redox reactions
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Redox Reactions
Reactions that involve reduction and oxidation are known as redox reactions.
Definitions of Oxidation
What is the oxidising agent in this reaction
oxidation state rules
"Ugly Monsters Cook Good Gourmet Food Helping Other Chefs"
How do we show oxidation states
We use bracketed Roman numerals to show oxidation states (e.g. copper (I) oxide). In ionic compounds, oxidation states match up with ionic charge (e.g. in copper (I) oxide, copper has an oxidation state of +1 and a charge of 1+).
We also use bracketed numerals to show the oxidation states of ions (e.g. ClO- is the chlorate (I) ion)
Oxidation state bracket common misconceptions
We also use bracketed numerals to show the oxidation states of ions (e.g. ClO- is the chlorate (I) ion).
However, students sometimes make the mistake of thinking that the oxidation state matches the charge here too. This is not the case (e.g. ClO3- is the chlorate (V) ion and has a charge of 1-)
In your exam, you may be given an equation and asked whether it describes a redox reaction. To answer this:
work out whether any oxidation states have changed. A redox reaction is any reaction in which oxidation states change.
What are Disproportionation reactions
Disproportionation reactions are reactions in which an element is both oxidised and reduced at the same time. For example, when a Cl2 molecule reacts with water, one chlorine atom is reduced to hydrochloric acid, and the other atom is oxidised to chloric (I) acid.
Definition of oxidation in terms of energy transfer
Reaction where electron are lost/loss of electrons
What is the oxidising agent
Reactant which gains electrons
What is the oxidizing agent in this reaction
Iodine is oxidising potassium so iodine is the oxidizing agent
(in other world potassium is being oxidised by iodine)
What do oxidation state tells us
We can assign oxidation states, to show how much an atom has been oxidised.
Difference between representing oxidation number and charge
In oxidation number its charge then number
In charge it is number then charge
What is the oxidation of an atom which has lost 1 electron
An atom which has lost one electron has a charge of 1+, and so an oxidation state of +1.
What is the oxidation state of copper in this reaction
IN this reaction the oxidation state of copper increases from 0 to +2
What is the oxidation state of copper in this reaction
The oxidation state of copper increases from +1 to +2
How do we write the oxidation states for copper in this reaction
Write the oxidation states in brackets using roman numerals
Reduction
When an atoms oxidation state decreases (gains electrons) we say it has been reduced
What is the oxidising agent and reducing agent in this reaction
Sulfur - oxidizing agent
Copper - Reducing agent
Redox Reactions summary
Oxidation is the loss of electrons; reduction is the gain of electrons.
When an atom is oxidised, its oxidation state goes up
When an atom is reduced, its oxidation state goes down
All oxidation reactions are also reduction reactions.
And we call these reaction redox
Oxidation in covalent bonds/ Oxidation without energy transfer
By defining a redox reaction as a reaction in which oxidation states are changed, we can say that, in a covalent compound, the element which is reduced is the most electronegative element and is the oxidising agent.
What is the oxidising and reducing agent in water
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. This means the electrons on average are closer to oxygen. So oxygens oxidation state decreases.
Therefore:
Oxygen is reduced (-2)
Hydrogen is Oxidised (+1 )
We can assign oxidation states to covalently bonded molecules as well as ionic compounds
if you are asked to identify the oxidising agent
In this reaction the oxidizing agent is sulfuric acid NOT sulfur.
Oxidising agent and Reducing agent
Oxidizing agent = reactant which gains electrons
Reduced - oxidation state decreases
What is the oxidizing agent
You might see reactant being replaced with species but thai can be confusing as species could refer to reactant or product and the oxidising agent is always the reactant
In summary
What do we need to remember when identifying the oxidizing agent
What does the word species mean
How to assign oxidation states
Coefficient and subscripts when assigning oxidation states
we don't include coefficients when assigning oxidation states to individual atoms! But we DO take into account subscripts. Yes! We DO take into account subscripts when working out total charge or for balancing, but NOT when assigning the oxidation state per atom.
