BIOL 111 - Exam 3
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Binary fission
Cell division in prokaryotes
Binary fission step 1
DNA replication
Binary fission step 2
Chromosome segregation - chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
Binary fission step 3
Separation - a new plasma membrane starts growing into the center of the cell, the cytoplasm splits apart and two daughter cells form that are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell
FtsZ Proteins
A protein that enables complete separation of the cell by assembling a cytoskeletal scaffold of the Z ring that constricts to divide the cell into two
FtsZ
Filamenting temperature sensitive mutant z
Organelle that divides via binary fission
Mitochondria
Mitochondrial fusion
Helps mitigate stress by combining partially damaged mitochondria
Mitochondrial fission
Needed to help create new mitochondria for quality control (removes the damaged mitochondria and can facilitate apoptosis during high levels of cellular stress)
G1-Phase duration
11 hours
S-Phase duration
8 hours
G2-Phase duration
4 hours
M-Phase duration
1 hour
How does cancer begin?
Gene mutation results in a faulty protein that regulates cell reproduction; tumors result when reproduction of mutated cells surpass growth of normal cells
Gametes
Eggs and sperm; have half the number of chromosomes (haploid)
Somatic cells
Body cells; have 2 matched sets of chromosomes (diploid)
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that pair in reproduction of diploid cells
Heterologous pairs
Genomes with pairs that do not match such as X and Y chromosomes in humans
Karyotype
Arranging the chromosomes by size
Eukaryotic DNA must be condensed into compact ______ to fit into the nucleus
Chromosomes
8 Histone proteins
Short stretches of DNA wrap around a core of this, like a string of beads
Nucleosome
The histone-DNA complex (the bead)
Linker DNA
DNA that connects to the nucleosome
Chromatin fiber
The resulting coiled structure from DNA wrapping around the histone-DNA complex and linker DNA
Interphase
1 - the time for normal cell growth and preparation for cell division
G0
Interphase - when the cell fully quiescent (not preparing to divide)
G1-Phase
Interphase - (first gap) cell grows and organelles are copied
S-Phase
Interphase - the cell synthesizes a complete copy of DNA in its nucleus
G2 Phase
Interphase - (second gap) the cell grows more, makes proteins, organelles and structures/proteins necessary for cell divison
Mitotic phase
2 - phase in which the replicated DNA and cytoplasm are split and the cell divides
G1 Checkpoint
Checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factor, and DNA damage
G2 Checkpoint
Checks for DNA damage and DNA replication completeness
Spindle checkpoint
Checks for chromosome attachment to spindle at metaphase plate
MPF
Maturation promoting factor - induces M-phase; made of Cyclin and CDK
Positive regulators
Move the cell cycle forward; cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases
Negative regulators
Stops the cell cycle (cued by DNA damage and overcrowding)
Retinoblastoma protein (Rb)
Negative regulator - monitors cell size and blocks DNA replication
p53
Negative regulator - halts cell cycle and recruits DNA repair proteins
p21
Negative regulator - inhibits CDK/cyclin complexes
How many mutations does it take on average for a cell to turn into a cancer cell?
6 mutations
T53
The most commonly mutated gene in cancer; codes for p53
HER2
A protein that helps breast cancer cells grow quickly
BRCA1/BRCA2
Genes that code for proteins that are key DNA repair proteins
BRCA 1 deficiency
Leads to abnormalities in most cell regulation checkpoints
Proto-oncogenes
Genes that control positive cell cycle regulators; pre-mutated does not cause disease until mutated (ex: HER2)
Oncogenes
Genes that cause a cell to become cancerous (ex: too many copies of HER2)
Tumor suppressor genes
Segments of DNA that codes for proteins that prevent the cell from undergoing uncontrolled division (ex: Rb, p53, and p21; not disease causing until mutated)
Cervical cancer
Associated with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV); the HPV E6 protein binds to p53 and promotes its degradation)
Benign tumors
Abnormal noncancerous collection of cells that grow slowly with even borders; can turn malignant
Malignant tumors
Abnormal cancerous collection of cells that grow quickly and spread via metastasis
Early Prophase
1
Chromosomes start condensing
Mitotic spindle starts forming
Late Prophase
1
Mitotic spindle starts organizing chromosomes
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Kinetochore
A complex of proteins at centromere that spindle fibers attach to
Centromere
Constricted region of duplicated chromosome
