Sexually Transmitted Infections/Pelvic Infections
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
sexually transmitted infections are disorders spread by ?
intimate contact
what STI can spread via lactation from mom to baby?
HIV
herpes genitalis
A sexually transmitted infection caused by a DNA virus, herpes simplex virus (HSV) (in and out of the nervous tissue)
Incubation period is 2-7 days
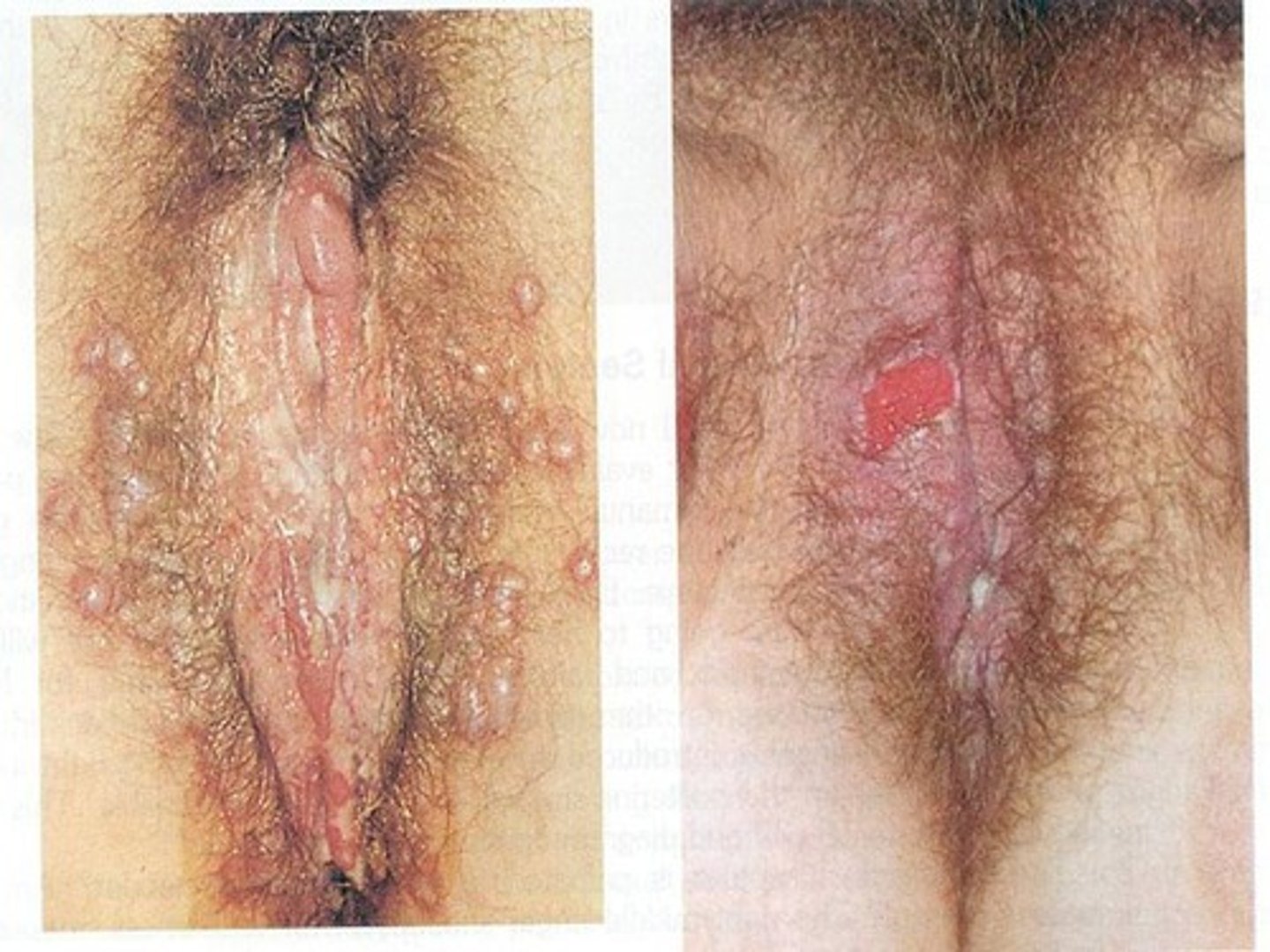
what is the clinical presentation of a prodrome of herpes genitalis?
Tingling, burning, itching; sensation/feeling before an outbreak starts
Fever, malaise, HA, myalgias
Inguinal lymphadenopathy
what is the clinical presentation of the initial outbreak of herpes genitalis?
Extensive lesions
Lasting 2-6 weeks without treatment
Systemic symptoms and lymphadenopathy are common
what is the clinical presentation of subsuquent outbreaks of herpes genitalis?
Lesions are localized, smaller, fewer in number, and typically confined to a constant area
Last 1-3 weeks without treatment
Systemic symptoms and lymphadenopathy are rare
what is the gold standard/most sensitive test for herpes genitalis?
HSV PCR
what are the 3 antiviral therapies that can be prescribed for herpes genitalis for the initial outbreak, subsequent outbreaks, and suppressive therapy?
Valacyclovir
Acyclovir
Famcyclovir
what are complications to herpes genitalis?
Psychological implications
Neonatal herpes
Cervicitis
Secondary infection
HIV patient with HSV should receive ? due to prolonged outbreaks and increased HSV shedding
suppressive therapy
Women with any potential history of HSV or a partner with HSV should be given suppressive therapy starting at how many weeks gestation?
36
condyloma acuminatum
Papillary growths affecting the perineum, anus, vulva, vagina, cervix, and oropharynx
Incubation period ranges from weeks to years
Caused by “low risk” strains of single stranded DNA virus, human papilloma virus (HPV)
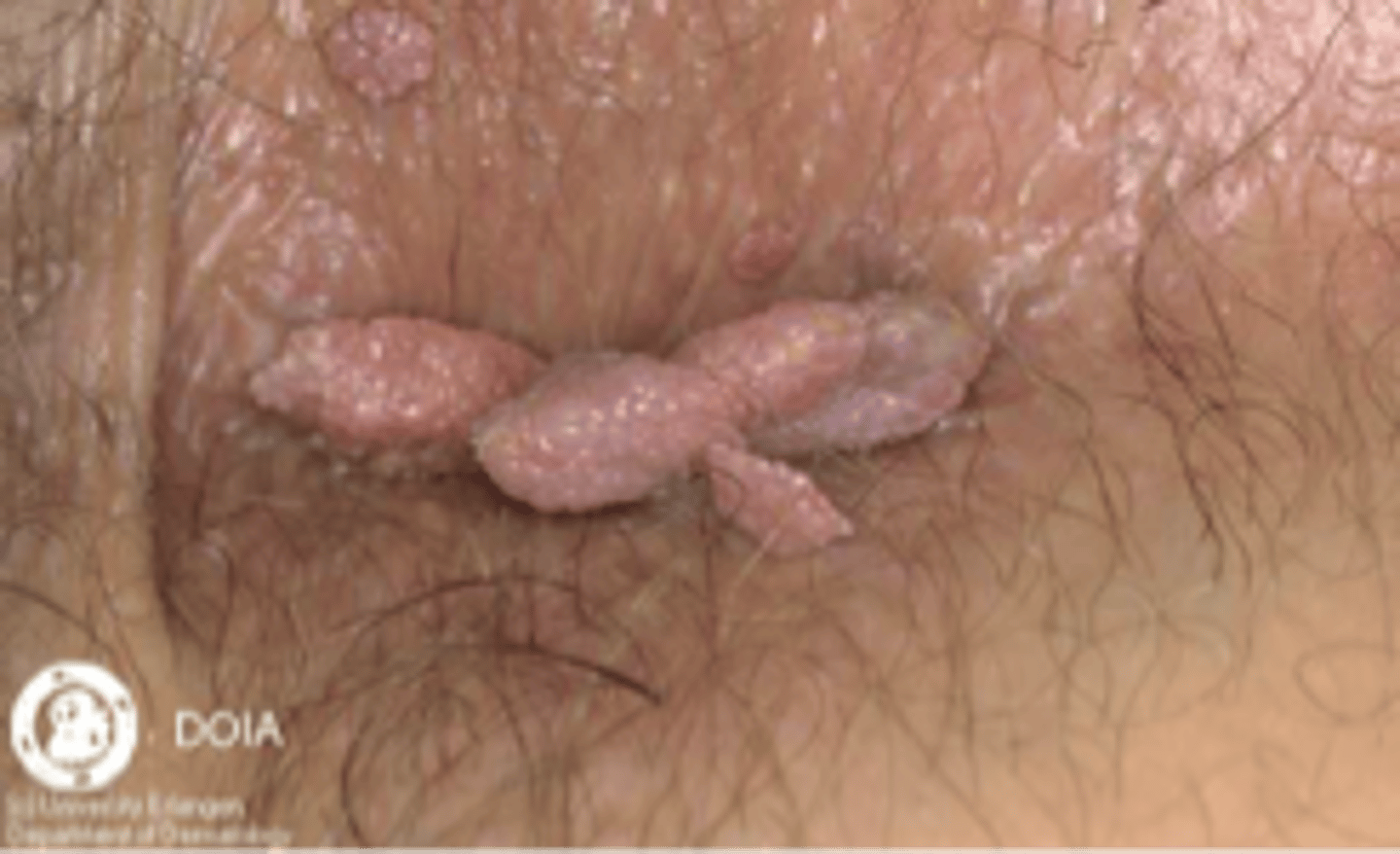
what strains of HPV typically cause condyloma acuminatum?