What is a monatomic ion
An ion with only 1 atom
H+ is a monatomic ion. So its oxidation state is equal to charge. Oxidation state = +1
He is a uncombined element. So its oxidation state is equal to 0. Oxidation state = 0
H2- is a monatomic ion. So its oxidation state is equal to charge. Oxidation state = -2
1st and 2nd oxidation state rules
The 1st oxidation state rule is that uncombined elements have an oxidation state of 0
The 2nd oxidation state rule is that monatomic have an oxidation state equal to their charge
What is the 3rd rule of oxidation
The sum of the oxidation states is equal to the overall charge of the compound
What is the oxidation state of sulfur in a sulfate ion (SO42-)
Overall charge of a sulfate ion is 2-
Oxygen has an oxidation state of 2-
There are 4 oxygens in a sulfate ion (2- x4 = - 8)
Oxidation state of sulfur (x) + oxidation state of oxygen (-8) = overall charge of sulfate =-2
To bring overall oxidation state to -2 sulfur must have a oxidation state of +6 (+6 - 8 = -2)
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen in sulfuric acid
H2SO4 has an overall charge of 0 so has an overall oxidation state of 0
SO4 has an oxidation state of -2 (-8 oxygen + 2 sulfur)
H2 oxidation state + -8 + -2 = 0
H2 = +2
Each hydrogen = +1
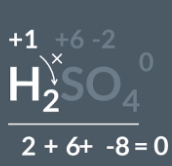
What is the oxidation state of copper in CuSO4
CuSO4 has an overall charge of 0
SO4 has an overall charge of 2-
Cu has an charge of 2+
How to work out the oxidation state of a element in a compound using rule 3
Identify the charge of the compound = oxidation state (e.g 2)
Identify any polyatomic ions and their charge (2-)
Calculate the charge of the other element (sum of oxidation states = overall oxidation state of compound)
-2 + x = 2
X = +4
What is the 4th rule of oxidation
If a group 1 atom is in a compound it always has an oxidation state of +1
What is the oxidation state of Na₂S
Sodium (Na) in sodium sulfate (Na₂S) is a group 1 metal so it must have an oxidation state of +1
With this in mind what is the oxidation sate of sulfur
The compound has a charge of 0 so an overall oxidation state of 0
(+1 x2) + x = 0
Sulfur oxidation state = -2
What is the 5ht rule of oxidation
If a group 2 atom is in a compound it always has an oxidation state of +2
What is the oxidation state of calcium
CaCO3 has an overall charge of 0
Ca is in group 2 so has charge of +2
+2 + x = 0
CO3 has oxidation state of - 2
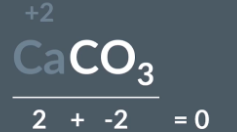
Naming group 1 and group 2 compounds
When naming group 1 and group 2 compound because Group 1 and Group 2 can only have 1 oxidation state (+1) or (+2) we don’t need to include bracket numerals in their full name
E.g Magnesium (II) chloride is just Magnesium Chloride
What is the 6th oxidation state rule
If fluorine is in a compound it always has an oxidation state of -1
UF4 has an overall charge of 0
F has an charge of -1
(-1 X 4) + x = 0
X = +4
What is the name of UF4
Uranium (IV) Fluoride
Usually rules
Rules 7 8 and 9 are called ‘usually rules’ as they can be overruled by rules 1-6
What is the 7th rule of oxidation states
Hydrogen if in a compound has an oxidation state of +1
HCl has an overall charge of 0
Hydrogen has an oxidation state of +1
+1 + x = 0
Cl oxidation state = -1
What is the 8th rule of oxidation states
Oxygen if in a compound has an oxidation state of -2
Al2O3 has an overall charge of 0 so overall oxidation state of 0
Oxygen has an oxidation state of -2
(-2 x 3) +(2x) = 0
2x = +6
Aluminum has oxidation state of (+3)
Subscripts and oxidation states (Remember )
REMEMBER to account for subscripts we are finding the oxidation state of Al not Al 2
What is the 9th rule of oxidation states
Chlorine in a compound has an oxidation state of -1
CuCl has an overall charge of 0 so has an oxidation state of 0
Cl has an oxidation state of -1
Copper has an oxidation state of +1
What is the full name of CuCl
Copper (I) Chloride
“When 7 8 and 9 get overruled
Rules 7 8 and 9 get overruled if it conflicts with a rule that came before it
What is the conflict in rules,
Here there is a conflict of Rule
Rule 4 - Group 1 atoms have a +1 charge
Rule 7 - Hydrogen has a +1 charge
If both Na and H has a +1 charge the overall oxidation state = 2 when it should equal 0.
