Learning Objectives Chapter 18
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe the structure & function of the mouth and throat.
-first part of digestive system
-responsible for ingestion, tasting, preparing food for digestion, & aiding in speech
-Trigeminal (V), Facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX), hypoglossal (XII)
Describe the structure & function of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
-first part of respiratory system
-responsible for receiving, filtering, warming, and moistening air
-olfactory (I)
Describe the oral cavity.
-also known as mouth
-formed by lips, cheeks, hard/soft palate, uvula, & tongue muscles
-contains tongue, teeth, gums, & salivary gland openings
*parotid, submandibular, sublingual
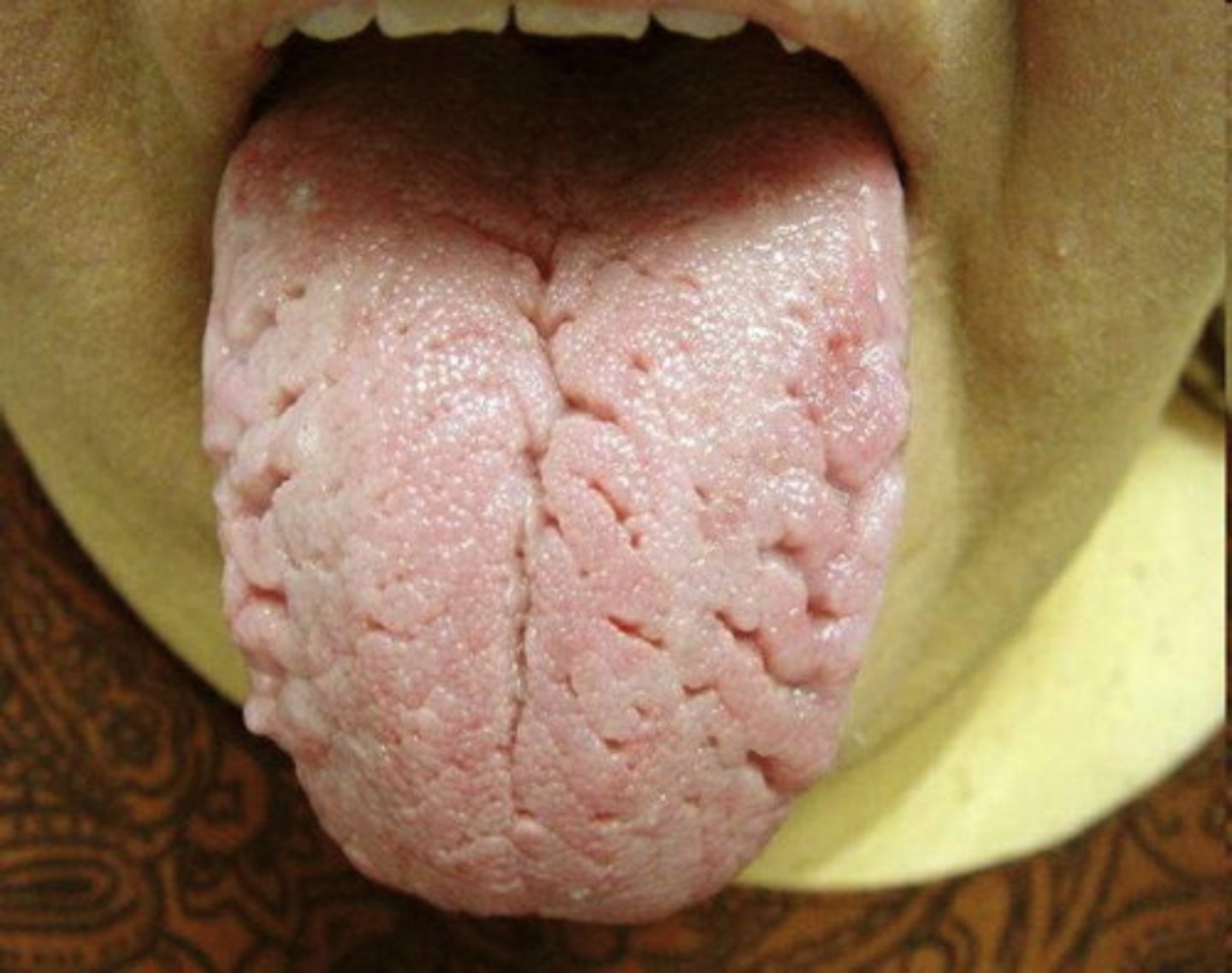
Describe normal tongue variations: fissured tongue
-not painful
-doesn't indicate disease
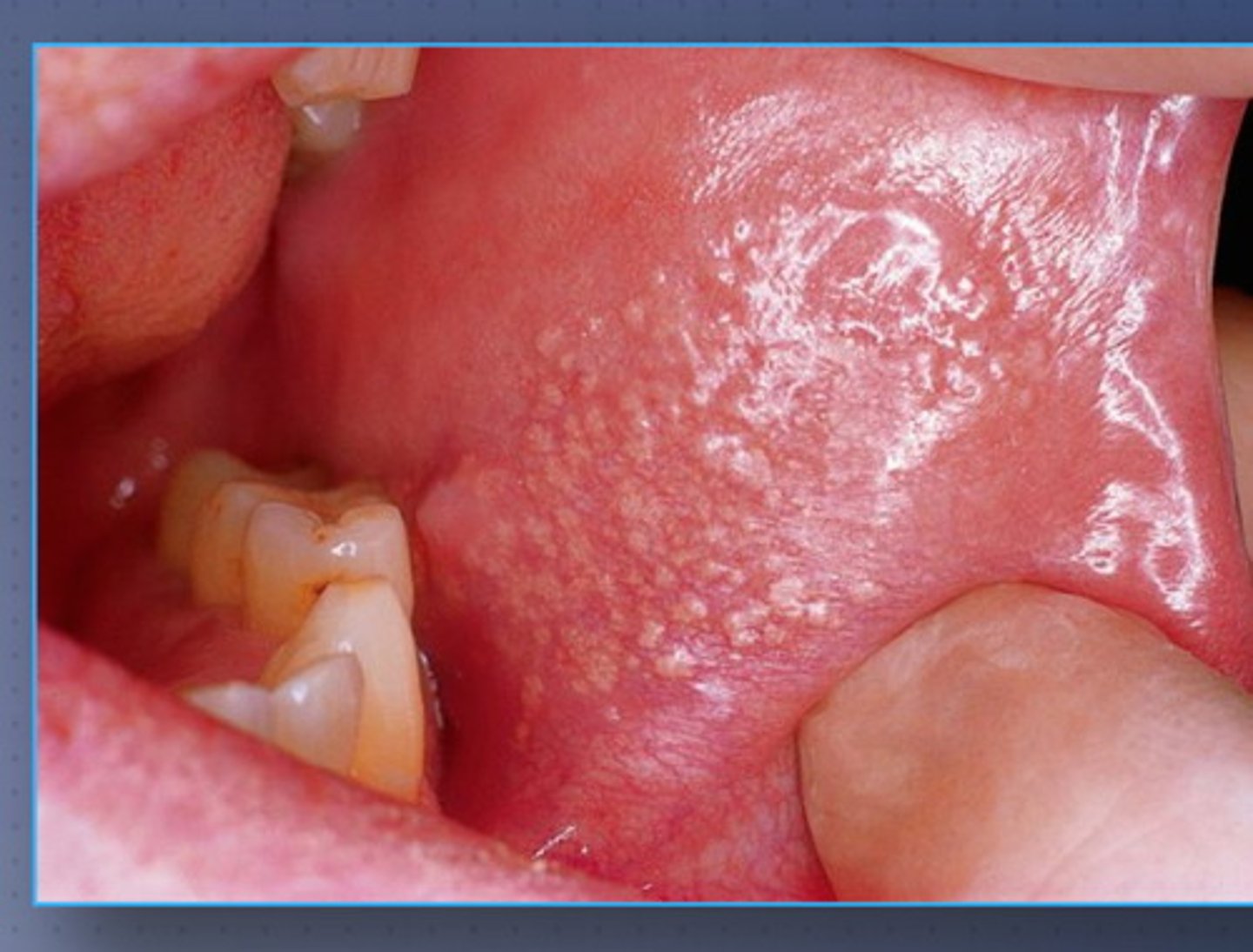
Describe normal tongue variations: Fordyce granules
-benign
-bottom of tongue
Describe the throat.
