Reinforcement and Punishment
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is reinforcement?
Reinforcement is a consequence that follows a behaviour, making it more likely the behaviour will occur in the future.
What does positive reinforcement do?
Positive reinforcement increases the probability of a behaviour occurring.
What is positive reinforcement in reinforcement theory?
Positive reinforcement involves presenting an appetitive stimulus following a particular behaviour, making it more likely the behaviour will occur in the future.
What is an example of positive reinforcement?
An example of positive reinforcement is saying, "You have worked really hard this month, here is a £500 bonus."
What effect does positive reinforcement have on behaviour?
Positive reinforcement increases the likelihood that the behaviour will occur in the future.
What is clicker training in rat training?
Clicker training involves pairing food with the sound of a clicker to reinforce desired behaviour
What is sniffer training in the context of rat training?
In sniffer training, rats learn to sniff a hole in a cage and are rewarded when they pause in the presence of TNT.
How do trainers reward rats during sniffer training?
Trainers click when the rat sniffs and pauses in the presence of TNT, then present a banana as a reward.
What is field training for the rats in Poling et al (2010)?
Field training involves teaching rats to detect TNT buried in the ground.
Why is timing (contingency) important in reinforcement?
Timing is important because reinforcement should be delivered immediately after the behaviour to strengthen the relationship between the target behaviour and the reinforcement.
What should reinforcement follow in order to be effective?
Reinforcement should follow the behaviour we want to increase.
How does consistency affect reinforcement?
The more consistently a reinforcer follows a behaviour, the stronger the reinforcing effects.
What might happen if the reinforcer follows other behaviours?
If the reinforcer follows other behaviours, those behaviours might be reinforced instead of the intended target behaviour.
What effect does negative reinforcement have on behaviour?
increases the likelihood of a behaviour
What happens during negative reinforcement?
Negative reinforcement involves the removal of a stimulus following a behaviour.
What is the key difference between positive and negative reinforcement?
In positive reinforcement, something is presented, while in negative reinforcement, something is removed.
What does negative reinforcement involve?
Negative reinforcement involves a behaviour that results in the removal or avoidance of an aversive stimulus or state, making it more likely the behaviour will occur in the future.
What is an example of avoidance behaviour?
An example of avoidance is pretending there is something very interesting up in the sky to avoid eye contact with someone you don't want to talk to.
What is the purpose of avoidance behaviour?
to prevent or escape from an uncomfortable or undesirable situation
Define ‘escape’
To behave in a way which removes an unwanted stimulus
What are unconditioned reinforcers?
Unconditioned reinforcers do not depend on a relation to other reinforcers, such as food, water, oxygen, warmth, sexual stimulation, or human touch.
What are conditioned reinforcers?
Conditioned reinforcers become effective due to their relation to another reinforcer, such as the clicker and pellet used in rat training to detect land mines.
What are generalised conditioned reinforcers?
They do not depend on any particular form of reinforcement for effectiveness, such as social attention (eye contact, praise), money, or course credit/grades.
What is punishment?
The technical definition is a decrease in behaviour
What is positive punishment?
Positive punishment occurs when a behaviour results in an aversive stimulus being presented, making it less likely that the behaviour will occur in the future.
What is an example of positive punishment?
An example of positive punishment is a teacher shouting at a child for behaving badly, causing the child to behave for the rest of the day.
What is the difference between positive and negative punishment?
In positive punishment, something is presented (aversive stimulus), while in negative punishment, something is removed
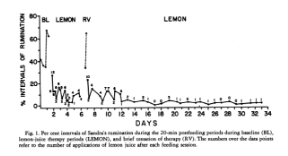
How did Sajwaj et al. (1974) use positive punishment to decrease rumination in an infant?
Sajwaj et al. (1974) decreased life-threatening rumination in a 6-month-old infant by contingent delivery of a small amount of lemon juice into the child’s mouth.
What is contingent exercise in positive punishment procedures?
Contingent exercise involves requiring a person to perform a (usually effortful) response that is not topographically related to the problem behaviour, and it is contingent on the occurrence of the problem behaviour.
What is overcorrection in positive punishment procedures?
It involves engaging in effortful behaviour that is related to the problem behaviour.
What is restitutional overcorrection?
Restitutional overcorrection involves correcting the environmental effects of the problem behaviour and restoring the natural environment
What is positive practice in overcorrection?
Positive practice involves engaging in correct forms of relevant behaviour, essentially practising the desired behaviour.
What is negative punishment?
Negative punishment occurs when a behaviour results in the removal of an appetitive stimulus, making it less likely that the behaviour will occur in the future.
What is an example of negative punishment?
An example of negative punishment is receiving a speeding fine, which leads to the behaviour (speeding) being less likely to occur in the future
What is response cost in negative punishment procedures?
Response cost involves the removal of a reinforcer following problem behaviour, resulting in a decrease in the future probability of that behaviour.
What types of reinforcers can be removed in response cost?
Reinforcers that can be removed include generalized conditioned reinforcers (money, tokens), tangibles (stickers), or preferred activities.
What is time-out in negative punishment procedures?
Time-out is the loss of access to positive reinforcers for a brief period following problem behaviour, which results in a decrease in the future probability of that behaviour.
What are some issues with punishment?
Positive: Punishment can be very effective and sometimes produce immediate results.
Negative: It can lead to emotional reactions, negative reinforcement of the punisher's behaviour, and fails to teach an appropriate replacement behaviour.
Why are punishment procedures avoided in modern-day behavioural treatments?
Punishment procedures are avoided in modern-day behavioural treatments, such as Applied Behaviour Analysis, because they can lead to negative side effects and are less effective in teaching appropriate behaviours.
What did Skinner advocate regarding punishment?
Skinner advocated against the use of punishment, emphasising the importance of reinforcing positive behaviours instead.