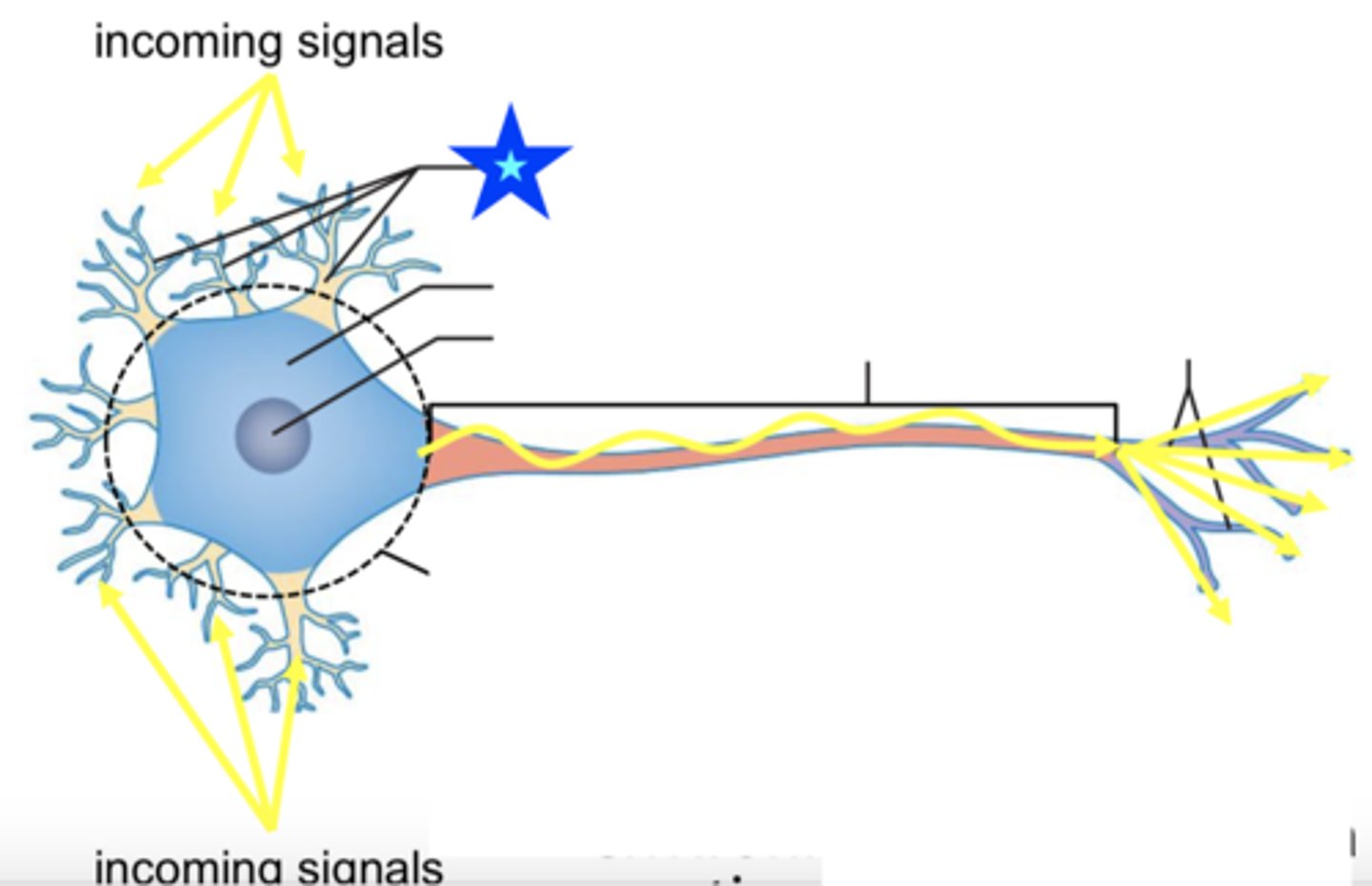
cell body
processing occurs; tend to be inhibitory
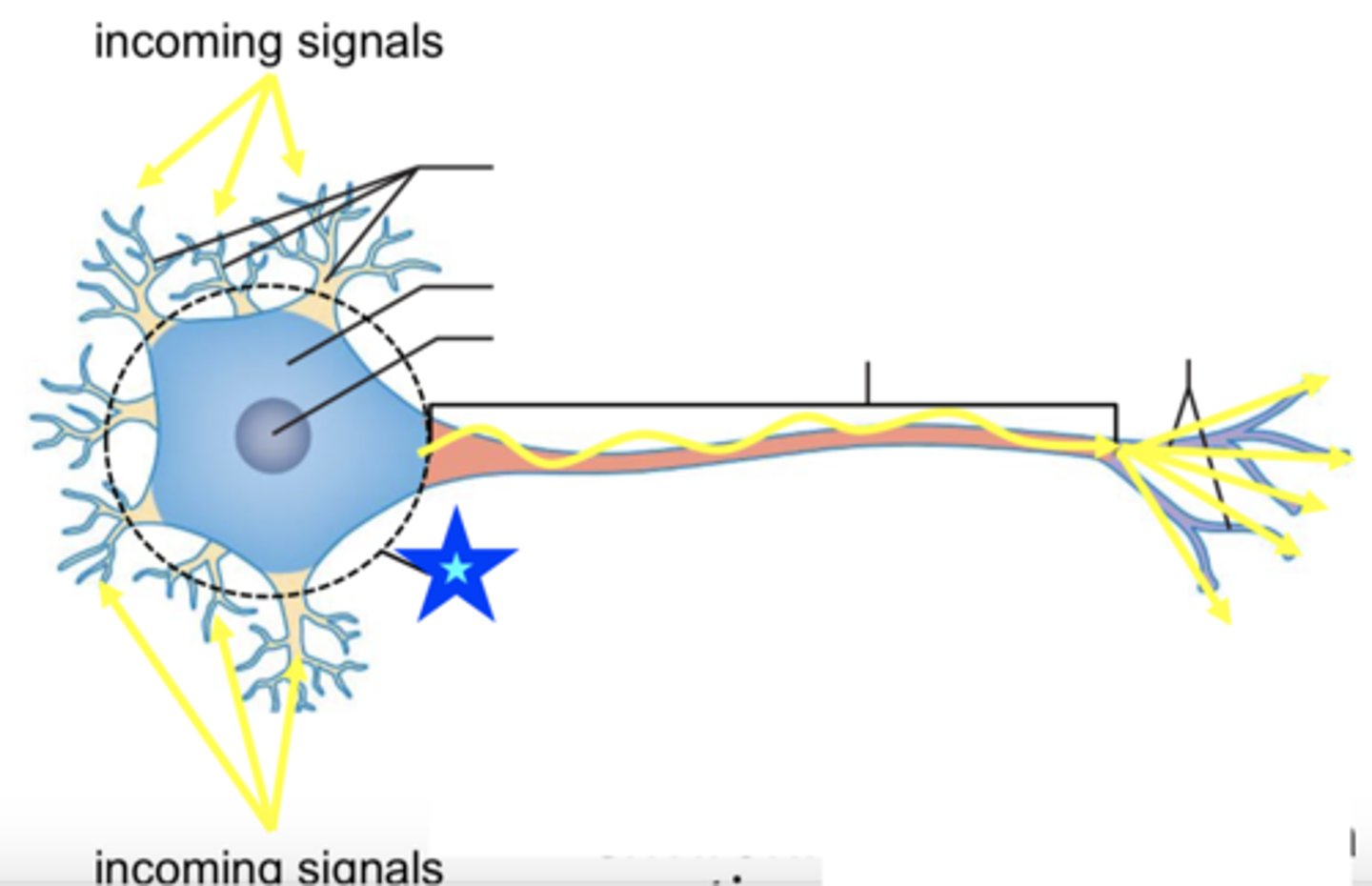
axon
carries out action potentials & branches into telodendria
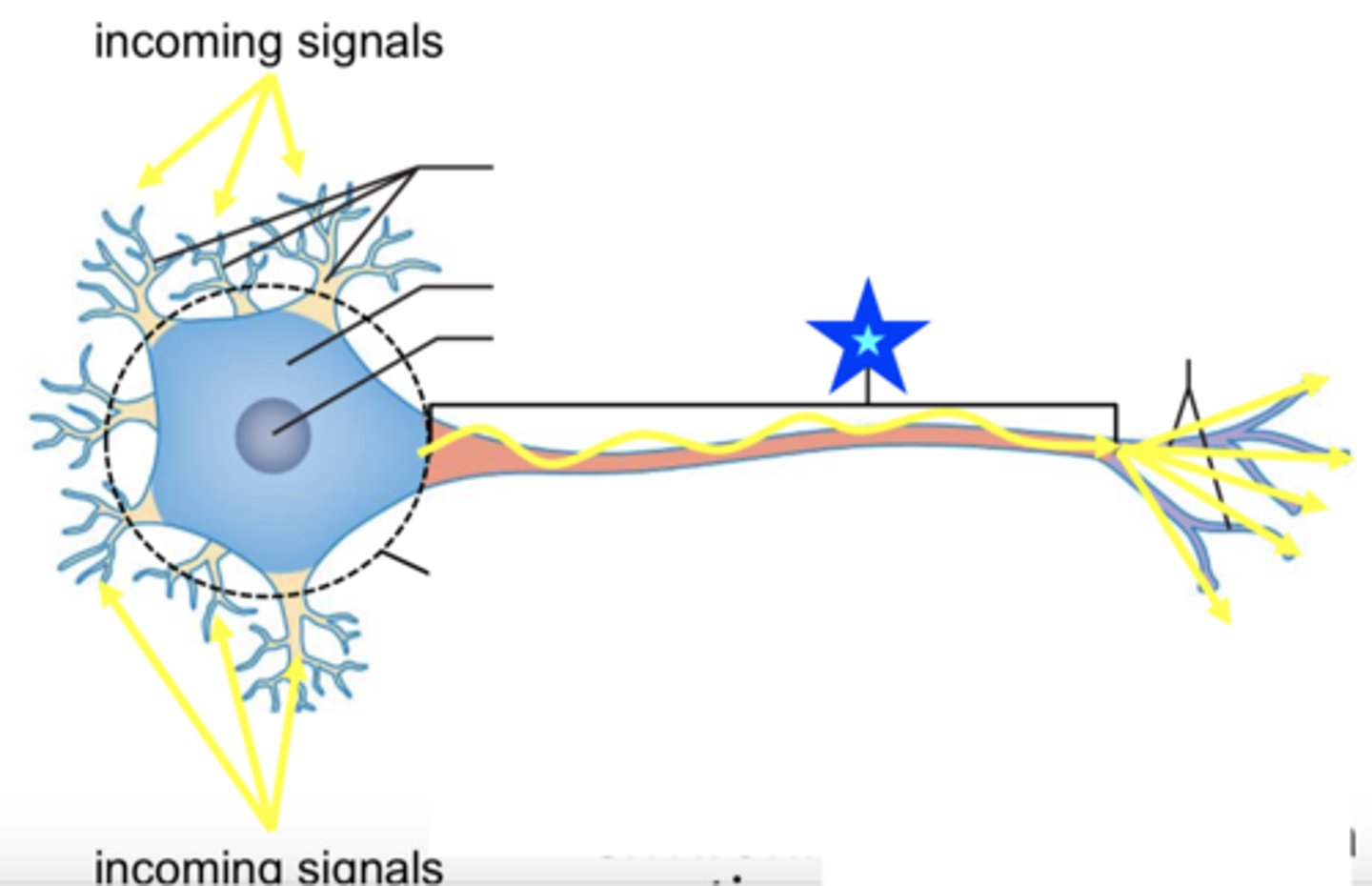
telodendria
ends in axon terminals
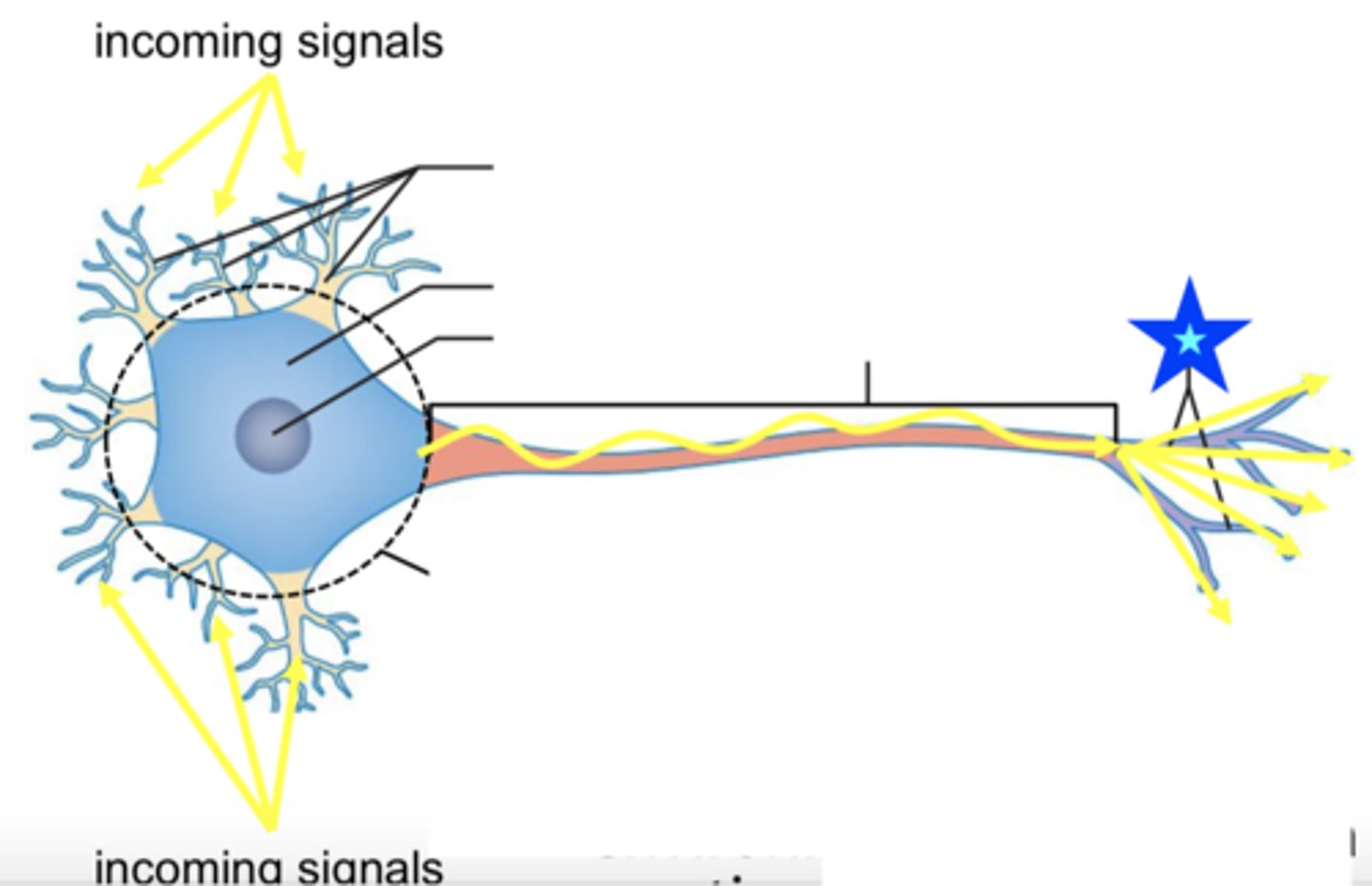
axon terminals
play a role in communication with another cell

anaxonic
difficult to discern, if present; rare in humans
bipolar
rare; occur in special sense organs
unipolar (pseudounipolar)
most sensory (afferent) neurons (which transmit impulses toward CNS)
multipolar
most motor (efferent) neurons (which transmit impulses from CNS to the rest of the body)
