lipids aktiv
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
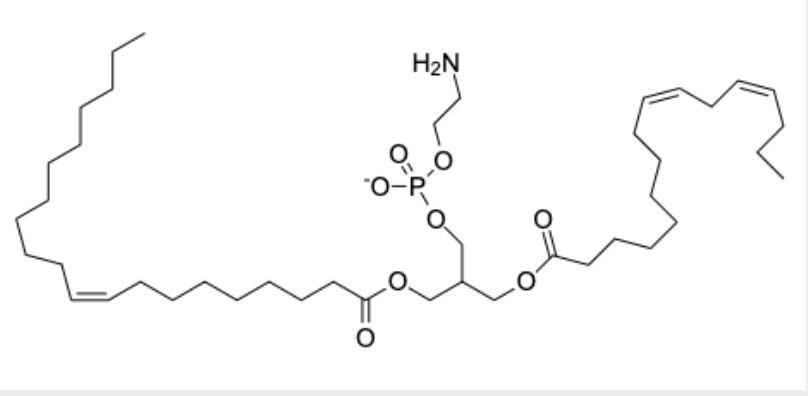
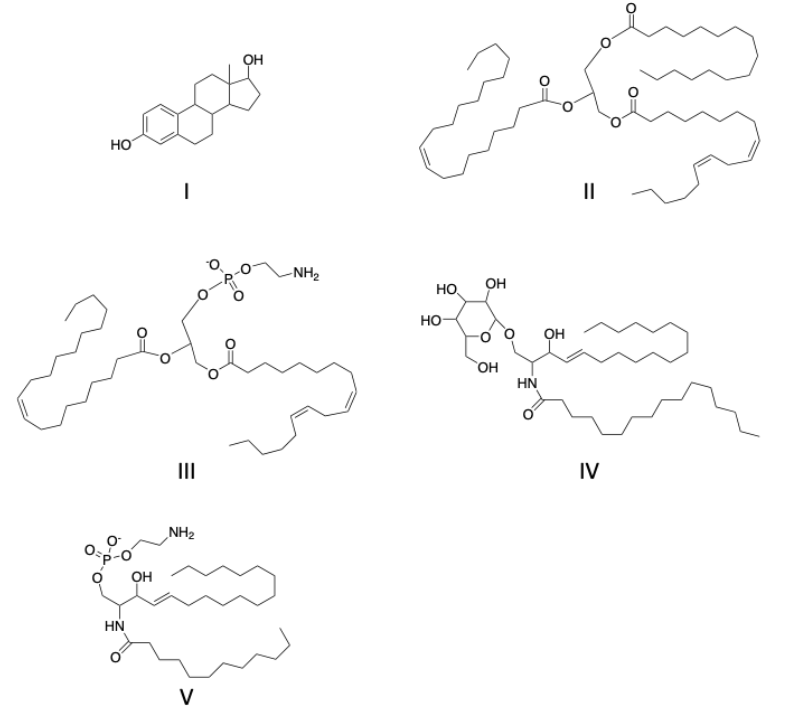
glycerophospholipid
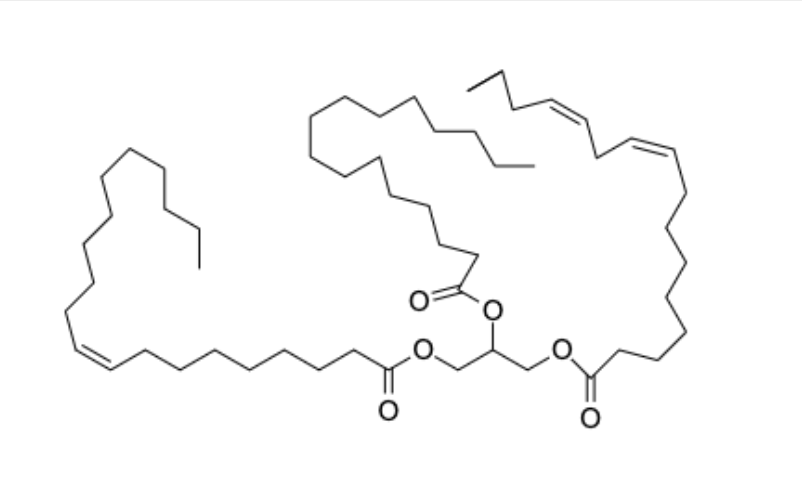
triglyceride
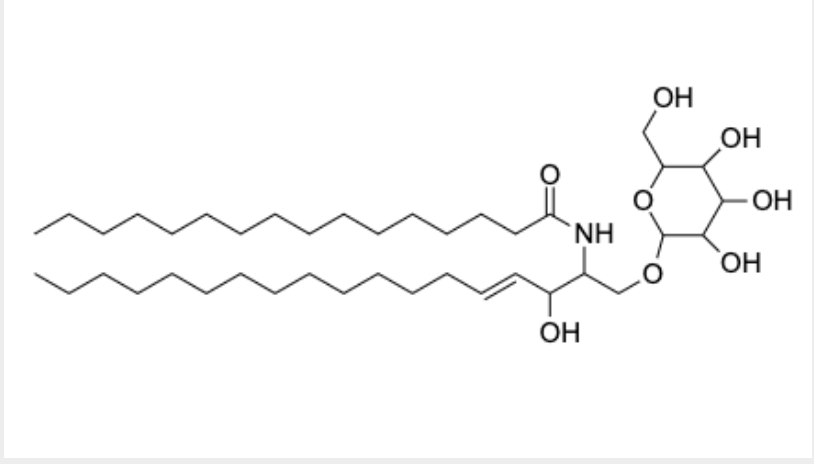
sphingolipid
subcategory cerebroside
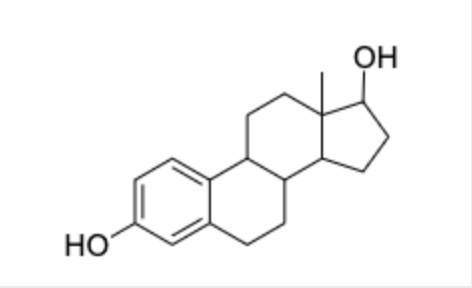
steroids
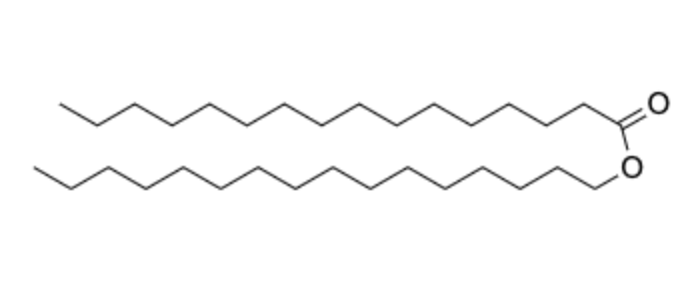
wax
which chemical components are found in sphingomyelins