Spindle fibers
Made of microtubules; protein structures that pull apart the genetic material in a cell during division
Centrosome
Contains the centrioles (in animal cells); location from which spindle fibers develop in cell division
Chromatids
Half of a duplicated chromosome
Metaphase
2
Chromosomes are lined up at the plate
Kinetochores should be attached to microtubules on opposite spindle poles (M-checkpoint)
Anaphase
3
Sister chromatids seperate
Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate and push ends farther apart via motor proteins
Telophase
4
Mitotic spindle degraded
New nuclei form
Chromsomes recondense
Cytokinesis
5
Cells start separating overlapping with telophase
Cytoplasm divides
Animal cells - cleavage furrow
Plant cells - cell plate
Plant cell division
Golgi vesicles with cell wall components are produced in interphase
Vesicles fuse and form cell plate which merges with the cell wall
Purpose of meiosis
Reduce the number of chromosomes in gametes
Provide genetic diversity
Restricted to germ cells
Meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes separate
Meiosis II
Sister chromatids separate resulting in 4 haploid cells
Interphase
1- G1, S1, G2
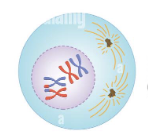
Prophase I
2 - Crossing over
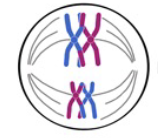
Metaphase I
3 - Tetrads line up (two homologous chromosomes that each already replicated into a pair of sister chromatids)
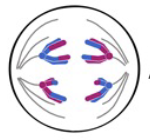
Anaphase I
4 - Homologous chromosomes separate
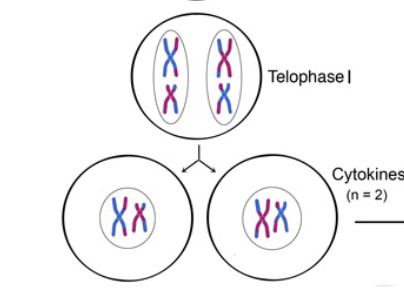
Telophase and Cytokinesis
5 - Homologs arrive at the opposite poles of the cell and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes; the cytoplasm is then divided into two daughter cells
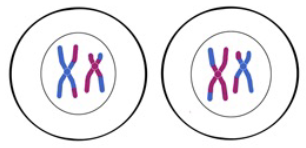
Prophase II
6 - Spindle fibers reform and attach to centromeres
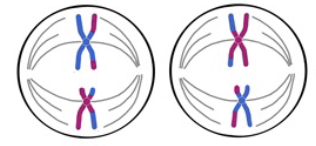
Metaphase II
7 - The sister chromatids align at the plate
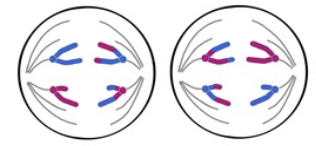
Anaphase II
8 - Chromosomes divide at the centromeres and each chromosome (previous chromatid) moves toward opposite poles of the cell
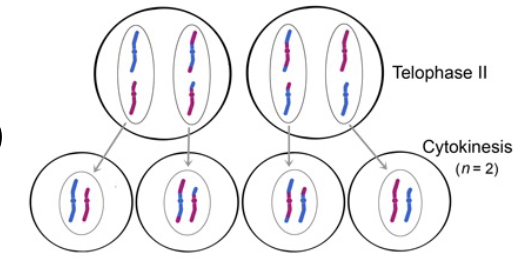
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
9 - Results in four distinct haploid cells with a single copy of each chromosome
How many autosome homologous pairs in humans?
22 autosomes
How many sex chromosomes in humans?
1 pair
Chiasma
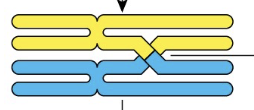
Recombinant chromatids
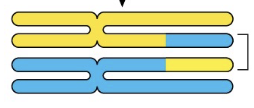
Synapsis
Fusion of chromosome pairs
Genes further apart are more/less likely to cross over?
More
Genes closer together are more/less likely to cross over?
Less
Nondisjunction
Separation errors; results in genetic abnormalities
When does nondisjunction occur?
Anaphase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II
Aneuoploidy
Daughter cells with too many or too few chromosomes; lethal
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
The alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another which results in genetic variability in meiosis
Down syndrome
Trisomy 21
Klinefelter syndrome
47, XXY; males
Low testosterone
Reduced muscle mass, facial hair and body weight
Produce little to no sperm
Turner syndrome
Missing X; females
Short stature
Delayed puberty; infertility
Heart defects and learning disabilities
Jacob’s syndrome
XYY; males
Low muscle tone
Very curved pinky finger
Tall and developmental delays
Gregor Mendel
Father of genetics; believed that traits were inherited as discrete units, demonstrating that traits are transmitted from parents of offspring independently of other traits and in dominant and recessive patterns
Blending Theory of Inheritance
The theory that progeny inherits characteristics as the average of the parents’ values of that characteristic; offspring create an intermediate
Dichotomous traits
Discrete traits that have only two contrasting phenotypic probabilities
Monoecious
Having male and female sex organs in the same plant
Genotype
Genetic makeup; the alleles are carried by an individual for each gene and traits are found at the same locus on corresponding chromosomes
Phenotype
Physical appearance
True breeding
A kind of breeding in which parents produce offspring that would carry the same phenotype; the parents are homozygous for every trait
Allele
A trait
Locus
Location on the chromosome that contains a certain allele
Gene
Codes for a certain characters (ex: flower color) and has its own genotype with two alleles one on each of homologous chromosomes
Testcross
An experimental cross of an individual organism of dominant phenotype but unknown genotype and an organism with a homozygous recessive genotype and phenotype