Honors Biology - Unit 6
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
10% rule
Only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next level; the rest is lost as heat and life processes.
Abiotic factor
Nonliving parts of an ecosystem (temperature, water, sunlight, rocks, soil).
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food using energy from sunlight or chemicals (producer).
Biotic factor
Living or once-living components of an ecosystem.
Calvin cycle
The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis that build sugars from CO₂ using ATP and NADPH.
Carbon fixation
The process of converting inorganic CO₂ into organic molecules (like G3P) during photosynthesis.
Chemical potential energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds of molecules.
Chlorophyll
The main green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
Chloroplast
The organelle where photosynthesis occurs in plant and algal cells.
Commensalism
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Competition
Interaction where organisms fight for the same limited resources (food, space, mates, etc.).
Dark reaction
Another name for the Calvin cycle; does not require light directly.
Energy pyramid
A diagram showing the flow of energy through trophic levels in an ecosystem.
Food chain
A single pathway of energy flow
Food web
Interconnected food chains in an ecosystem
G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)
A 3-carbon sugar produced in the Calvin cycle; can be used to build glucose and other molecules.
Glucose
A 6-carbon sugar (C₆H₁₂O₆) that stores chemical energy for cells.
Granum
A stack of thylakoids
Grana
Multiple stacks of thylakoids
Heterotroph
An organism that must consume other organisms for energy (consumer).
Keystone species
A species that has a disproportionately large effect on its ecosystem; its removal causes major changes.
Light reaction
First stage of photosynthesis; light energy is converted to chemical energy (ATP & NADPH) and oxygen is released.
Mutualism
A symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit.
NADP⁺
an electron carrier molecule
NADPH
the reduced form of NADP⁺ that carries high-energy electrons to the Calvin cycle
Parasitism
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is harmed.
Photosynthesis
The process where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, CO₂, and H₂O into glucose and oxygen.
Photosystem
A cluster of chlorophyll and proteins in the thylakoid membrane that captures light energy.
Pigment
A molecule that absorbs specific wavelengths of light.
Predation
Interaction where one organism (predator) kills and eats another (prey).
Radiant energy
Energy that travels in electromagnetic waves, such as sunlight.
RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate)
A 5-carbon molecule that reacts with CO₂ in the Calvin cycle.
Rubisco
The enzyme that attaches CO₂ to RuBP during carbon fixation.
Stroma
The fluid-filled space inside a chloroplast surrounding the grana; site of the Calvin cycle.
Symbiosis
A close, long-term relationship between two different species.
Trophic cascade
A chain reaction in an ecosystem that occurs when changes at one trophic level affect many other levels.
Trophic levels
Feeding levels in an ecosystem (producers, primary consumers, etc.).
Thylakoid
Flattened membrane sacs inside chloroplasts where light reactions occur.
True
True or False: The main energy source for all life on Earth is the sun.
Decomposer
A ________ is a type of consumer that obtains energy by breaking down organic matter.
Autotroph
A ______ is an organism capable of producing its own food.
Heterotroph
A ________ is a type of consumer that only eats other animals.
Herbivore
A ________ is a type of consumer that only eats plants.
Omnivore
A ________ is a type of consumer that eats both plants and animals.
Scavenger
A ________ is a type of consumer that eats dead plants or animals.
b. Mushroom
Which of the following is an example of a biotic factor?
a. Sunlight
b. Mushroom
c. Soil
d. Lake Erie
c. Temperature
Which of the following is an example of an abiotic factor?
a. Sunflower
b. Caterpillar
c. Temperature
d. Grizzly Bear
10%
What percentage of energy is transferred from one organism to the next in a food chain?
