7- Cardiac markers
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
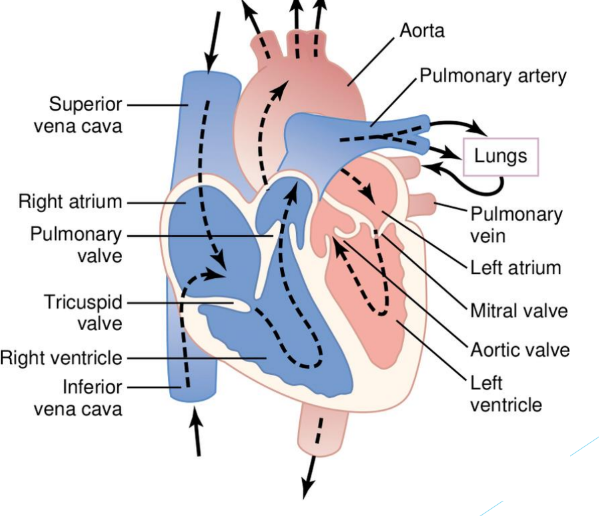
Cardiac anatomy
• Enclosed by pericardium
• Walls made up of three muscle layers- epicardium, myocardium and endocardium
• 4 chambers- atria and ventricles
• Atrioventricular and semilunar valves
• Blood vessels- aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein
Cardiac cycle
• Venous return of blood during diastole
• AV valves open and atria contract
• Ventricles contract, AV valves close and SL valves open
Ways heart diseases progress
• Ischaemia- inadequate blood/oxygen supply caused by blockage of blood vessel, reversible
• Infraction- cell death after prolonged ischaemia
Coronary artery disease
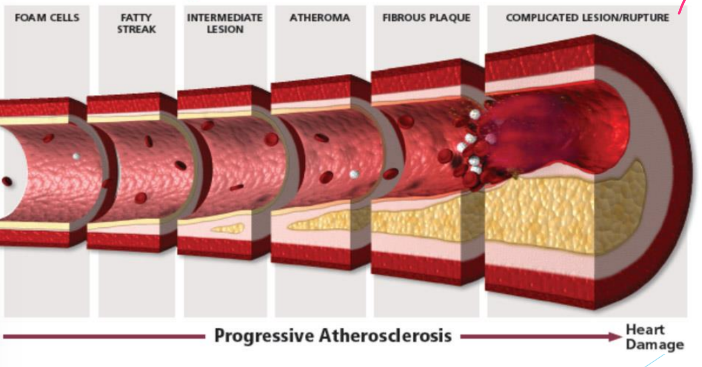
• Largely caused by atherosclerosis, plaque formation
• Made up of lipids, cell debris, foam cells (macrophages that engulf cholesterol), calcium
• Covered by fibrous cap made up of collagen and smooth muscle cells
• Lumen narrows and blood flow is reduced, plaque can break off into a clot
Syndromes stemming from coronary artery disease
• Stable angina
• Acute coronary syndromes- unstable angina, non-ST elevated MI, ST-elevated MI
Angina
• Heart pain with no damage to cardiac muscle
• Advanced atherosclerosis, pain on exertion due to ischaemia as blood supply cannot be increased across restricted vessels
• Stable- reversible, same risk factors as CHD
• Unstable- rupture of fibrous cap, blockage in vessel, pain at rest
Acute myocardial infraction
• Gross necrosis of the myocardium as a result to prolonged ischaemia to the area
• Blood supply to coronary muscle reduced below critical point due to plaque rupture and supsequent coronary thrombosis
• Coronary thrombosis- crushing chest pain, electrocardiogram changes (PQRST), release of cardiac muscle enzymes / markers
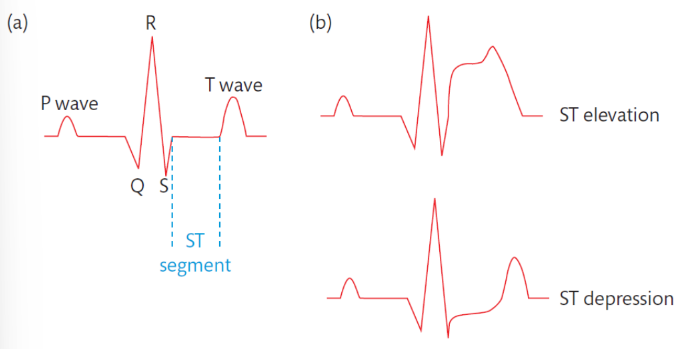
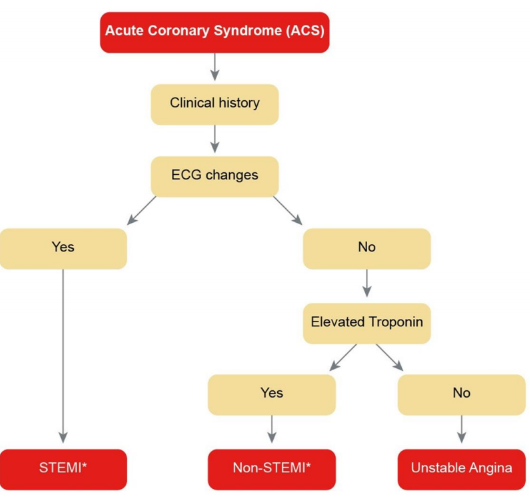
ECG changes during AMI
• ST elevation- complete blockage of coronary artery, severe
• ST depression- partial blockage
Diagnosis of AMI
• History, clinical presentation
• Changes in ECG, may take up to 24h
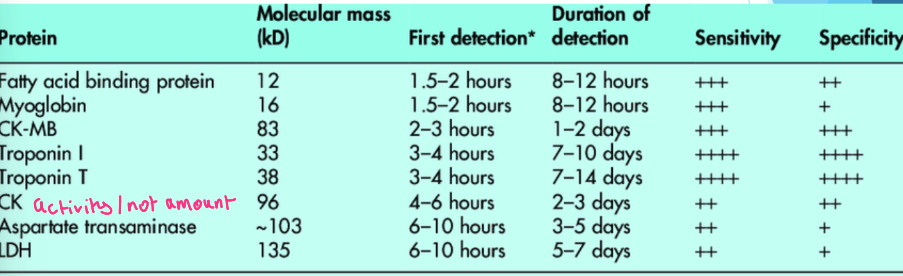
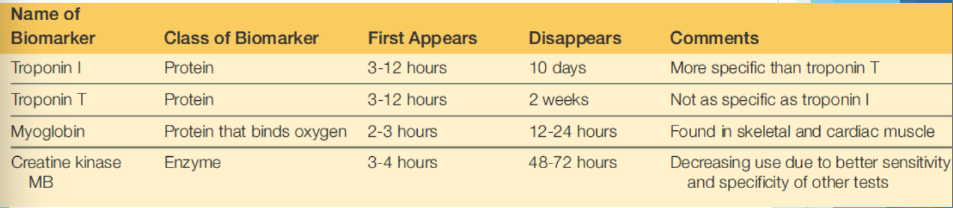
• Cardiac markers- troponin, myoglobin, creatine kinase, lactose dehydrogenase, aspartate transaminase
• Activity of enzymes measured, not amount
Usefulness of markers
Troponin complex structure and location
• Composed of 3 subunits
• Troponin C- binds calcium
• Troponin I- inhinitory component
• Troponin T- tropomyosin binding
• Found in myofibrils, released into circulation upon injury
• Isoforms vary between cardiac and skeletal muscle
Troponins used as cardiac markers
• Two isomers of troponin C, heart and skeletal are identical, not useful
• Cardiac specific- cTnT, cTnI