usually pseudounipolar neurons that transmit impulses toward CNS
sensory (afferent) neuron
usually multipolar neurons that transmit impulses from CNS to the rest of the body
motor (efferent) neuron
an axon that carries sensory information to the CNS
afferent fiber
an axon that carries impulses away from the CNS
efferent fiber
monitor the outside world and our position within it
somatic sensory neurons
monitor internal conditions and the status of other organ systems
visceral sensory neurons
collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
ganglion
sensory receptors that monitor the digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, and reproductive systems, and provide sensations of distention (stretch), deep pressure, and pain (pain, pressure)
interoceptors
sensory receptors that provide information about the external environment in the form of touch, temperature, or pressure sensations and the more complex senses of taste, smell, sight, equilibrium (balance), and hearing (being full, full bladder)
exteroceptors
monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints (body position, balance, movement)
proprioceptors
cells of the CNS and PNS that support and protect neurons; specialized support roles; 50% of your brain; outnumber neurons 10:1
neuroglia
CNS neuroglia
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
PNS neuroglia
satellite cells and schwann cells
-most abundant glia
-forms blood-brain barrier (BBB)
-CNS
astrocytes
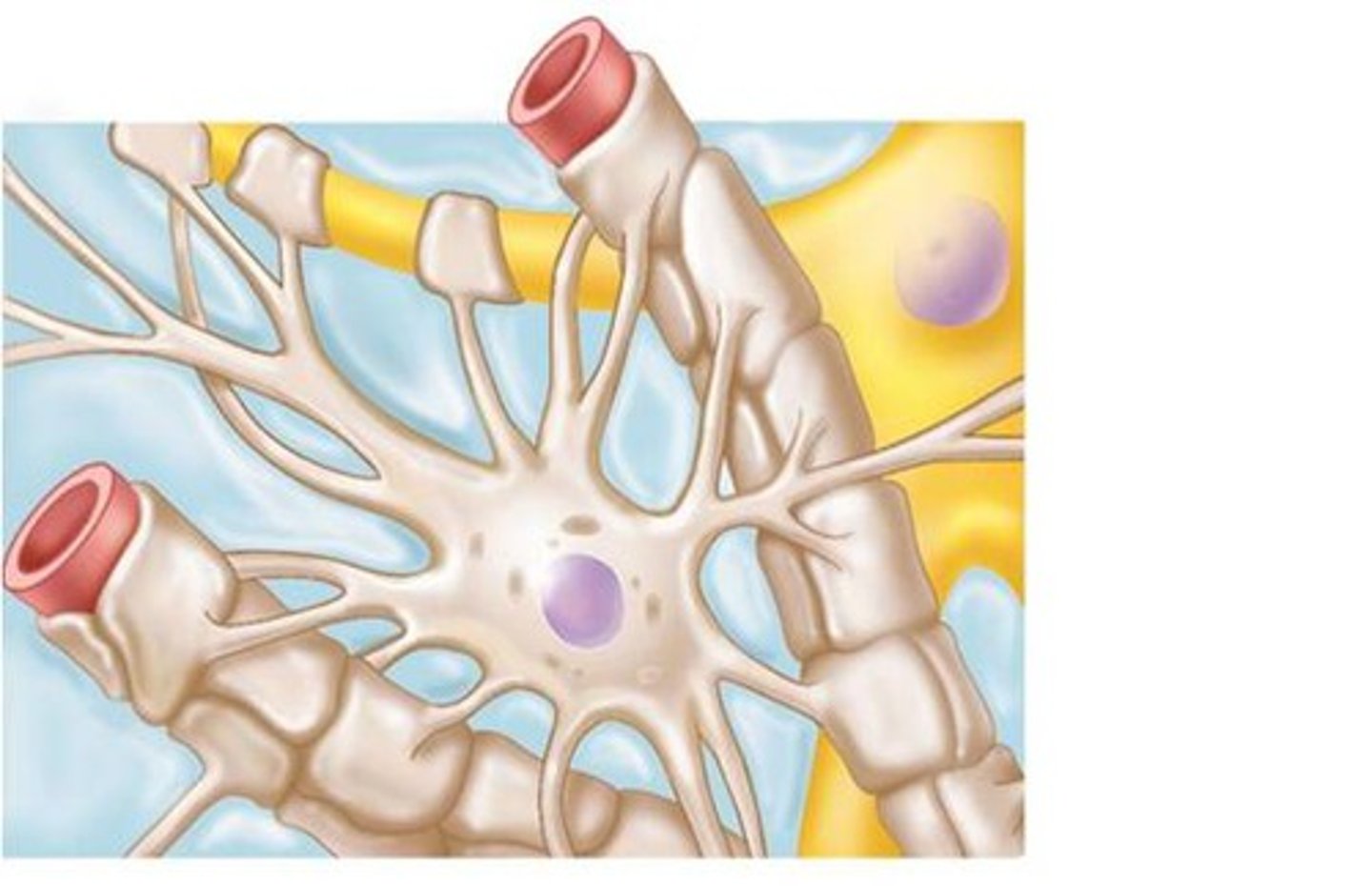
-protect against invaders
-dispose of pathogens, debris, and waste
-CNS
microglia
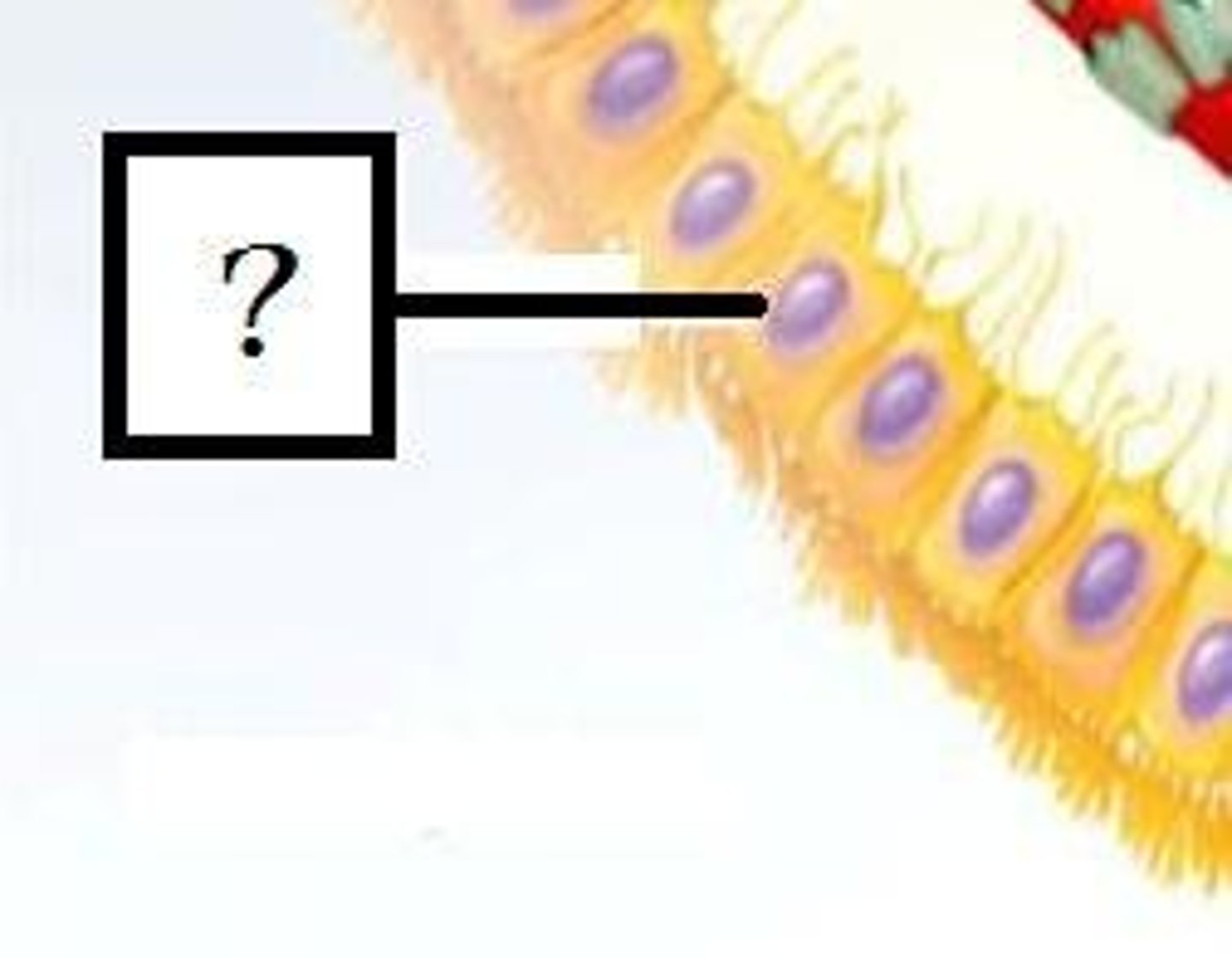
-line cavities in CNS
-produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
-cilia circulate CSF in cavities
-CNS
ependymal cells
-support and wrap CNS neurons with myelin (helps to protect and aids in functions of neurons)
-CNS
ogliodendrocytes
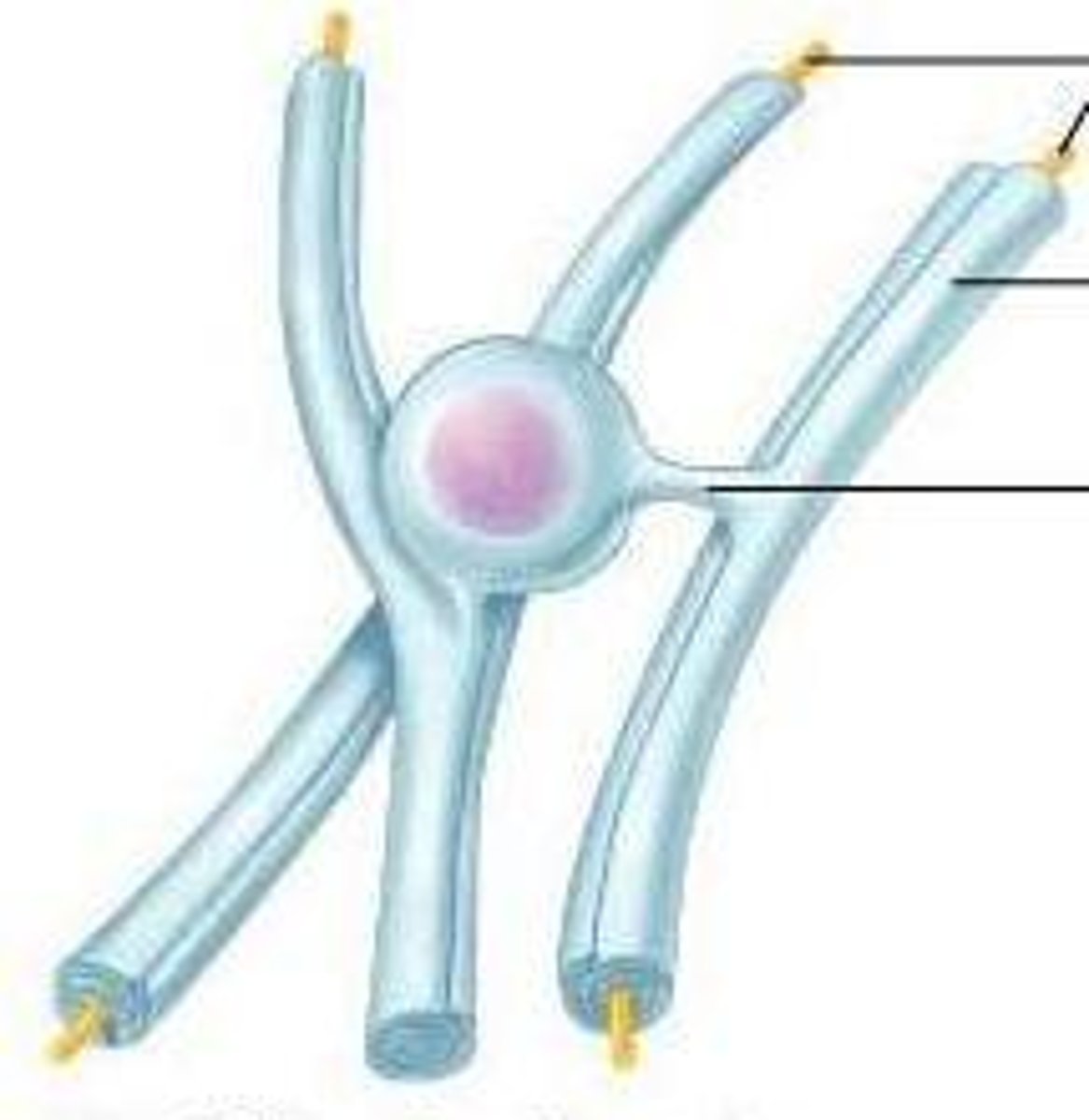
-surround and protect cell bodies of PNS neurons
-PNS
satellite cells
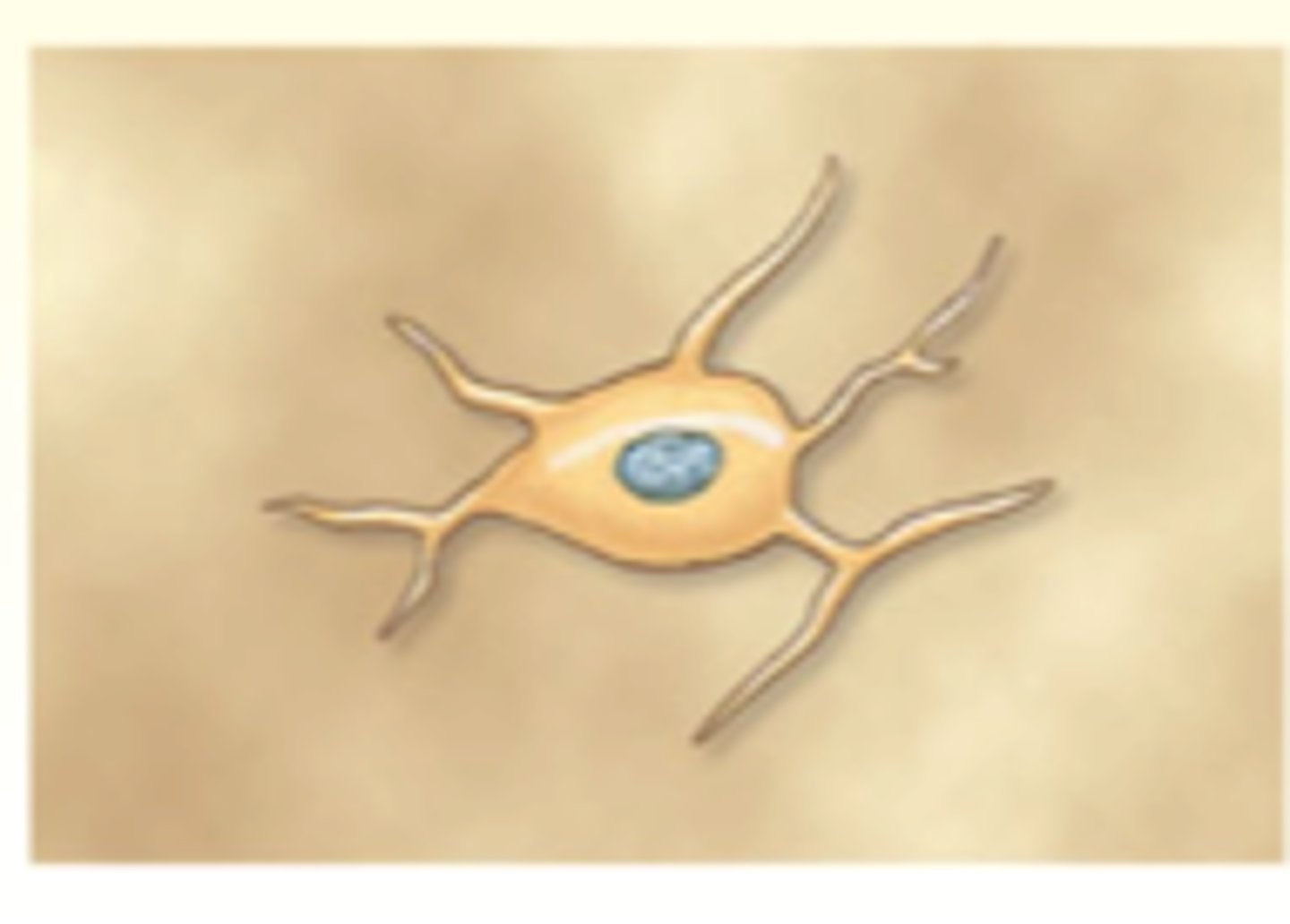
-wrap themselves around axons
-produce layers of myelin
-PNS
schwann cells
filtering mechanism of the capillaries that carry blood to the brain and spinal cord; created by astrocytes
blood-brain barrier (BBB)
fluid bathing the internal and external surfaces of the CNS; secreted by the choroid plexus; made and circulated by ependymal cells; floats and cushions CNS tissue; allows circulation and waste removal; produced by filtering plasma through the blood through the BBB
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
-an insulating sheath around an axon; consists of multiple layers of neuroglial membrane; significantly increases the speed at which an axon potential travels along the axon
-made by ogliodendrocytes in the CNS
-made by schwann cells in the PNS
myelin
are all axons myelinated?
