Chapter 5 Cell membrane and transportation
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Plasma membrane
The selectively permeable barrier that encloses a cell and regulates the transportation of nutrients, water and waste.
Polar amino acids
Located in interior region of protein or
extend into extracellular fluid & into cytosol, (cytoplasm) They’re also found on the on the surface if the proteins interacting with the aqueous environment.
Non polar amino acids
They’re within the membrane. Specifically located on the proteins surface and interacts with fatty acids in interior membrane. They also anchors protein into membrane
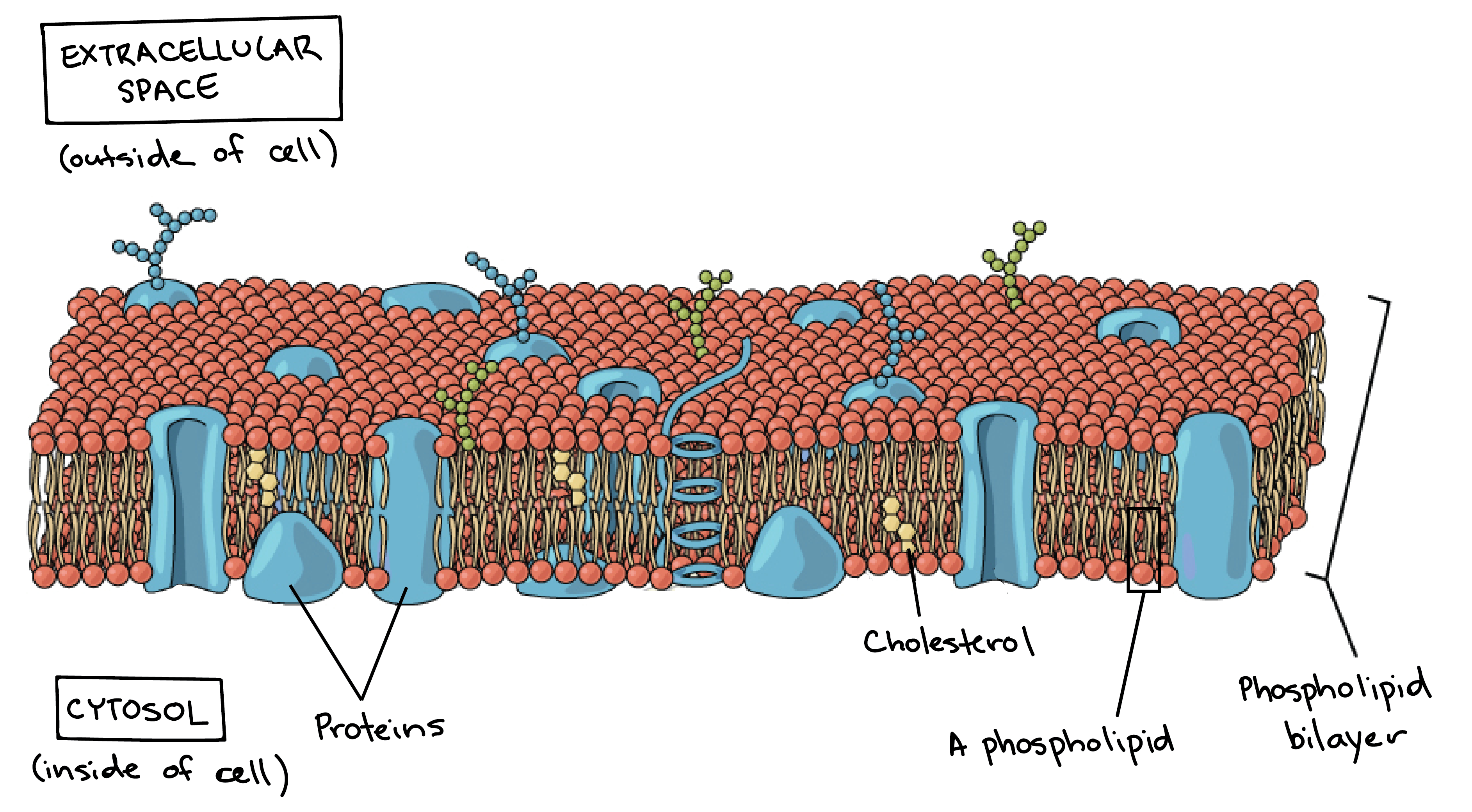
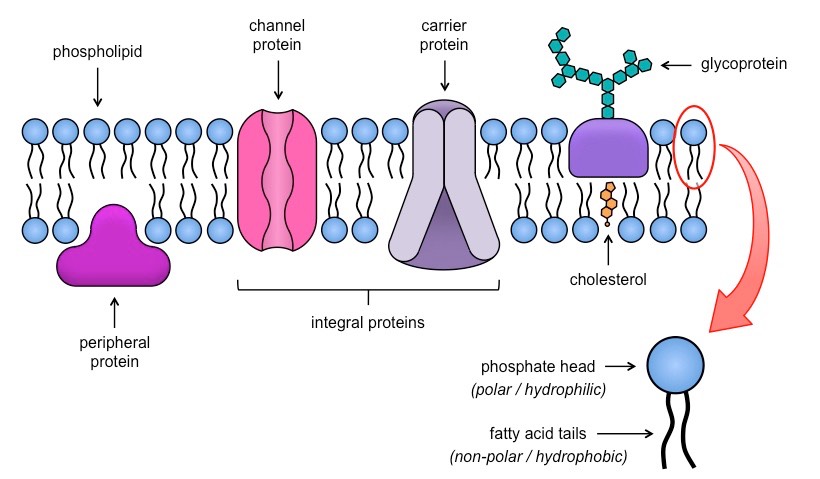
Fluid mosaic structure
The plasma membrane is made up of phospholipid molecules that are embedded with proteins, steroids, glycoproteins and glycolipids that can flow around the surface of the cell.
FMS and the bilayer arrangement results in the membranes semi-permeability. The hydrophobic interior allow some substances to cross easier than others.
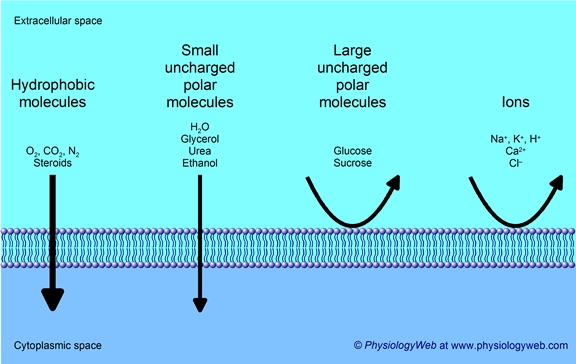
Easy passage
Gasses, small non-polar molecules and small uncharged polar molecules, like water, can pass through the membrane easily.
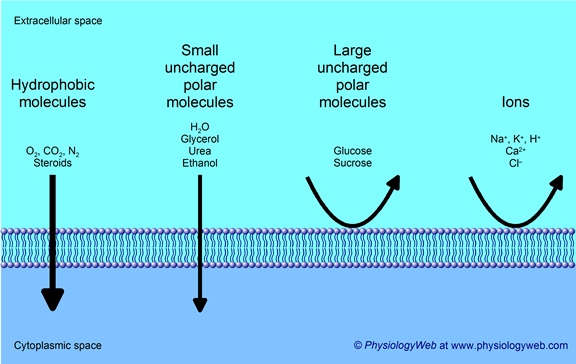
Difficult passage
Large polar molecules, like glucose, and ions cannot pass through the membrane easily. They require embedded channels and transport proteins.
