Final Exam - Breast and Prostate Cancers
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
4 diagnostic tests for breast cancer
breast self-examination
mammography
ultrasonography or MRI
tissue analysis (BIOPSY!!!!)
when should a breast self-examination be completed?
5-7 days after menses
when should a woman receive a mammogram?
ANNUALLY after the age of 40 years
when should a woman get an MRI/ultrasonography for breast cancer? biopsy?
if the mammogram shows anything suspicious; if a mass is found, a biopsy will be needed to confirm cancer
what happens during a mammogram?
a breast is mechanically compressed both vertically and horizontally while simultaneously having radiologic pictures taken of them, ensuring their are no abnormalities/growths
3 surgical biopsies done for women to rule out breast cancer?
excisional
incisional
wire needle localization (helps indicate WHERE the tumor is so that the surgeon can easily remove it)
breast cancer - biopsy (POST-OP NURSING CONSIDERATIONS)
usual pre/post-op education for the patient
monitor effects of anesthesia and surgical site
use of a supportive bra (COMPRESSION), to decrease move of the breast, as movement causes pain
avoid jarring or high impact activities for 1 week after the procedure
follow-up appointment for results
what is the risk of developing breast cancer (PERCENTAGE? ratio?)
12%, or 1 in 8
the risk of developing breast cancer increases with what?
AGE!!! (about 2-3 invasive breast cancers are found in women age 55 or older)
breast cancer- risk factors
female gender (1% occur in men)
age
personal and family history, including genetic mutations (BRCA!!!)
usually get it before menopause/early with BRCA gene
hormonal factors (early menarche and late menopause)
increased breast feeding = increased protection from pre/post menopausal breast cancer, as it delays their menstrual periods
exposure to radiation
history of benign breast disease
obesity
alcohol intake
GIVING BIRTH after age 30
breast cancer - how does having menses influence breast cancer formation?
the MORE menstrual cycles a woman has, the HIGHER RISK of breast cancer
breast cancer - what is important to know about pregnancy?
pregnancy decreases menstrual cycles, meaning that the more times that you are pregnant, the LESS LIKELY CHANCE that you will get breast cancer, ESPECIALLY if before age 30
guidelines for EARLY DETECTION of breast cancer
Women in 20s and 30s: clinical breast exam at east every 3 years; then annually after age 40 years
Mammography annually beginning at age 40 years
Women at increased risk (family hx, +BRCA) may have earlier initial screening, shorter screening intervals, or additional screening procedures such as ultrasonography or MRI
Beginning in 20s, educating women on the benefits and limitations of BSE
breast cancer - assessment findings
usually found in the upper outer quadrant of breast (axillary), but can be anywhere
nontender, fixed, and hard lesions with irregular borders
advanced signs: skin dimpling, nipple retraction, skin ulceration, orange peel appearance, nipple discharge
positive mammogram, but no symptoms
breast cancer stages (tumor size)
0 - VERY small; inside the glands
1 - less than 2 cm
2 - 2-5 cm
3 - 5 cm and larger
4 - ANY size (as long as it has spread)
breast cancer stages - lymph nodes
0 - NO CANCER
1 - NO CANCER
2 - affected by cancer
3 - affected by cancer (cancer has reached the muscles and skin)
4 - affected by cancer
breast cancer stages - 5 year survival rate
0 - 100%
1 - 100%
2 - 87%
3 - 61%
4 - 20%
breast cancer - SURGICAL management
modified radical mastectomy (take all breast tissue AND surrounding lymph nodes)
total mastectomy (leaves some lymph nodes)
breast conservation therapy
sentinel node biopsy, axillary lymph node dissection
post-mastectomy (CONCERNS)
lymphedema (swelling that results form lymph system having trouble draining like it normally would)
hematoma or seroma formation
infection
implant failure/rejection (HIGH INCIDENCE IN THESE PATIENTS !!)