HPV 6 and 11
how does condyloma acuminatum present?
Whitish or flesh-colored papillomatous growths with “cauliflower” appearance ranging from small single lesions to large coalescing growths
Recurrence is common
why can you diagnosis condyloma acuminatum with acetic acid application?
HPV has large nucleus so it will look white with acid
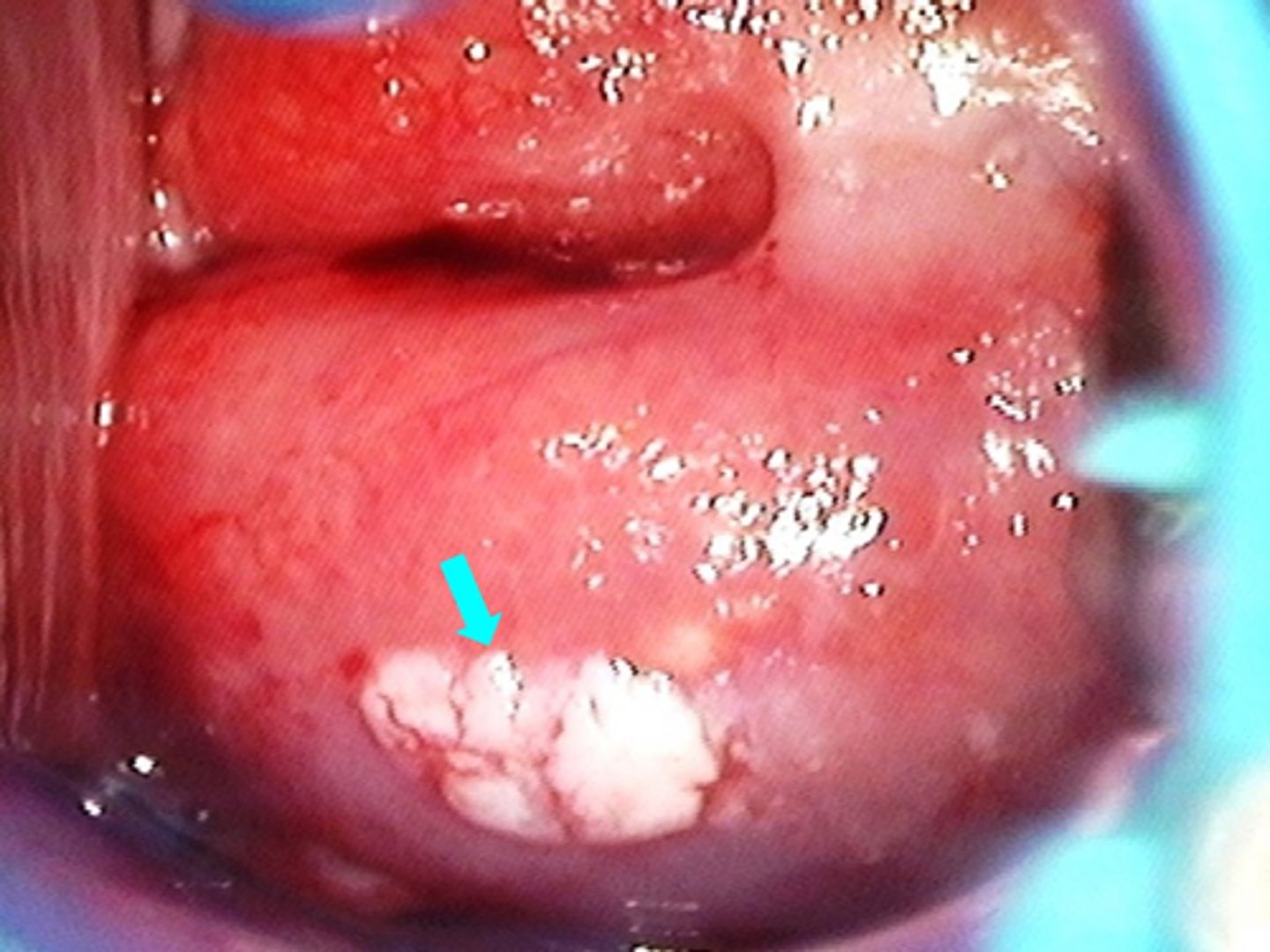
what are treatment options for condyloma acuminatum?
Trichloroacetic acid (office)
Podophyllin (office)
Surgical options: Cryosurgery, electrosurgery, laser surgery, simple resection
Home treatments: Imiquimod (Aldara, Zyclara)
Podofilox (Condylox)
Sinecatechin (Veregen®)
condyloma in pregnancy
Grow fast, bleed more
Risk of transmission to infant during vaginal delivery
Genital warts, laryngeal papilloma, and rarely infection of the pulmonary parenchyma
what is a great way to prevent condyloma acuminatum other than condom use?
Gardasil vaccine
bacterial vaginosis is NOT sexually transmitted but what is it associated with?
high risk behavior (multiple sex partners, new sex partners, lack of condom use)
trichomoniasis
Sexually transmitted vaginal infection caused by Flagellated protozoan Trichamonas vaginalis
Incubation period is unknown
Excellent cure rate
how does trichomoniasis present?
Asymptomatic
Purulent malodorous thin discharge, frothy, bubbly, (green, yellow, thin)
Vaginal irritation
Dyspareunia
Dysuria
Erythema of the vulva/vagina
Punctate hemorrhages on the cervix “strawberry cervix”
what is the treatment for trichomoniasis?
Metronidazole (Flagyl) or Tinidazole
Metronidazole, Tinidazole, or Secnidazole
Empiric treatment for trichomoniasis is appropriate in certain circumstances t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
what are complications of trichomoniasis?
Cervicitis
Salipingitis
PPROM and preterm delivery
gonorrhea
A highly contagious sexually transmitted infection that caused by Gram-negative diplococcus, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Can involve any mucous membrane, most common site of infection is the genitourinary tract
Incubation period of 2-7 days
Excellent cure rate
how does a localized infection of gonorrhea present?
Purulent vaginal discharge (yellow, green)
Vaginal irritation
Urinary frequency
Dysuria
Rectal discomfort
Pelvic pain
Acute pharyngitis/tonsillitis
Conjunctivitis
how does a disseminated infection of gonorrhea present?
Septicemia
purulent arthritis
Endocarditis
Meningitis
what is the gold standard way to diagnosis gonorrhea?
nucleic acid amplification
what is the treatment for gonorrhea?
Ceftriaxone
Empiric treatment for gonorrhea is NOT appropriate in certain circumstances t/f
false
1 multiple choice option
what are complications of gonorrhea?
Cervicitis
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Salpingitis
PPROM and preterm delivery
Opthalmia neonatorum
High rates of Chlamydia coinfection
Reinfection is common
chlamydia
A highly contagious sexually transmitted infection caused by Gram-negative bacteria, Chlamydia trachomatis
Incubation period of 7-14 days
Excellent cure rate
how does chlamydia present?
Asymptomatic
Mucopurulent discharge
Urinary symptoms
Pelvic pain
Cervical erythema and hypertrophy
what is the gold standard way to diagnose chlamydia?
nucleic acid amplification
how do you treat chlamydia?
azithromycin or doxycycline
Empiric treatment of chlamydia is appropriate in certain circumstances t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
what are complications of chlamydia?
