Week 11 - Learning Perspective
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Classical Conditioning
Learning through association of stimuli.
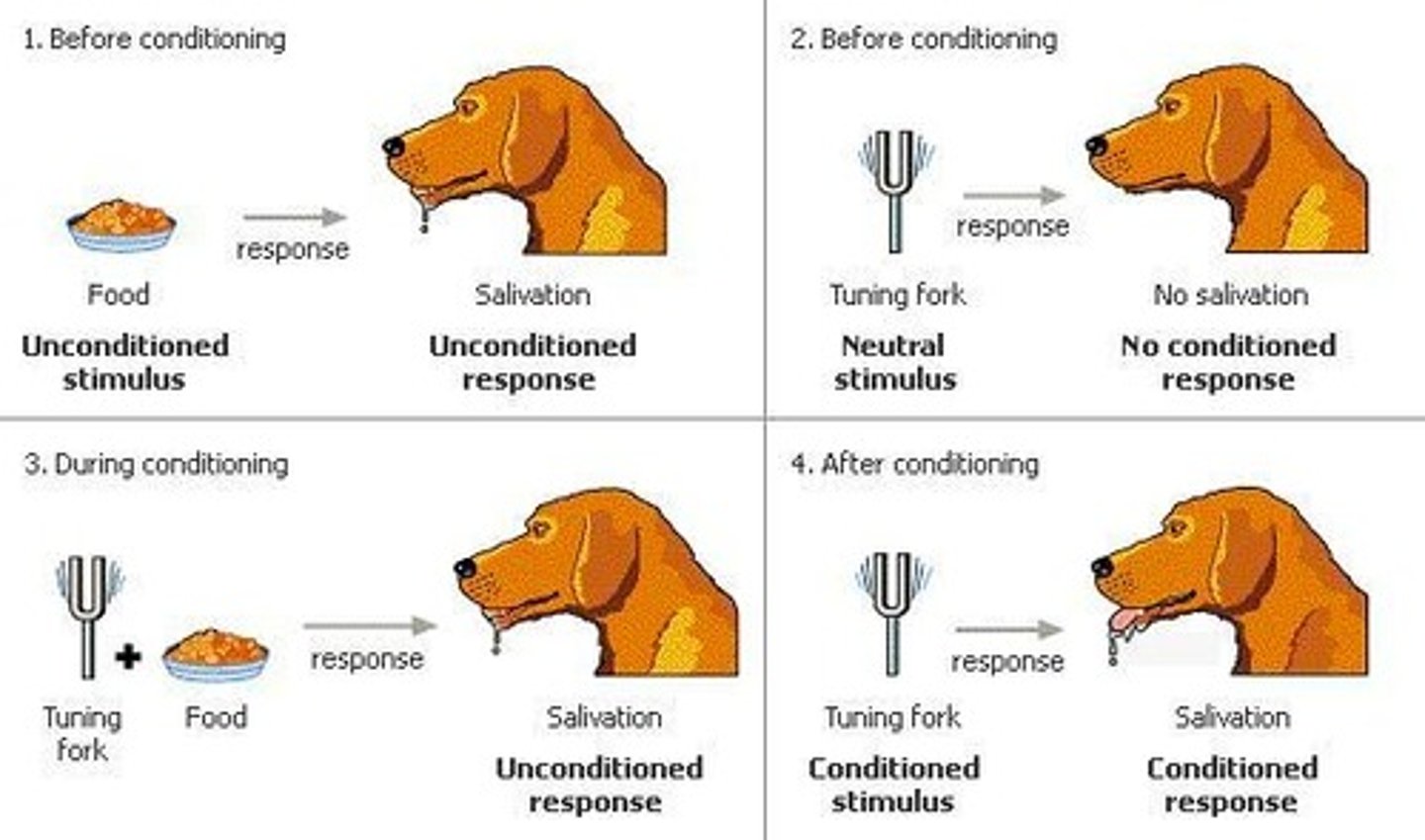
Reflex
Existing connection between stimulus and response.
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Stimulus that naturally triggers a response.
Unconditioned Response (UR)
Automatic response to an unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Initially neutral stimulus that gains significance.
Conditioned Response (CR)
Learned response to a conditioned stimulus.
Before Conditioning
Only reflex exists with US and UR.
During Conditioning
CS paired with US to create CR.
Testing Conditioning
Present CS alone to check for CR.
Generalization
Responding similarly to similar stimuli.