-also known as pharynx
-located behind nose and mouth
-muscular passage for food and air
-nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
Describe tonsils.
-masses of lymphoid tissue located in pharynx
-palatine tonsils: most commonly removed
-lingual tonsils: base of the tongue
-pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids): up towards nasopharynx
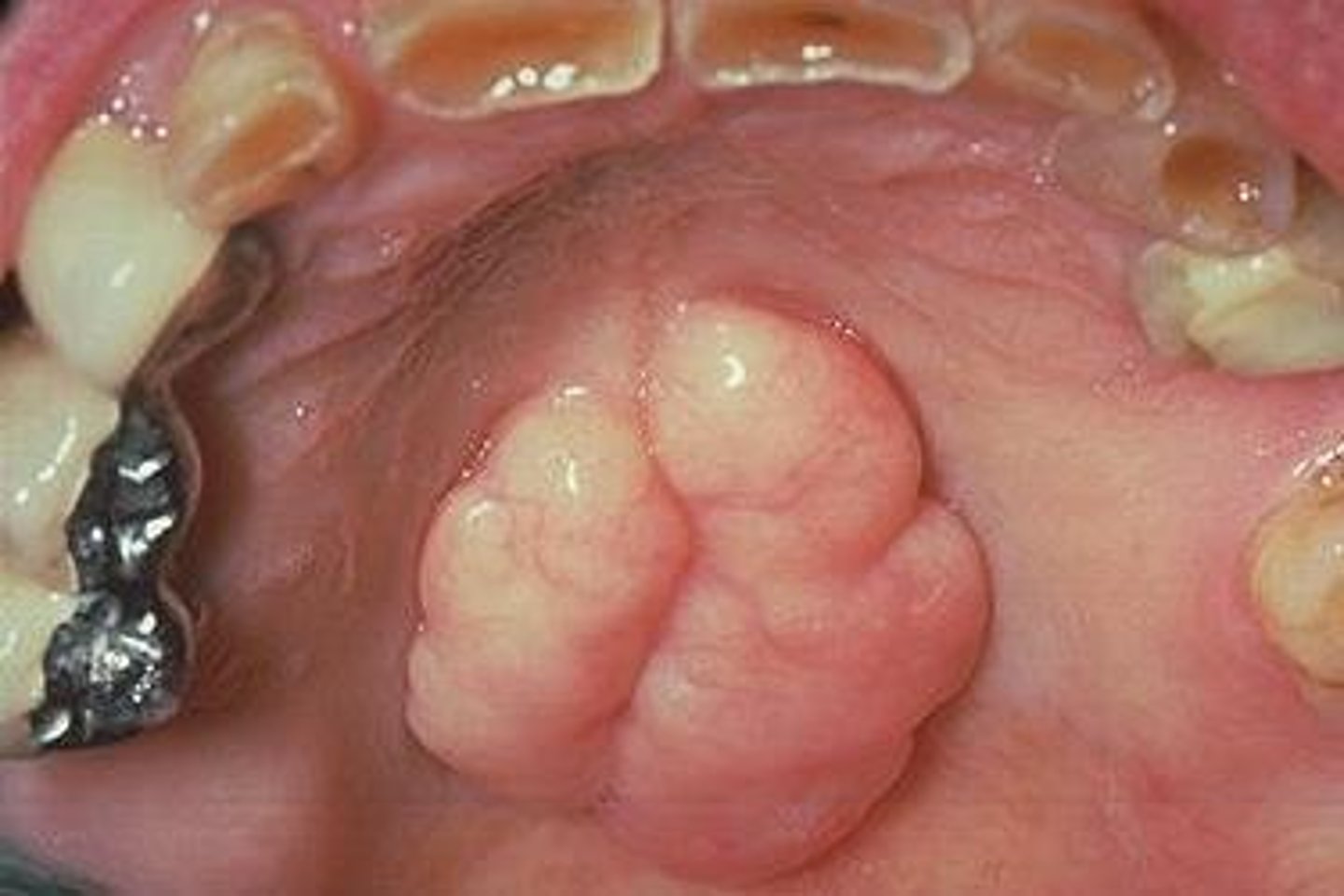
Describe physical variations of the oral cavity: torus palatinus
-benign
-boney structure
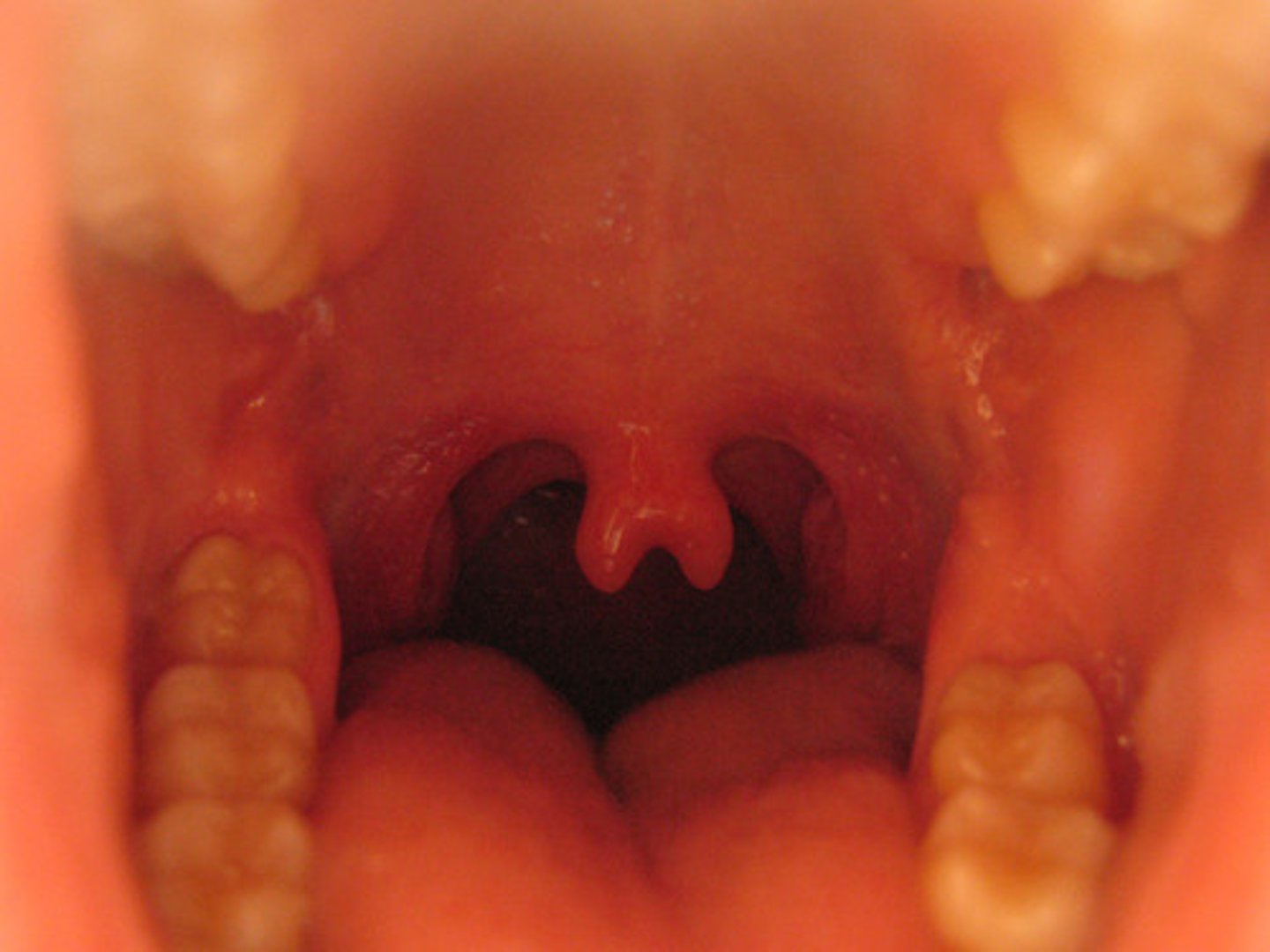
