Dental materials: Elastomeric Impression Materials (Polyvinyl Siloxane Vs Polyether)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The key factors for use of impression materials are?
• Accuracy: which is the ability of a material to replicate intraoral surface details.
• Dimensional Stability: the ability of a material to retain its absolute dimensional size over time.
• Tear Resistance: the ability of a material to resist tearing in thin sections (e.g. through the thin-edged material surface within the gingival sulcus).
14 Ideal requirements of impression materials
•Be biocompatible: non toxic and non irritant.
• Have acceptable taste, colour and smell.
• Have adequate shelf life for storage.
• Be easy to manipulate.
• Have suitable working and setting times.
• Be elastic to allow removal from undercuts without permanent deformation.
• Have adequate strength (so they do not tear or break on removal from the mouth).
• Give accurate reproduction of tissue details.
• Be compatible with cast or die materials.
• Adhere to the impression tray.
• Have good flow.
• Possess dimensional stability.
• Be disinfected without any changes to properties.
• Be economic/inexpensive.
Elastomeric impression materials
The term elastomeric means having elastic or rubberlike qualities.
• They are used when an extremely accurate impression is essential.
There are different viscosities/consistencies available for some of the elastomeric impression materials:
• Light-bodied: also referred to as syringe/wash type.
- Used as it can flow into and around the details of the prepared tooth.
- Placed on and immediately around the prepared teeth with the use of a special syringe or extruder guns tips.
• Medium, Heavy and very heavy-bodied (Putty): also referred to as “tray-type” materials and are much thicker.
- They are used to fill the tray. Their stiffness helps force the light-bodied material into close contact with the prepared teeth and surrounding tissues to ensure a more accurate impression of the details of a preparation.
Elastomers for Consideration
Consistency of the elastomeric impression materials- dependent on the amount of filler incorporated into the material.
• Silicones:- Wide range of viscosities available varying from: putty, to a heavy, medium and/or a light bodied material consistency (for addition silicones).
Two components of an elastomer are: base and catalyst. How are they packaged?
Base and Catalyst/Accelerator can be packaged as:
• Paste in a tube /in a syringe • Cartridge • Putty in a jar
Uses of Elastomers of Varying Consistencies
• Light bodied consistency: used in double mix impression technique (single step, two phase) in conjunction with a high filler loaded increased viscosity material (e.g. heavy bodied consistency) in a customized tray.
- Another use is putty/wash technique (single or two step phase impression technique). Here it is used in combination with a highly filled putty in a stock tray.
• Medium bodied consistency: can be used as a single material in a single step impression technique in a customized tray.
- Or it may be used in combination with a light bodied material in a single step two phase technique also in a customized tray.
Describe Elastomers Two-paste systems
–Two tubes: pastes mixed by hand
– Two putties: mixed/kneaded by hand
– Cartridge & Extruder Gun: automix tips used
– Cartridge & Motor-driven Mixer: automix tips used
• Set by base-catalyst chemical reaction
• Warmth and moisture affect setting
• Must use a tray adhesive (especially if tray not perforated)
Methods of mixing
Hand mixing
Static automixing
Dynamic mechanical mixing
Advantages of hand vs machine mixing
Hand Mixing
• No expensive appliances required • Easily stored
Machine Mixing
• Mixing time reduced • Quality of mix consistent • Less material wasted • Cleaner method of mixing
Describe Addition Silicones (8)
• “Polyvinylsiloxanes” – silicone polymer
• Two pastes or two putties
• Hydrophobic by nature: surfactants added to increase wettability
• Very accurate & fast setting (2 min WT, 6 min ST- slight variations)
• No byproducts
• Avoid contact with latex (gloves, rubber dams): inhibit set of polyvinylsiloxanes
• Use non latex gloves
• Low setting shrinkage & very stable
Handling Addition Silicone
• Mix equal amounts of pastes, or automix
• Apply light-body material to tooth through syringe
• Load tray with heavy-body consistency paste
• Set tray over prep site
• Set in 4 – 7 minutes
• Rinse & disinfect
Whats the Composition Addition Silicone
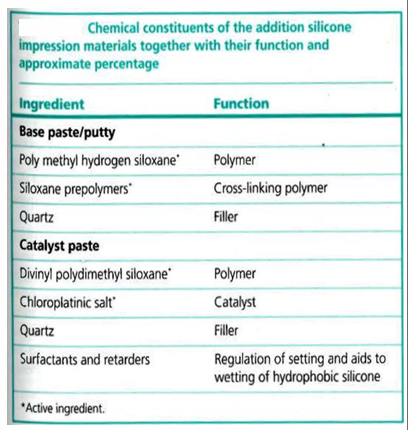
Addition Silicone : Polyvinylsiloxane (PVS) 10 Advantages
• Short setting time • Good tear resistance • Great accuracy & surface detail • No bad taste • Good dimensional accuracy
• Good storage stability • Low permanent deformation
• Wide range of viscosities • Easy to disinfect
• Can be poured after 1 week (multiple pours possible)
Addition Silicone : Polyvinylsiloxane (PVS) 7 Disdvantages
• May have poor wettability (unless surfactant added)
• Two pastes to mix • Low tear strength • Expensive
• Sulfur in latex gloves & rubber dam inhibits polymerization
• Pouring of stone used to be delayed by 1-2 hrs, liberation of H2 gas***
• More rigid than CS & difficult to remove around undercuts
What affects PVS working and setting time?