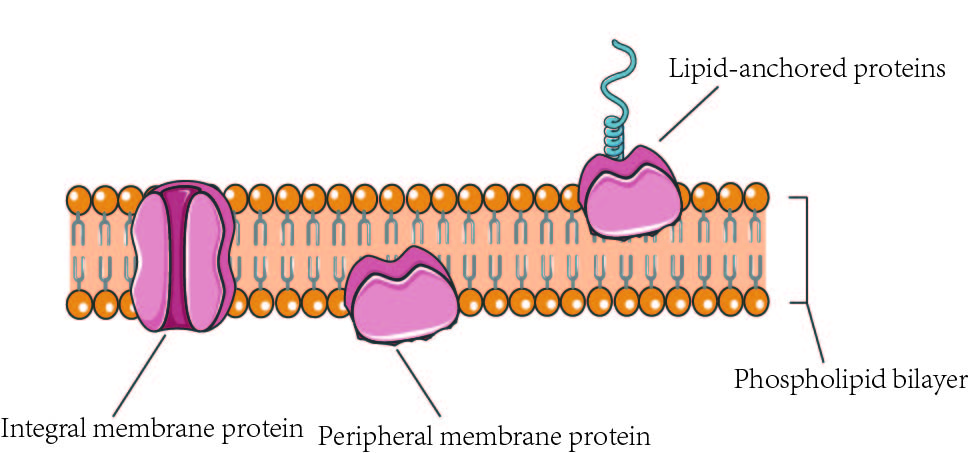
Integral proteins
Located through the bi-layer, from the outside of the cell to the inside. They function in the transport of molecules and, maintaining the structure.
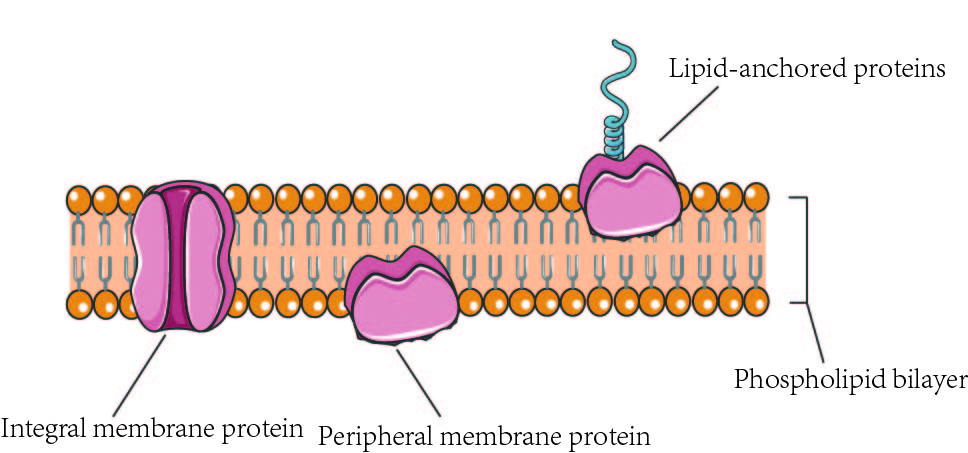
Peripheral Proteins
They’re loosely bounded to one side of the membrane. Serving as sites for attachment of the cytoskeleton on the inside of the cell and the attachment of the ECM.
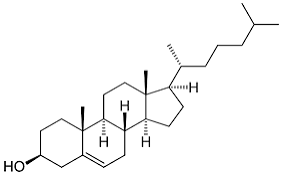
Cholesterol
Helps keep the cell membrane flexible, and the cell membrane of plants from freezing. They also reduce fluidity at moderate templates and hinders solidification at low temperatures.
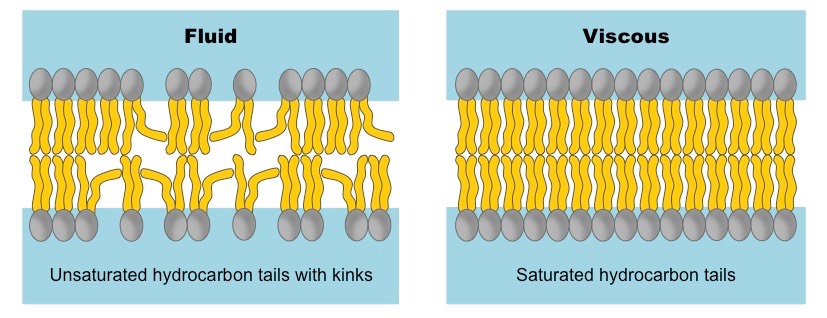
Fluidity
Allows the membrane to change their shape and movement based off the environment and temperature. The tails are unsaturated and not packed tightly.
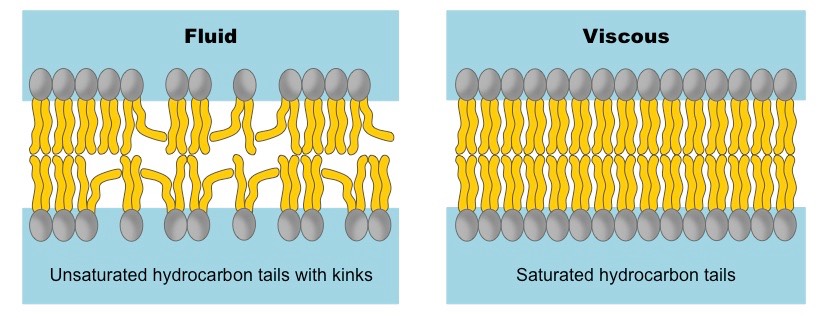
Viscous
A cell membrane resisted to flow. They’re saturated and tightly packed. High cholesterol levels increases the viscosity of a cell membrane.
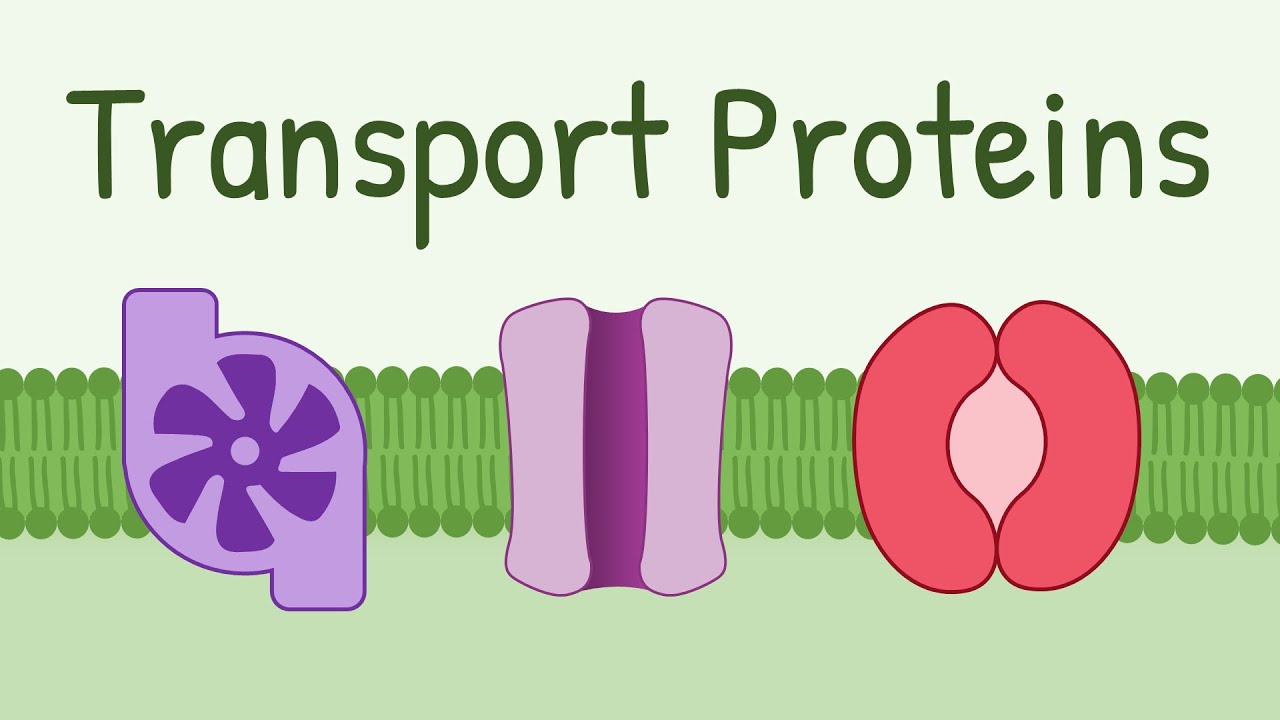
Transport protein (Channel proteins)
Function by having hydrophobic channels that haves enzymes that help move food and water. Some use ATP.