Describe physical variations of the oral cavity: bifid uvula
split uvula, looks like two
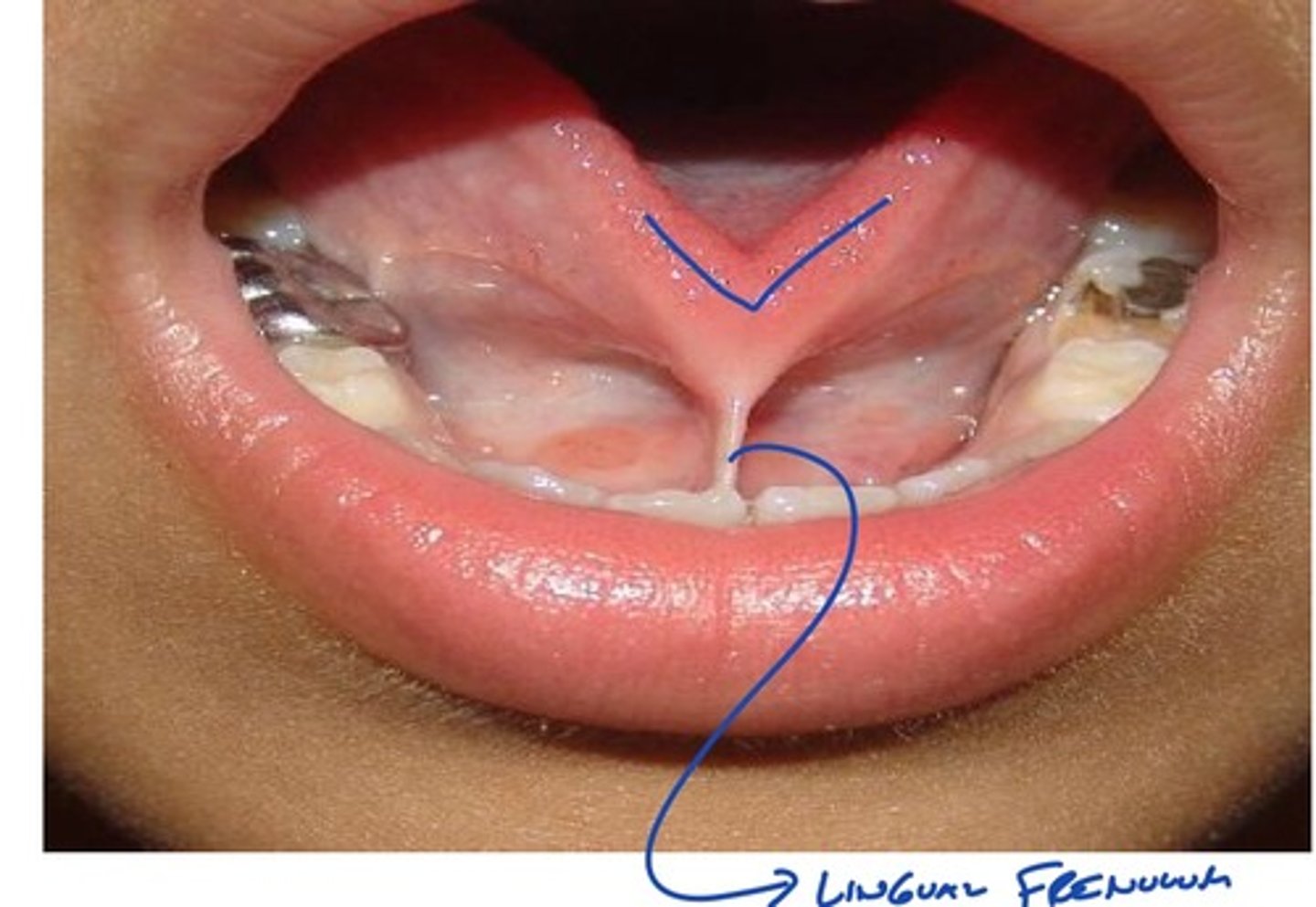
Describe physical variations of the oral cavity: shortened frenulum
-seen in children
-tongue tied: creates speech problems
-can get it clipped
Describe the nose.
