(M) Lesson 10-Colligative Properties of Solution
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
G.R.E.S.A
A problem-solving method or format used in math and science, particularly in physics, that helps organize information and approach problems systematically. It stands for Given, Required, Equation, Solution, and Answer.
Colligative Properties
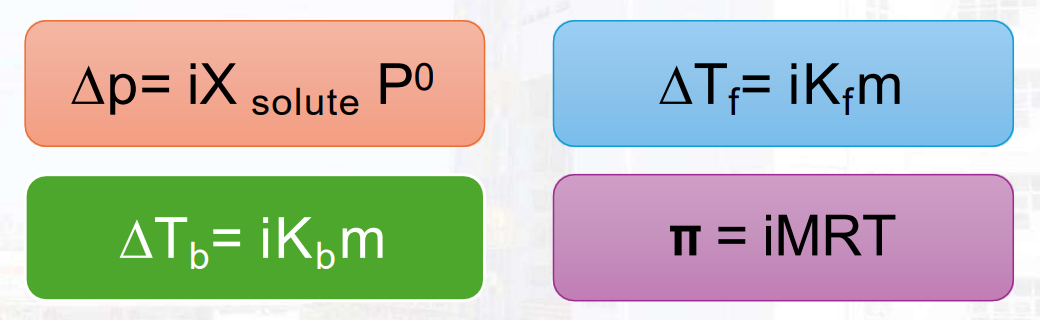
Property that does not depend on the kind of water (like intensive property) but specifically on the amount of solute present in a solution. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Colligative Properties of Solutions
• Comes from the latin word “root” means collection.
• Dependent on the number of atoms and molecules.
• Affected by the AMOUNT of dissolved particles in a solution and NOT the type of particles.
• Heating to a higher temperature is necessary to bring the solvent to a boiling point when you have to undergone both solutes and atmospheric pressure.
Boiling Point Elevation
The raising of the normal boiling point of a liquid by adding a non-volatile substance to it.

Freezing Point Depression
The decrease in the freezing point of the solvent due to the addition of solute to form solution.

Vapor Pressure Lowering
• Is the pressure of a vapor in contact with its liquid or solid form.
• The relationship between the vapor pressure of the solution and the vapor pressure of the solvent depends on the concentration of the solute in the solution. This relation is based on Raoult’s Law name after the French chemist Francois Marie Raoult.
Raoult’s Law
A relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist Francois Marie Raoult in 1887. It states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of liquids is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture.

Osmosis Pressure
Is the pressure that must be applied to pure solvent to prevent the solvent from passing into a given solution by the process of osmosis.

Electrolyte
A substance that forms ions when dissolved in water.
Non Electrolyte
A substance whose aqueous solutions do not contain ion.
Colligative Properties Of Electrolyte Solutions
Physical properties of solutions that depend on the concentration of solute particles, but not on their chemical identity.