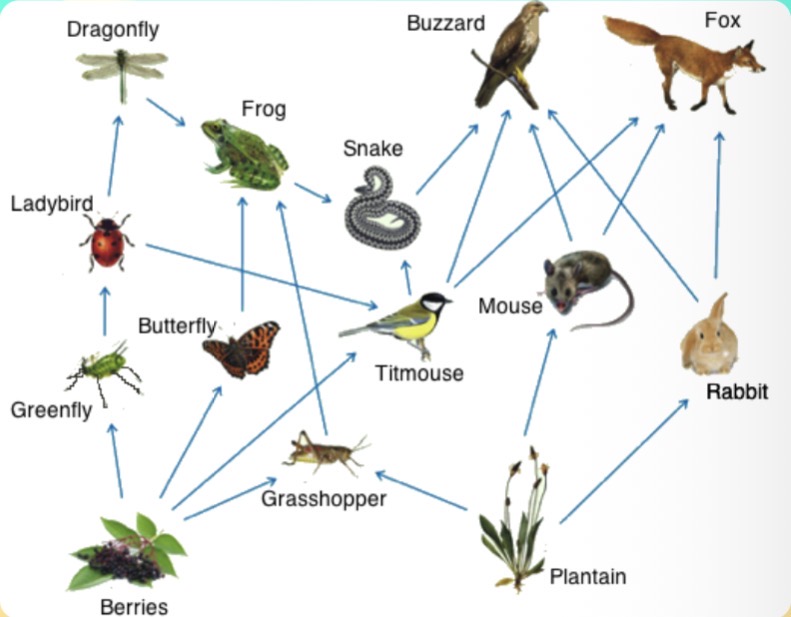
Frog
Which organism in the food chain is a secondary consumer?
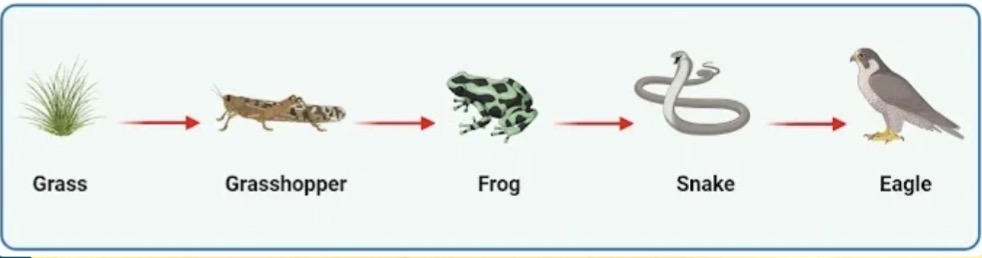
Hawk
Which organism from the options provided would receive the lowest amount of energy?
Snake
Which organism in the food chain is a tertiary consumer?
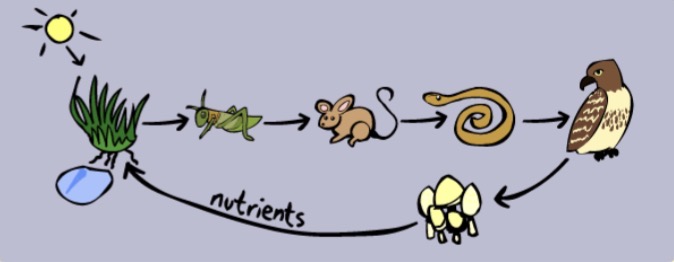
Mouse
In the given food web, which organism is an OMNIVORE?
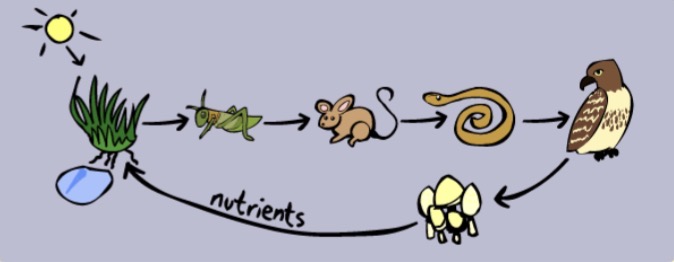
All of the above!