-external portion & internal nasal cavity
-external nose: bridge, tip, two oval openings called nares
-internal nose: nasal cavity, septum, Kieselbach area, superior, middle, inferior turbinates
-olfactory nerve receptors located in upper part of nasal cavity and septum
Describe the sinuses.
-four pairs
-frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal, sphenoidal
-decrease the weight of skull, act as resonance chambers during speech
-normally filled with air --> fluid during illness or allergies
Describe biological and cultural variations.
-color differences
-structure of uvula, teeth, lips, palate
-hyperpigmentation of buccal mucosa by age 50
-benign leukoedema
-cleft uvula, lip, or palate
-number and size of teeth
-periodontal disease varies in number and severity by ethnic group
-oral disease, cancer, sinusitis
Describe older adult considerations.
-smell & taste abilities decrease (medications & neurodegenerative diseases)
-gums recede and become ischemia and fibrotic
-tooth surfaces worn and more susceptible to tooth loss and periodontal disease
-difficulty in teeth/denture hygiene
-teeth may appear longer due to age related gingival recession
-oral mucosa drier and frailer due to degeneration of epithelial lining in salivary glands
-varicose veins on tongue ventral surface
Describe the collection of subjective data.
Lifestyle and Health Practices:
-smoking or tobacco-less practices
-alcohol
-dental care
Describe equipment needed for the physical examination.
-nasal speculum
-tongue depressor
-short, wide-tipped speculum attached to head of otoscope
Describe how to prepare to obtain objective data.
Preparation:
-refine examination technique
-aware ethnocultural phenomena
-know age related changes
-identify and understand relationship between structures
Describe how to collect objective data relating to the mouth.
-inspect lips, teeth, buccal mucosa, Stensen ducts (inside cheeks), Wharton ducts (under tongue)
-inspect and palpate tongue
-check tongue strength, anterior tasting ability
-inspect hard/soft palate
-note odor
-inspect tonsils, uvula, posterior pharyngeal wall
Describe how to collect objective data relating to the nose and sinuses.
Nose:
-inspection and palpation: inspect and palpate external nose, check airflow patency through nostrils, inspect internal nose
Sinuses:
-palpation: palpate sinuses (cannot inspect)
Describe nose abnormalities.
-nasal polyp: growth in nasal cavity
-perforated septum: opening between right and left parts of nasal cavity; seen in piercings, snorting drugs, and extended nasal spray use
Describe tonsilitis.
Grading scale:
1+: visible
2+: midway between tonsillar pillars and uvula
3+: touch uvula
4+: touch each other
Describe abnormalities of the mouth and throat.
Mouth:
-herpes simplex type I (cold sores)
-cheilosis of lips: cracking at the corners of the mouth
-lip carcinoma
-leukoplakia: white tint on tongue underside
Throat:
-hairy leukoplakia: yeast looking on tongue side
-candida albicans infection: yeast infection
-vitamin B12 deficiency: smoothing taste buds
-black hairy tongue: antibiotics destroy normal mouth flora
-tongue carcinoma
-canker sore: ulceration of gum tissue
-gingivitis: gums are inflamed and bleed easily
-receding gums: aging
-Kaposi sarcoma lesions: AIDs
-acute tonsilitis: inflammation, white spots
-streptococcal pharyngitis: strep throat; very red, sore throat
Describe Oropharyngeal cancer.
Risk factors:
-tobacco/marijuana use
-heavy and frequent alcohol use
-HPV virus; oral sex
-prolonged sun exposure/fair skin
-gender: male
-over the age of 45
-poor oral hygiene, diet/nutrition
-weakened immune system
-chewing betel nut
Describe sinusitis (sinus infection).
Risk factors:
-nasal passage abnormality
-aspirin sensitivity
-medical condition (COPD, cystic fibrosis) or weakened immune system
-hay fever, allergic condition
-asthma
-regular exposure to pollutants
Seek medical advice if...
-shortness of breath
-stiff neck
-vision changes
-confusion
-severe headache and swollen forehead
-pain of swelling around eyes
-repeated episodes not responding to treatment