TV4101 - SAM - Haemostasis 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Primary Haemostasis involves?
When does it occur?
1st haemostasis when BV is damaged but clot is unstable and can be easily washed away


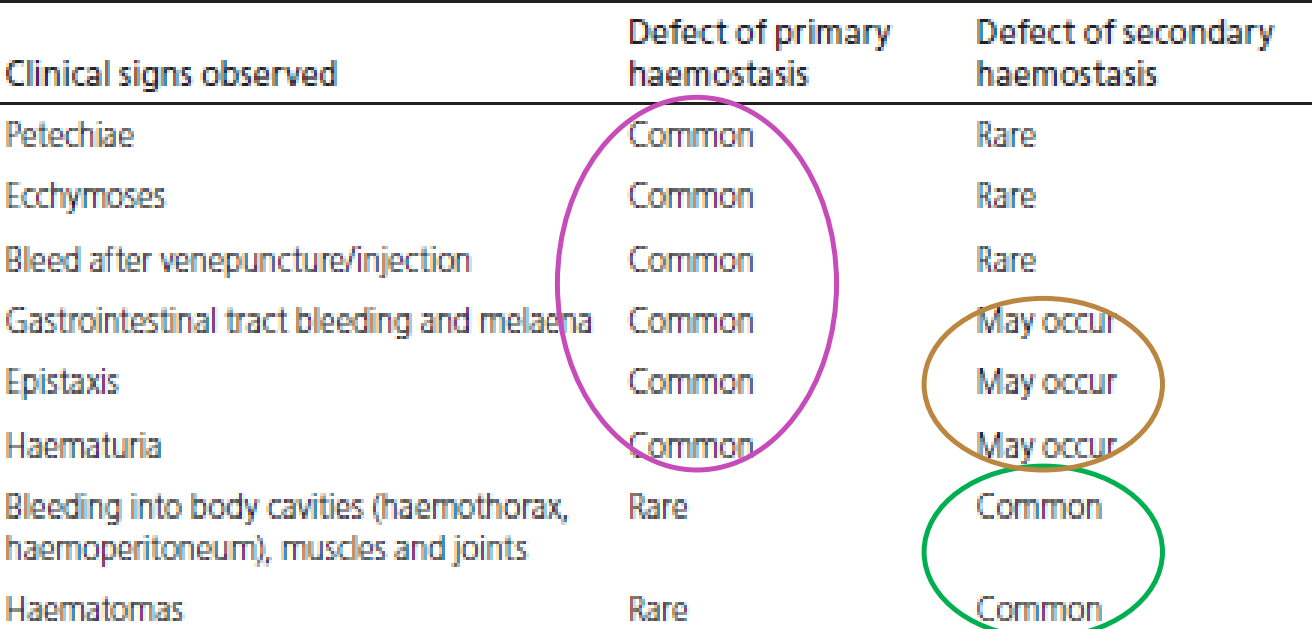
Primary vs 2ndary
Of these defects - how common is the defect from primary or secondary respectively
2ndary Haemostasis involves?
Tertiary Haemostasis - Involves?
Why?
Clot needs to break down or else blood flow is impacted → hypoxia → death