Increased: Temperature, Humidity, Viscosity
-Mean working time @23°C
Condensation silicone 3,3min
Addition silicone 3,1min
-Mean setting time @ 23°C
Condensation silicone 11min
Addition silicone 8,9min
-Mean working time @37°C
Condensation silicone 2,5min
Addition silicone 1,8min
-Mean setting time @ 37°C
Condensation silicone 8,9min
Addition silicone 5,9min
Disinfection of Elastomeric Impression Materials
Disinfection necessitated. Impressions disinfected by immersion in disinfectant solution from 10 for up to 30 min). Alternatively a disinfectant spray may be used.
The following disinfectants are used:
• Neutral Glutaraldehyde (2% solutions)
• Acidified Glutaraldehyde (2% solutions)
• Phenols
• Iodophor (Iodine solutions 1%)
• Chlorine solutions
Name and define the types of Tray Adhesives
Condensation Silicone: polydimethyl silicone is used. It reacts with the impression material and ethyl silicate to bond physically to the tray. Addition silicone: As above, but Ethyl acetate and naphtha may also be used.
Mechanical Properties To Consider for Condition slicones
• Permanent Set Ideally, when the impression is removed from an undercut, the deformation that results should be totally and immediately recoverable. it is important that the elastomeric materials are removed from the mouth by a sharp tug. PS: CS > AS
• Tear Strength The tear strength of the impression material is also important when an impression is taken of the dentate patient. A tear strength too high may give rise to difficulties in removing the impression from the mouth in cases where the impression material has flowed into the interdental spaces. TS: CS > AS
Mechanical properties (mostly) in favour of Addition silicones
• Stiffness The stiffness of the impression material once it has set can be a major consideration factor (in the case of removal from undercuts). Stiffness: CS < AS
• Dimensional Stability and Accuracy Is affected by the amount of filler present, in that the higher the filler loading, the smaller the shrinkage. The amount of light bodied material used should always be kept to a minimum. DS:AS > CS
• Reproduction of Surface Detail All of the elastomeric impression materials are able to reproduce the details of the surface very accurately when a low-viscosity material is employed. The lower the viscosity, the better the reproduction
Describe Polyethers and their manipulation
• No reaction by-product produced • Shorter working and setting time • Only comes in a single • Stiff material viscosity • Very popular: “Impregum” • No need to pour immediately
Manipulation:
1.Mix equal lengths of paste; or extrude through the automix cartridge tip
2.Load syringe and apply to tooth through tip
3.Load tray and invert over area for impression
4.Allow to set; 4 – 6 minutes
5.Remove from mouth
6.Rinse & disinfect
Polyether Composition
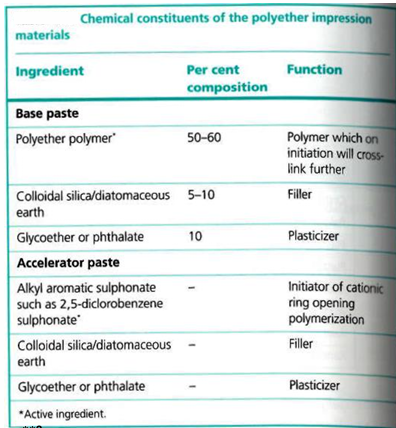
Polyether 7 Advantages
• Short setting time • Single viscosity • Good stability
• Good tear strength • Bad taste • Most difficult to remove from mouth
• Stiff when set • Clean & easy to use
• Good surface detail reproduction
• If kept dry**, will be dimensionally stable for up to 1 week
Polyether 6 Disadvantages
• Bad taste • Most difficult to remove from mouth • Stiff when set
• Clean & easy to use • Good surface detail reproduction
• If kept dry**, will be dimensionally stable for up to 1 week
• Expensive • Storage conditions of impressions is critical
• Cannot be left in disinfectants for long