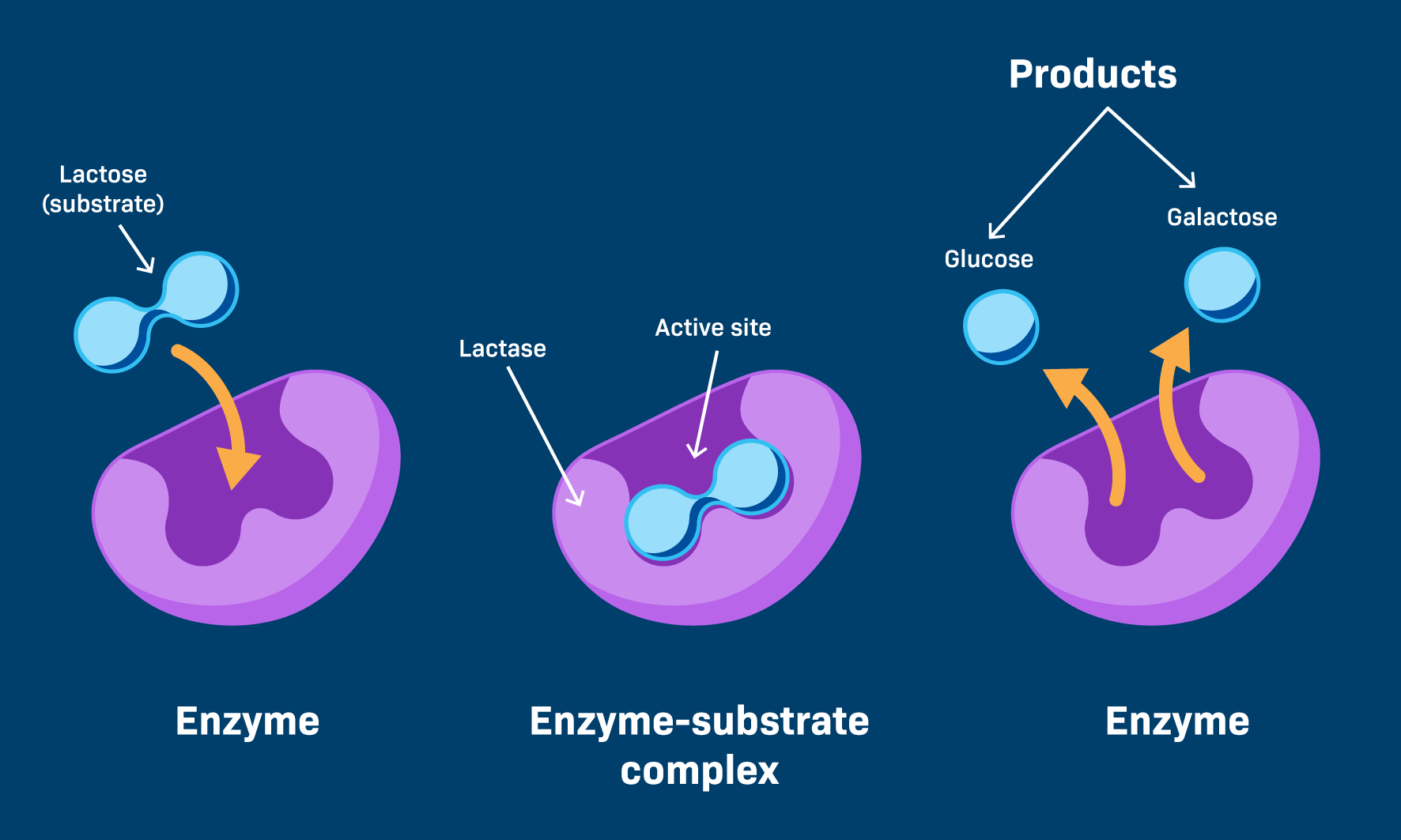
Enzymatic protein
Control metabolic processes by functioning at catalysts. It uses a active site.
Attachment proteins
Attachment points for the cytoskeleton and ECM. Stabilizing internal organelles and the cell.
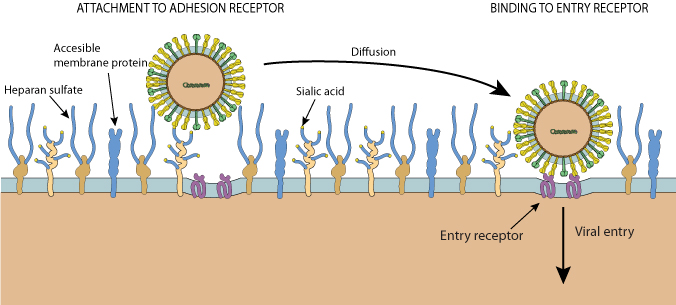
Cell to cell recognition
Function is communication and recognition using carbohydrates, glycoproteins and glycolipids. Its useful in the immune system.
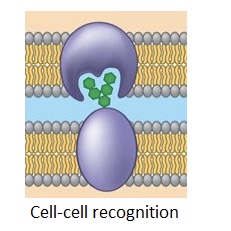
Intercellular Joining
Stitching cells together to make tissues. Its used in various types of junctions.
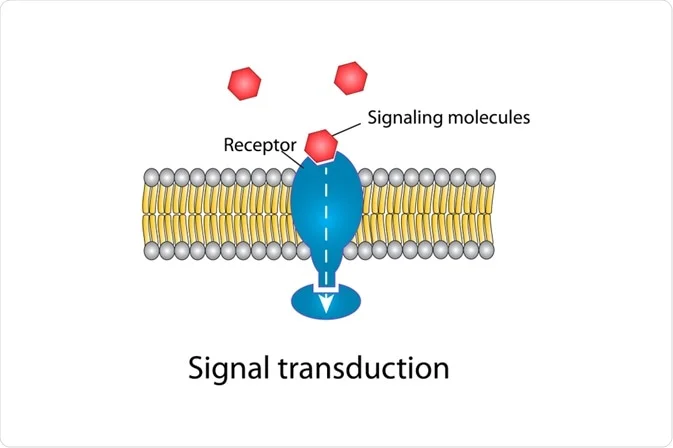
Signal Receptors
Catching hormones or other materials, circulating in the blood. It uses a receptor site.