an alcohol
a phosphodiester
an amide
an alkene
how many fatty acids are involved in making sphingolipid
one
how many fatty acids are required to make a glycerophospholipid
two
identify the number of fatty acids that are used to make a triacylglycerol or triglyceride
three
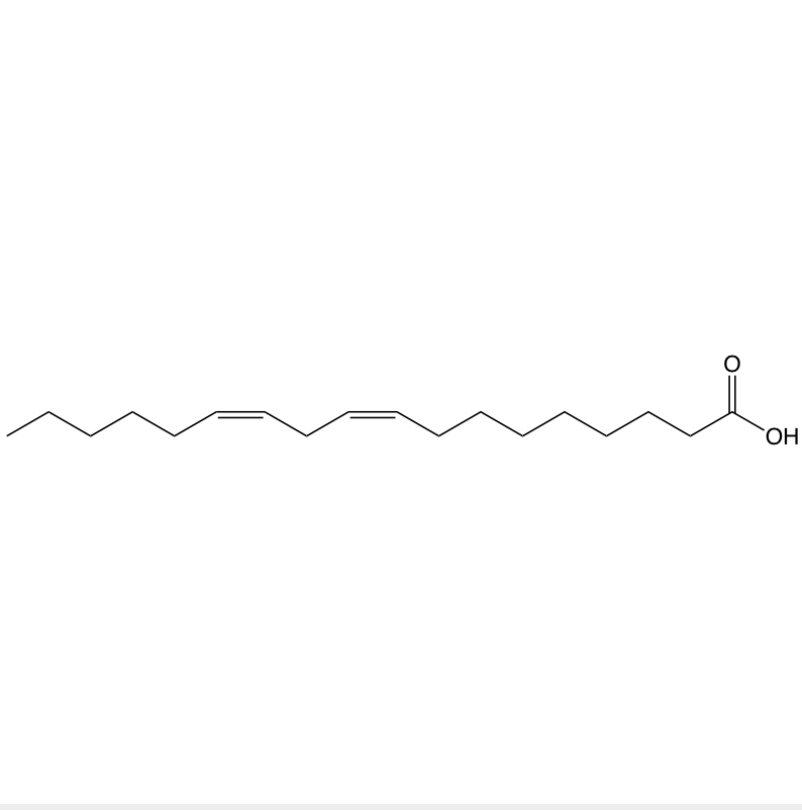
number of carbons and unsaturated or saturated
unsaturated, 18
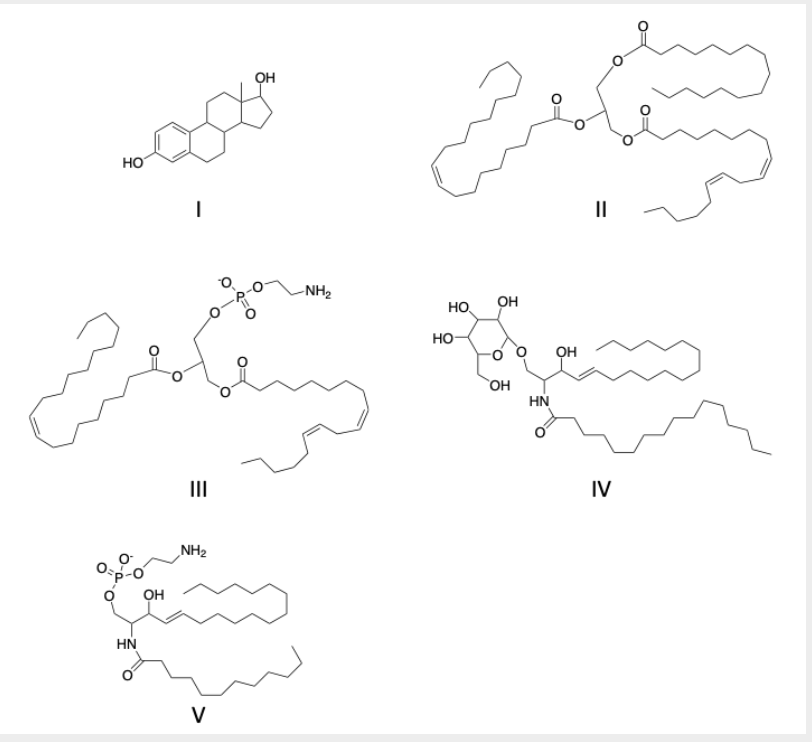