Finish table
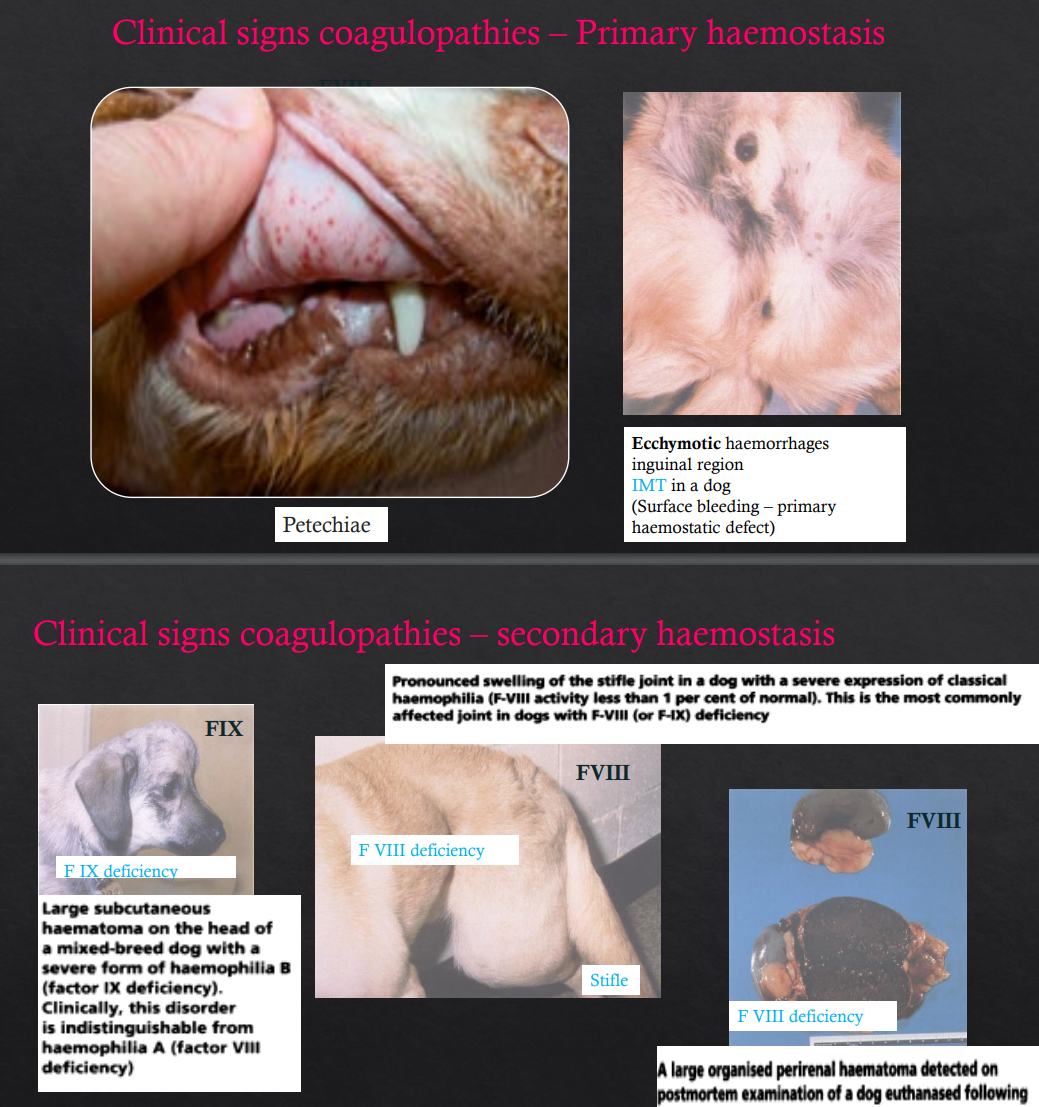
Which is more commonly in superfiical mm bv damage to resolve it?
Which is in deep body cavities more often?
Primary
Secondary
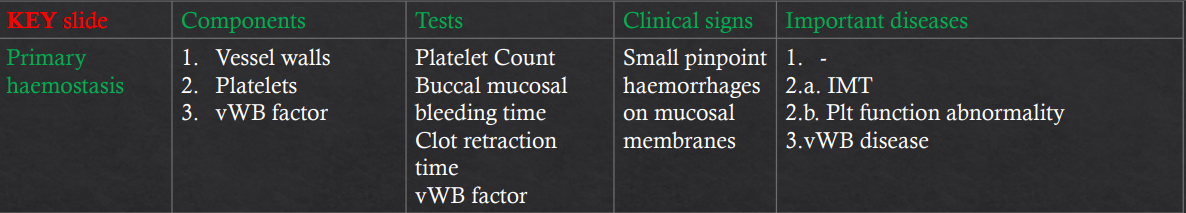
2ndary haemostasis
Components?
Tests?
CX?
Important Dz?

2ndary haemostasis
Components?
Tests?
Important Dz?