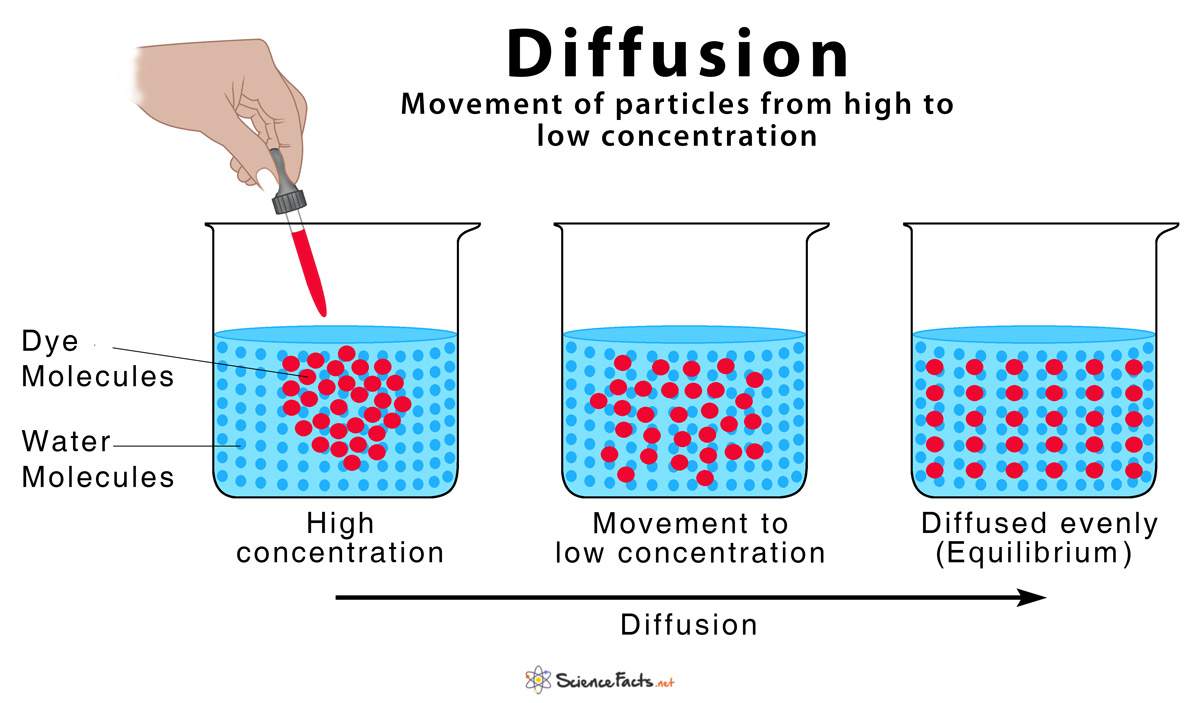
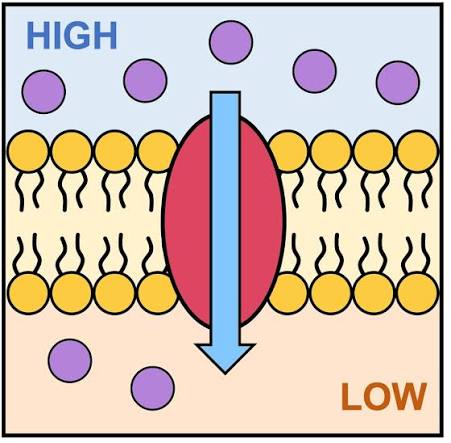
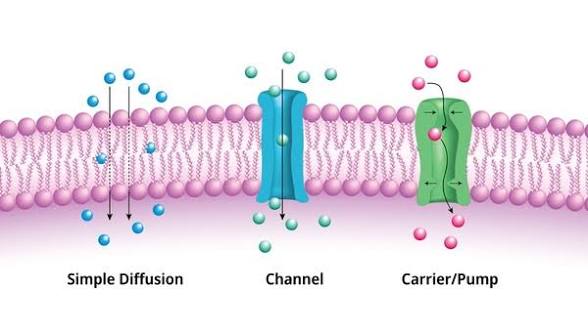
Diffusion
The movement of particles from areas of high concentrations to low concentrations. The goal is equilibrium.
Passive transport
Movement from high to low concentration without the use of ATP. It plays a primary role in the import and export of materials and waste.
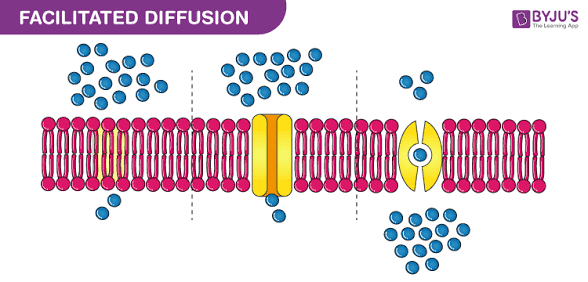
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion with the help of transport proteins, without energy.
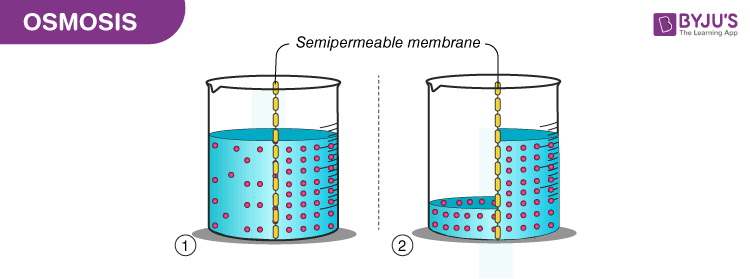
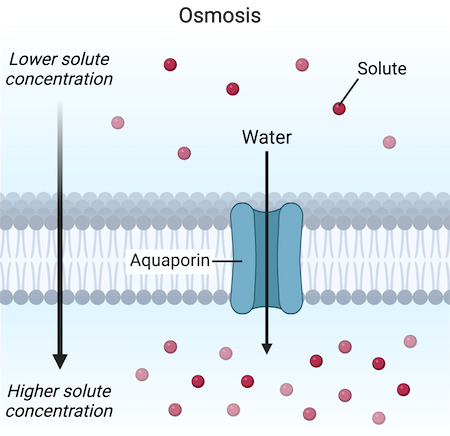
Osmosis
The transportation of large quantities of water with the use of a Aquaporin.
Aquaporin
Specific channels that allow large quantities of water to pass through the membrane.
Carrier proteins
Alternates between 2 shapes, moving a solute across the membrane in both directions.