In the given food web, which is a primary consumer?
a. Prairie dog
b. Squirrel
c. Grasshopper
d. Blue jay
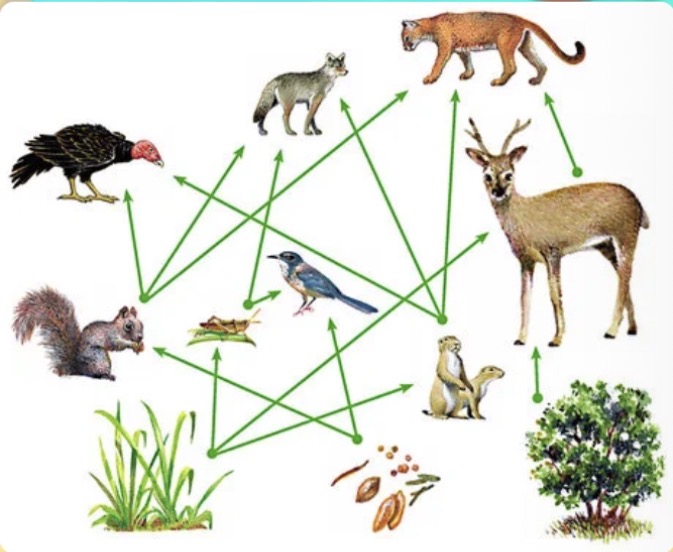
d. All of them
In the given food web, what would happen if there was a drought?
a. The food web would collapse
b. Decomposers would thrive
c. Organisms would move to other ecosystems
d. All of them
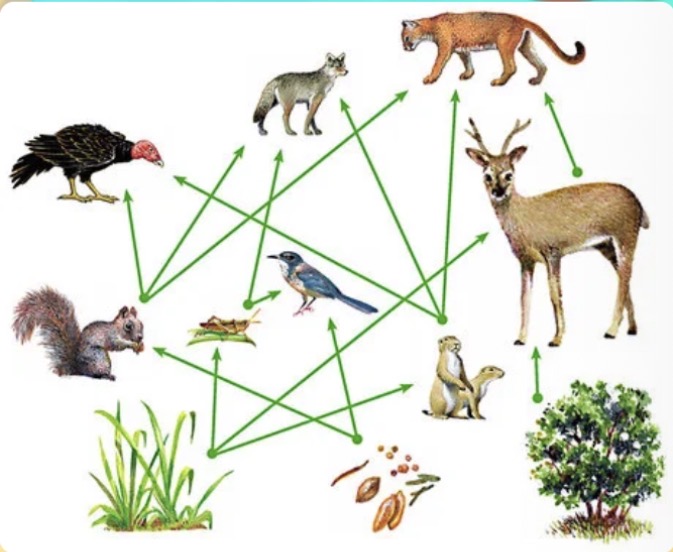
a. Deer population would decrease
In the given food web, what would most likely happen if a wolf moved into the ecosystem?
a. Deer populations would decrease
b. Cougar numbers would increase
c. Vulture numbers would increase
d. Plant numbers would decrease
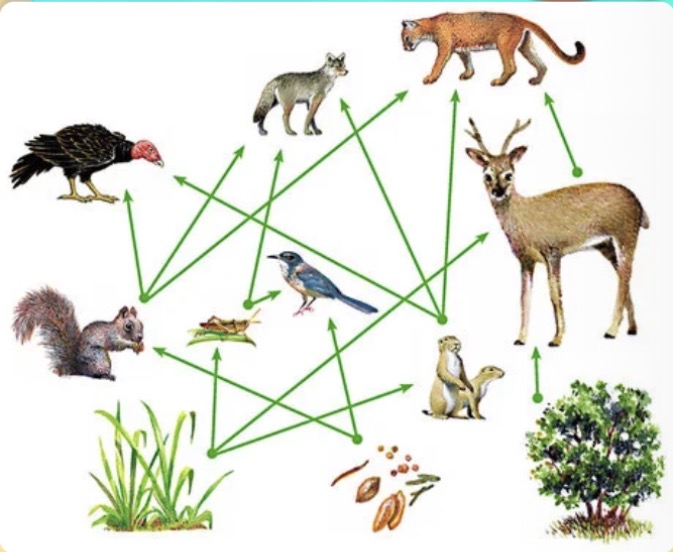
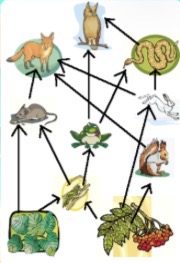
Flow of energy
What does an arrow represent in a food web?
Foxes and buzzards
Which organisms have the LEAST amount of energy in this food web?