Sample Collection
What is used?
Catheter aspects?
Citrate vaccum tube
Avoid heparinised catheters (affects coagulation)
Non-heparin catheters can be used but flush with 5ml saline and then discard 6x dead space (5ml)
Sample Collection
Care is important - we need to minimise?
Term for doing this?
Traumatic venepuncture leads to?
Activation of PLT, coagulation and fibrinolytic systems
“Clean Stick” - free flowing blood and clean venepuncture on first attempt
Exposure of Tissue factor → activates pathways to be tested (causes coagulation)
Sample Collection
Vaccuum?
Mixing?
Avoid excess vaccum - may cause turubulance and platelet activation
Mix immediately - gentle but thorough
Sample Collection
Volumes aspects
Clinical sig of underfilling?
Underfilling may cause prolonged PT and APTT (falsely claims dz)

Sample Collection
Aspects when lab is kinda far away and need to keep it relatively stable
Keep it cold when its sent

What is the functional role of inhibitors of haemostasts like Anti-thrombin III?

Dx tests for Haemostasis - Primary
What aspects do we test?
How do we test them?
Specimen type used if applicable?

Purpose of vWB?
With damaged vessel → help platelets stick to vessel and each other → aggregation

Dx tests for Haemostasis - Primary Haemostasis
PLT concentration
Methods to count? Features?
If less than 3 plt per high power field - you must count ten fields to get accurate count

Dx tests for Haemostasis - Primary Haemostasis
PLT function
Methods to count? Features?

Dx tests for Haemostasis - Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test via Buccal Mucosal Bleeding time
What might inc BMBT?