identify the phospholipids and what kind
molecule III is a glycerophospholipd
molecule V is a sphingolipid
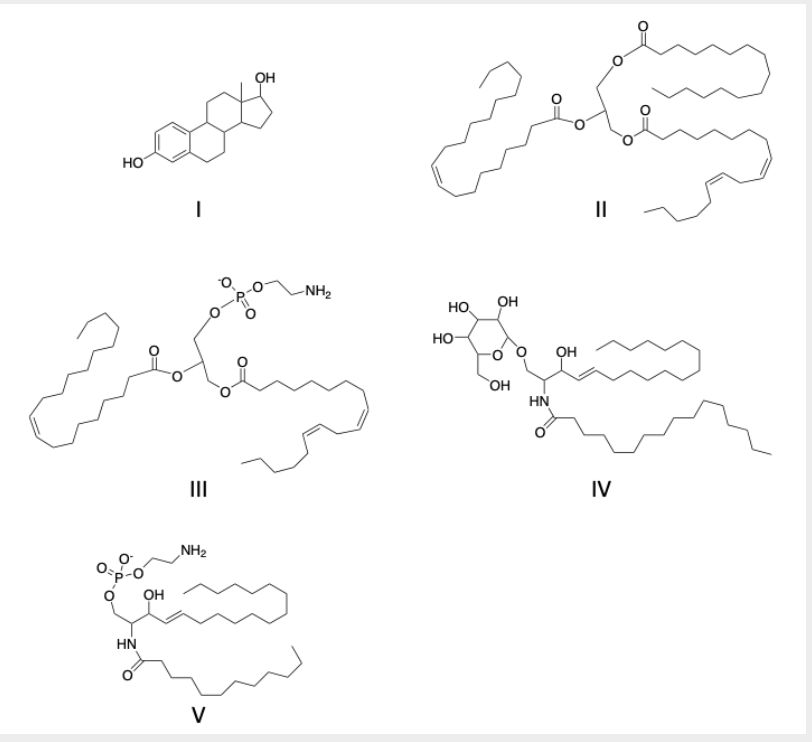
identify the steroid molecule(s)
molecule I
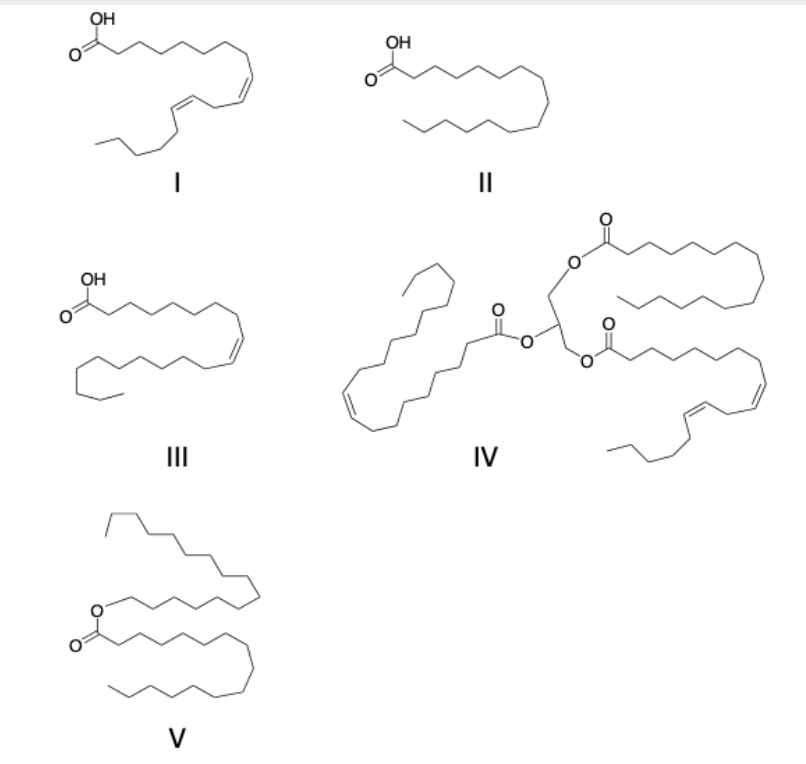
The monounsaturated acid(s)
Molecule III
identify polysaturated fatty acid(s)
II and V
Identify the structure(s) that are waxes
molecule V
waxes have
one ester bond between fatty acids and a long chain alcohol
identify glycerophospholipids