Because Rule 4 is higher then Rule 7 it overall rule 7
Na has a charge of +1
H has a charge of -1
For all metal hydrides
Rule 4 overruled Rule 7 and hydrogen always has a -1 charge
How to remember the oxidation states of the 4 elements (Rule 6 -8) - F, H, O , Cl
Oxidation states correspond to the group number the element is in
How to remember the order of rules 6-8
In hydrogen peroxide:
According to Rule 7, hydrogen has an oxidation state of +1
According to Rule 8, oxygen has an oxidation state of -2
In this case hydrogen has an oxidation state of 1+ (2x 1+ = “2+)
Oxygen has an oxidation state of 1 - (2 x 1- = 2-)
What is the oxidation state of Pb in PbO₂
common misconceptions: naming ions
Sometimes student think that because this molecule (ClO2-) has a charge of -1 Chlorine has an oxidation state of -1 THIS IS NOT THE CASE. -1 represent the overall charge of the molecule and we have to workout the oxidation state of chlorine using the oxidation state rules
How do we name this ion ?
Work out the oxidation states of Cl and O
Molecule has a 1- charge
Rule 8 (oxygen has a oxidation state of -2) overrules rule 9 (chlorine has an oxidation state of -1)
x + (-2 x 4) = -1
X = 7
Deduce the chemical formula of
The molecule has an overall charge of 1-
‘Ate’ means the molecule has oxygen in it
We know oxidation state of Manganate is +7 (VII)
To gte from +7 to -1 we need to -8
The oxidation state of O is -2 (oxidation state rule 8)
_2 x 4 = -8 so we have 4 molecules of oxygen
Write out chemical formula (MnO4 - )
In the exam you can get a question asking to
To do this
Use the oxidation state rules to deduce the oxidation states of each element
Identify if it is a redox reaction - if the oxidation state of at least 1 element has changed

deduce the oxidation states
state whether this reaction is a redox reaction
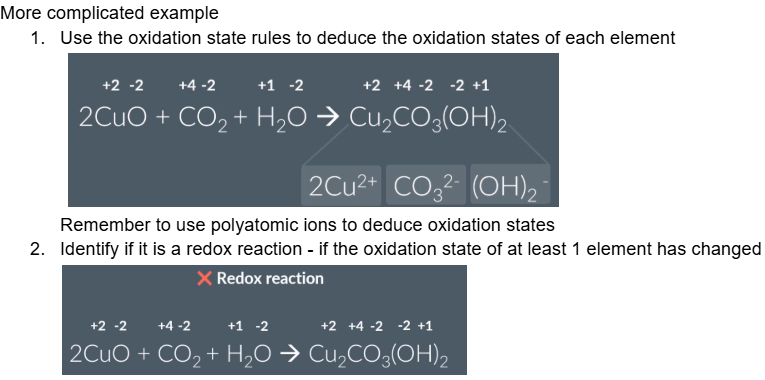
Summary of identifying redox reactions using oxidation states
What is a disproportionation reaction
A reaction in which an element is both oxidised and reduced in the same reaction is called a disproportionation reaction.
For example why is this reaction a disproportionation Reaction
The oxidation state of chlorine changes from 0 to -1 in HCl but to +1 HClO. Therefore the Cl in HCl was reduced and the Cl in HClO was oxidised
Disproportionation reactions are...
Redox reactions because oxidation states change
A balanced equation
Equations must be balanced not only in terms of the number of atoms of each element, but also in terms of the number of electrons. There are 2 methods to doing this (the electron method and the oxidation state method)
What are half equations
Half-equations are equations which include only the oxidising agent (or reducing agent), and the atoms and electrons needed to balance the equation. For example:
Explain the method we use for reactions which take place in an acidified aqueous solution
We use the electron method which involves the following steps:
When do we use the electron method and when can we use the oxidation state method
The electron method is your only choice when not all of the reactants and products are known with certainty.
