Inhaled medicines
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Physical perspective of the purpose of the air way
Heat and humidify the inhaled air (Conditioning).
Remove particles from the inhaled air by deposition (ie. act as a filter).
Where should particles ideally not reach
Alveoli - smaller particle <10um may
Why delivery to the lungs?
local effect: e.g. bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, mucolytics
systemic effect: e.g. volatile anaesthetics (halothane), ergotamine tartarate (migraine), peptide drugs (insulin) (avoids first pass effect)
Rapid onset of action
Smaller doses than oral formulations and hence less systemic and GI adverse effects
Relatively comfortable
How to overcome the barrier of delivery/ penetrate into he airways
Drugs are delivered in the form of an aerosol
What is an Aerosol?
Suspension of liquid or solid particles in a gas → sufficiently small to remain airborne for a considerable time
•dispersion of solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas
In order to be effective the aerosol particles must
Deposit in the appropriate lung region
In the right quantity
Overcome physiological barriers and respiratory defence mechanisms
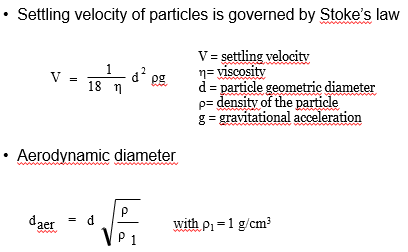
What is aerodynamic diameter?
Diameter of a (“pretend”) sphere with a density of 1g/cm3 that has the same settling velocity in air as the particle of interest
What settling velocity of particles is governed by…
Stoke’s law
Aerodynamic diameter fomula and stokes law
V = settling velocity
h= viscosity
d = particle geometric diameter
r= density of the particle
g = gravitational acceleration
Respirable fraction of an inhaled medicine definition
Percentage of drug present in aerosol particles less than 5 μm in size and hence likely to be deposited
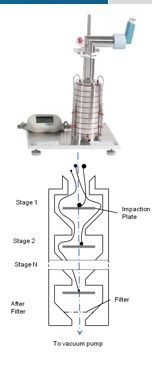
How to determine respirable fraction
Particle sixing techniques
Anderson Cascade Impactor
Next Generation Impinger
Next Generation Impinger
7 stages
Calibrated to flow rate required
Powder collected in cups after each stage
Size distribution information and prediction of site of deposition in the lung
Anderson Cascade Impactor
picture
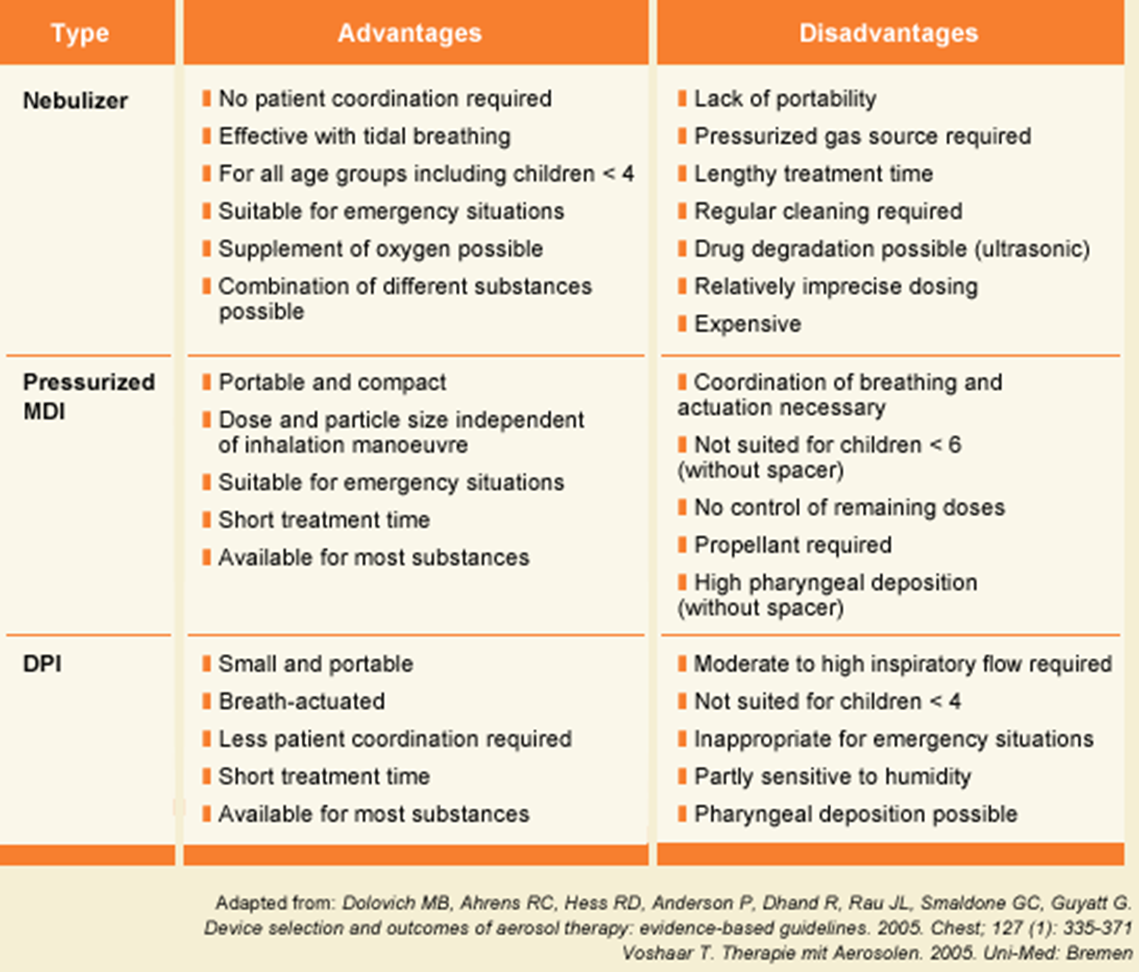
3 types of inhalers:
Nebulisers
Pressurised metered dose inhalers (pMDI) → most used/convient
Dry powder inhalers (DPI)
Nebulisers
Aqueous drug solution/suspension aerosolised into droplets