Discrimination
Responding differently to distinct stimuli.
Higher Order Conditioning
Using a conditioned stimulus for further conditioning.
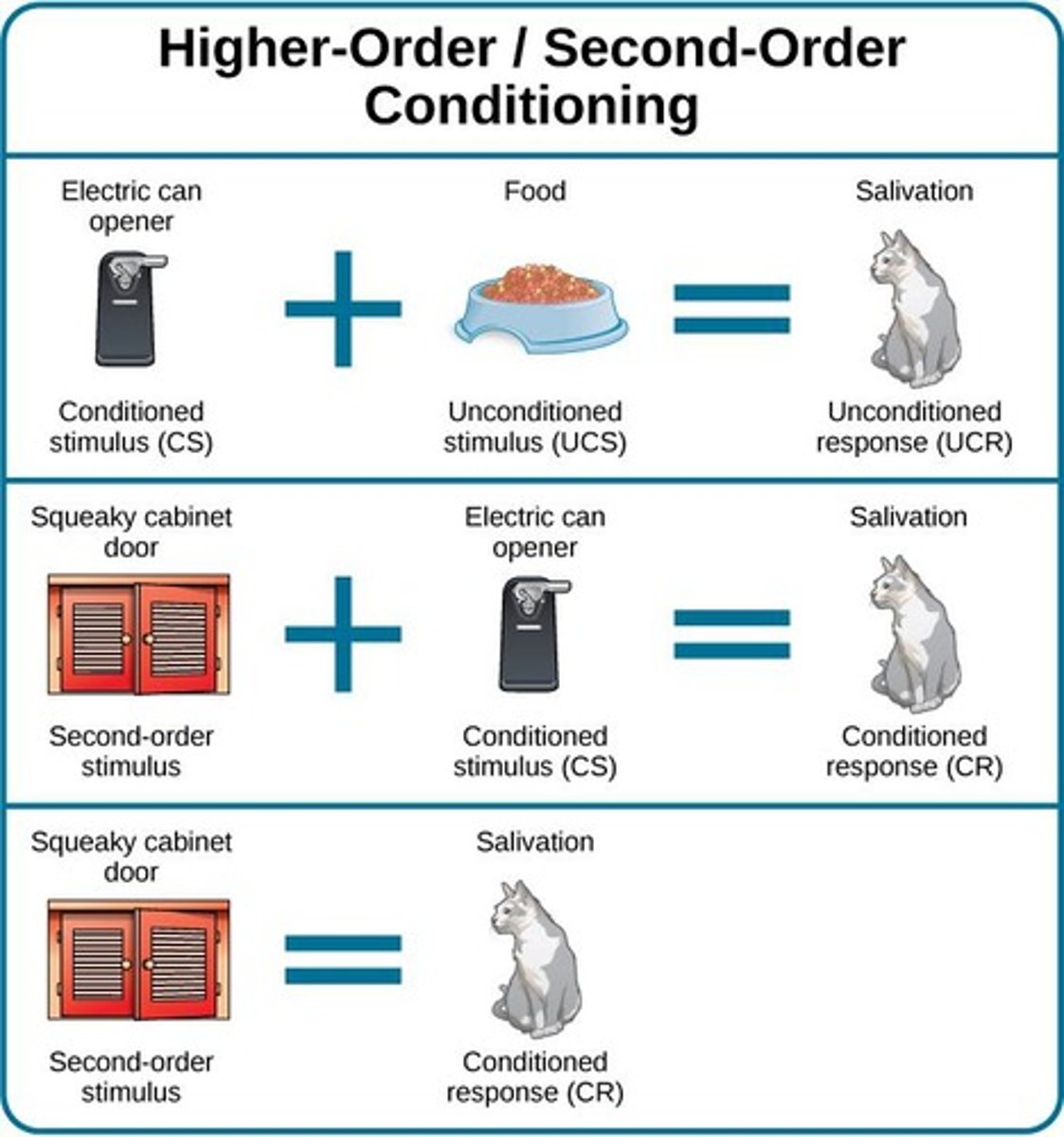
Frequency of Pairing
More pairings increase likelihood of conditioning.
Strength of US
Strong US can condition with one pairing.
Example of Conditioning
Jello causing nausea illustrates conditioning.
Conditioning Evidence
CR indicates successful conditioning has occurred.
Response Intensity
CR is similar but less intense than UR.
Stimulus Timing
CS must precede US for effective conditioning.
