the dave exam
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes the cameras, lighting, and documentaries lectures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What does a camera actually do? how does it turn what you’re seeing into a video?
It converts light into a useable and controllable electronic video signal
what are the 3 basic types of video cameras?
consumer camcorders
ENG/EFP/Pro-sumer
Professional, studio
fill in the blanks: light is reflected off an object and gathered by a _____. the light is then _____ and focused on the _______ _______.
lens, split, imaging device
fill in the blanks: the imaging device transforms the light into electrical energy called a “video signal”. the signal is ______ and _______, then reconverted into video pictures
amplified, processed
what are 3 important factors for deciding what type of camera you should choose for your project?
type and size of imaging chip
pixel size and number of pixels
lens quality
how does light get converted to a signal in a camera?
through an imaging chip
what are the 2 basic chips in tv production?
ccd: charge coupled device
cmos: complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor
what’s the biggest difference between TV and film imaging chips?
aspect ratio
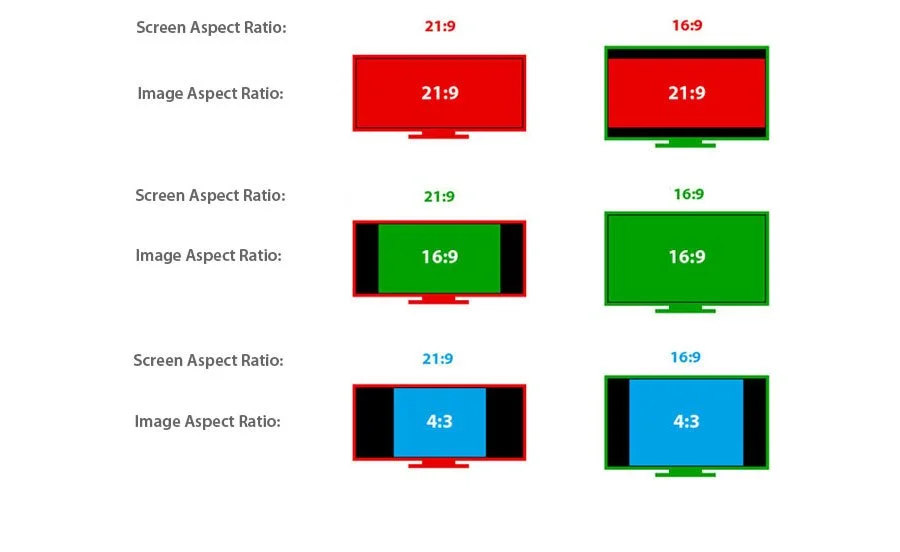
what is aspect ratio?
the ratio between the width and height of a frame

what is voltage?
the potential difference between two points which causes current to flow in the circuit
what is current?
the rate of charge flow between two points caused by voltage
do you need to watch out for voltage or current?
the human bosy has a high resistance to electric current, so without sufficient voltage a dangerous amount of of current can’t flow through the body. in short, watch out for both!
what is a wire?
a single piece of a conductor. can be copper, aluminum, or another material

what is a cable?
a bundle of wires. it’s capable of carrying more electricity at a higher current to supply higher demand pieces of equipment like lights, fans, or effects gear

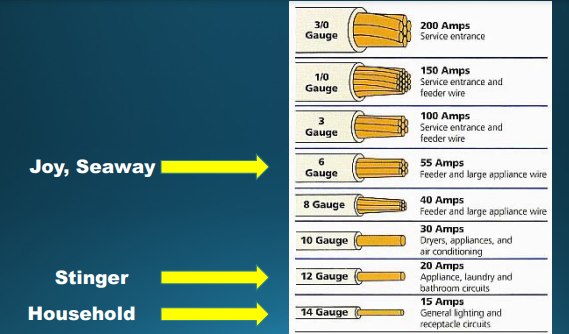
what is gauge?
the “strength” of a cable. in north america, AWG is standard. as gauge goes up, so does the ability to carry more power and current.
what are some key gauge numbers?
12 gauge is a key number
14 gauge is common in households
cheap extension cords can be as low as 16 gauge
what are the gauges of some common wires?
what is the power formula?
watts ÷ volts = amps
what is CRI?
the ability of a light source to properly and faithfully reveal the colour of an object compared to an ideal/natural light source. The highest possible CRI is 100 and is attributed to a perfect black body
what is colour temperature?
the “colour” of white light emitted by a light source based on a perfect black body at a given temperature
what is a black body radiator?
any object that fully absorbs all frequencies of light (ex: the sun). all objects are black body radiators, the amount of radiation and position in the spectrum depends on the object temperature and its emissivity

