New innovations lectrue 4
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
concept development and testing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Fuzzy Front End
⚫ NPD strategy
⚫ Idea generation
⚫ Idea selection
⚫ Concept development
because the product concept is still fuzzy. By the end of the project, most of the fuzz should be removed.
Stages of Concept/Project Evaluation
⚫ Screening (pretechnical evaluation)
⚫ Concept testing
⚫ Full screen
⚫ Project evaluation (begin preparing product
protocol)
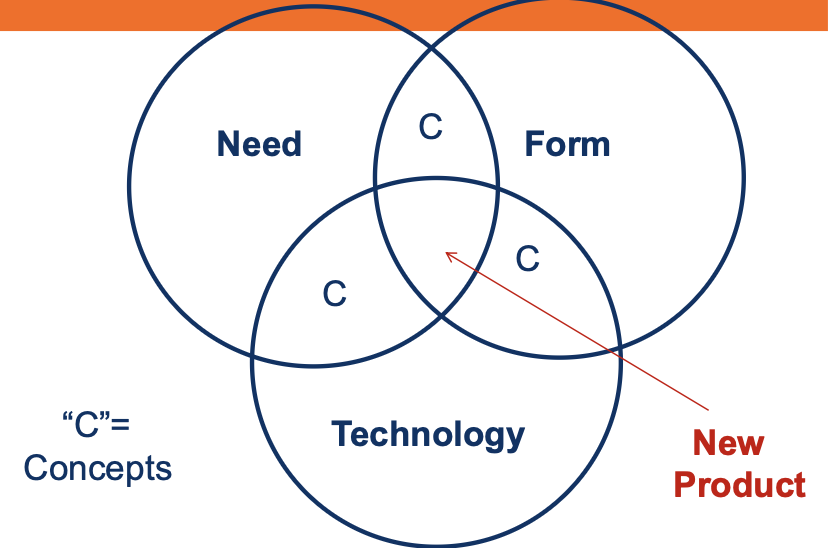
Required Inputs to the Creation Process
⚫ Form (the physical thing created, or, for a service, the set of steps by which the service will be created)
⚫ Technology (the source by which the form is to be attained)
⚫ Benefit/Need (benefit to the customer for which the customer sees a need or desire)
⚫ Technology permits us to develop a form that
provides the benefit!
Some Patterns in Concept Generation
⚫ Customer need → firm develops technology →
produces form
⚫ Firm develops technology → finds match to
need in a customer segment → produces form
⚫ Firm envisions form develops → technology to
product form → tests with customer to see
what benefits are delivered
⚫ Note: the innovation process can start with any
of the three inputs!
New Product Concepts & the New Product
What is a Product Concept?
⚫ A product concept is a verbal or prototype
statement of what is going to be changed and
how the customer stands to gain or lose.
⚫ Rule: You need at least two of the three inputs
to have a feasible new product concept, and all
three to have a new product.
What a Concept Is and Is Not
lanning & Development, ’11
YES “Learning needs of computer users can be met
by using online systems to let them see training
videos on the leading software packages.” (good
concept; need and technology clear)
NO “A new way to solve the in-home
training/educational needs of PC users.” (need
only; actually more like a wish)
NO “Let’s develop a new line of instructional videos.”
(technology only, lacking market need and form)
Best Sources of Ready-Made New Product Concepts
⚫ New Products Employees
– Technical: R&D, engineering, design
– Marketing and manufacturing
⚫ End Users
– Lead Users
⚫ Resellers, Suppliers, Vendors
⚫ Competitors
⚫ The Invention Industry (investors, etc.)
⚫ Miscellaneous (continued)
Best Sources of Ready-Made New Product Concepts (continued)
⚫ Miscellaneous Categories
– Consultants
– Advertising agencies
– Marketing research firms
– Retired product specialists
– Industrial designers
– Other manufacturers
– Universities
– Research
laboratories
– Governments
– Printed sources
– International
– Internet
Examples of common product
concept elements that works
⚫ Convenience: Products that save customers time and make things easier.
⚫ Usability: User interfaces that are pleasing and productive to use.
⚫ Quality: The non-functional qualities of a product such as durability and reliability.
⚫ Functionality & Performance: Products that solve customer problems such as efficient solar panels or fast bicycles.
⚫ Price: A price-based concept such as "affordable luxury."
⚫ Lifestyle: A product for a lifestyle such as a car designed for people who enjoy outdoor activities such as fishing or snowboarding.