post-op mastectomy (nursing interventions)
ARM BAND on side of mastectomy (cannot draw labs/blood pressures on that arm due to lymphedema)
relieve pain and discomfort
inform patient regarding common postop sensations
maintain privacy for first time seeing incision (due to disturbed body image)
BRA WITH BREAST FORMATION!!
provide information about home plan of care (taking care of JP drains (how to drain, managing tubing, etc))
support coping and adjustment; counseling and referral
monitor for potential complications (lymphedema, hematoma/seroma, infection)
lymphedema - nursing interventions/education
SCDs for arms (to promote movement away from the extremity)
elevate arm above the heart
ARM BAND!!
avoid rapid movements that could cause centrifugal pooling of fluid in hands or legs
avoid heat to limbs (heat can increase blood flow (NO HOT BATHS OR SAUNAS)
avoid strain/pressure that can obstruct lymph flow (such as tight fitting clothing or jewelry)
avoid carrying heavy objects on the AFFECTED side
do NOT cross legs while sitting OR sit in one position for more than 30 minutes
why do hematomas and seromas usually form after a mastectomy?
lack of JP drain care
post-op mastectomy (PATIENT EDUCATION)
surgical site management and care of drains (which are usually removed after approximately 7-10 days)
shower on second post-op day and wash the incision and drain site with soap and water
patients are taught arm exercises on the AFFECTED side to perform 3x a day for 20 minutes at a time until full range of motion is restored (generally 4-6 weeks)
heavy lifting (more than 5-10 pounds/ “gallon of milk”) is avoided for about 4-6 weeks
3 NONSURGICAL management techniques for breast cancer
radiation
chemo
hormonal therapy
breast cancer - RECONSTRUCTIVE PROCEDURES
tissue expander followed by permanent implant
tissue transfer procedures
nipple-areola reconstruction
prosthetics
reconstructive breast surgery
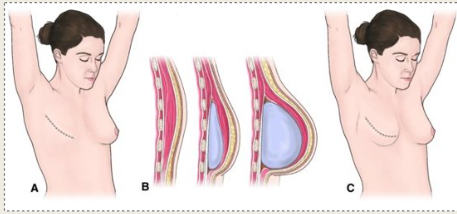
what reconstructive procedure is this?
breast reconstruction with tissue expander
breast cancer - what is important to note PRIOR to getting tested for BRCA gene?
must ASK the patient prior to doing it to know if they WANT TO KNOW !!! (results can be nerve-wracking)
breast cancer - quality of life and survivorship (what does it help dictate?)
helps dictate the type of treatment the patient receives (surgery, chemo, radiation, palliative)
2 diseases of the MALE breast
gynecomastia (MALE BREASTS), which is a risk factor for breast cancer
male breast cancer
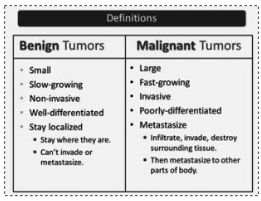
Benign tumors VS. malignant tumors (chart)
post breast biopsy (what to expect)
ice pack to ice your breast RIGHT AFTER
small amount of bloody drainage from biopsy area or on the dressing
mild-moderate discomfort, tenderness, and bruising at site
titanium clip may be placed during biopsy (permanent marker to identify the area where the breast tissue was removed)
steri-strips or sutures and a small bandage at the site
post breast biopsy - pain control techniques
OTC pain medications (ASA, ibuprofen, naproxen, tylenol) unless otherwise instructed
ICE (every 15-20 min, with 40-45 min breaks for 4-6 hours following the procedure)
post breast biopsy - SITE CARE techniques
remove the outer gauze dressing 24 hours after the procedure
steri-strips (paper tape) will come off on their own in about 5-7 days
sutures will dissolve within 2 weeks after the biopsy
keep the wound clean and dry
may bathe the area when the outer gauze is removed; gently pat around the incision
do NOT soak in a bathtub, swim, or get into a hot tub for 7 days after the biopsy
wear a soft, comfortable, supportive bra (such as a sports bra) for 2 days and 2 nights, including sleeping in it for 2 nights; pad the incision with a soft cloth or gauze if it rubs against the bra
post breast biopsy (when to call the provider)
fever of 100.4 degrees F (38 C) or higher
pain is NOT controlled by medications
redness, heat, or swelling at biopsy area
increased bleeding or pus coming from the biopsy area
biopsy results should be available in 3-5 days
what is the second most common cancer AND the second most common cause of cancer death in men?