Plants carry out photosynthesis
Carbon moves into living things from the atmosphere when...
a. Producers from photosynthesis, consumers from food
Carbon is critical to life for biomolecules and energy. How do living things get carbon?
a. Producers from photosynthesis, consumers from food
b. Plants from air, animals from air
c. Animals from food, plants from water
d. Both from water
Glucose and O2
Which products are being created during the BOXEDportion of the carbon/oxygen cycle?
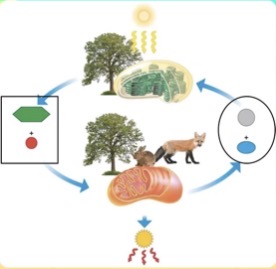
CO2 and H2O
Which products are being created during the CIRCLEDportion of the carbon/oxygen cycle?
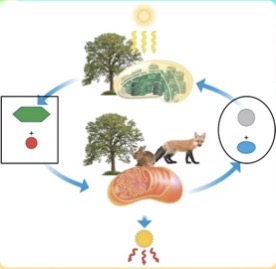
Commensalism
The relationship between a squirrel (gains food and shelter) and a tree (gains nothing) is best described as...
Parasitism
The relationship between a tapeworm (gains food and shelter) and a human (gets sick) is best described as...
Mutualism
The relationship between a gobie fish (gains shelter) and a shrimp (gains protection) is best described as...
Keystone species
a species an ecosystem depends on greatly
Producers
Which level of the energy pyramid has the most energy?
3.05 kJ
If the grasshopper has 305 kJ of energy, how much will the SNAKE have?
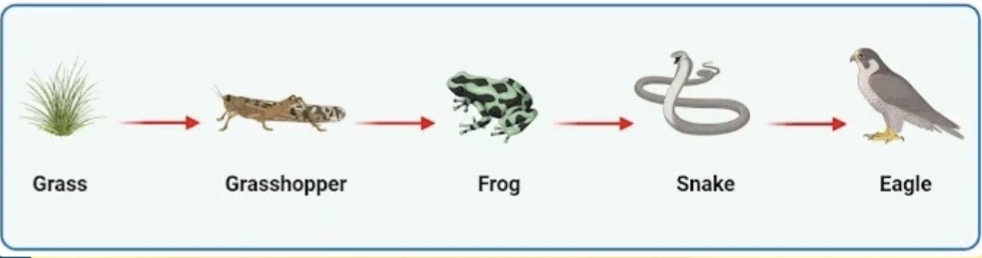
Trophic cascade
powerful indirect interactions that can control entire ecosystems
Autotroph
Organisms that use sunlight to get energy = ?
Heterotroph
Organisms that get energy from food = ?
c. For plants to capture sunlight to make glucose
What is the ultimate goal of photosynthesis?
a. For plants to turn food into radiant energy for the sun
b. For plants to break down glucose to generate ATP and NADPH
c. For plants to capture sunlight to make glucose
d. For plants to use glucose to make carbon dioxide
a. ATP
Which of these compounds is made in the light reactions?
a. ATP
b. NADP+
c. H2O
d. CO2
Carbon dioxide
Fill in the equation: 6A + 6 water---B--> C + 6D. What is A?
Light
Fill in the equation: 6A + 6 water---B--> C + 6D. What is B?
Glucose
Fill in the equation: 6A + 6 water---B--> C + 6D. What is C?
Oxygen
Fill in the equation: 6A + 6 water---B--> C + 6D. What is D?
Blue
Which color (wavelength) of light supports greater growth in plants?
Chloroplast
Which organelle does photosynthesis take place in?
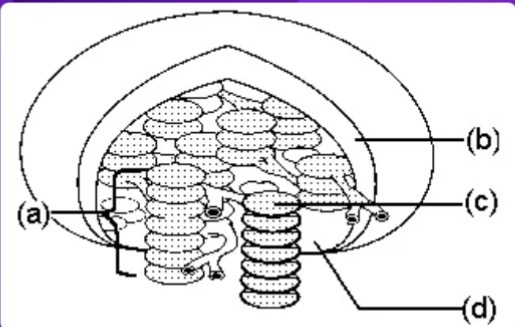
a
Granum = letter ___?