⚫ Status: Products that are designed to communicate wealth or another type of status such as conspicuous conservation.
⚫ Culture: A product that exemplifies culture, subculture or super-culture. For example, wine with a well known terroir.
⚫ Risk: Products that reduce a risk such as healthy food or a safe vehicle.
⚫ Values: Products that conform to the customer's values in
areas such as environmental stewardship, animal welfare and fairness to people.
⚫ Experience: The end-to-end customer experience such as the experience of buying, unpackaging, viewing, touching and tasting a macaron.
⚫ Quality of Life: A product that frees a customer from something they find unpleasant. For example, a mobile device with few features for customers who value simplicity.
The Life-Cycle of a Concept
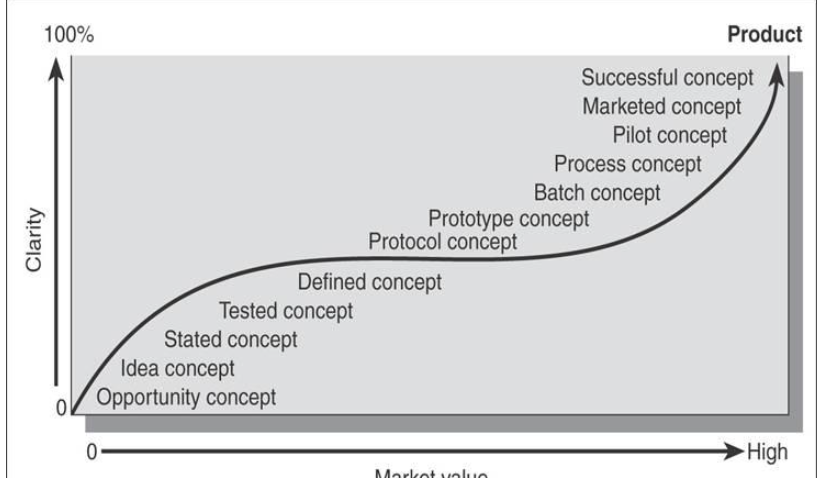
How to assess & evaluate a concept?
?
Analytical Attribute Techniques
⚫ Basic idea: products are made up of attributes -a future product change must involve one or
more of these attributes.
⚫ Three types of attributes: features, functions,
benefits.
⚫ Theoretical sequence: feature permits a
function which provides a benefit.
Examples of Features
⚫ Dimensions
⚫ Source ingredients
⚫ Services
⚫ Esthetic characteristics
⚫ Performance
⚫ Trademarks
⚫ Components
⚫ Materials
Feaute and benefit examples
⚫ Functions
– How the product is actually working
⚫ Benefits (can be many things)
– Uses
– Saving (time, effort)
– Sensory enyoyments
– Nonmaterial well-being
– Economic gain