Complementary Processes
Generalization leads to discrimination in learning.
Learning Examples
Tying shoes, riding bikes, skiing illustrate learning.
Rules of Learning
Understanding rules aids in learning processes.
Extinction
Weakening of conditioned response when unconditioned stimulus is absent.
Spontaneous Recovery
Reappearance of conditioned response after extinction.
Emotional Conditioning
Classical conditioning involving emotional reactions as conditioned responses.
Avoidance Motivation
Motivation to avoid negative stimuli, like the color red.
Personality Development
Likes and dislikes formed through conditioning experiences.
Instrumental Conditioning
Active learning process where behaviors are influenced by consequences.
Law of Effect
Behaviors followed by satisfying outcomes are repeated.
Habit Hierarchy
Order of responses based on past reinforcement experiences.
Reinforcement
Strengthens behavior by providing satisfying outcomes.
Reinforcers
Events that increase likelihood of preceding behaviors.
Primary Reinforcers
Directly satisfy biological needs like hunger or thirst.
Secondary Reinforcers
Gained value through association with primary reinforcers.
Punisher
Unpleasant outcomes that decrease preceding behavior likelihood.
Primary Punishers
Aversive events that are intrinsically unpleasant.
Secondary Punishers
Aversive due to association with primary punishers.
Positive Reinforcement
Adding a stimulus to increase behavior likelihood.
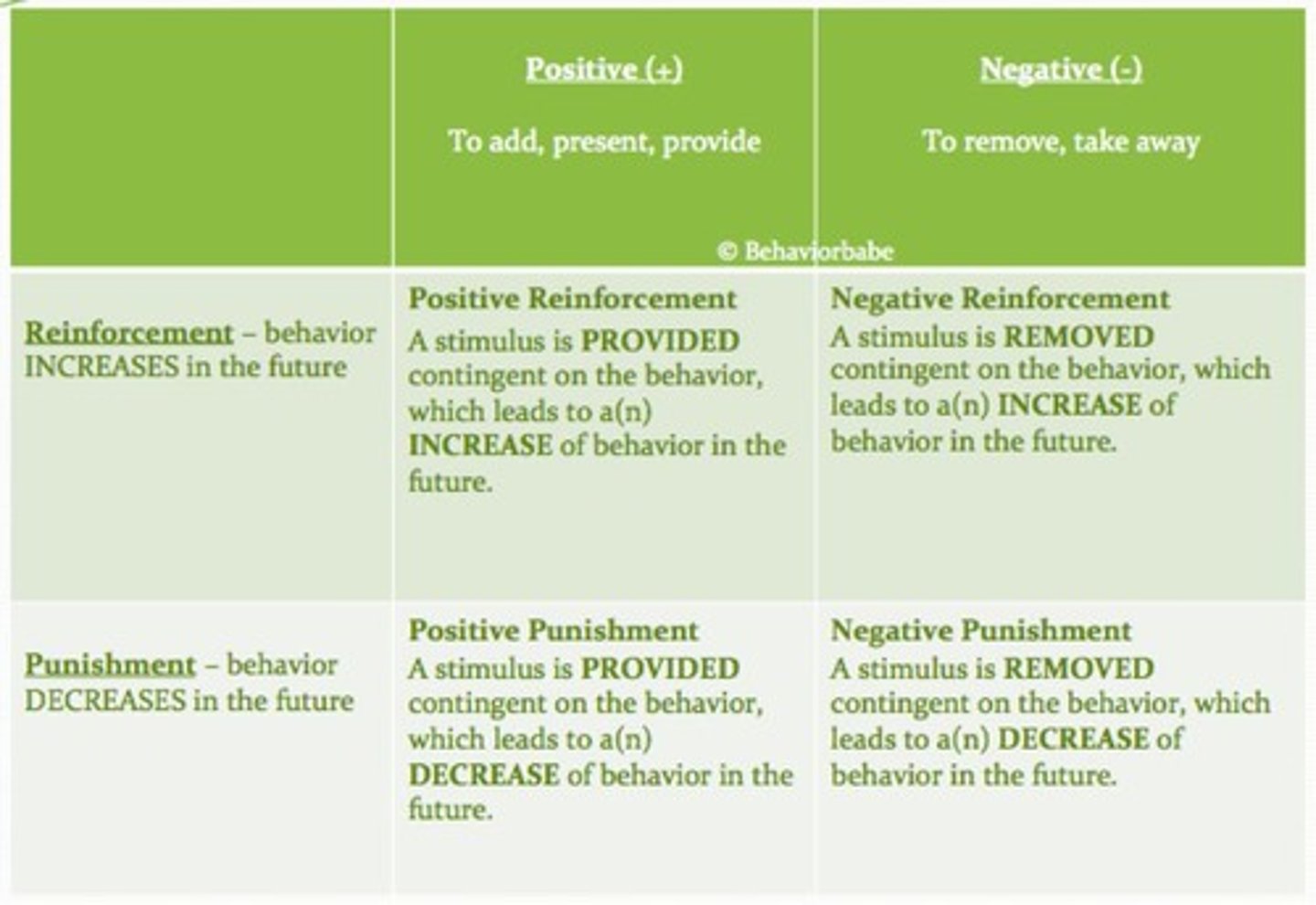
Negative Reinforcement
Removing an unpleasant stimulus to increase behavior likelihood.