Cervicitis
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Salpingitis
PPROM and preterm delivery
Fitz-Hugh Curtis Syndrome
Conjunctivitis, otitis media, or chlamydial pneumonia from vaginal delivery
Lymphogranuloma Vereneum
High rates of Gonorrhea coinfection
Reinfection is common
lymphogranuloma venereum
Sexually transmitted infections of inguinal lymphatic channels caused by L serotypes of gram-negative bacteria, Chlamydia trachomatis
Rare in the US
M > F
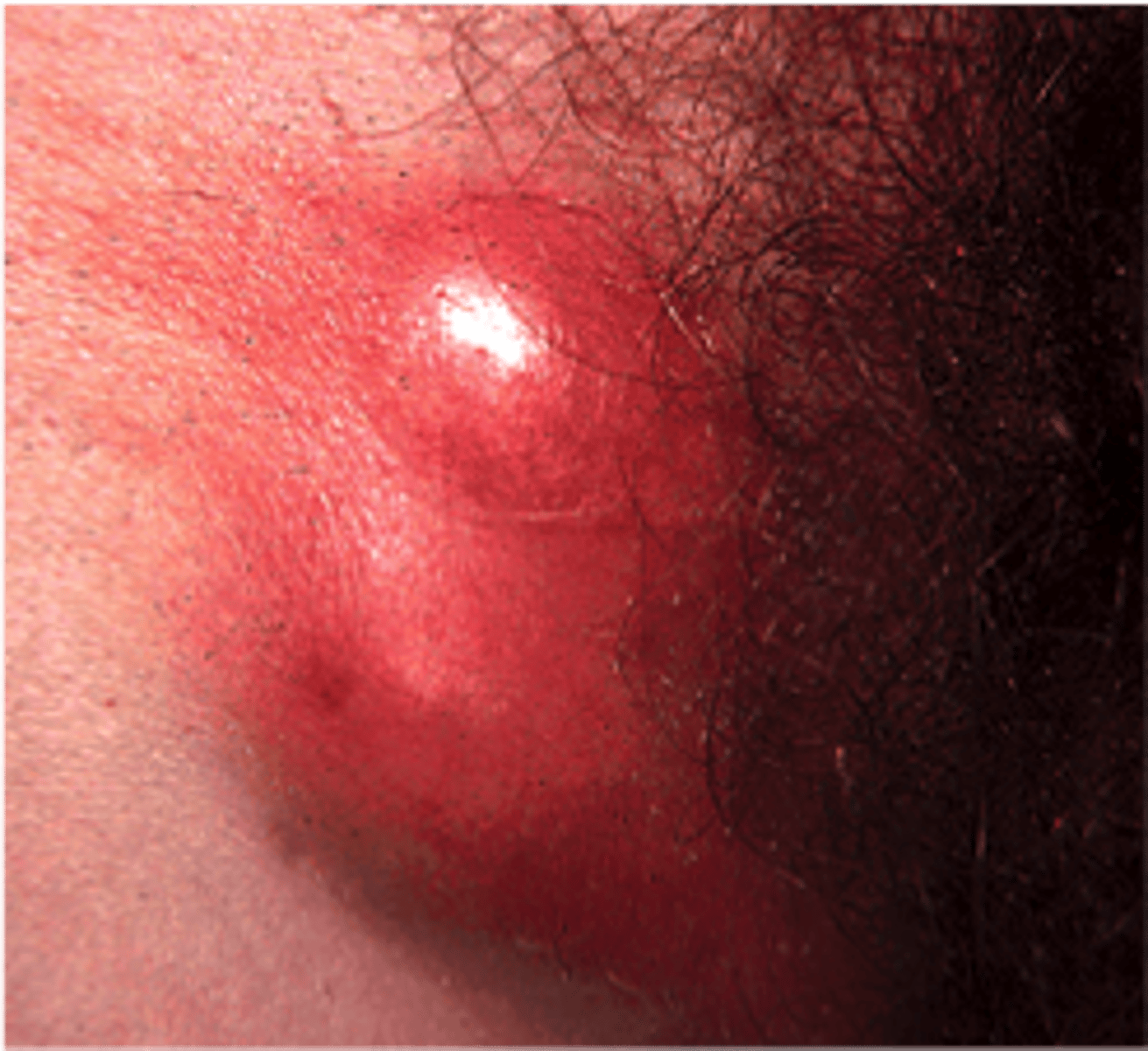
how does lymphogranuloma venereum present?
Extremely tender inguinal or femoral lymphadenopathy above and below the inguinal ligament, with a groove along the ligament
Genital ulcer may be present at the exposure site
Rectal symptoms
Constitutional symptoms
how is lymphogranuloma venereum treated?
Doxycyline
what are complications of lymphogranuloma venereum?
Scarring
Vulvar elephantiasis
Vulvar narrowing
Colorectal fistula
Sigmoid stricture
Frozen pelvis
Infertility
how do you prevent lymphogranuloma venereum?
Condom use
Any person who has had intimate contact with the patient within 60 days of diagnosis should be screened, cultured, and offered treatment
chancroid
A sexually transmitted bacterial infection of the genitals caused by Gram-negative rod, Haemophilus ducreyi
Incubation period of 4-10 days
Rare in the US
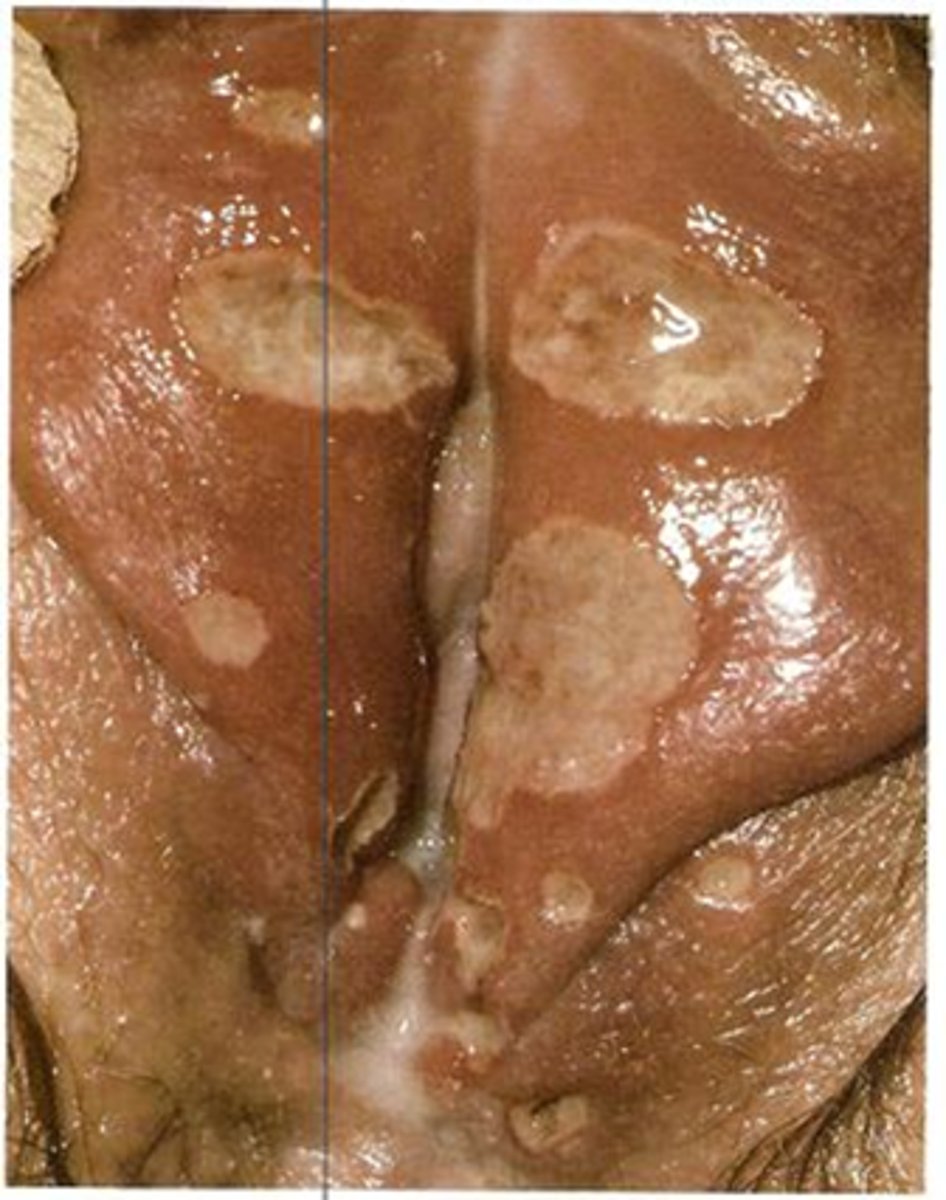
how does chancroid present?
Multiple painful necrotizing ulcerations
Foul smelling discharge
Painful inguinal lymphadenopathy
how is chancroid managed?
Genital hygiene
Fine needle aspiration of fluctuant lymph nodes
Azithromycin
Ceftriaxone
what are complications of chancroid?
Inguinal Scarring
Fistula formation
Secondary infection
what is the prevention for chancroid?