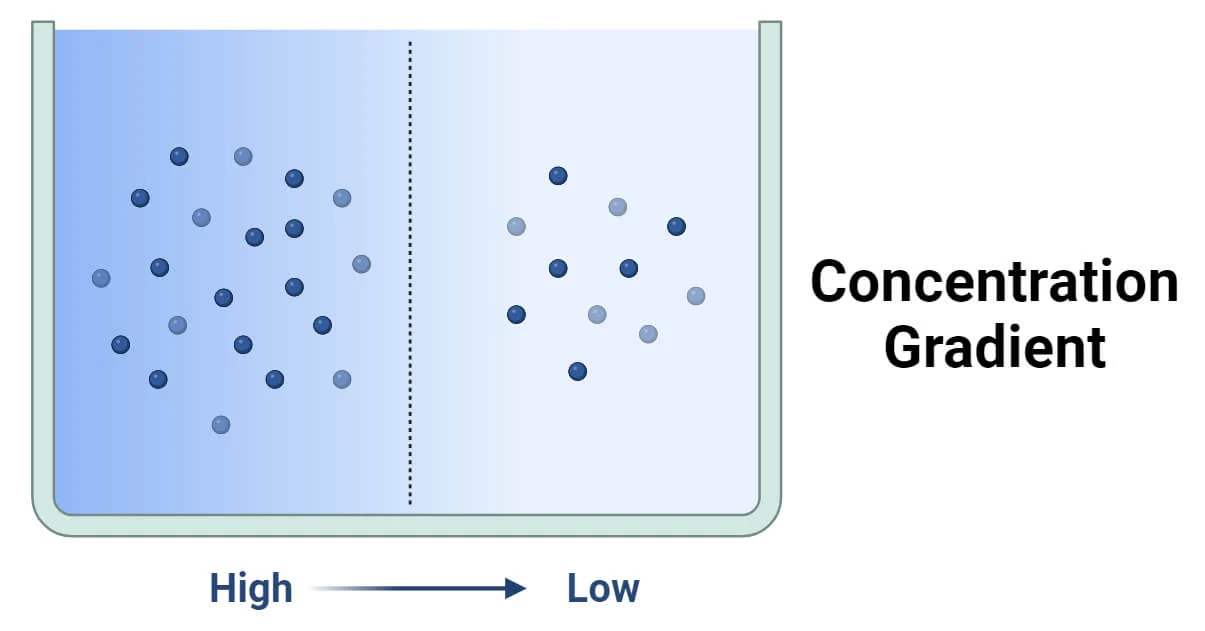
Concentration Gradient
Potential energy drives diffusion from low to high concentrations.
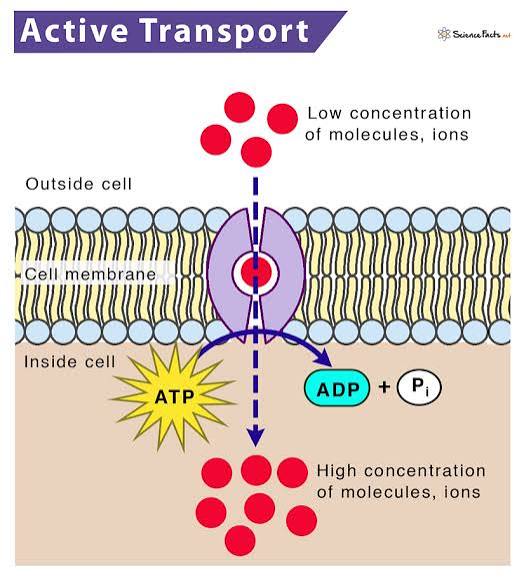
Active Transport
Molecular movement from low to high concentrations that require energy and uses a proton pomp. It helps transport charged and large polar molecules.
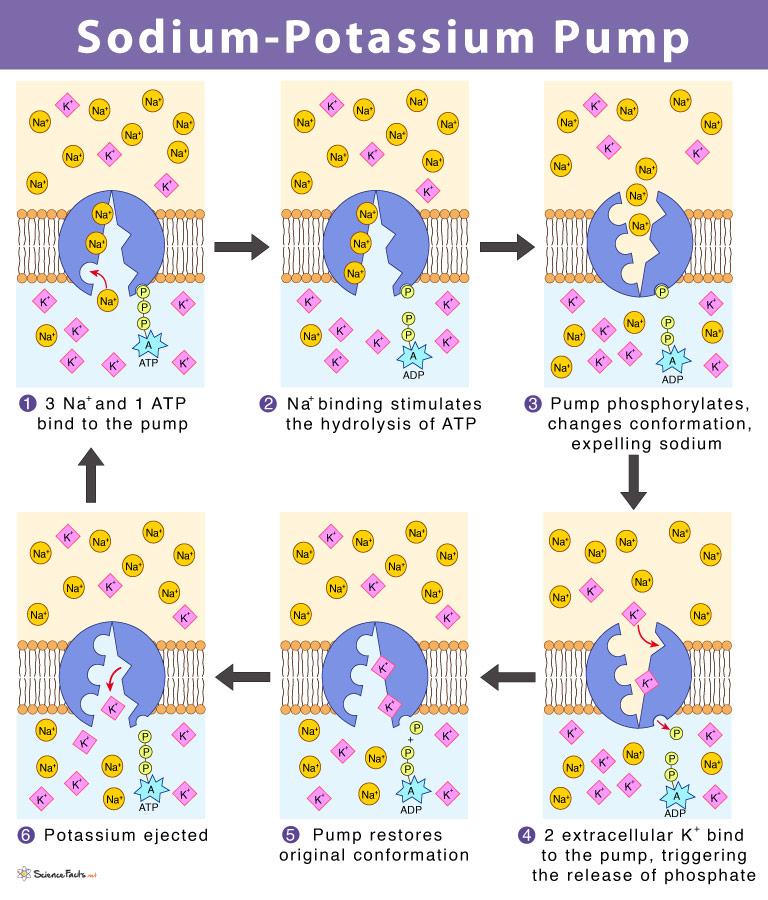
Sodium Potassium pump
The pumping of 3 Sodium ions out the cell to insert 2 potassium ions into the cells. It requires energy from ATP by phosphorylation (attaching a phosphate ion to a structure to make it work) activating the protein to grab and move molecules.
Membrane Potential
The voltage difference across a cell's plasma membrane, created by the unequal distribution of ions inside and outside the cell. Membranes may be polarized by the movement of ions across the membrane.
It gives the cell the ability to do work involving the transport of molecules.
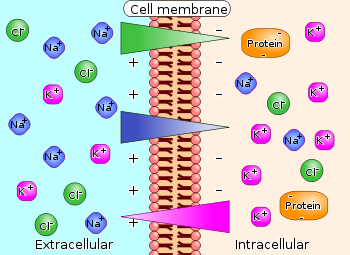
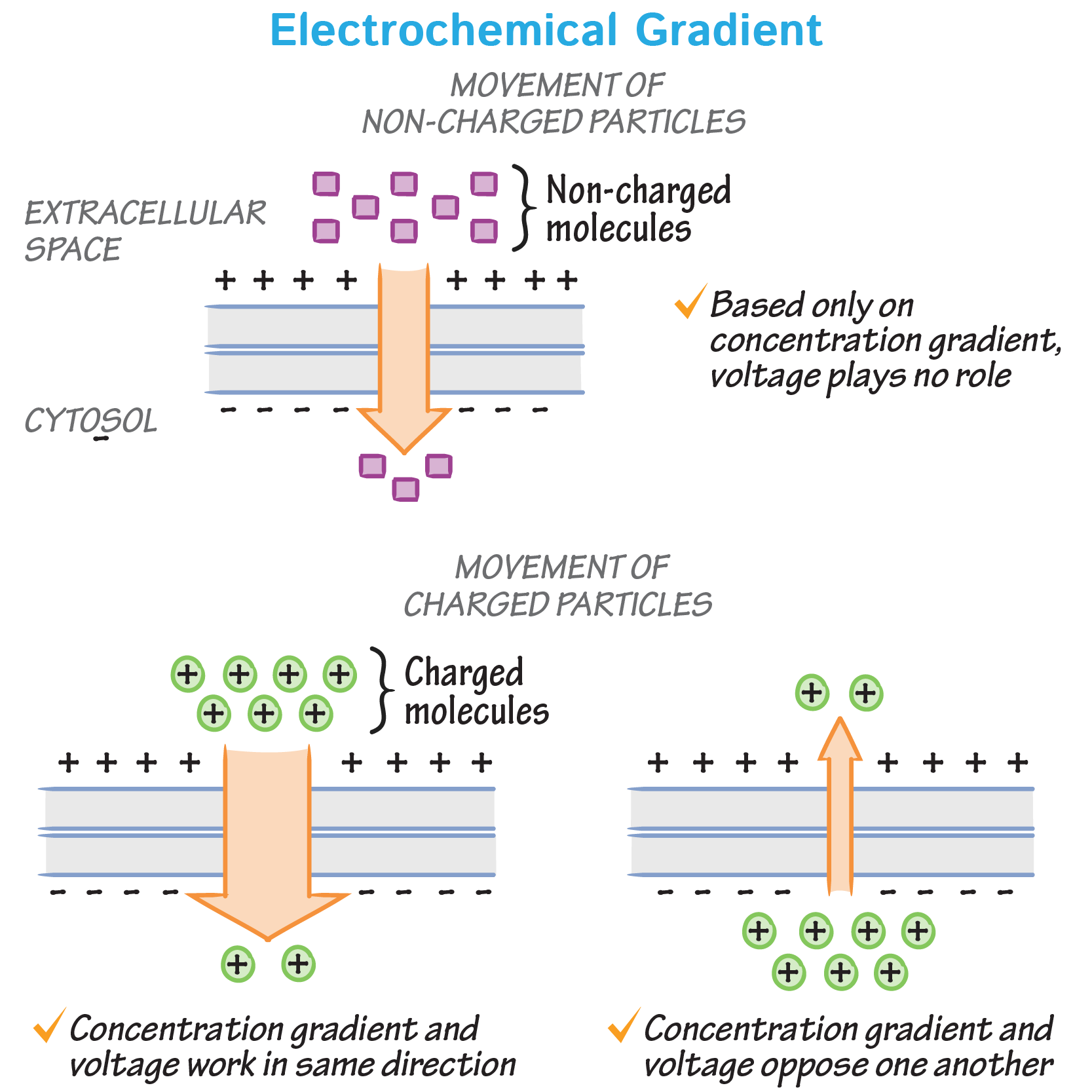
Voltage gradient
Voltage gradient (difference in charge across the membranes) that works on positive and negative ions.