molecule III
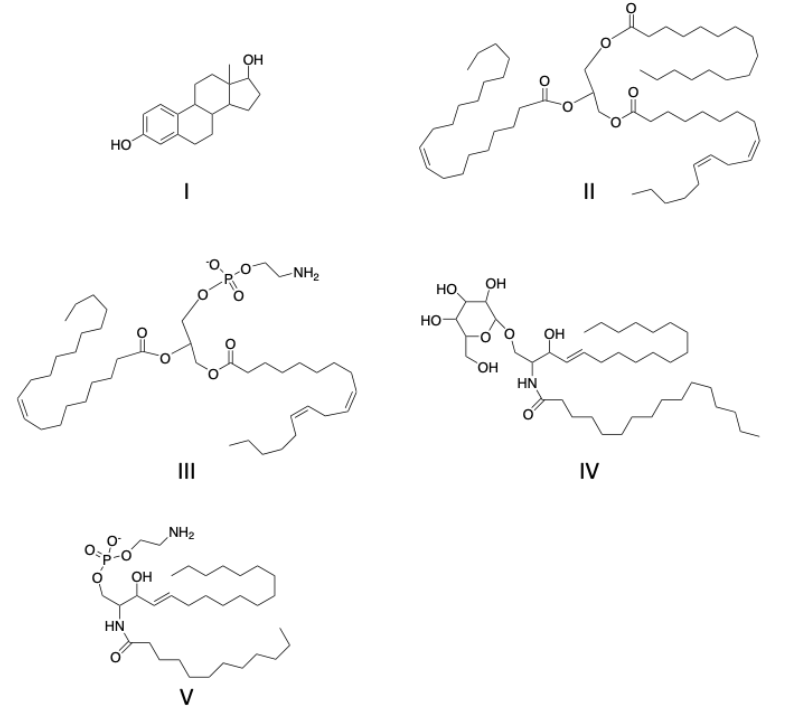
identify the prostaglandins
zero
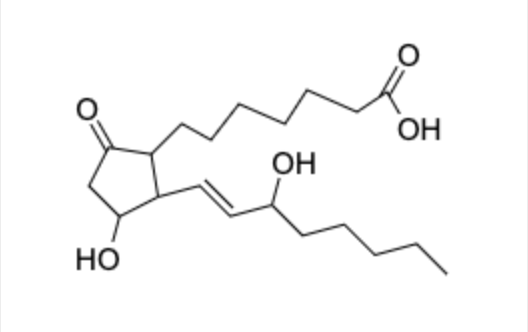
what type of molecule is this
prostaglandin
prostaglandins have what functional groups
twenty carbon fatty acid
ketone, alcohol, alkenes
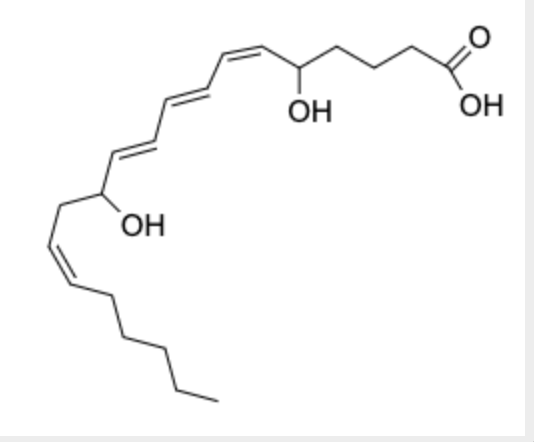
identify the molecule
leukotriene
structure of leukotriene
20 carbon-carbon fatty acid, carboxylic acid, three alkenes and no rings
what does omega 3 mean when referring to fatty acids
there is a double bond three carbons away from the omega carbon, the last carbon on the chain
oils have a _____ melting point than fats
lower
ceramides are most soluble in
ether
which has a higher melting point saturated or unsaturated fats
saturated fats have a higher melting point than unsaturated fats due to their molecular structure, which allows them to pack more closely together.