Any person who has had intimate contact with the patient within 10 days of diagnosis needs to be treated
granuloma inguinale
Sexually transmitted chronic ulcerative vulvitis caused by Gram-negative rod, Klebsiella granulomatis
Incubation period is 8-12 weeks
Rare in the US
M>F
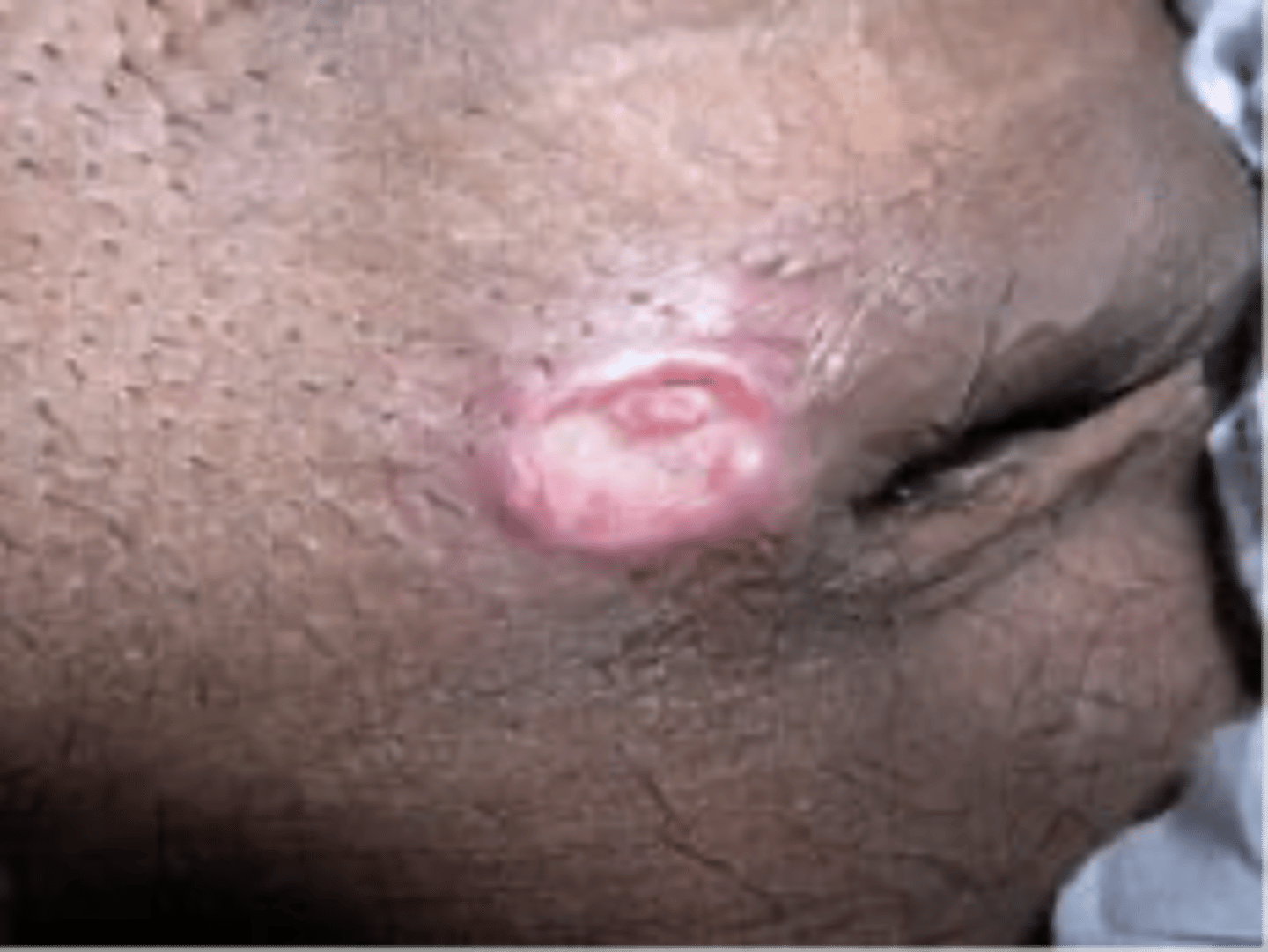
how does granuloma inguinale present?
Papule -> painless ulceration associated with well demarcated erythema
Ulcers are slowly progressing
Involve vulva, perineum, inguinal region
Malodorous discharge and bleeding from the ulcer
Poor healing, susceptible to secondary infection
"Kissing ulcers" from autoinoculation on adjacent skin
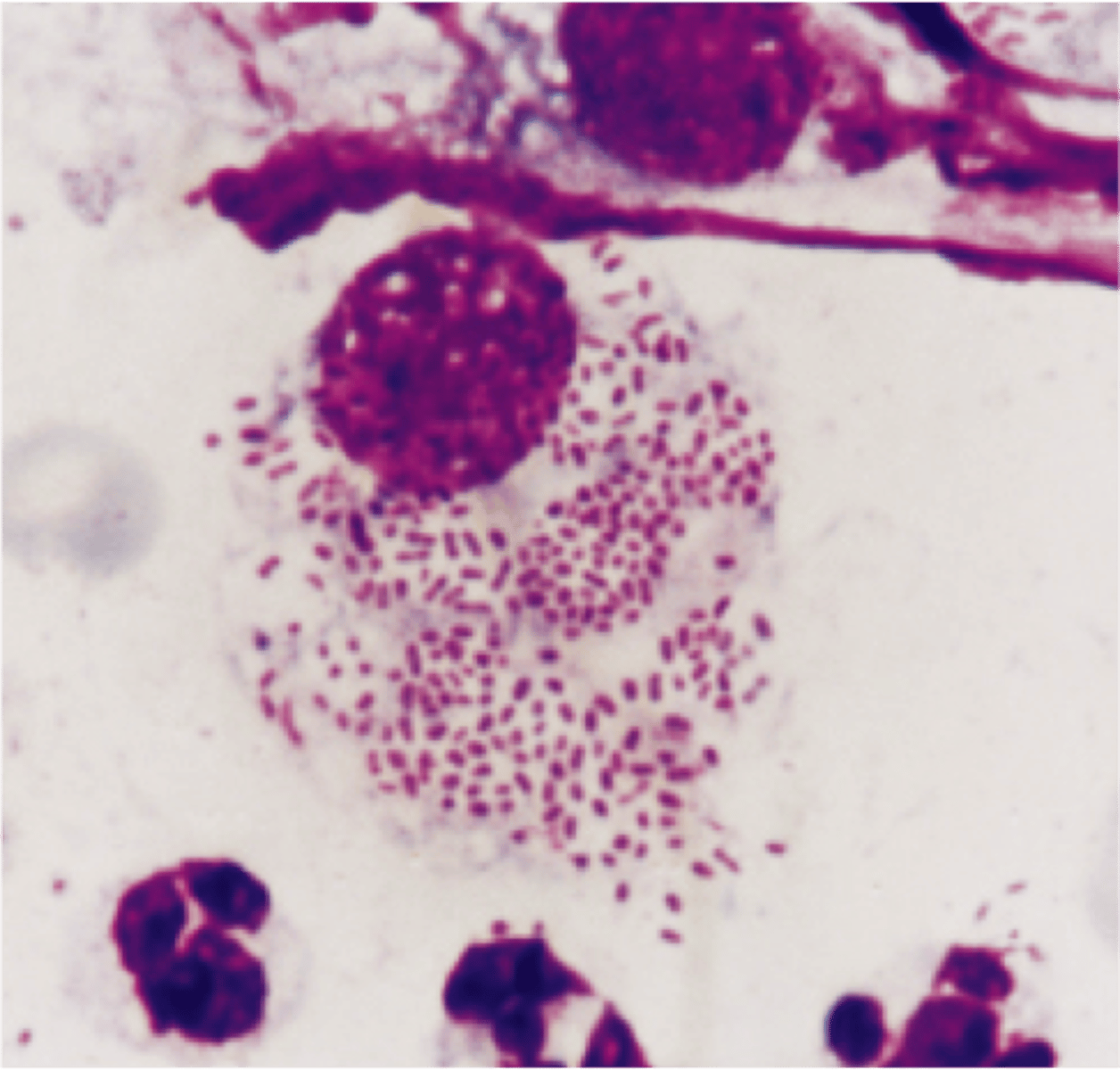
how is granuloma inguinale diagnosed?
Donovan bodies identified by staining of culture or biopsy
how is granuloma inguinale treated?
Azithromycin
what are complications of granuloma inguinale?
Scarring
Hypopigmentation
Damage to lymphatic system
Secondary infection
Narrowing of urethra, vagina, or anus
Osteomyelitis, polyarthritis
how do you prevent granuloma inguinale?