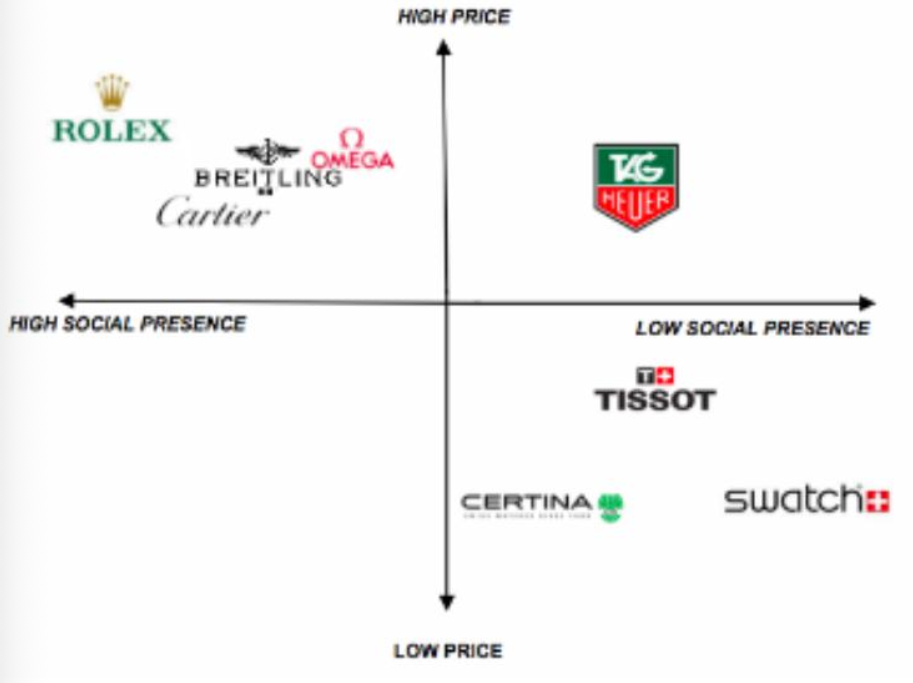
Gap Analysis
⚫ Determinant gap map (produced from
managerial input/judgment on products)
⚫ Attribute rating (AR) perceptual gap map
(based on attribute ratings by customers)
⚫ Overall similarity (OS) perceptual map (based
on overall similarities ratings by customers)
Determinant gap map (produced from
managerial input/judgment on products)
Determinant gap map (produced from
managerial input/judgment on products)
Attribute rating (AR) perceptual gap map
(based on attribute ratings by customers)
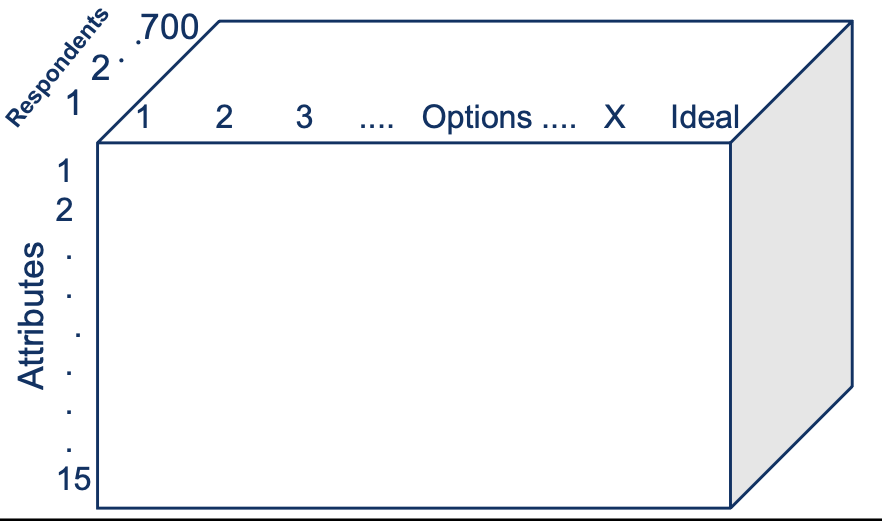
Data Reduction Using Multivariate
Analysis
⚫ Factor Analysis
– Reduces the original number of attributes to a smaller number of factors, each containing a set of attributes that “hang together”
⚫ Cluster Analysis
– Reduces the original number of respondents to a
smaller number of clusters based on their benefits
sought, as revealed by their “ideal brand”
Overall similarity (OS) perceptual map (based
on overall similarities ratings by customers)
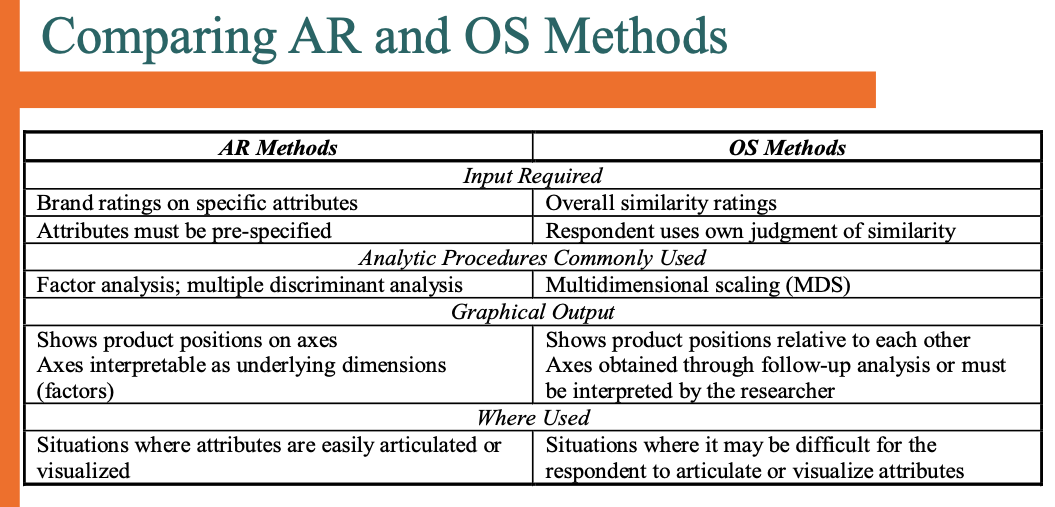
Failures of Gap Analysis
⚫ Input comes from questions on how brands differ (nuances ignored)
⚫ Brands considered as sets of attributes;
totalities, interrelationships overlooked; also
creations requiring a conceptual leap
⚫ Analysis and mapping may be history by the time data are gathered and analyzed
⚫ Acceptance of findings by persons turned off by
mathematical calculations
Trade-Off (Conjoint) Analysis
⚫ Put the determinant attributes together in
combinations or sets.