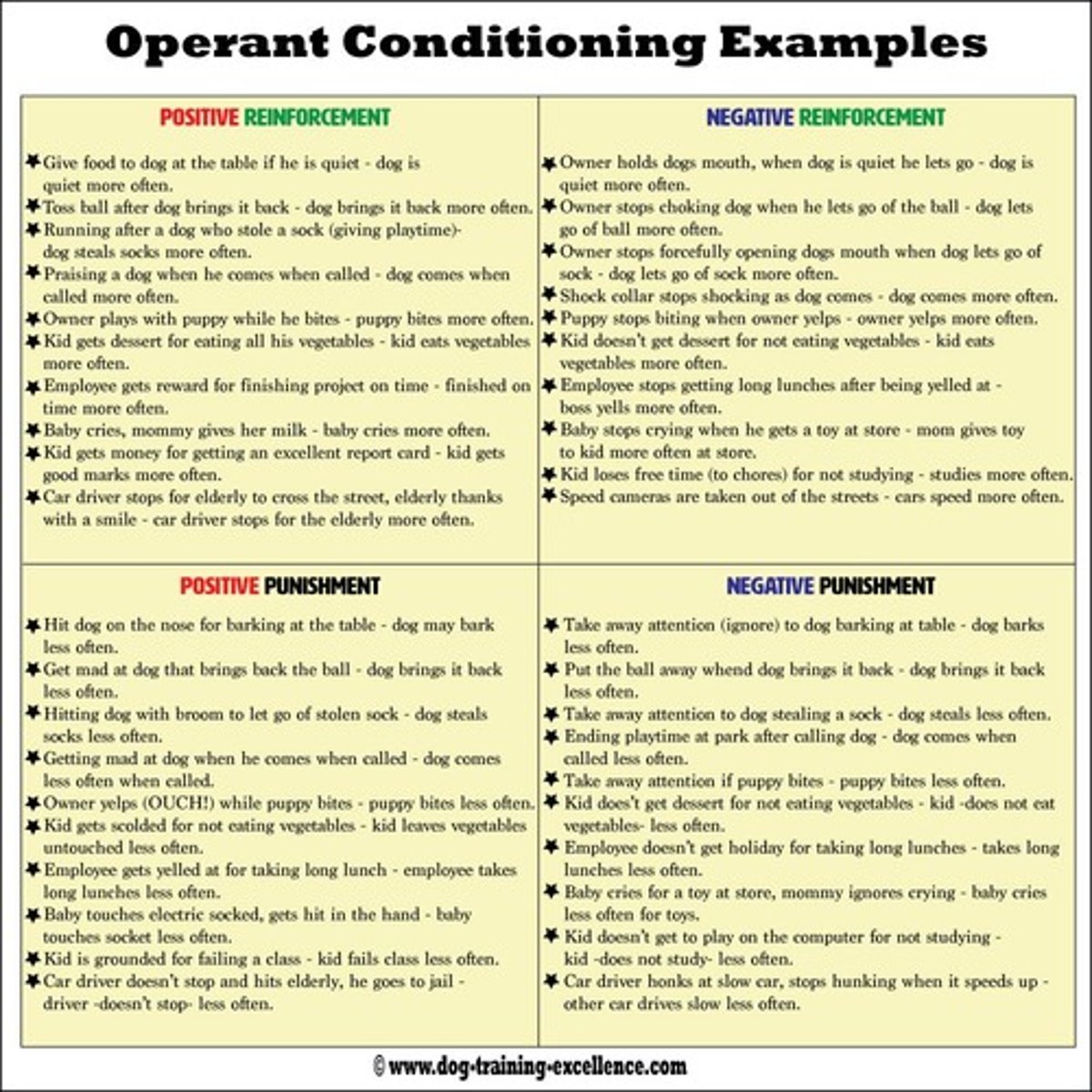
Positive Punishment
Adding an aversive stimulus to decrease behavior likelihood.