Initiation of therapy immediately after exposure may offer suppression
Any person who has had intimate contact with the patient within 60 days of diagnosis should be screening and offered treatment
syphillis
A sexually transmitted disease caused by Spirochete, Treponema pallidum affecting multiple systems
Can be passed from mother to fetus via transplacental vertical transmission
Incubation period is 10-90 days
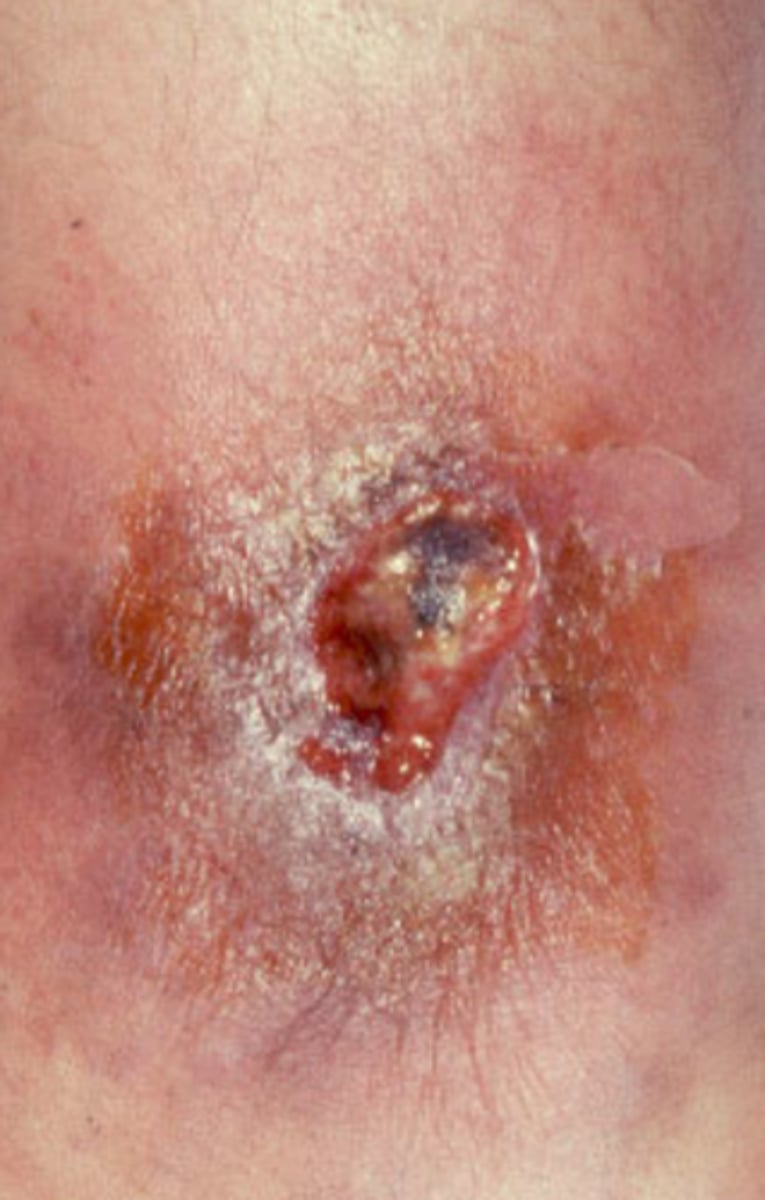
primary syphilis
10-90 days after initial infection
Chancre: firm, painless, papule or ulceration with a raised border
Regional lymphadenopathy
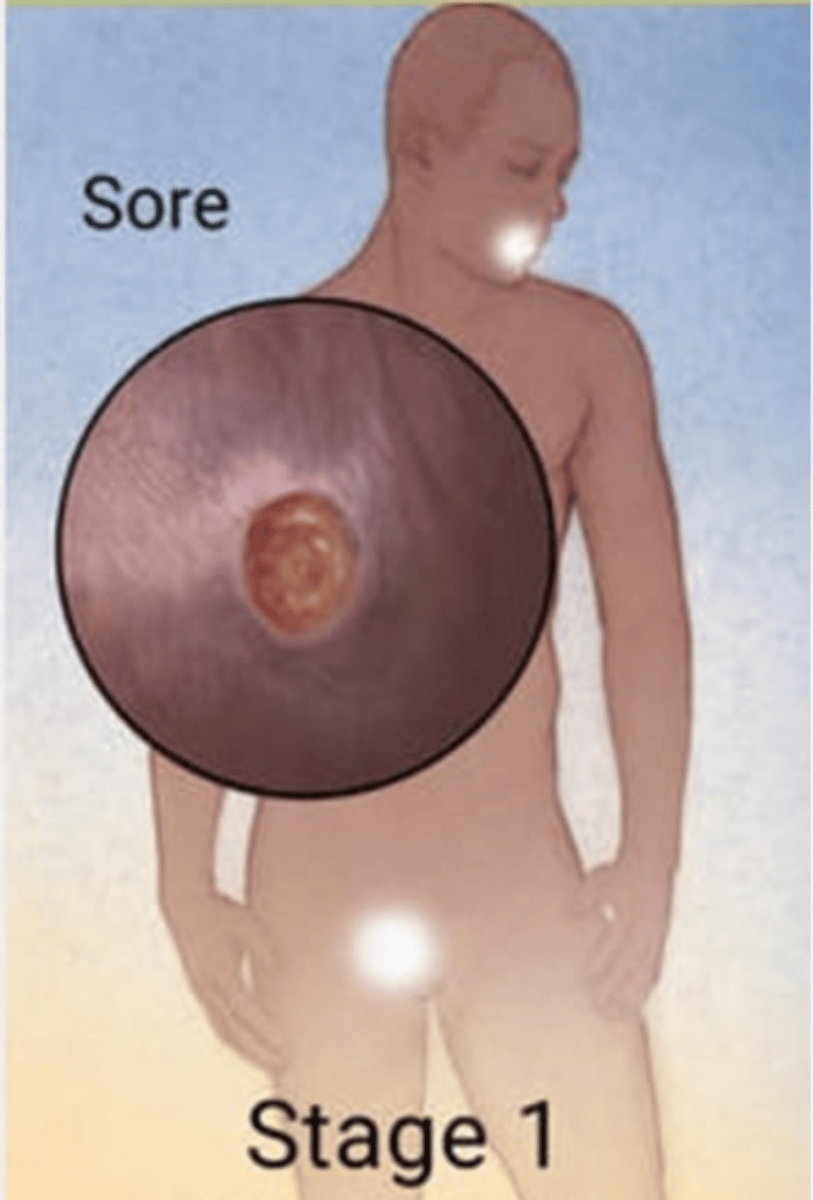
secondary syphilis
2 weeks to 6 months after initial infection
Systemic infection from homogenous spread
Viral syndrome
Rash: Diffuse, B/L papulosquamous lesions involving the palm, soles, and other skin surfaces
Other possible symptoms: pharyngitis, hepatitis, alopecia
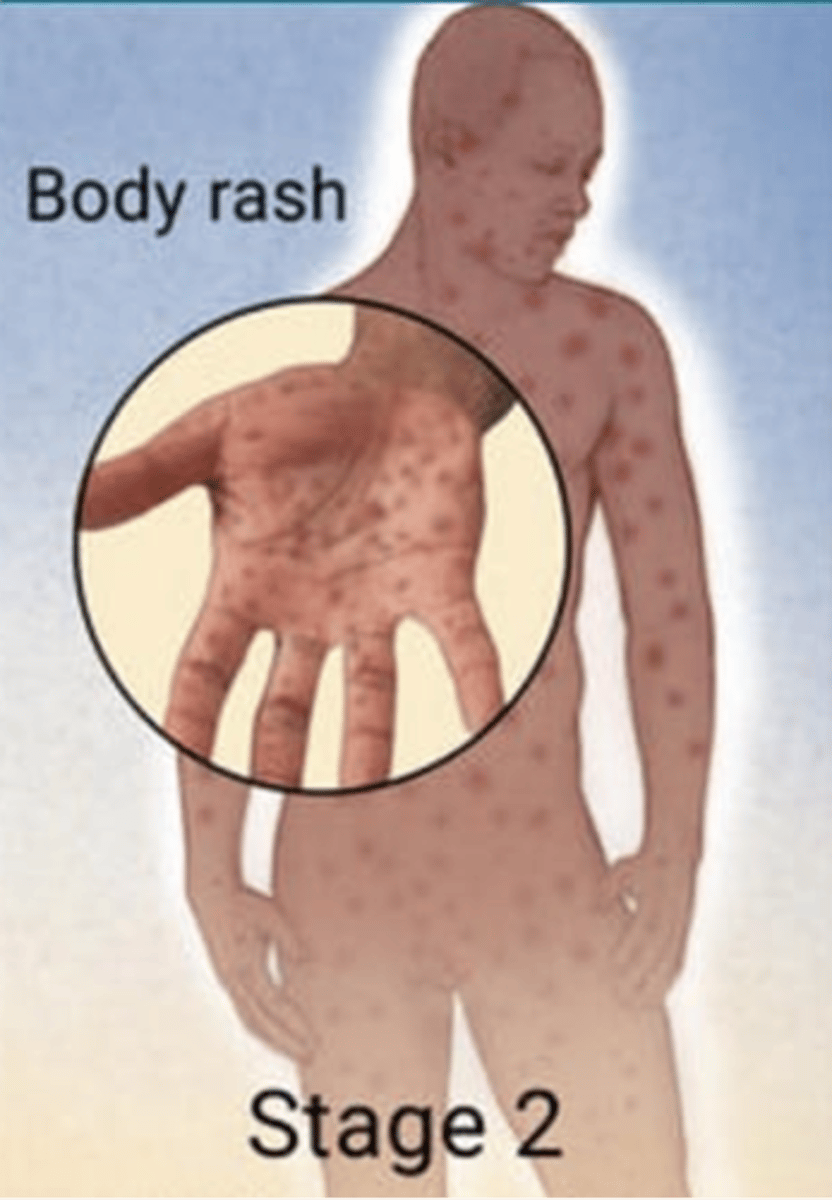
tertiary syphilis
Years after initial infection
Occurs in 1/3 of untreated cases
Skin, subcutaneous tissue, bone, viscera: Granulomatous lesions (of subcutaneous tissues)
Cardiovascular: Aortic insufficiency or aortic aneurysm
Psychiatric: Memory loss/dementia, personality changes
Neurologic: Numbness, paresthesias, paralysis, seizures
EENT: Eye pain, vision changes, blindness, pupillary changes, hearing loss; Argyll-Robertson pupil
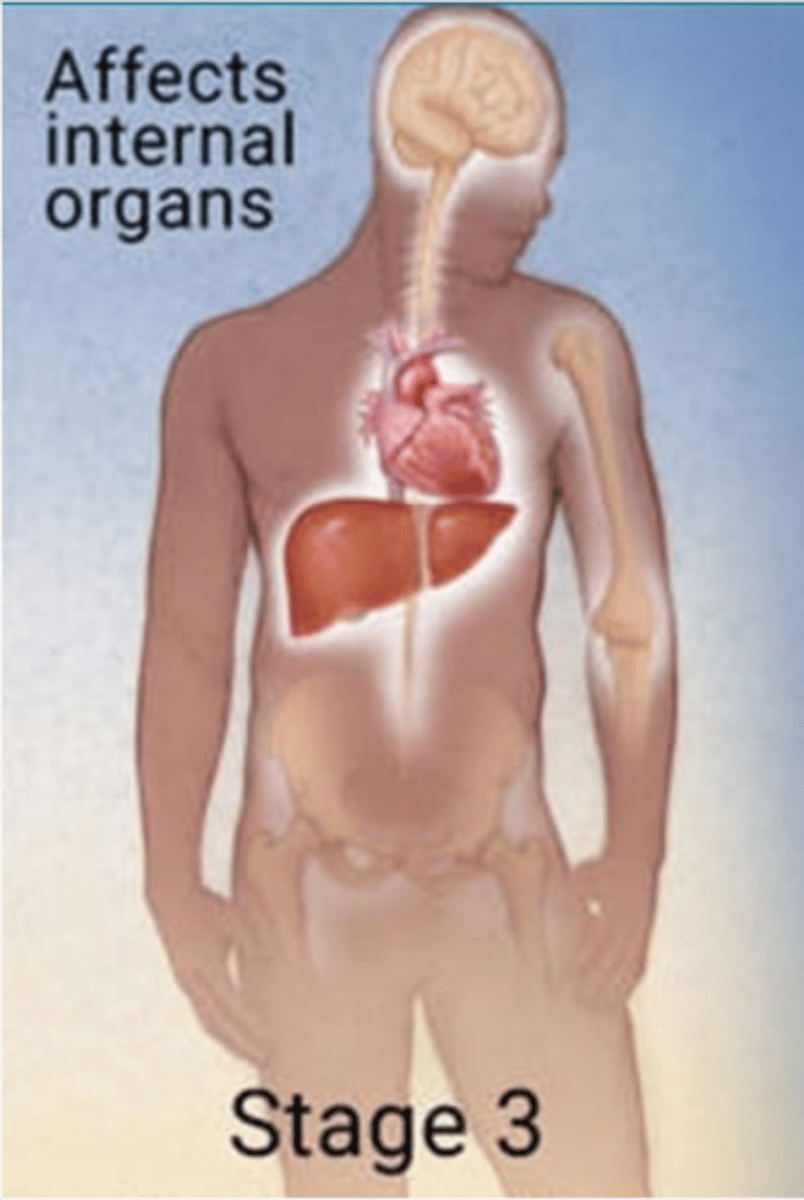
neurosyphilis
an infection of the CNS that can occur in any stage of syphilis (most common in tertiary)
early neurosyphilis vs late presentation
Early: meningitis, meningovascular disease, ophthalmic or auditory dysfunction, cranial nerve palsy