The inside of the cell in negative and the outside is positive.
For charged ions a Voltage gradient is created so there’s potential to perform work. Forces in electrochemical gradients drive the diffusion of ions.
Electrogenic Pump
A protein that moves ions across a cell membrane, generating an electrical potential difference (voltage) across it. Its involved in the processes of the electron transportation chain of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
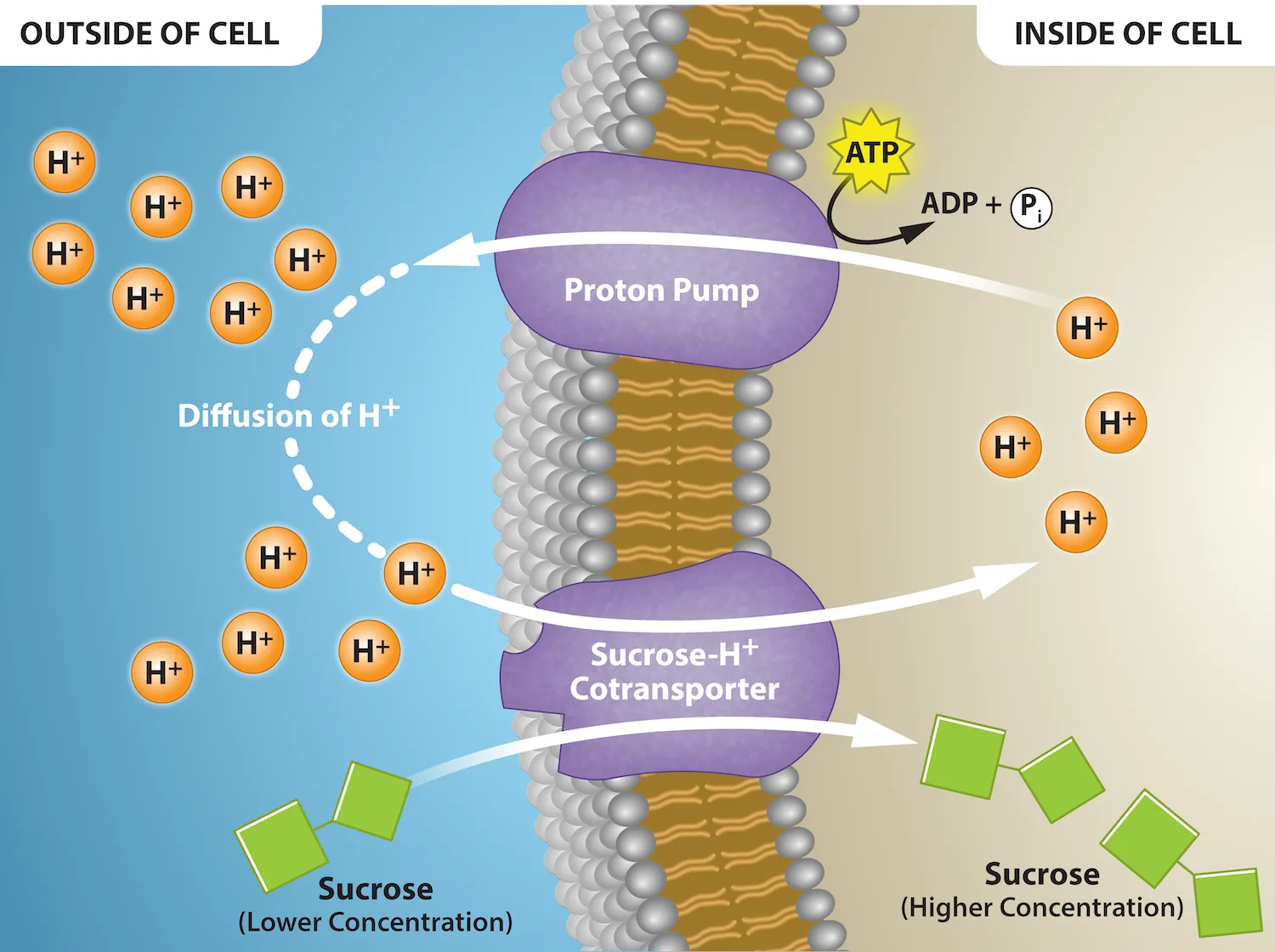
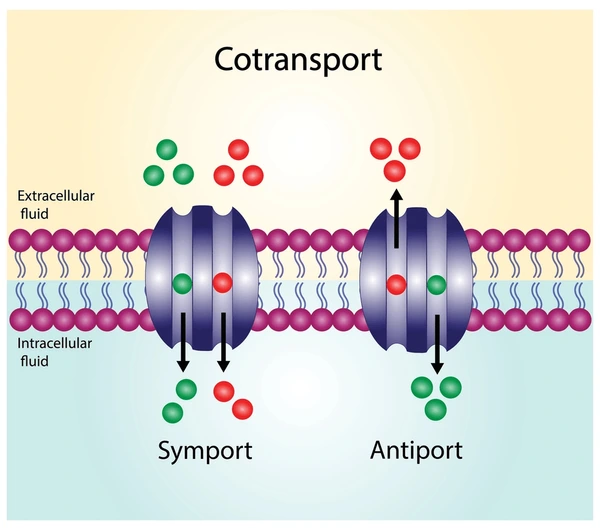
Co- transport
Active transport driven by a concentration gradient. Two substances move across a cell membrane together using a single protein carrier
Protons (H+) act as a party invitation.
Very important in helping plant and animal cells be able to take up glucose and sucrose via active transport.