Negative Punishment
Removing a pleasant stimulus to decrease behavior likelihood.
Color Impact on Performance
Red color negatively affects test takers' performance.
Emotional Arousal Patterns
Individual differences in emotional responses to stimuli.
Positive Reinforcement
Adding pain to reduce unwanted behavior.
Negative Reinforcement
Withdrawing something good to discourage behavior.
Time Out
Temporary removal from positive reinforcement.
Discriminative Stimulus
Stimulus that influences behavior occurrence.
Stimulus Control
Behavior cued by discriminative stimuli.
Contextual Cues
Changes in situation alter behavior cues.
Generalization
Applying learned behaviors across different settings.
Extinction
Behavior fades when no longer reinforced.
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcement provided every time behavior occurs.
Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcement given only some of the time.
Partial Reinforcement Effect
Partially reinforced behaviors resist extinction.
Social Learning
Learning by observing others' behaviors.
Cognitive Learning Theory
Focus on mental processes in learning.
Social Reinforcement
Acceptance and attention from others as rewards.
Self-Reinforcement
Reinforcing oneself after achieving a goal.
Self-Punishment
Reacting negatively to one's own behavior.
Vicarious Emotional Arousal
Experiencing emotions indirectly through others.
Behavior Acquisition
Learning behaviors faster with continuous reinforcement.
Adjustment Period
Time needed to adapt to new teaching methods.
Training Cues
Using signals to guide behavior in training.
Behavioral Tendencies
Patterns of behavior influenced by reinforcement.
Empathy
Sharing another's emotional experience, less intensely.
Sympathy
Feeling concern for someone else's suffering.
Vicarious Classical Conditioning
Learning through observing others' emotional responses.
Vicarious Reinforcement
Learning by observing others rewarded for behavior.
Outcome Expectancy
Mental model linking actions to potential reinforcers.
Reinforcer
Stimulus that strengthens behavior tendencies.
Efficacy Expectancy
Confidence in ability to perform desired actions.
Self-Efficacy
Belief in one's capability to execute behaviors.
Public Speaking Efficacy
Confidence affects performance in speaking engagements.
Relapse Prediction
Efficacy influences likelihood of drug use relapse.
Role of Awareness
Conditioning requires awareness of unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Response
Response triggered by conditioned stimulus after learning.
Observational Learning
Learning by watching others perform actions.
Attention in Learning
Focus is crucial for effective observational learning.
Retention
Memory representation of observed behaviors.
Imaginal Coding
Creating mental images of observed actions.
Verbal Coding
Describing observed actions to oneself mentally.
Production
Ability to replicate learned behaviors.
Learning Sequences
Remembering order aids in learning and recall.
Model Characteristics
Attractiveness and power enhance observational learning.
Aversive Event Expectation
Anticipating negative outcomes can trigger responses.
Therapeutic Efficacy
Restoring efficacy enhances problem-solving abilities.
Observational Learning
Learning by watching others' actions and consequences.
Bandura's Experiment
Children imitated aggression towards an inflated doll.
Acquisition
Learning behaviors through incentives and reinforcement.
Symbolic Models
Aggressive behaviors observed in media influence actions.
Behavior Potential
Possibility of performing learned behaviors from observation.
Desensitization
Reduced emotional response from repeated exposure to violence.
Behavior Modification
Therapeutic techniques to change maladaptive behaviors.
Systematic Desensitization
Gradual exposure to phobias while learning relaxation.
Counterconditioning
Replacing undesired responses with opposite or neutral responses.
Anxiety Hierarchy
List of feared stimuli ranked by intensity.
Exposure Treatments
Directly confronting feared stimuli to reduce anxiety.
Flooding
Immediate exposure to the most feared stimulus.
Contextual Cues
Environmental triggers that elicit cravings or responses.
Contingency Management
Reinforcement strategies to encourage desired behaviors.
Shaping Behavior
Gradually reinforcing behaviors towards a desired goal.