Late: gait disturbance, dementia
latent syphilis
serologic evidence of infection but no symptoms
what are 2 serological tests for syphilis? explain each
Nontreponemal tests
Generalized antibody detection
Titers may correlate with disease activity and can be used to follow treatment success
Treponemal tests
Detection of anti-treponemal antibodies
Cannot be used to follow treatment success
how do you treat syphilis?
Benzathine Pen G
Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
Febrile reaction that occurs in 50-75% of patients treated with PCN in early syphilis
how do you treat syphilis for your patient is allergic to pencillin?
doxcycline, tetracycline, or densenitiation
a patient comes into your obgyn office. she is sexually active patient, has pelvic pain and, no other definitive cause can be identified for the pain. she has cervical, uterine, and adnexal motion tenderness. what is her suspected diagnosis?
PID
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Inflammation of the upper female genital tract caused by a microbial infection often C trachomatis &/or N gonorrhoeae
how does PID present?
Symptoms may be subtle
Acute onset of pelvic pain
Purulent vaginal discharge
Associated pelvic pressure or LBP
Nausea
Headache
Fever
Abdominal/pelvic tenderness to palpation
Cervical, uterine, or adnexal motion tenderness
Decreased bowel sounds
Painful bimanual exam!
what are lab findings that would be present for PID?
Numerous WBCs on wet mount
Elevated WBCs
Elevated C-reactive protein or SED rate
Positive STD culture
Endometrial biopsy showing endometritis
you do a transvaginal sono on your patient with suspected PID. what may you see?