However, when the exam specifies the reactants and products, and asks you to balance the equation, it is quicker and easier to use a different method, using oxidation states.
What is the oxidation state method
identify the element which is reduced and the element which is oxidised.
work out the change in their oxidation states.
determine the coefficients required for oxidation states to cancel.
Finally, with these coefficients set, balance the atoms in the rest of the equation.
In some cases, you can set the coefficients of the reactants, and then balance the atoms in the products. However, there are some cases where you need to set the coefficients of one of the products first (e.g. if some atoms of sulfur are oxidised, but others aren’t). Once you have a balanced equation, you can use it to write half-equations.
How to write a half equation
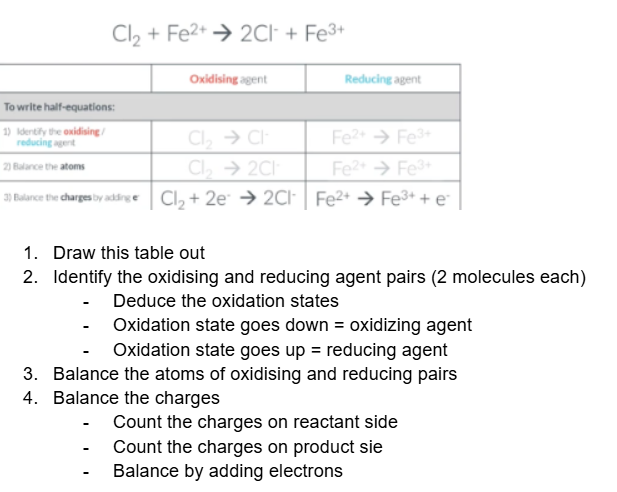
For example:

what do you after completing this table
After completing table the next is to make sure the electron number is the same for both half equation
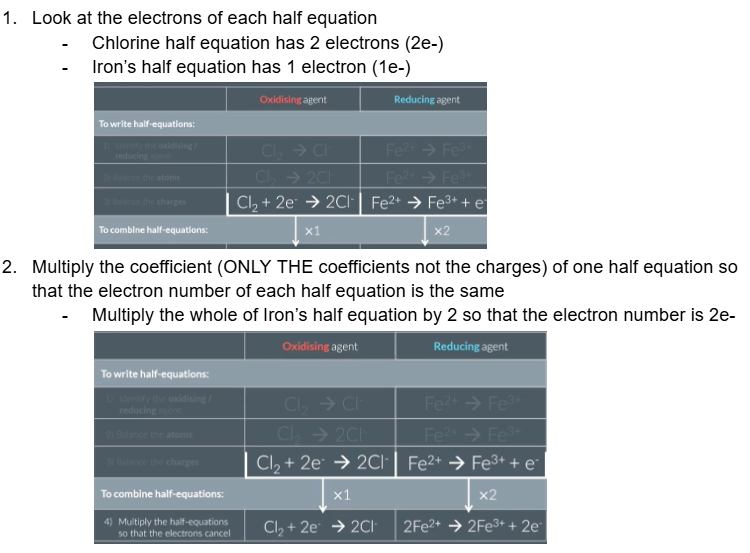
Look at the electrons of each half equation
Multiply the coefficient of one half equation so that the electron number of each half equation is the same
For example:
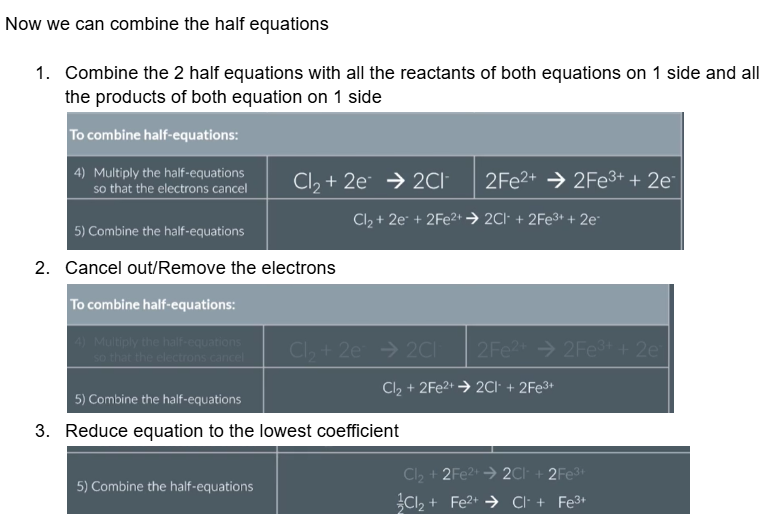
Now we can combine the half equations
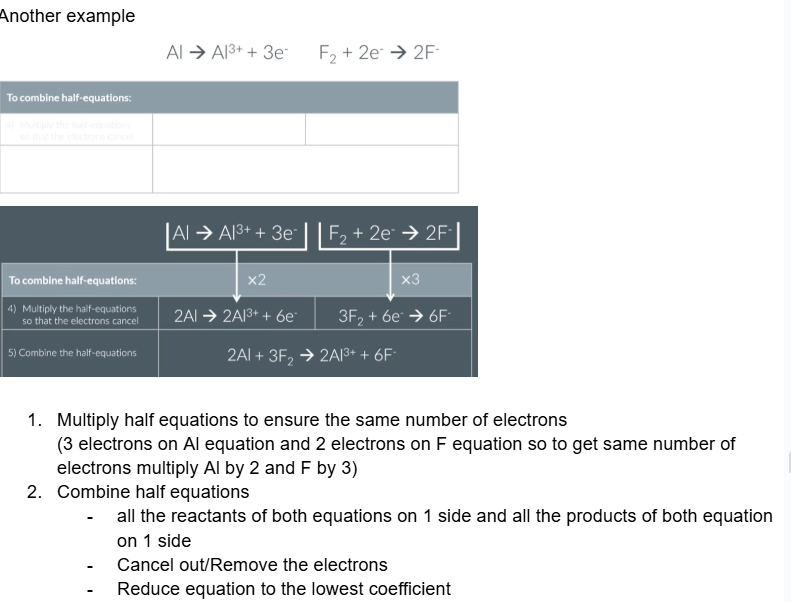
Another example
What are the overall steps for writing a half equation

What should we write when the exam asks for an ionic equation
There is also one important piece of new information: when the exam asks for an ionic equation, it means a net ionic equation. Only give a complete ionic equation if the question specifically asks for one
Molecular Equations
Note that ionic compounds are given an empirical formula, like FeCl2. So in a molecular equation, compounds are represented as if they were molecules, even if, in reality, they would have dissociated into ions.