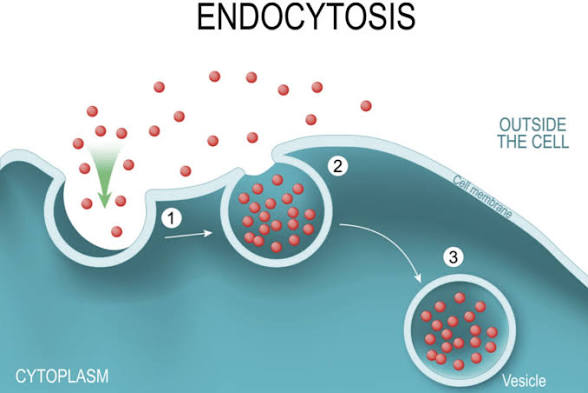
Endocytosis
Moving materials into a cell
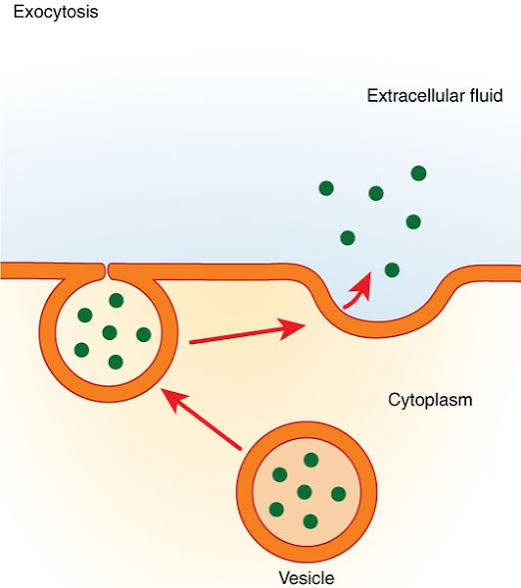
Exocytosis
Moving materials out of a cell
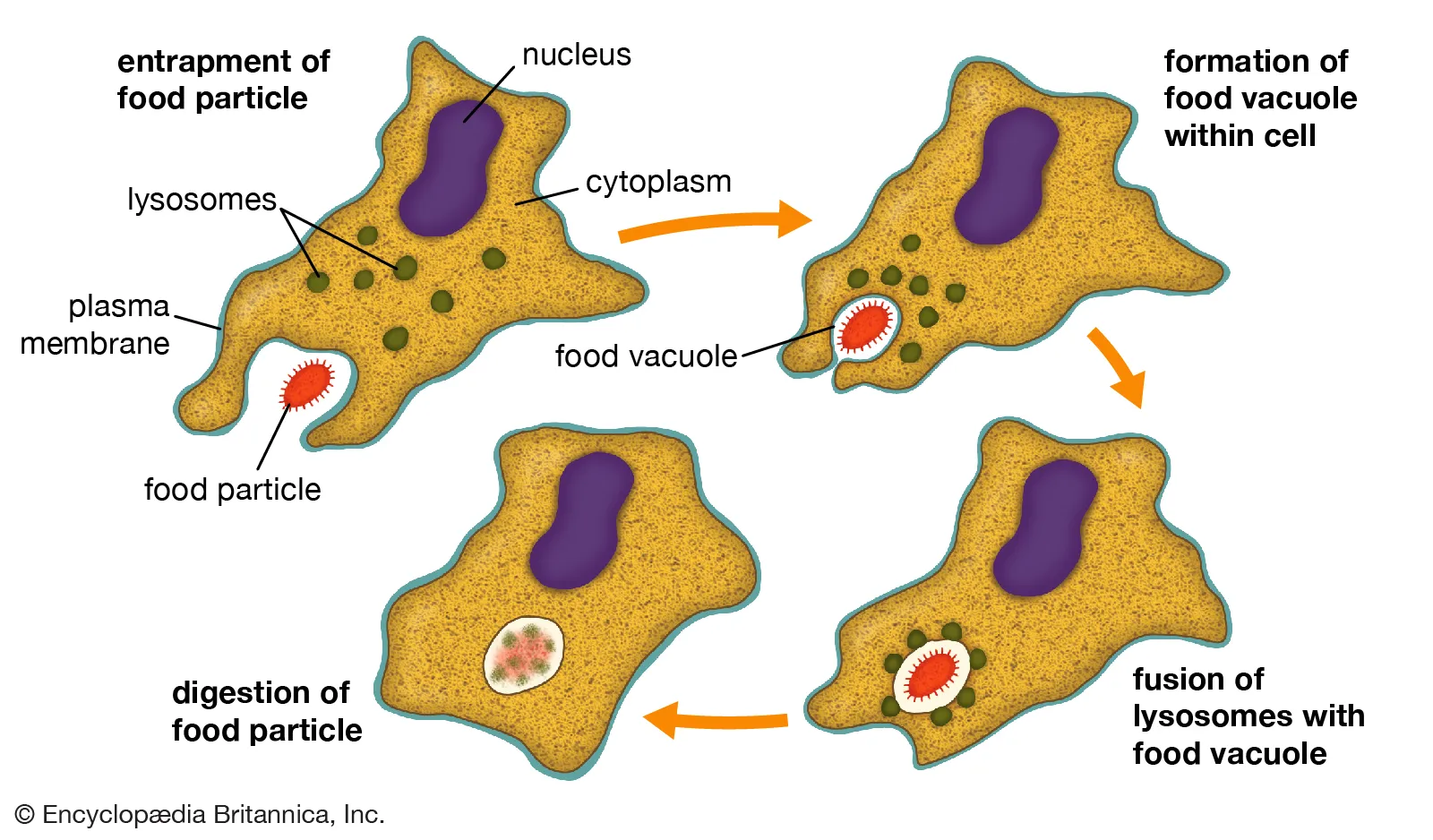
Phagocytosis
The ingestion of materials. The food vacuole will be digested after fussed with lysosomes.
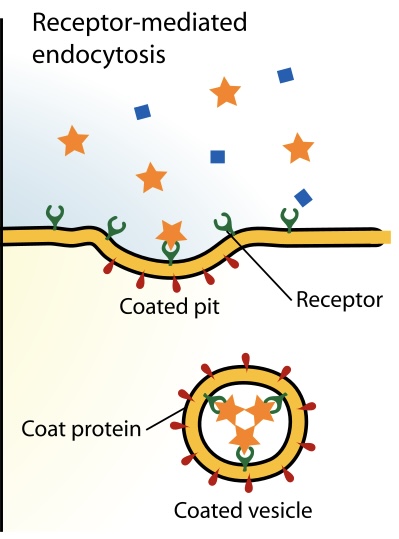
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
A cellular process for selectively taking up specific molecules from outside the cell. It involves the binding of a ligand (the molecule) to a specific receptor on the cell's surface, which triggers the binding of the plasma membrane to form a vesicle containing the ligand and its receptor
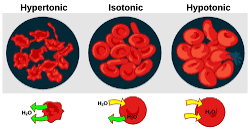
Hypotonic
Less solute and more water in the cell. It usually bursts and its lysed.
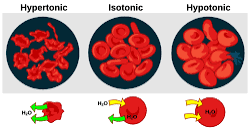
Hypertonic
More solute, less water in a cell. Its typically shriveled.