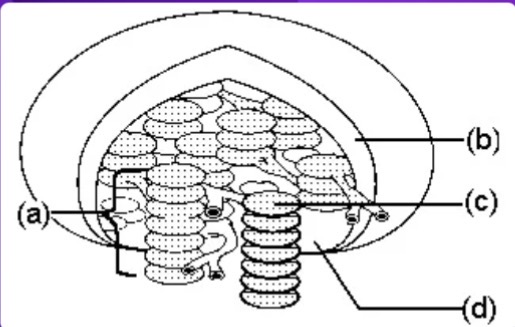
C
Thylakoid = letter ___?
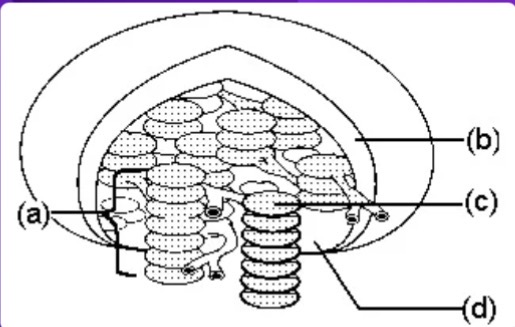
D
Stroma = letter ___?
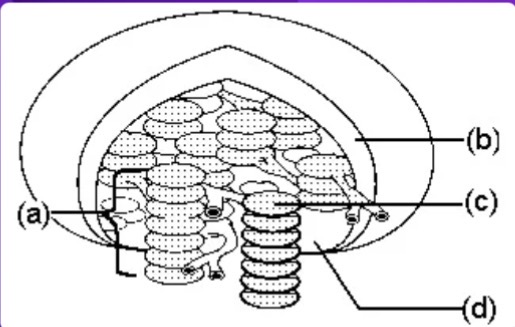
C
Where do the light reactions take place?
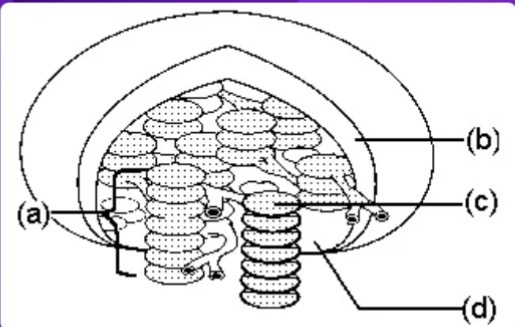
D
Where do the dark reactions take place?
Green
Which color does chlorophyll reflect?
b. An electron is excited
What happens when light hits a photosystem within a chloroplast?
a. A proton is excited
b. An electron is excited
c. A neutron is excited
d. Nothing happens
c. To replenish electrons lost in Photosystem II
Why is water split during the light reaction?
a. To charge an ATP molecule
b. To charge a NADPH molecule
c. To replenish electrons lost in Photosystem II
d. To replenish electrons lost in Photosystem I
Glucose
The dark reactions of photosynthesis are responsible for producing this compound...?
c. Both
The Calvin cycle uses what product(s) of the light reactions?
a. ATP
b. NADPH
c. Both
d. Neither
Rubisco
Which enzyme participates in the process of carbon fixation during the dark reactions?
G3P
Which high-energy compound is produced during the dark reactions, and is later used to construct glucose?
RuBP
Which compound is regenerated during the dark reaction to be available for carbon fixation?
False
T or F: Plants are only capable of performing photosynthesis and not cellular respiration.
c. Each process produces what the other needs
Which of the following statements regarding photosynthesis and cellular respiration is TRUE?
a. Both utilize the same reactants
b. Both processes end up creating the same products
c. Each process produces what the other needs
d. Cellular respiration only occurs during the day when photosynthesis occurs
b. Increased CO2 in the atmosphere allow photosynthesis to happen quicker
Which of the statements is FALSE regarding photosynthesis and climate change?
a. Deforestation leads to an increase of CO2 in the atmosphere
b. Increased CO2 in the atmosphere allow photosynthesis to happen quicker
c. Warmer temperatures can slow the process of photosynthesis
d. Rising temperatures can alter weather patterns and water availability
c. Wind
Which of the following factors would NOT have an affect on the rate of photosynthesis?
a. Water availability
b. Light intensity
c. Wind
d. CO2 concentration