⚫ Respondents rank these sets in order of
preference.
⚫ Conjoint analysis finds the optimal levels of
each attribute.
What is Conjoint used for?
⚫ Deciding which features a new product should have
⚫ Deciding what price to charge
⚫ Understanding market segments
⚫ Forcasting sales
Practical considerations
⚫ Total level of all attributes should not exceed 20
⚫ Total profiles asked should not exceed 20 (often
between 10-20)
⚫ A sample size of 200-250 is generally sufficient
for consumer products or services
⚫ There should be no correlation between any two
attributes!
Assumptions & limitations
⚫ Assumes perfect information
– Customers well educated on all products…
⚫ Assumes perfect distribution
– All products always available…
⚫ Simplifies the market
– Not all options included…
⚫ Forces all brands to have the same features & prices
Some Qualitative Attribute Analysis
Techniques
⚫ Checklists
⚫ Relationships Analysis
⚫ + many others...
Why is design so important?
⚫ For companies:
– A mean to create a real brand identity
– Support their corporate identity (visual equity)
– Through design they can create brand name
awareness = a tool for differentiation
⚫ For consumers:
– Today, you do not only buy a product
because it is useful but also to express something through this product
– Identify brands they like (fit their Image)
==> Brands try to keep the same
design spirit/style.
Major elements in the Design mix
⚫ Performance
– Function
– Market research
⚫ Quality
– Material
– Workmanship
– Not optimal but
affordable Q for
the target market
⚫ Durability
– Function of P & Q, but also
visual durability
⚫ Appearance
– Pleasing Style/form
– “Form follows function”
⚫ Cost
– Work within budget
A split in Design Society
⚫ Functionalists
– Working towards putting good functional performance, quality and durability into the design.
– Normally responsive to marketing research and
technical research.
A split in Design… cont.
⚫ Stylists
– Working towards putting good outer form into the design.
– Working out of inspiration and tend to pay less
attention to cost.
– Normally resist a marketing orientation
I.e., Two approaches to design
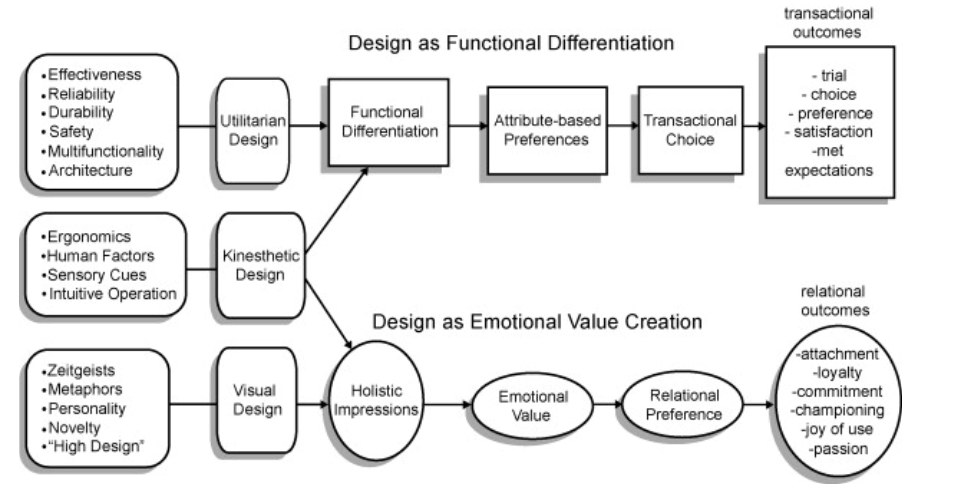
The Product development process w designer