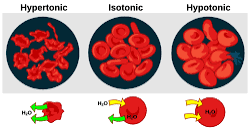
Isotonic
Equal Solute and water
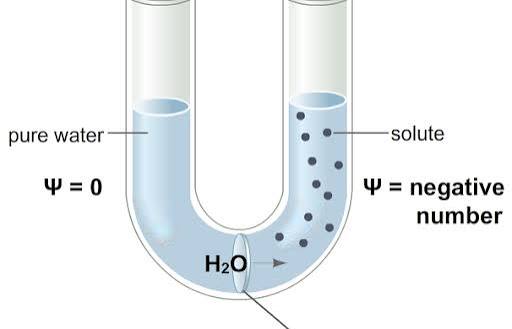
Water potential
Predicts the direction in which water will floor including factors like solute concentration and physical pressure.
Toncity
The ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water based on the concentration of the solutes outside the cell compared to the inside.
Pancrine
A type of local signaling, Cell-to cell contact here local messages travel; short distances to the target cell.
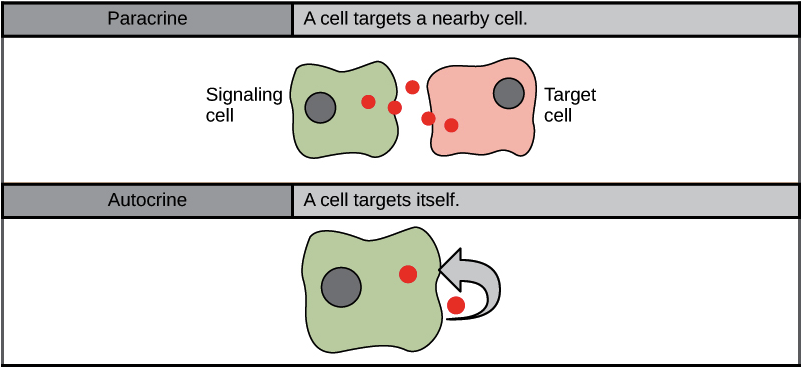
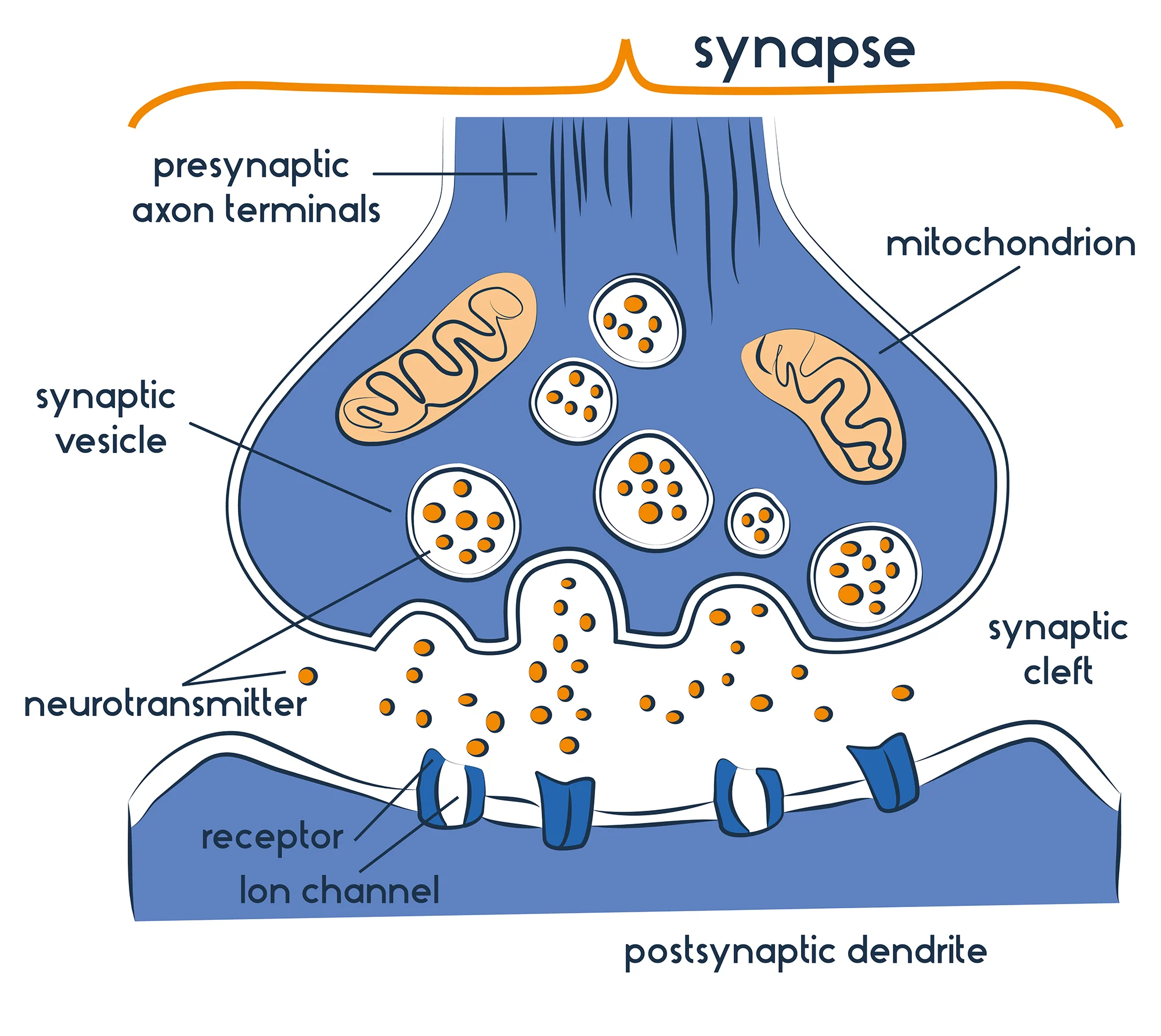
Synaptic
Electric signals travels through a nerve cell to trigger neurotransmitter secretion.
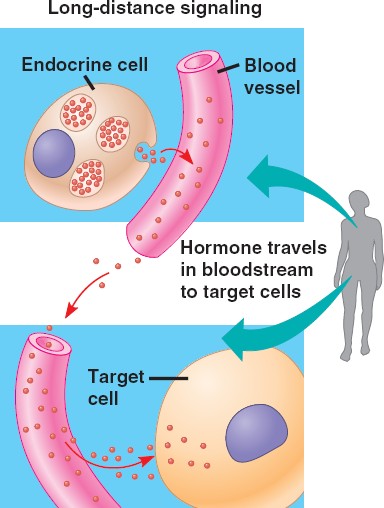
Long distance
A type of hormonal signaling where hormones travel via the circulatory system to reach the target cell.
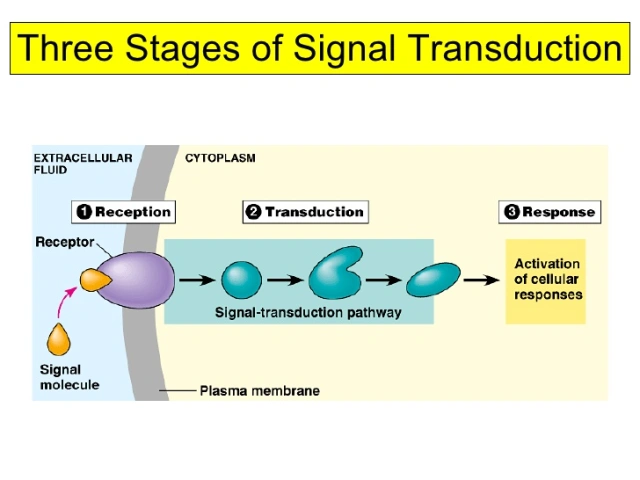
Cell communication
Reception- Ligand attaches to a receptor protein changing the shape and initiating transduction.
Transduction- The signal travels through cells, and is converted into another signal.
Response- The cell responds to the signal.