exercise 42 urea hydrolysis (urease test) KTTK (MB. LAB)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Know what molecule urease breaks down and what that molecule is
converted to
Can be hydrolyzed to ammonia and carbon dioxide if urease is available to catalyze reaction
Know why phenol red was added to the urea agar tube
Phenol red is pH indicator used to show whether alkalinization of media through production of ammonia occurs
Know what the difference is between using urea agar versus urea broth
Lab manual mentions using urea broth which is similar to urea agar, but not quite the same
• It’s only nutrient source other than urea is trace amount of yeast
• Contains buffers strong enough to inhibit alkalinization of media by slower-urease positive organisms
(Urea agar differentiates between rapid, slow and no urease activity. Urea broth can only differentiate between rapid and non-rapid urease activity)
Know why (application) the urease test is used
• Used to determine ability of microbe to produce the enzyme urease
• Used to differentiate organisms based on ability to hydrolyze urea
• Urinary tract pathogens from genus Proteus may be distinguished from other enteric bacteria by their rapid urease activity
• Also used to identify Helicobacter pylori which is associated with
• Gastric and duodenal ulcers
• Stomach cancer
orange or yellow
(-)No urea hydrolysis; urease is absent or not produced in enough quantity to produce results in 24 hours; or the organism cannot live in urease broth.
pink/magenta
(+)Rapid urea hydrolysis; urease was produced.
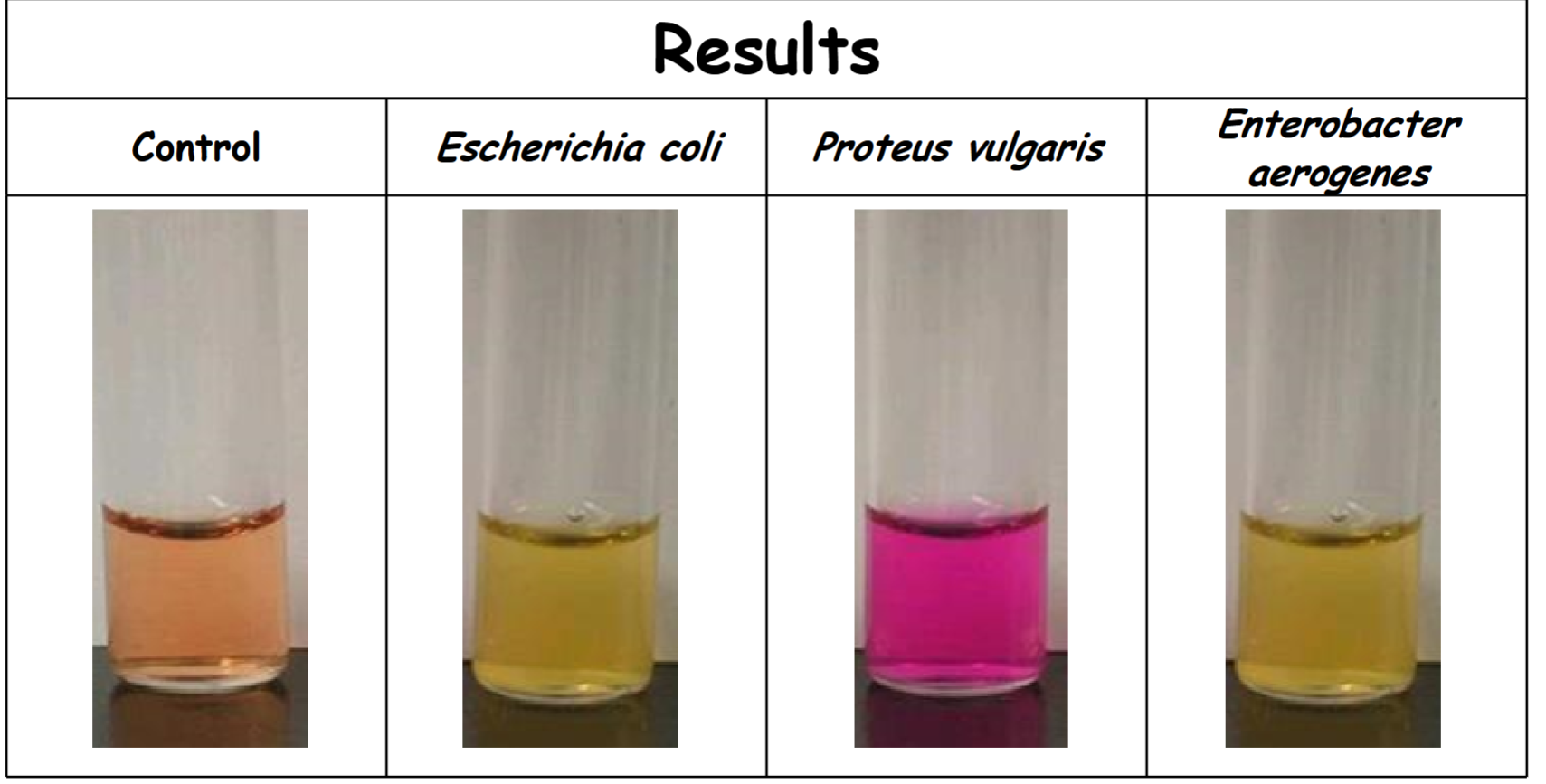
urea broth
broth control: no urea hydrolysis (-)
Escherichia coli: no urea hydrolysis (-)
Proteus vulgaris: Rapid urea hydrolysis; urease was produced (+)
Enterobacter aerogenes: no urea hydrolysis (-)
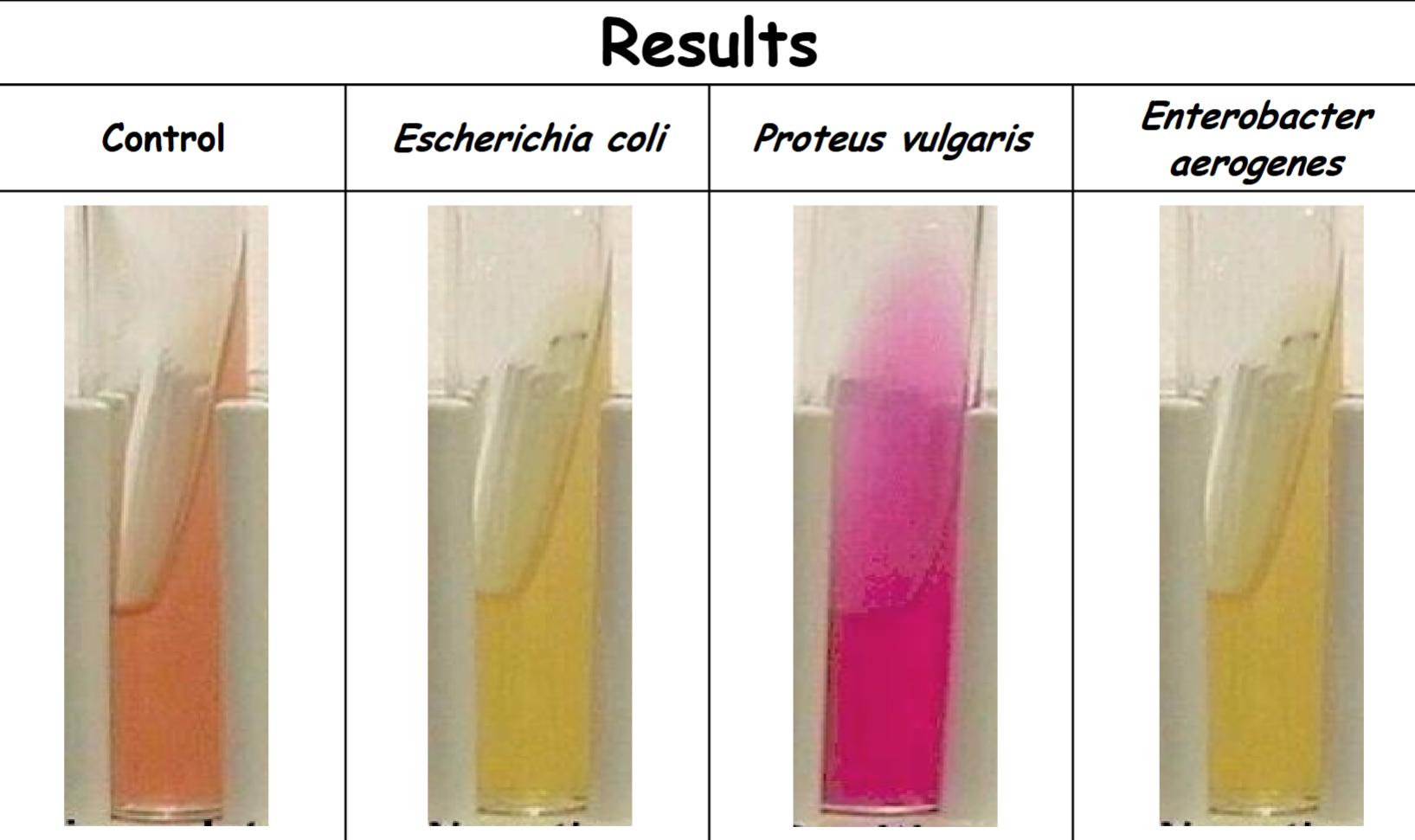
Urea agar
agar control: no urea hydrolysis (-)
Escherichia coli: no urea hydrolysis (-)
Proteus vulgaris: Rapid urea hydrolysis; urease was produced (+)
Enterobacter aerogenes: no urea hydrolysis (-)

urea broth image
urea agar image