Energy provided by compressed air or ultrasound
pMDI
Drug formulated in a liquefied gas under pressure
Aerosol formed by evaporation of the gas at atmospheric pressure
Issues with pMDI
Large proportion of patients are unable to co-ordinate actuation with inhalation
Particles leave the pMDI at a high velocity → high deposition in the oro-pharynx (back of throat)→ Consequence: low % deposition in the lung
Can improve with a spacer, but inconvenient
DPI
Drug normally with other solid excipients in a dry powder state
Aerosolisation by patient’s own inhalation
Delivers a dry powder, no solvent is involved
DPI as an alternative to pMDI
Breath actuated (no coordination required)
As a drug and excipients in a dry form tend to be more stable than drug dispersed in a solvent as in pMDI
Traditionally seen as difficult to formulate a suitable powder
Main components of DPI
Drug powder or blend of drug powder with excipients
Drug reservoir or pre-metered doses (cartridge, blister, capsule)
Body of the device
Cap to protect powder from dust, moisture
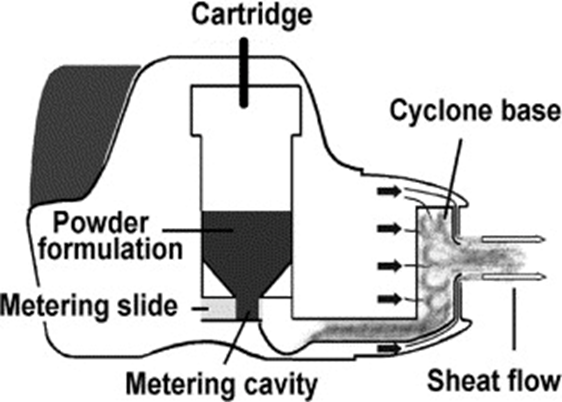
The patient’s inspiratory flow is used to: (DPI)
Fluidize the static powder blend
De-aggregate particle agglomerates into inhalable particles
•Dose delivered and deposited into the lungs depends on the patient’s inspiratory flow rate (hard to predict and reproduce!)
Main issues with DPI
•Particles < 5 µm (AS NEEDED TO PENETRATE THE LUNG) are extremely cohesive (due to large surface area compared to mass)
Moisture increases agglomeration (ensure powders stay dry)
Solution to DPI
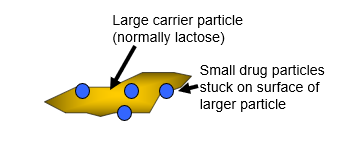
•Drug blended with a carrier powder with large particle size (typically lactose). This means drug must be separated from this carrier particle to be inhaled.
•Spherical particles (eg. spray-dried powders) can reduce particle contact area and hence aggregation.
•Protection from moisture (blister pack, use of desiccant)
DPI formulation
Carrier particles (50-100μm) are needed to stop small (< 5μm) drug particles aggregating (this is known as an ORDERED MIX).
To be effective for delivery the small drug particles must be separated from the carrier during inhalation
Large lactose particles deposit in the oro-pharynx
Drug deposits in the lungs
Types of DPI
unit does devices
Multiple unit does devices
Reservoir devices
advantages and disadvantages of inhaler types