Dx tests for Haemostasis - Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test via Buccal Mucosal Bleeding time
What are normal times?
What is prolonged time?
Prolonged Time > 5 minutes in small animals
(dog normal < 4 minutes, cat < 3 minutes)
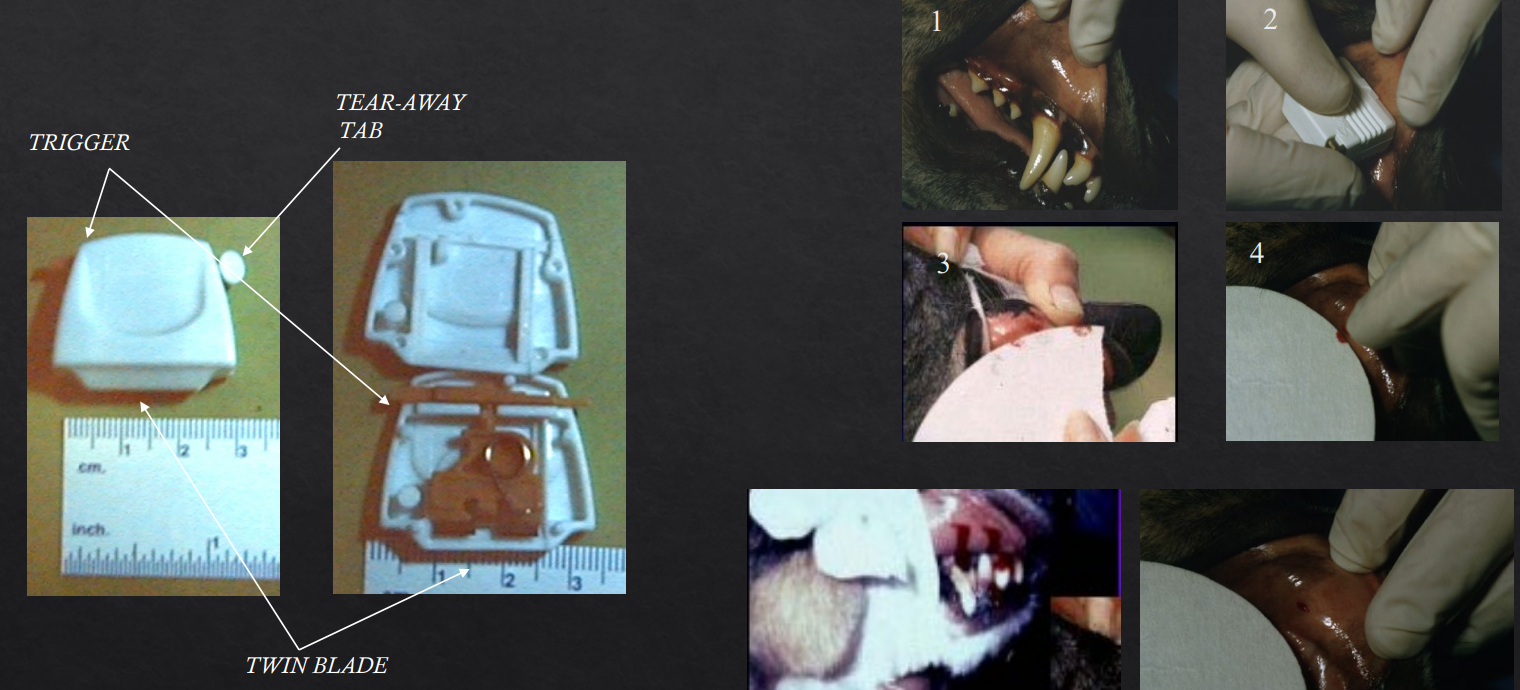
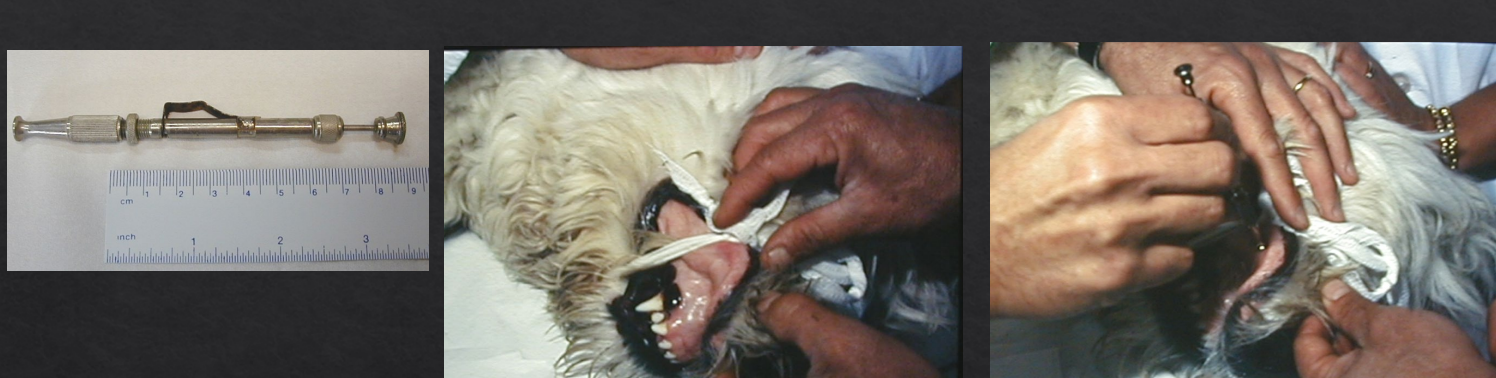
What is this?
What is it for?
How it is used? Steps?
Simplate Device
Primary Haemostasis - PLT function test via Buccal Mucosal Bleeding time
Roll up upper lip and secure with gauze strip
Make a cut in lip using device and start the time
a. Cut is 5mm x 1mm - superficial enough to only need Primary haemostasis resolution
Filter paper is used to blot awat excess blood without touching or disturbing incision
End point - when bleeding stops
What is this?
What is it for?
Reference values?
If above these values i.e. increased, what can be interpreted
BMBT performed by Francke needle
Measuring BMBT for Platelet function of primary haemostasis
Dog, horse, cow 2- 5 min (cat < 3minutes)
Indicates vascular lesions or capillary fragility lack of platelets and/or defects of platelet function
Primary Haemostasis
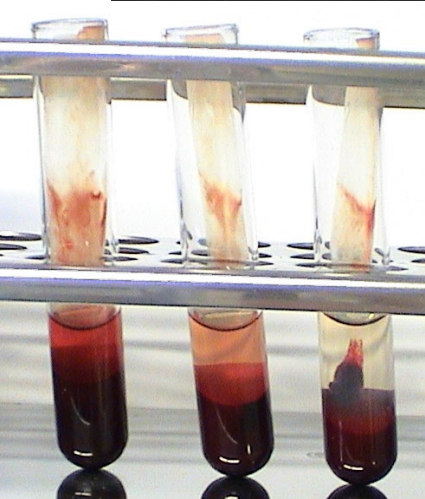
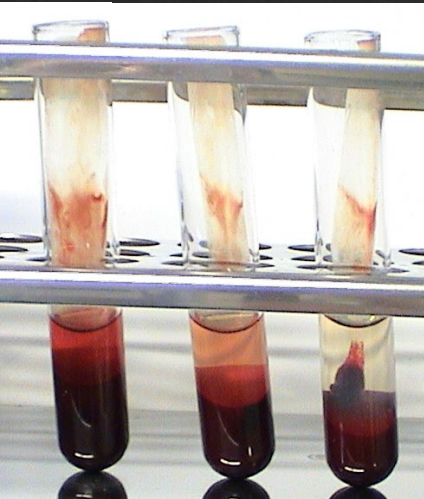
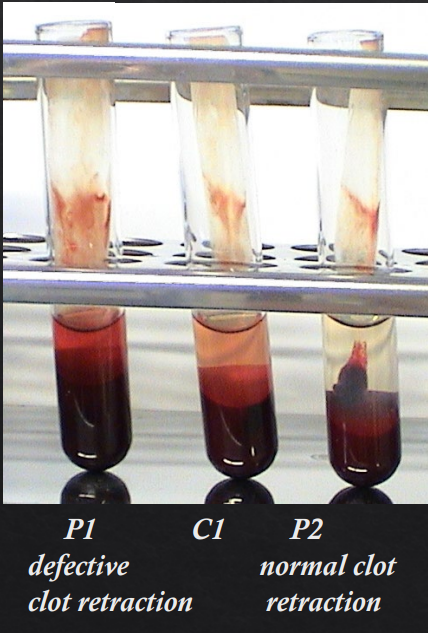
PLT function test for Clot Retraction Time (CRT)
Technique?
2ml blood from two animals and a control animal in glass tubes with anticoagulant to clot at 37 degrees
After 1 hour, compare clot retraction in 3 vials and serum prod should be 30-50%
Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test for Clot Retraction Time (CRT)
Which is which in each of these vials?