This molecular equation is a redox equation
Make sure to balance all equations
Ionic Equations
Half Equation
Types of equations summary
When BALANCING ATOMS ( step 2 of writing half equationsO in redox reactions which take place in aqueous, acidified solutions:
For example this reaction takes place in aqueous, acidified solutions.
Summary for writing half equation for reaction that takes place in aqueous, acidified solutions.
Step 6/Last step
Check equation is balanced for both atoms and charges
For example
Step 6/Last step
Check equation is balanced for both atoms and charges
There is 2Mn, 16 H and 18 O on reactant side
There is 2Mn, 16 H and 18O on product side
THe overall charge of the reactant side is 4+
The overall charge of the product side is 4+
When do we use the oxidation method and when do we use the electron method
Note - we can use the electron method for both types of questions but the oxidation state method (an easier method) is only used if the question includes all of the reactant and products
Sometimes an exam will give you an equation and ask you to balance it in these case
Rather then suing the electron method it is easier to work out the changes in oxidation state and adjust the coefficient so that these changes cancel
Balance this equation
For example: Balance this equation
Sometimes an element in a reactant appears in a product with 2 different oxidation states. For example Sulfur appears in the reactant with an oxidation state of (+6). Sulfur appears in the product side as NaHSO4 with an oxidation state of (+6) and as S with an oxidation state of 0. For these cases:
FOr these cases we establish the coefficient of 1 of these products 1st and then work out the coefficient for the other reactants and products