PROSTATE CANCER
prostate cancer - 3 risk factors
increasing age
familial predisposition
African American race
prostate cancer - manifestations
early disease has few or no symptoms; symptoms of METASTASIS may be the first manifestations sometimes
symptoms of urinary obstruction (indicating BPH); blood in urine or semen, painful ejaculation
when does health screening for prostate cancer initiated?
STARTING AT AGE 50!!
2 examinations that can be done to indicate prostate cancer
yearly prostate surface antigen (PSA) - a blood test that raises concern for prostate cancer
regular prostate exam (falling out of practice due to PSA being more sensitive)
prostate cancer - general treatments
prostatectomy
radiation therapy
hormonal therapy
chemotherapy
prostate cancer - nursing assessment (what to assess)
how has their underlying disorder (BPH or cancer) affected their lifestyle
urinary and sexual function (may have a “dry” climax)
health history
nutritional status (malnutrition, with every cancer, develops insidiously)
activity level and abilities
prostate cancer (surgery/treatment of CHOICE!!)?
TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate)
go in through the urethra and remove the prostate the same way you went in (less invasive than laparoscopic)
is prostate cancer fast or slow growing? what does this mean?
VERY SLOW GROWING, meaning that when it IS detected, it usually is not super grown yet and prostate removal is indicated)
TURP - what is done post-operatively?
POST OP CBI (continuous bladder irrigation)
patient will also go home with a catheter until their follow-up appointment
TURP (prostatectomy) - COMPLICATIONS
hemorrhage
UTI
catheter obstruction
complications with catheter removal (UNABLE TO VOID)
urinary incontinence (part of the bladder neck may be removed)
sexual dysfunction
CBI - steps taken to assess a blocked catheter
check the saline irrigation for remaining volume, height of stand, and level of fluid in drip container
check the drainage bag for amount, color, consistency, and position
adjust the irrigation tubing clamps to ensure continuous flow rate
assess the catheter and the tubing for patency, kinking, traction, and leakage
check fluid balance/bladder washout chart(s) for signs of urine/washout fluid retention
percuss and/or palpate patient’s bladder
ascertain patient’s degree of discomfort by asking patient to rate on 1-10 scale, comparing it with previous rating
consider if there was a history of previous catheter blockage
consider the size of the indwelling catheter
TURP/surgery - goals BEFORE/AFTER surgery
BEFORE - adequate preparation and reduction of anxiety/pain
AFTER - maintenance of fluid volume balance, relief of pain and discomfort, ability to perform self-care activities, and absence of complications
TURP - post-op pain relief techniques (NURSING CONSIDERATIONS)
monitor urinary drainage and keep catheter patent
assessment of pain (bladder spasms cause feeling of pressure and fullness, urgency to void, and bleeding from the urethra around the catheter)
medication and warm compresses or sitz baths to relieve spasms
analgesics and antispasmodics
encourage patient to walk and to avoid sitting for prolonged period
prevent constipation
irrigate catheter AS PRESCRIBED!!
TURP - post-op nursing considerations
patient/family education for home care (urinary drainage device and recognition and prevention of complications (usually home foley until follow-up))
regain bladder continence (KEGELS!!!, regaining control is a GRADUAL PROCESS, and can take up to a year)
avoidance of straining, heavy lifting, and long car trips (6-8 weeks!!!)
assessment and referral of sexual issues
TURP - post op (DIET?)
encourage fluids and avoid coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods!!