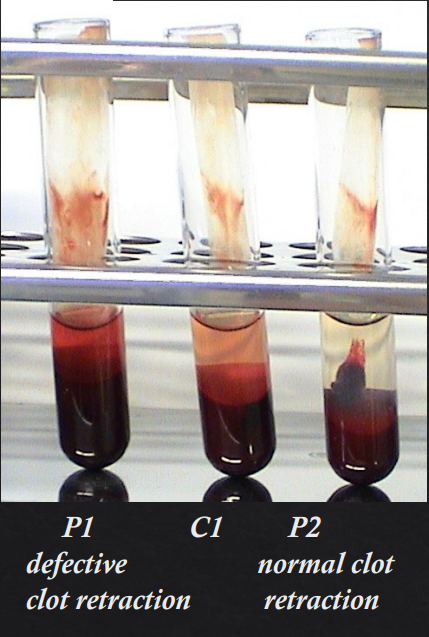
Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test for Clot Retraction Time (CRT)
Interpretation
Clot retraction should be recorded as X? based on X?
Normal, equivocal, or defective, based on a normal retraction of about 30-50%
Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test for Clot Retraction Time (CRT)
Interpretation
What can produce defective clot reaction?
What inc clot reaction?
• Thrombocytopenia/pathy, erythrocytosis, and hypofibrinogenaemia produce a defective clot retraction.
• Anaemia increase clot retraction.
Primary Haemostasis
PLT function test for Clot Retraction Time (CRT)
Interpretation
Clot lysis?
In DIC the clot is often small and ragged, partially disintegrated (due to excess of plasmin), and after 24 hours the clot modification are more pronounced
Primary Haemostasis - vWF
Testing vWF using Ag assay
What samples are used?

Primary Haemostasis - vWF
Testing vWF using Ag assay
Analytical Interpretation
Is reported as?
Reported as % relative to pool of healthy species reference
Primary Haemostasis - vWF
Testing vWF using Ag assay
Analytical Interpretation
The different parameters and meaning?
Dog with vWF : Ag >70% are considered free of vWD trait
Dog borderline vWF : Ag 50-69% carrier, but no risk (repeat test)
Dog with vWF: Ag <50% considered carriers of vWD trait
: transmit trait to offspring
: risk of clinical vWD increased with lower vWF : Ag
Dog that bleed – most <35%
Primary Haemostasis - vWF
Testing vWF using Ag assay
Analytical Interpretation
Falses and causes?

Primary Haemostasis - vWF
Testing vWF using DNA
How do?
Results?