no
-progressive destruction of myelin sheaths in both the PNS and CNS
-result is a loss of sensation and motor control that leaves affected regions numb and paralyzed
demyelination
contains high concentrations of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-)
extracellular fluid (ECF)
contains high concentrations of potassium ions (K+) and negatively charged proteins
intracellular fluid (cytosol)
-difference in electrical potential between the inside and outside of a cell
-caused by unequal balance of ions and charged molecules on either side
-the more imbalance on one side, the harder it is to cause further imbalance (it will start to push back)
-a cell's electric "charge"
membrane potential
-the membrane potential of a normal cell under homeostatic conditions
-ions move through leak channels
resting membrane potential
-typically generated at axon hillock
-a sequence of ion movements and electrochemical changes in excitable cells
action potential
changes in the membrane potential that cannot spread far from the site of stimulation
graded potential
the membrane potential at which there is no net movement of a particular ion across the plasma membrane
equilibrium potential
the sum of the chemical and electrical forces acting on an ion across the plasma membrane
electrochemical gradient
in a typical cell at rest, there is a higher potassium (K+) concentration ________ the cell
inside
in a typical cell at rest, there is a higher sodium (Na+) concentration ________ the cell
outside
in a typical cell at rest, there is a higher chloride ion (Cl-) concentration ________ the cell
outside
resting membrane potential of a neuron
-70mV
threshold for an action potential
-55 - -60mV
passive ion channels; always open
leak channels
active channels that open or close in response to specific stimuli
gated ion channels
open or close when they bind to specific chemicals or ligands
chemically gated (ligand gated) ion channels
open or close in response to changes in the membrane potential
voltage gated channels
open or close in response to physical distortion of the membrane surface (such as when pressure is applied due to the touch of a hand); deals with senses
mechanically gated channels