what is the primary function of cholesterol when embedded in a membrane
structure (makes it more rigid!!)
what is the primary function of eicosanoids
signaling
eicosanoids influence
inflammation, pain, vascular constriction/relaxation
identify the primary function of glycerophospholipids
structure
make up lipid bilayers in membranes
identify the primary function of sphingolipids
structure
name the classes of sphingolipids
ceramides (simplest class of sphingolipids)
glycosphingolipids
one or more sugar attached
sphingophospholipids
ceramides with phosphate containing head group
sphingomyelins (contains phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine head group)
gangliosides
contain multiple sugars and have sialic acid and c
primary function of triacylglycerols
energy
primary function of waxes
protection
function of sphibngomyelins
nerve cell membrane unit
what kind of biological activity do prostaglandins have
hormonal activity
functions of lipids
energy storage
structural component
energy source
steroid hormones
unsaturated fatty acids can be converted into saturated fatty acids by what
hydrogenation
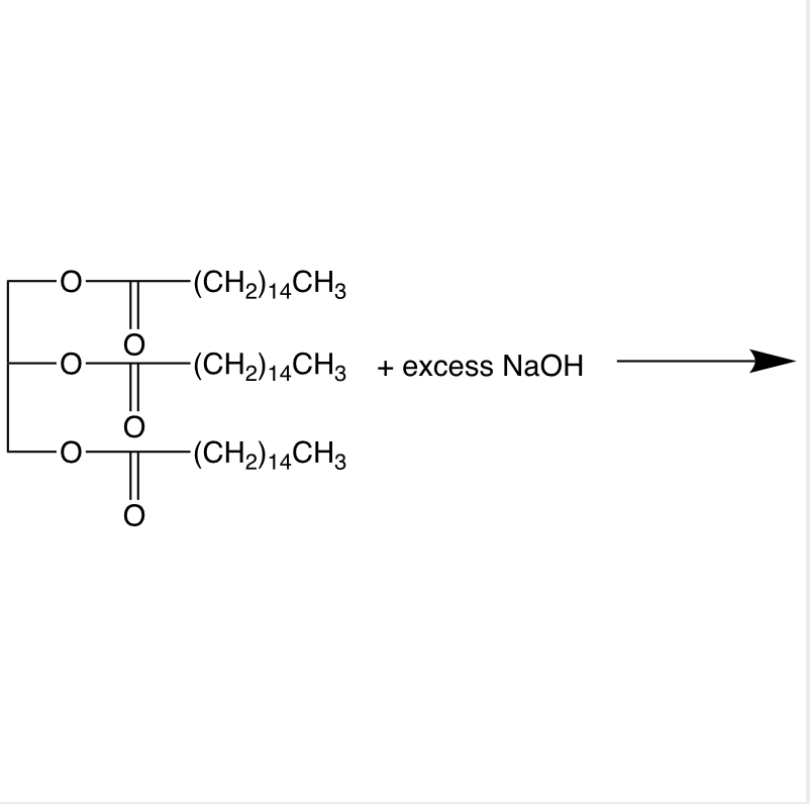
what type of lipid reaction is shown here
soap!
what type of functional group can react with a fatty acid to form an ester
alcohol
isoprene units are ____ carbon compounds that are building blocks for several terpenes and steroids
five
what is the name for lipids derived from isoprene units
terpenes
how do NSAIDS like aspirin and ibuprofen reduce inflammation
reducing production of prostaglandins and synthesis of other eicosanoids. reduces blood clotting.
which lipids are synthesized from arachidonic acid
leukotrienes
prostaglandins
thromboxanes
types of eicosanoids
leukotrienes, prostaglandins and thromboxanes
structural difference between glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelins
sphingomyelins have a sphingosine group and glycerophospholipids do not