• cTnT- 11 unique amino acids provide specificity, small amount found in skeletal muscles but can be increased in patients with muscular dystrophy
• cTnI- unique to cardiac muscle, one isomer identified
Myoglobin
• Oxygen binding protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle
• Is found in the cytoplasm and has a low molecular weight, increases rapidly after injury but is not specific
Creatine kinase
• Catalyses formation of phosphocreatine from creatine and ATP
• Cytosolic form is a dimer composed of M and B subunits
• Three isoenzymes- CK1 (BB), CK2 (MB), CK3 (MM)
• Mitochondrial form has two isoenzymes- CKMB (more heart specific), CKMM (heart and skeletal)
Lactate dehydrogenase
• Catalyses reduction of pyruvate to (L)-lactate using NADH as electrol donor
• High activity in skeletal muscle, liver, heart, kidney, RBC
• Not tissue specific, increases in many conditions
• Composed of four subunits of two peptides
• LD1 (H4- heart, kidney, RBC), LD2 (H3M), LD3 (H2M2), LD4 (HM3), LD5 (M4- liver, skeletal muscle)
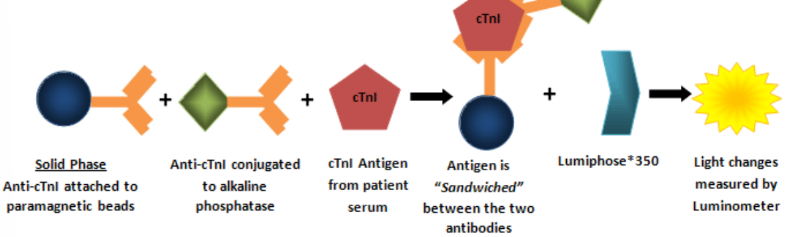
Troponin measurement
• Troponin I- serum or used, monoclonal antibody immunoassay, 7-30 minute run time
• Troponin T- quantitative, serum or plasma used, immunoassay specific from cTnT, lateral flow assay can also be used
Measurement of myoglobin and creatine kinase
• Myoglobin- serum or plasma used in monoclonal immunoassay, allows for early AMI detection, also used as predictor for myocardial injury
• CK- enzymatic, immunoassay detection (100% specific), electrophoresis
Criteria for AMI diagnosis and properties of ideal cardiac marker
• Evidence of myocaridal ischaemia, rise and fall in troponin, at least one troponin result > or equal to 99th percentile
• Ideal marker should provide early AMI diagnosis
• Assist in risk stratification, monitor treatment, detect relapse, results within 60 minutes
Which markers are used in the clinical setting
• Troponins cTnT and cTnI (more specific)- stay elevated and have caridiac specificity, most useful 12h after MI, useful for late presentation, not useful for relapse as they stay elevated for days
• Myoglobin- not used for diagnosis, only confirmatory, released and cleared quickly, poor specificity (<80%)
Tests used to estimate risk of CHD
• Lipid screen- LDL, HDL, cholesterol, triglycerides
• CRP- indicates inflammation but increased levels are associated with future risk of cardiovascular events (high-sensitivity CRP used to detect low levels)
• Homocysteine- increased levels indicate developing CAD, used to screen those with family history
Natriuretic peptides
• Ring shaped molecules that promote sodium and water excretion
• Four subtypes- ANP, B type ANP (BNP), C type, D type
• B type produced by atria and ventricles, released when heart is stretched due to volume overload
• Hypervolaemia is commonly caused by heart failure which often occurs as a result of damage to the heart my MI