Hyperemia
Dilated uterine cavity
Thickening of the tubes
Fluid in the uterus or tubes
Free-fluid in the pelvis
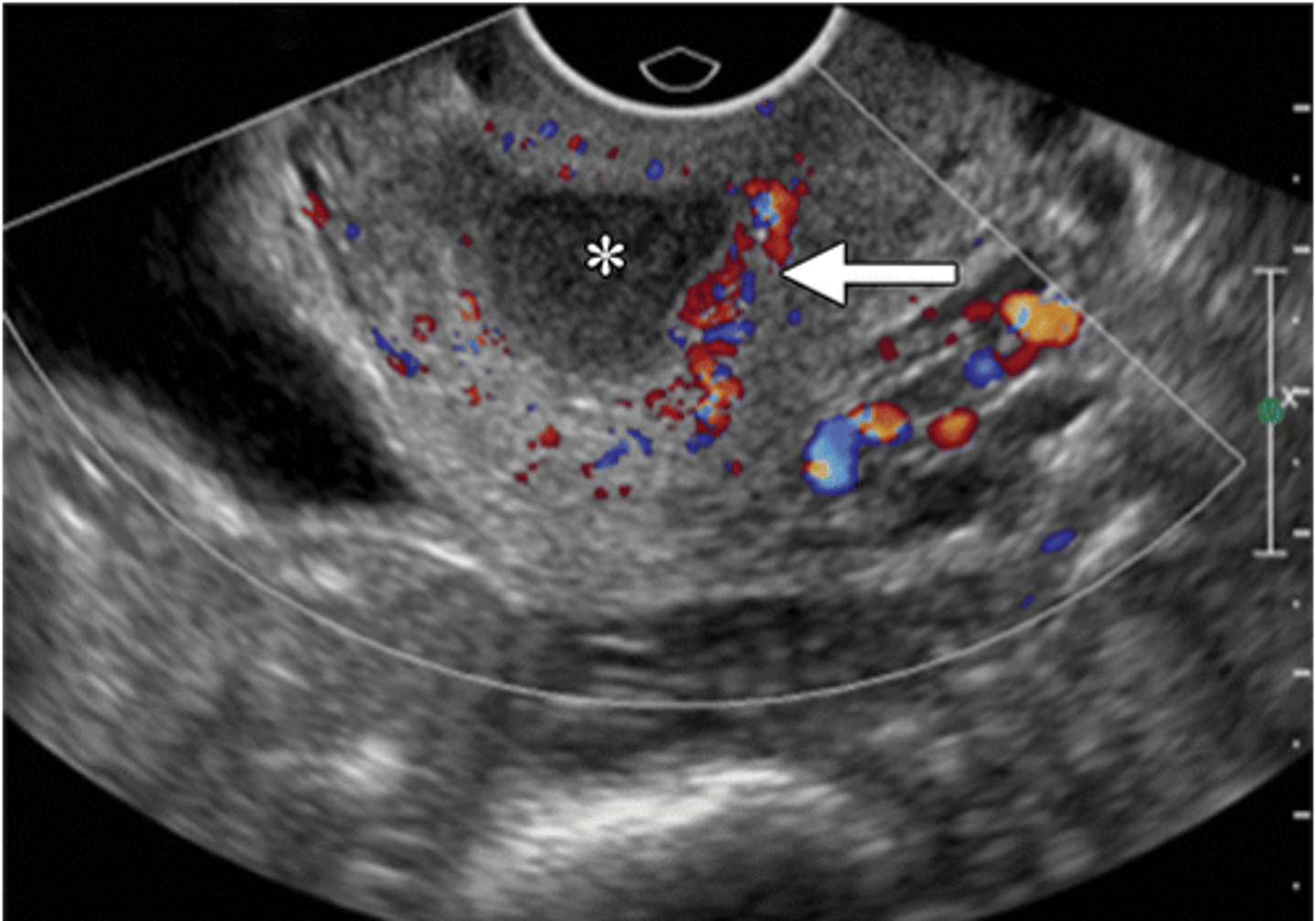
what does early PID look like
fluid-filled distended endocervical canal (*) with surrounding hyperemia (arrow)
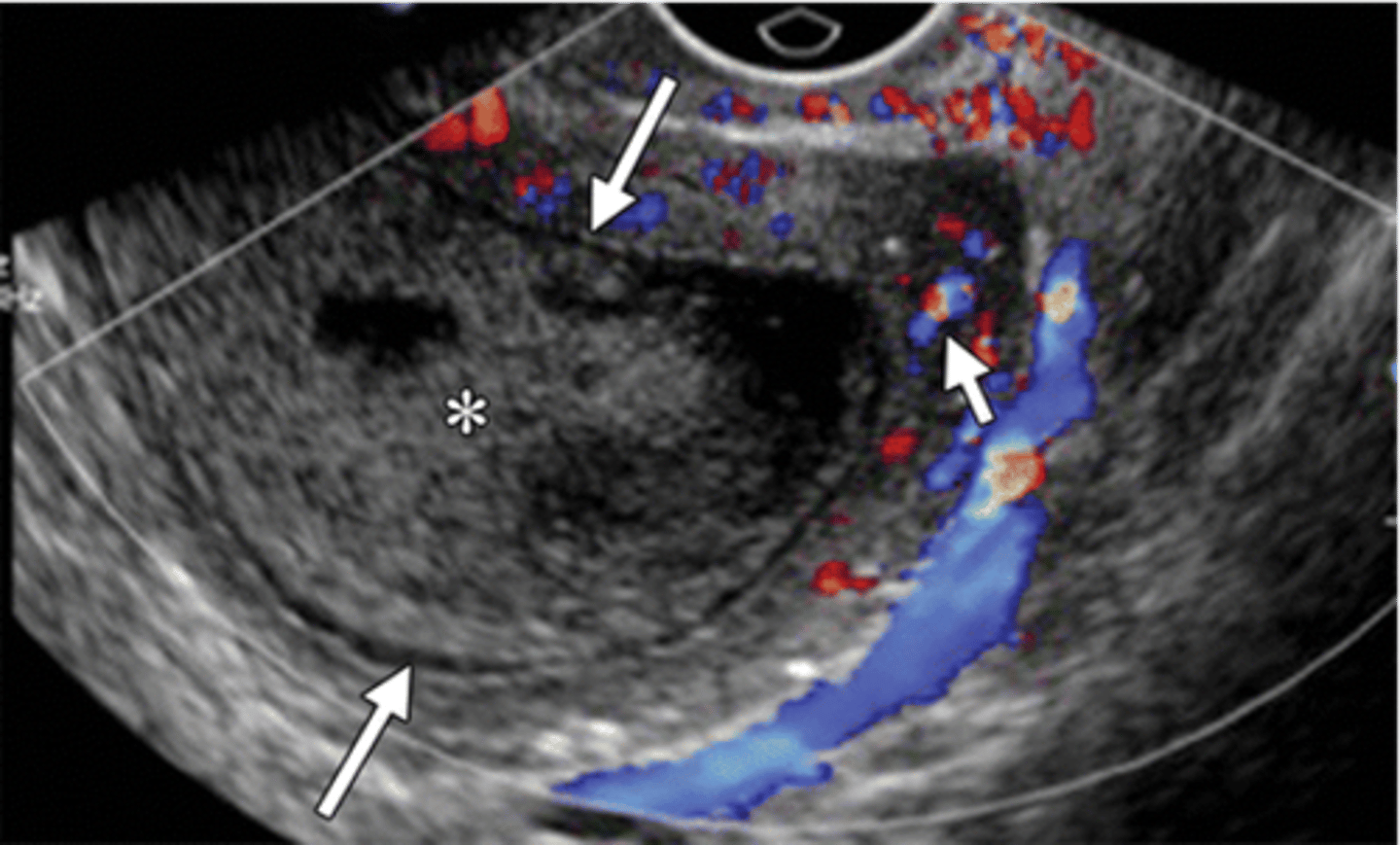
what does late PID look like?
dilated endometrial canal (long arrows), hyperemia of myometrium (short arrow), uterine wall thinning
what is the treatment for PID?
broad spectrum antibiotic!
Cefoxitin + Doxycyclin IV x 24 hours OR Clindamycin + Gentamycin IV x 24 hours Then Doxycyclin PO x 14 days OR Azithromyin PO x 7 days W/ OR W/O Metronidazole PO x 14 days for anaerobic coverage
when should a patient with PID be hospitalized and be on inpatient therapy?
Surgical emergency
Pregnancy
No response to outpatient therapy within 72 hours
Severe systemic illness
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Non-compliance
what are complications to PID?
Peritonitis
Ileus
Pelvic thrombophlebitis
Abscess
Infertility
Ectopic pregnancy
Chronic pelvic pain
Adhesions
Gonococcal arthritis
Sepsis/shock
what if your patient with PID has an IUD?
IUD does not need to be removed unless infection is not responding to treatment
Risk of PID with IUD is only elevated for the first 21 days after insertion
Actinomyces should be considered in cases of PID with IUD
tubo-ovarian abscess
Abscess of the adnexa associated with PID
Symptoms can vary to Mild ---- acute abdomen ---- to septic shock
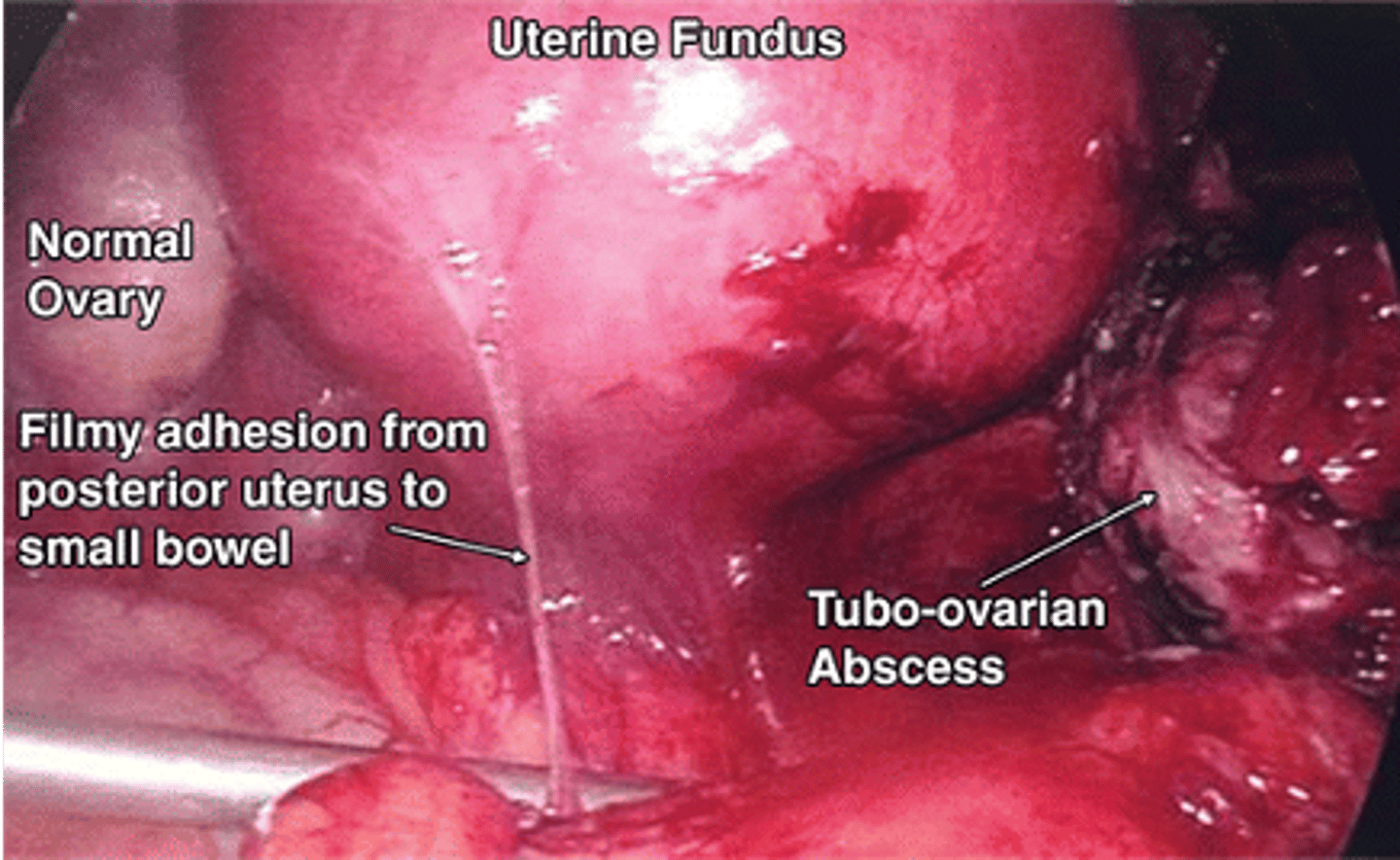
Tubo-ovarian abscess in postmenopausal women is typically due to what?