-open at -55mV
-activation gate opens on stimulation, letting sodium ions into the cell
-inactivation gate closes to stop the entry of sodium ions
-found along the axon
voltage gated sodium (Na+) channels
-open at +30-40mV
voltage gated potassium (K+) channels
-resets an action potential
-powered by ATP
-exchanges 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions
-pumps sodium to the outside, brings potassium in
sodium potassium exchange pump
any shift from the resting membrane potential toward a less negative potential
depolarization
the process of restoring the normal resting membrane potential after depolarization
repolarization
an increase in the negativity of the resting membrane potential (the loss of positive ions)
hyperpolarization
-the membrane potential at which an action potential begins
-typically -55 - -60mV
threshold
-in an unmyelinated axon, an action potential moves along by ________
-slow because there re always voltage gated Na+ channels opening, and more Na+ rushing into the cell
continuous conduction (propagation)
-an action potential in a myelinated axon moves by ________
-faster because the new influx of Na+ renews the depolarized membrane
saltatory conduction (propagation)
specialized site where a neuron communicates with another cell
synapse
-direct link via gap junctions
-fast
-action potentials in one neuron can trigger action potentials in other connected neurons
electrical synapse
-involve neurotransmitters
-slow
-easy to control
-one neuron sends chemical signals to another cell
chemical synapse
separates presynaptic and postsynaptic cells in a chemical synapse
synaptic cleft
chemical compounds released by one neuron to affect the membrane potential of another
neurotransmitters
sends a message in a chemical synapse
presynaptic cell/neuron
receives a message in a chemical synapse
postsynaptic cell/neuron
order of events at a cholinergic synapse
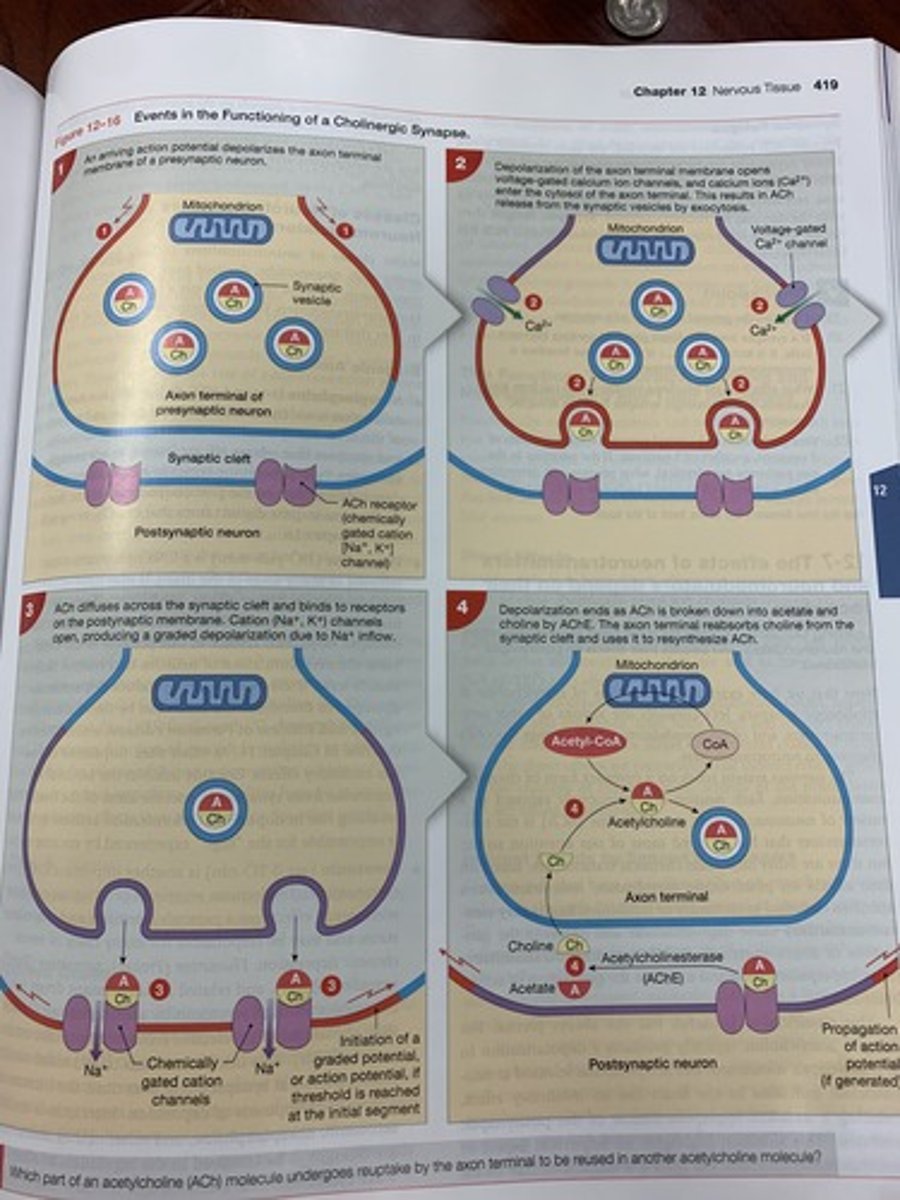
synapse that releases ACh (acetylcholine)
cholinergic synapse
-most widespread neurotransmitter
-released at:
1) neuromuscular junctions involving skeletal muscle fibers
2) many synapses in the CNS
3) all neuron-to-neuron synapses in the PNS