describe tungsten lights (description, advantages and disadvantages)
description:
high colour temperature
throw lots of light
advantages:
dimmable
low cost
don’t use mercury
disadvantages:
get very hot
high power requirement
may explode

describe HMI bulbs (description, advantages and disadvantages)
description:
used to recreate sunlight
advantages:
high light output
more efficient than incandescent bulbs
high colour temperature
disadvantages:
expensive
contains mercury
can explode if dropped

describe fluorescent bulbs (description, advantages and disadvantages)
description:
can be used relatively close to subject
often used to light interiors
advantages:
high efficiency
low cost
lightweight
disadvantages:
can sometimes flicker
some have low CRI
contain mercury

describe LED bulbs (description, advantages and disadvantages)
description:
monochromatic
throw less light than other bulbs
advantages:
soft, even lighting
low power consumption
can be battery powered
disadvantages:
expensive
what is a documentary?
a non-fiction film without actors whose purpose is to convey factual information
a compelling documentary should be…
compelling, has emotion, entertaining, and based on facts
describe the types of documentaries
observation:
puts the audience as the “eyewitness”
the camera appears to be unseen
interview:
uses interviews to make a contrast between sequences
structured in intercut fragments of observations, or completely uninterrupted
describe different types of recreations of events documentaries may use
dramatization:
used to portray people and events the filmmaker doesn’t have access to irl
should be based on fact
mise-en-scene:
what the directors and producers put into the frame
ex: a documentary about lights has an interview with lights in the background
exposition:
the line of argument which is what the film is saying
sequences that lead the audience to make their own conclusion
what is a mockumentary?
a film/tv show that portrays itself as a serious documentary, but satirizes its subject
what is the ken burns effect?
adding motion (zooms, pans) to still images in a documentary
what are the 2 biggest factors that affect depth of field?
iris and sensor size
how do you calculate zoom factor?
divide the larger focal length by the smaller focal length (ex: a 70-300 lens becomes 300 ÷ 70 = 4.3x)
what is phantom power?
the process of delivering DC power through the mixer to a microphone
If you wanted a more compressed image, would you use a long or wide lens?
long lens
what are the 3 most basic chip sizes?
⅔ inch, ⅓ inch, ½ inch
what does gain do?
it amplifies the image, so when it’s turned up its at the expense of the noise
do cameras use AC or DC?
DC
what is time code?
a specific number assigned to every frame in a video. it can be set to match the actual time
what’s the difference between free-run and record-run?
free-run is like a clock, but record-run only starts when you’re recording
what is HD resolution?
1080 × 1920
What is an ND filter? What does it stand for?
neutral-density
decreases the amount of light coming into the camera without changing the colour temperature (sunglasses for the camera)
what is the first thing you should do when you put your eye in the eyepiece?
adjust the diopter
Which has more depth of field- wide-angle lens or narrow-angle lens?
narrow-angle lens
What are two ways to control depth of field?
chip size and iris
distance
what does XLR stand for?
ground, lead, return
what’s the approximate range of human hearing?
20 hz - 20,000 hz
what are some things you should put on an invoice?
your name
your contact info
the job you did
the invoice date and number
according to dave, what percent of every cheque should you put away for taxes/just in case?
40%
what are the 2 main bodies you pay taxes to?
federal government
provincial government
what does a macro lens do?
it lets you shoot within a minimal focal distance
what type of microphone are the wireless mics in the camera kits?
dynamic mics