malignancy
how do you diagnose tubo-ovarian abscess?
Sonography reveals a multiloculated adnexal mass
CT can rule out other causes of an acute abdomen
Bilateral involvement can occur
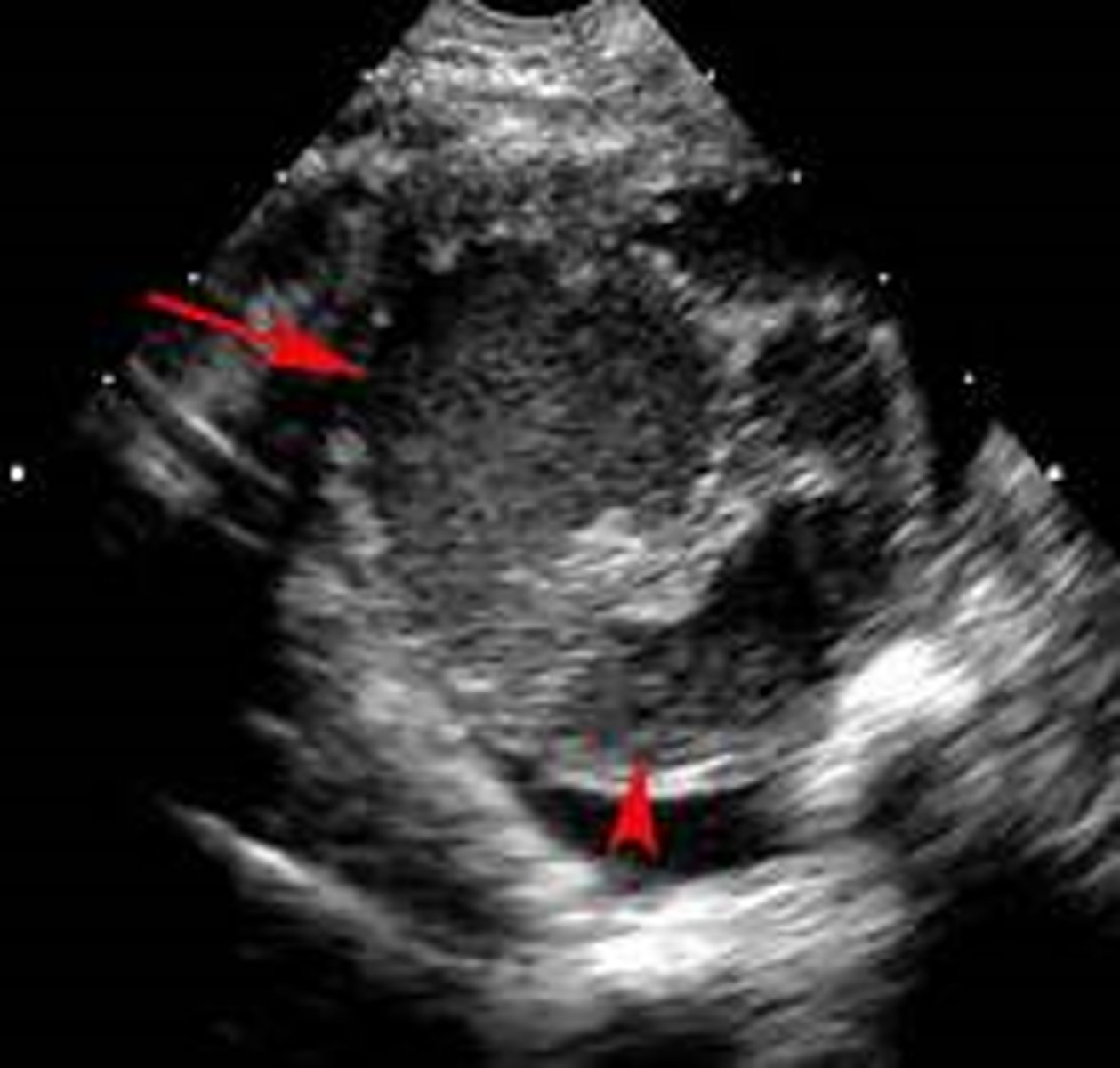
how do you manage a tubo-ovarian abscess?
IV antibiotics followed by oral antibiotics
Image guided drainage or surgeries
Rupture is a surgical emergency due to resulting peritonitis
If IUD is present it should be removed
postpartum endomyometritis
Postpartum polymicrobial infection of the uterus from genital tract organisms
Presents with fever and uterine tenderness in the early postpartum period
what is the treatment for postpartum endomyometritis?
Broad spectrum antibiotics
Clindamycin IV, PLUS
Gentamicin IV, PLUS
Ampicillin IV
what are complications and prevention for postpartum endomyometritis?
Complications: Peritonitis, Pelvic abscess
Prevention:Prophylactic antibiotics, Decrease rates of chorioamnionitis
what are examples of postoperative infection of any remaining pelvic structure following gynecologic surgery caused by vaginal organisms?
Vaginal cuff cellulitis
Infected vaginal cuff hematoma
Salpingitis
Pelvic cellulitis
how do patients with postop pelvic infections present?
Edematous vaginal cuff
Purulent discharge
Induration and tenderness of the vaginal cuff
Pelvic pain
Fever
what is the broad spectrum antibiotics used to treat post op pelvic infections outpatient and inpatient?
Outpatient: Clindamycin PO x 10 days, PLUS Flagyl PO x 7 days
Inpatient: Clindamycin IV, PLUS Gentamicin IV, PLUS Ampicillin IV
what are complications of a post op pelvic infection?
Pelvic abscess
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Adhesions
Septic pelvic thrombophlebitis
Septicemia
how do you prevent postop pelvic infections?
Preoperative treatment of cervicitis/vulvovaginitis
Iodine-like preparation to the vagina
Preoperative antimicrobial prophylaxis
Adequate hemostasis intraoperatively
toxic shock syndrome
A febrile illness caused by bacterial toxins entering the bloodstream, usually associated with gram positive Staph aureaus or Strep pyogenes, rare
how does toxic shock present?
Symptom onset is rapid
Fever
Hypotension
Diffuse macular rash
Dizziness/syncope
Constitutional symptoms
Desquamation of palms and soles
how is toxic shock diagnosed?
Vaginal culture for S. aureus and group A strep
CBC reflecting thrombocytopenia and anemia
Abnormal coagulation studies
Abnormal renal and liver studies
how is toxic shock treated?
Removal of anything that could be the cause
Antibiotics coverage to include MRSA (Clindamycin IV for 10-14 days, PLUS Vancomycin IV)
what are complications of toxic shock?
Recurrence
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Shock
Organ failure
Death
what are prevention measures to acoid toxic shock?
Lower absorbency tampons
Regularly change tampons, avoid overnight use
Practice good hygiene