4) all neuromuscular and neuroglandular junctions in the parasympathetic division of the ANS
acetylcholine
-affects mood, appetite, and sleep
-usually inhibitory
-antidepressants/SSRIs
serotonin
-inhibits the reabsorption of serotonin by axon terminals which leads to increased serotonin concentration at synapses (over time, the increase may relieve the symptoms of depression)
-side effects: anorexia and insomnia
fluoxetine (prozac)
-emotion, attention, pleasure
-"reward system": links stimuli with positive feelings
-aids in learning, encourages behavior
-dark side: addiction and impulsive behavior
dopamine
-death of cells that normally produce dopamine
-symptoms: tremor, hypokinesia, rigidity, dementia
-treatment with L-DOPA
parkinson's disease
-increases heart rate and alertness
-"fight or flight"
norepinephrine
synapses that release norepinephrine
adrenergic
-amino acid
-primary excitatory neurotransmitter
-alter ion movement across the membrane
glutamate
-primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
-ex: xanax
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
cause depolarization and promote the generation of action potentials
excitatory neurotransmitters
cause hyper polarization and suppress the generation of action potentials
inhibitory neurotransmitters
causes the membrane potential to move towards the threshold; depolarization in a postsynaptic cell
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
causes the membrane to move away from the threshold; hyperpolarization in a postsynaptic cell
inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
-dominated by the cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons
-outside of spinal cord
white matter
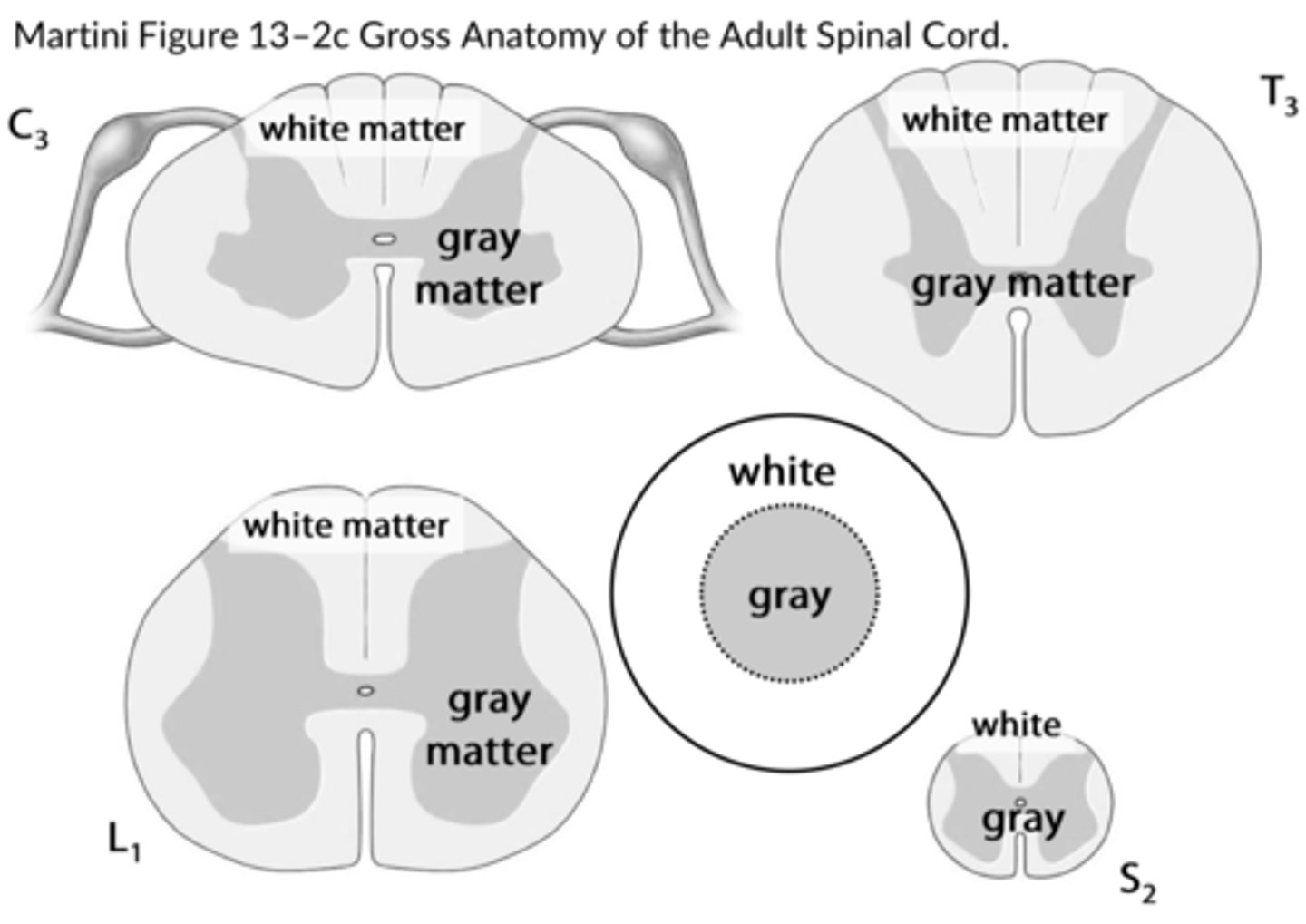
-contains large numbers of myelinated and unmyelinated axons
-inside of spinal cord
gray matter
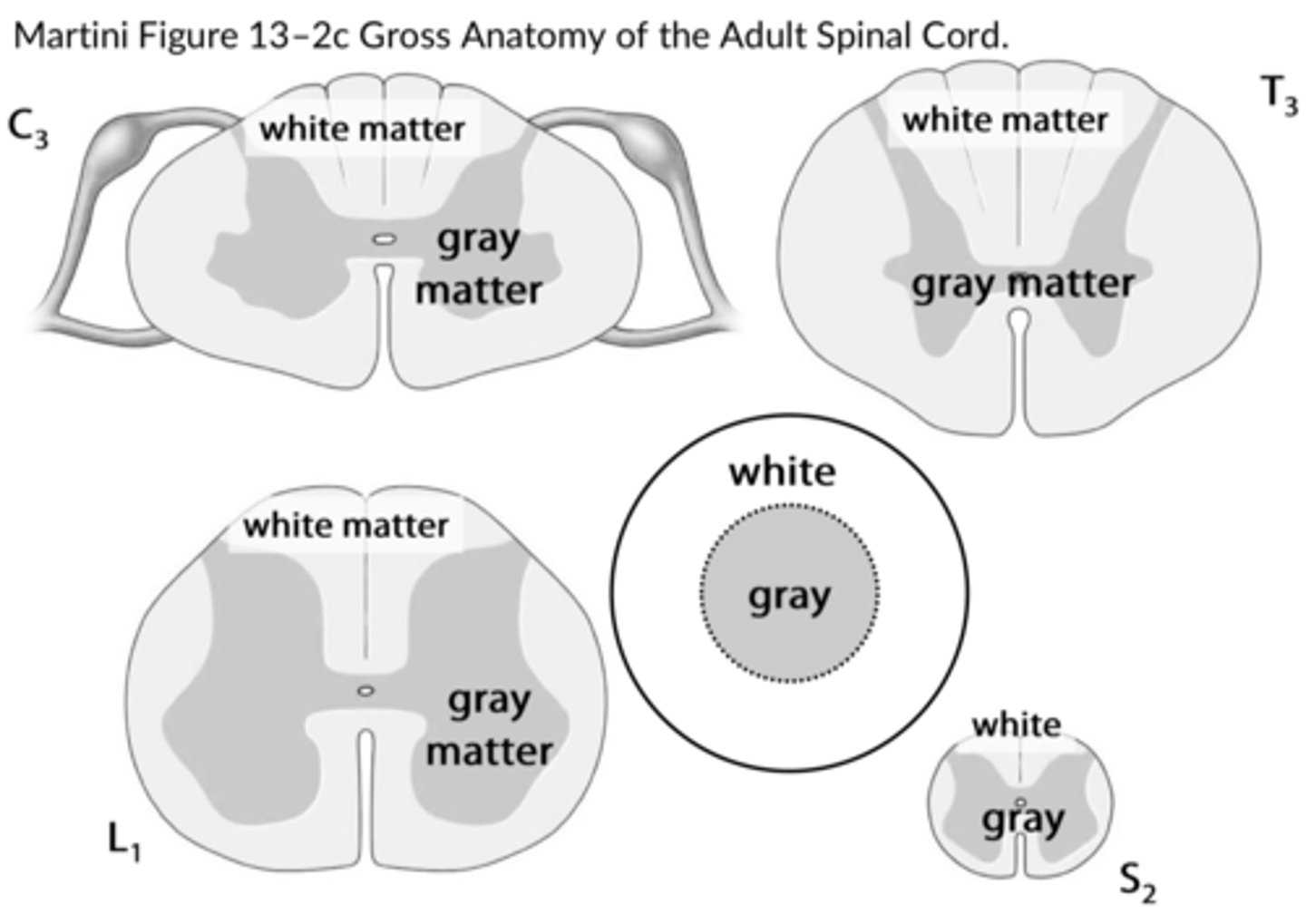
how many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
how many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
12
cervical enlargement
nerves that supply upper limbs
lumbosacral enlargement
nerves that supply lower limbs
conus medullaris
main spinal cord doesn't reach coccyx
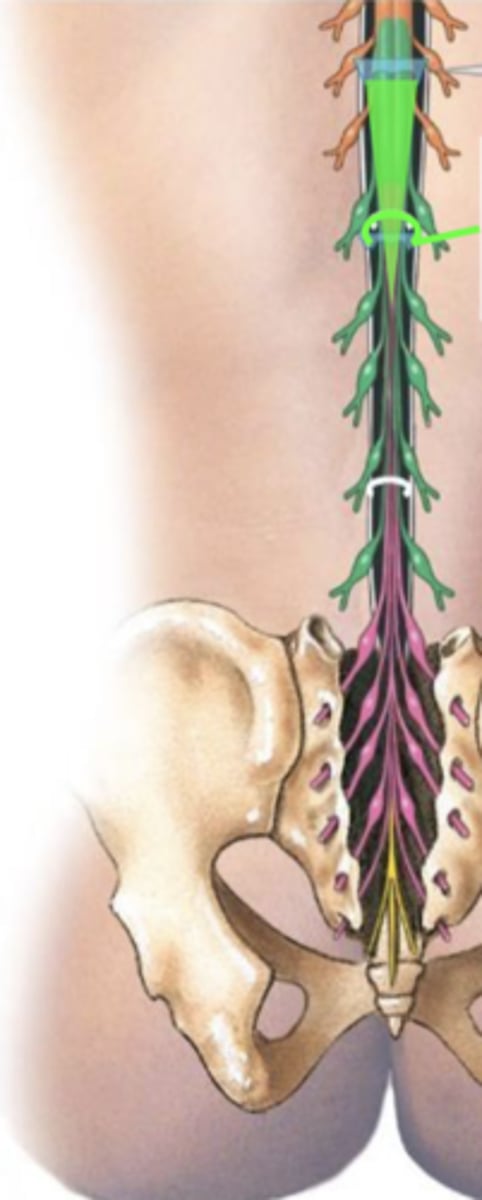
cauda equina